Method for separating and reclaiming metal nickel and tin from waste materials containing nickel and tin
A separation and recycling, waste technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, to achieve the effect of wide application, high added value and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Get 10 grams of waste alloy materials containing nickel and tin, add excessive sulfuric acid and nitric acid to dissolve, and analyze the main components as follows:
[0021]
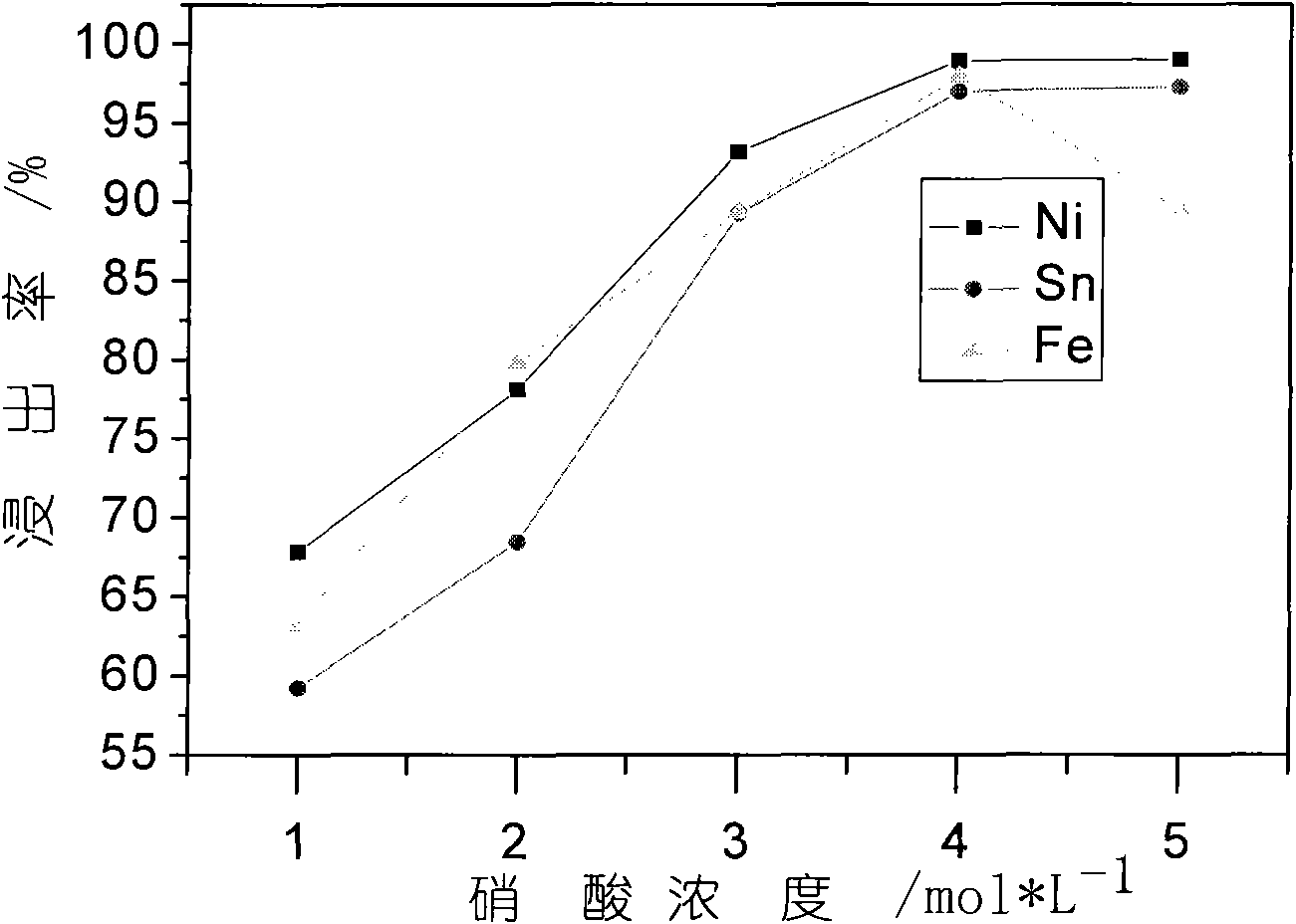
[0022] In order to fully improve the utilization rate of the acid and facilitate the adjustment of the pH value of the final leaching solution, the present invention uses two-stage acid leaching. The first stage of acid leaching process: prepare a mixed acid of 1mol / L sulfuric acid and 4mol / L nitric acid, take 20L of acid and 2Kg nickel-tin scrap alloy material, and add it to the reactor with a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1. The reaction temperature was 80° C., mechanically stirred, and filtered after a reaction time of 10 hours. The composition analysis of the obtained solution was as follows.
[0023]
[0024] The second stage of acid leaching process: the remaining hydrogen ions in the first stage of the leaching solution reach about 1mol / L, and nickel-tin scrap alloy materials need to be u...
