Method for efficiently expressing and producing T4 lysozyme through recombinant hansenula polymorpha in constitutive mode
A polytype Hansenula, high-efficiency expression technology, applied in the field of high-efficiency expression and production of T4 lysozyme, to achieve the effect of broad antibacterial spectrum, strong antibacterial activity, and extended shelf life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
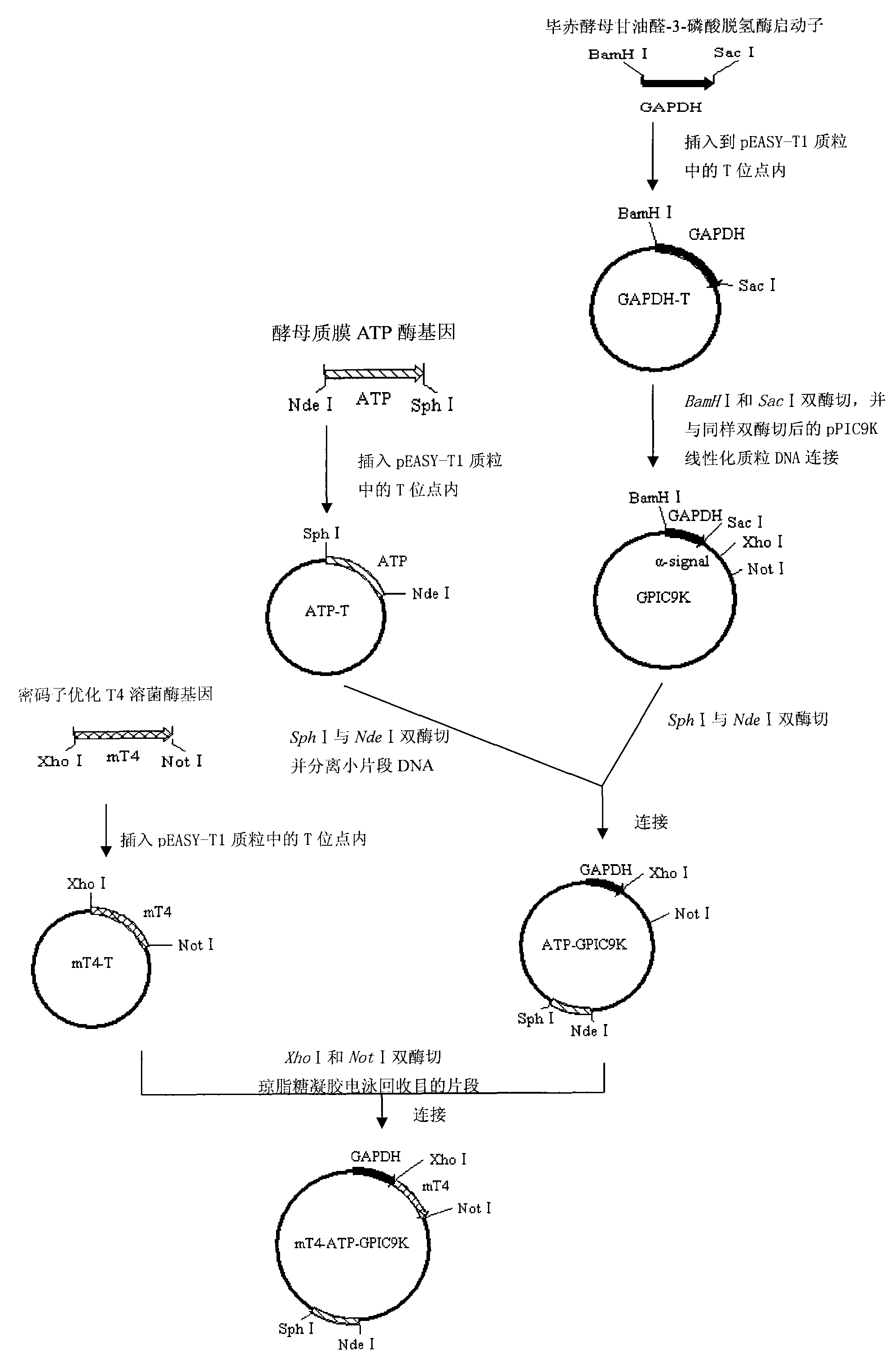
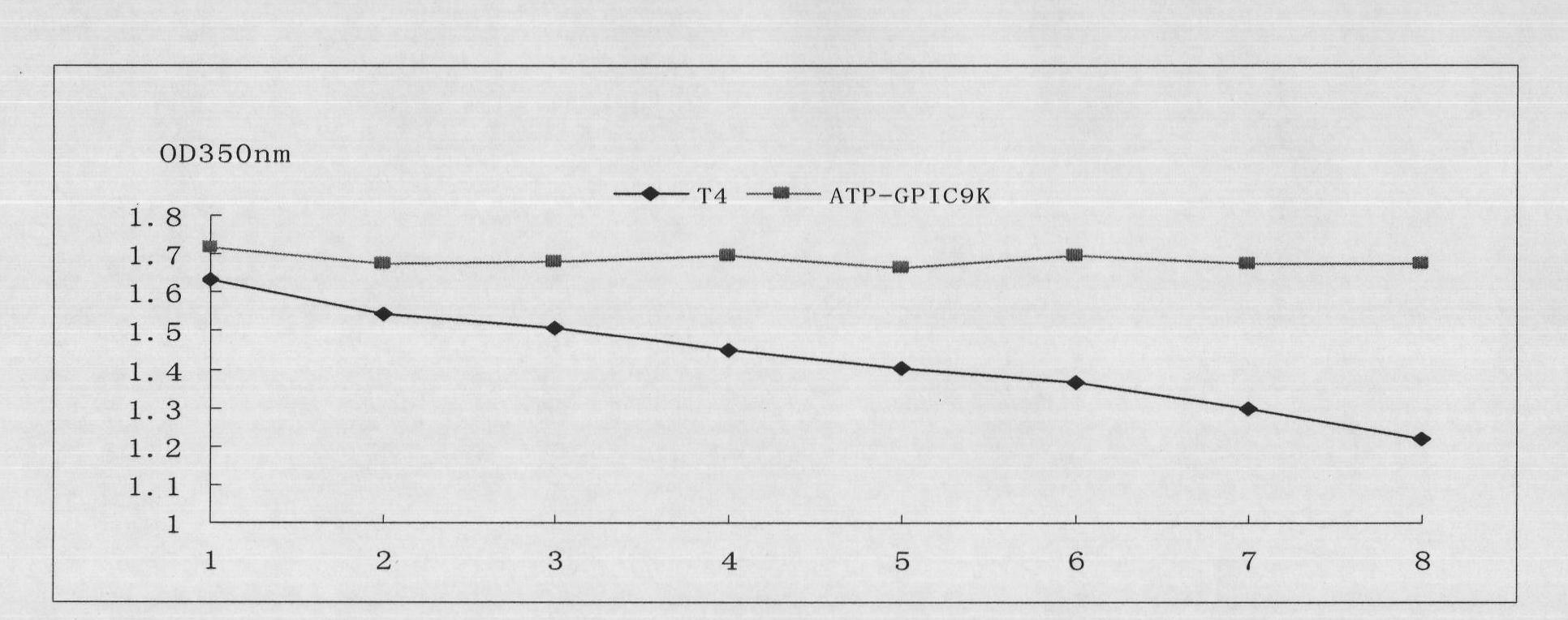
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: Artificial synthesis of T4 lysozyme gene after codon optimization
[0043]The T4 lysozyme gene is derived from T4 bacteriophage, and its codons are closer to prokaryotes, while Hansenula belongs to eukaryotes, so they have certain differences in gene codon preferences, and this difference is likely to affect Stability and expression efficiency of T4 lysozyme gene and its transcript in Hansenula cells. In order to improve the biological yield of T4 lysozyme, according to the DNA sequence and amino acid sequence (GenBank, accession number: NY000866) of the published T4 lysozyme gene, under the premise of not changing its amino acid sequence (see SEQ ID NO.1), according to The codons preferred by yeast (Sharp P M, et al., 1986), the DNA coding sequence of the new T4 lysozyme mature protein was artificially designed and synthesized, and the T4 lysozyme gene after codon optimization and transformation was compared with that before transformation , 138 nucleoti...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: Cloning of T4 lysozyme gene
