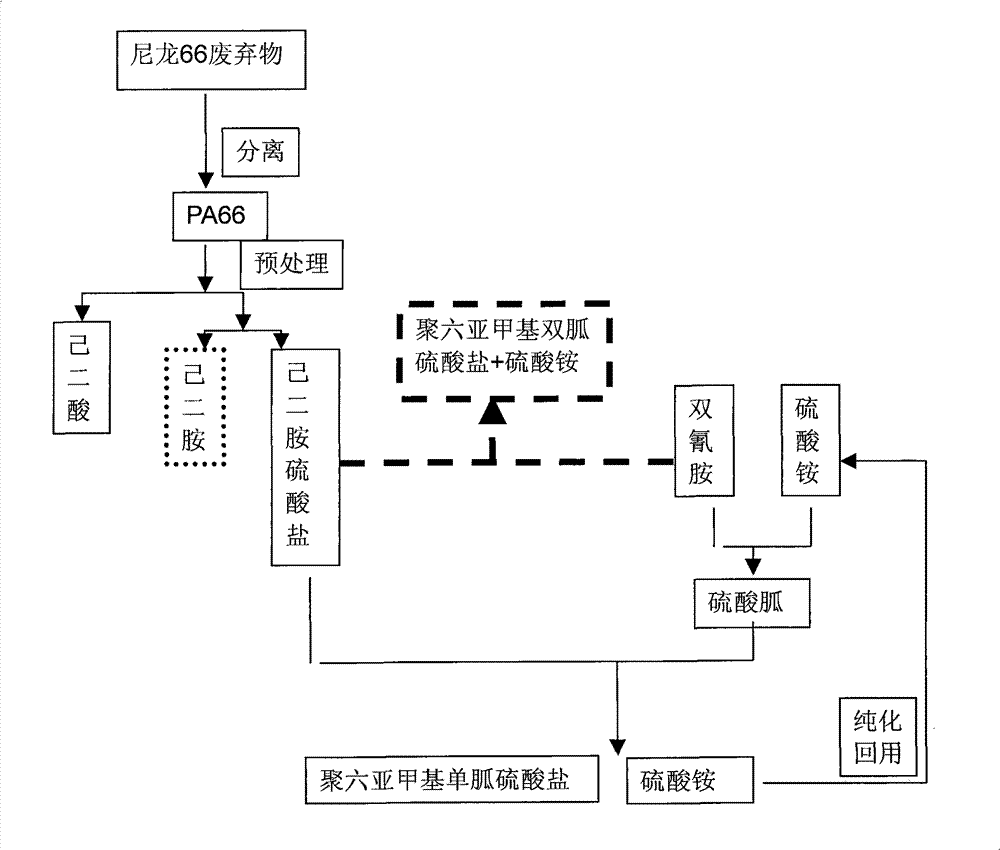
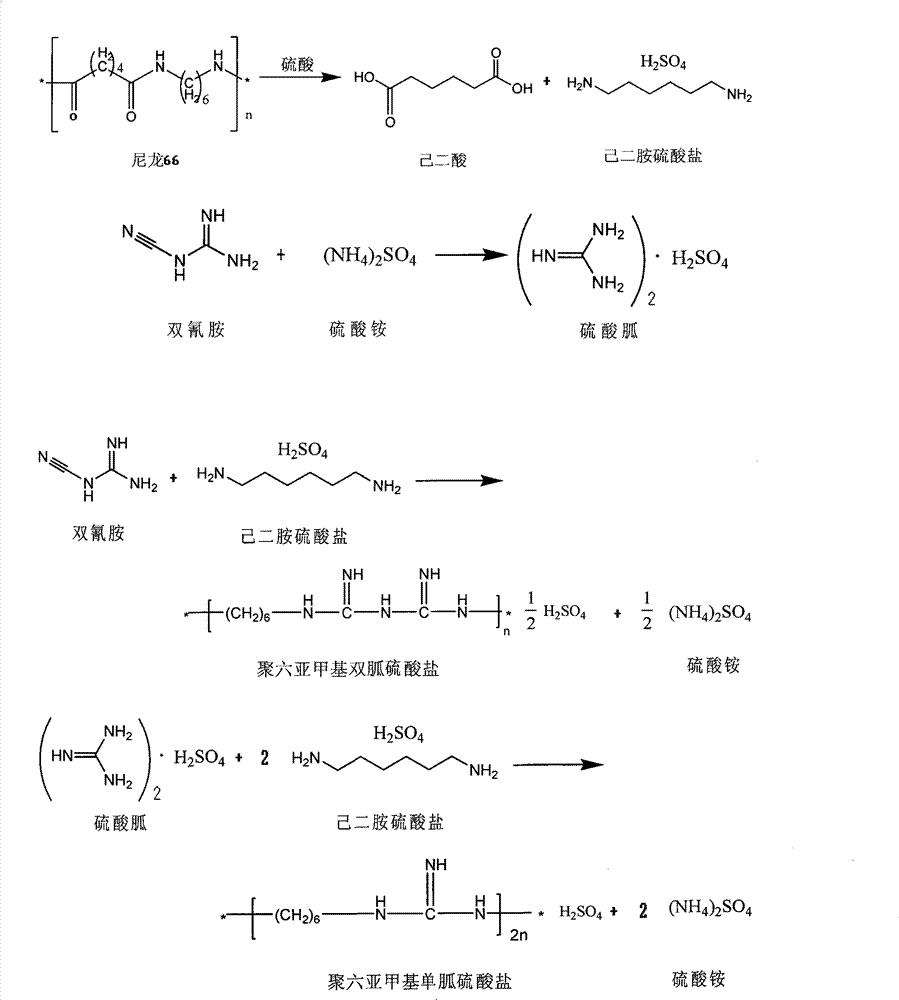
Method for producing adipic acid, hexamethylenediamine sulfate and polyhexamethylene (di)guanidine sulfate from nylon-66 through depolymerization
A technology of polyhexamethylene biguanide and polyhexamethylene monoguanidine, which is applied in the field of disinfectant polyhexamethylene monoguanidine sulfate, can solve the problem of difficult separation of hexamethylenediamine, the depolymerization product, easy corrosion of equipment, Short service life and other problems, to achieve the effect of low volatility, lower requirements for production equipment, and lower production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] (1) Acid hydrolysis section: first add 2200Kg of water to the reactor, then add 1000Kg of 98% industrial sulfuric acid, then add 1000Kg of nylon-66 waste while heating, and react for 10 hours under normal pressure and 100-110°C. The reaction conversion rate reaches more than 96%, and the acid hydrolysis solution is obtained;
[0036] (2) Adipic acid refining section: cool down the acid hydrolysis solution to 30-50° C., and separate with a coarse filter to obtain crude adipic acid crystals. Heat the water temperature in the decolorization kettle to above 90°C. At this time, gradually add crude adipic acid solids equivalent to 50% of the water weight ratio. After dissolving, add activated carbon equivalent to 3% by weight, stir and decolorize, and use a plate and frame filter Separating activated carbon and insoluble impurities, then cooling and crystallizing, filtering, and drying to obtain pure adipic acid with a purity of more than 99.7%, 500Kg, and a yield of 77%;
...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Acid hydrolysis section (1), adipic acid refining section (2) and hexamethylenediamine sulfate refining section (3) are the same as in Example 1.