Embodiment 2
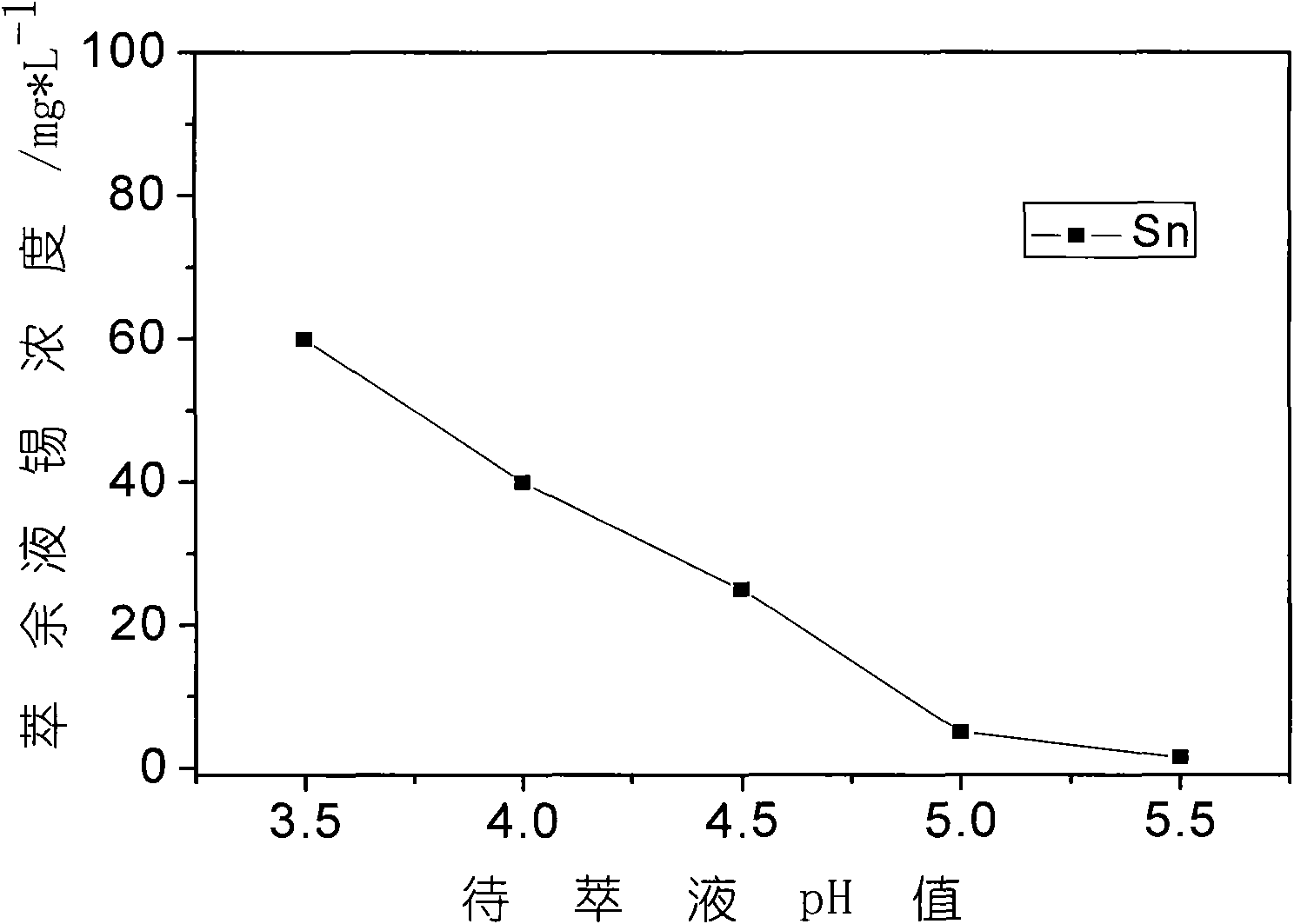
[0027] Prepare sodium carbonate solution 2mol / L, transfer the 20L leachate obtained in Example 1 into a clean reactor, the reaction temperature is 80°C, and accompanied by mechanical stirring, use 2mol / L sodium carbonate solution to neutralize, the sodium carbonate solution speed Follow the method of first fast and then slow, when the speed of bubble disappearing slows down, reduce the liquid addition speed to 20ml / min, adjust the pH value of the solution to 4.5, settle for 8 hours, and filter. At this time, tin and iron enter the slag as hydroxides, and most of the nickel remains in the filtrate. The obtained nickel-containing solution is about 35L, which is used for extraction and removal of impurities, and its composition is shown in the following table. The recovery rate of nickel in this process is 98.2%.
[0028]
Embodiment 3
[0030] The tin-iron filter residue that obtains in the example 2 is transferred in the clean reactor, adds enough 20% sodium hydroxide solution, and the control reaction temperature is 90 ℃ and with mechanical stirring, reacts for 6 hours, and the pH value of the whole process is always equal to or higher than 14. The original yellow color of the filter residue gradually changed to reddish brown, the tin was fully dissolved, and the iron impurities still existed in the form of slag. Solid-liquid separation, removal of iron slag, to obtain pure sodium stannate solution. The sodium stannate solution is concentrated and crystallized, and the prepared sodium stannate product meets the GB / T 23278-2009 standard. Sodium stannate crystals are re-dissolved with ammonia water at pH = 13.5 and temperature is 60°C, and then recrystallized to prepare ammonium stannate crystals; decompose the ammonium stannate crystals at 450°C for 3 hours to obtain porous tin dioxide Powder material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com