[0045] The above artificially synthesized T4 lysozyme gene DNA fragment was directly inserted into the T site of the pEASY-T1 (purchased from Beijing TransGenic Company) plasmid, and the bacteria containing the intermediate plasmid vector mT4-T were obtained according to the method provided by the company. Cloning, and then, through DNA sequencing, it was determined that the T4 lysozyme gene contained in it was correct and complete (DNA sequencing was completed by Beijing Biaokai Technology Co., Ltd.).
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Cloning of Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter
[0047] According to the known Pichia glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence (GenBank: U62648.1), synthesize primers F and R located at both ends of the promoter, wherein F is 5'-AT GGATCC TTTTTTGTAGAAATGTCTTGGTGTC-C-3' (underlined part is BamH I cutting point) (see SEQ ID NO.5), R is 5'-AT GAGCTC TGTGTTTTGATAGTTGTTCAATTGAT TG-3' (the underlined part is the cut point of Sac I) (see SEQ ID NO.6), using Pichia pastoris genomic DNA as a template (for the genome extraction method, see page 485 of "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide, Third Edition"), Using F and R as primers, the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence (GAPDH) was amplified by PCR, and the amplified fragment was directly inserted into the T site of the pEASY-T1 plasmid, according to the company's According to the provided method, a bacterial clone containing the intermediate plas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com