[0041] (4) In the preparation section of polyhexamethylene mono(bi)guanidine sulfate, the dicyandiamide and ammonium sulfate powder with a molar ratio of 1:1 are dropped into the reactor, under nitrogen protection, stirred for 10-30 minutes, and heated to 180 ℃, stirred and reacted for 3 hours, slowly added the hexamethylenediamine sulfate powder obtained in the refining section of hexamethylenediamine sulfate, and continued the reaction for 6 hours to obtain a mixture of polyhexamethylene monoguanidine sulfate and ammonium sulfate, which was melted with nitrogen while it was hot. The reaction solution in this state is slowly pressed into a separation tank filled with absolute ethanol, stirred thoroughly and filtered, and the ethanol filtrate of polyhexamethylene monoguanidine sulfate is distilled under reduced pressure to re...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Acid hydrolysis section (1), adipic acid refining section (2), hexamethylenediamine sulfate refining section (3) and polyhexamethylene mono(bi)guanidine sulfate preparation section (4) are the same as in Example 2.
[0044] Add 300Kg of hot water (70±5°C) to the crude ammonium sulfate white powder obtained after the above filtration, stir, dissolve and filter, evaporate and concentrate under reduced pressure until crystals are precipitated, cool, filter, and vacuum dry to obtain 195Kg of refined ammonium sulfate Solid, the yield is above 83%. According to the reaction equivalence ratio, fresh ammonium sulfate is properly supplemented and recycled to the polyhexamethylene mono(bi)guanidine sulfate preparation section (4).
[0045] The general molar ratio herein refers to allowing the molar ratio to fluctuate by 10% on the basis of equivalent reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com