Method for evaluating rice planthopper-resistant property of rice
A rice planthopper and rice technology, applied in the field of pest control, can solve problems such as the number of resistance identification populations in the field, the impact of natural disasters on non-target pests, the deviation between the resistance level and the actual resistance performance in the field, and the large annual difference. , to achieve the effect of simple method, reliable resistance results and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Network room construction and community design
[0027] Choose a paddy field that is relatively convenient for drainage and irrigation, and use a joint eight-type single greenhouse with a width of 8 meters, a length of 80 meters, a pipe spacing of 0.6 meters, a top height of 2.5 meters, and a shoulder height of 1.5 meters. A 30cm wide field ridge was built in the middle to divide the greenhouse into two. The greenhouse is covered with 80-mesh nylon yarn, and a layer of 80-mesh nylon yarn, which is 30cm wider than the perimeter of the shed door, is installed on the outside of the shed door. The ground is compacted with mud to prevent rice planthoppers or other insects from entering the net. .
[0028] Set up plots according to the number of varieties, and the average width of each plot is 2 meters. Seed soaking, germination, sowing, transplanting and other operations were carried out as usual. Hybrid rice varieties are transplanted in single copies, and japo...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Effects of Different Fertilizer Levels on the Insect Resistance of Rice Varieties
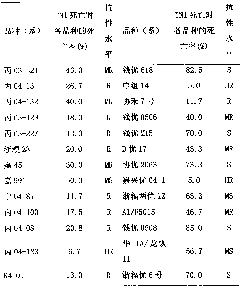
[0035] Using the net house made in Example 1, the resistance of varieties TN1, IR26 and IR36 to brown planthopper under different nitrogen fertilizer levels was determined. When nitrogen fertilizer was used at 250kg / ha, the resistance levels of IR26 and IR36 to brown planthopper were sensitive and moderately resistant, respectively, while when no nitrogen fertilizer was used, the resistance levels of both were moderately sensitive and resistant. The susceptible variety TN1 was not affected by fertilizer levels (Table 2).
[0036] Table 2 Resistance of rice varieties to BPH under different nitrogen levels
[0037]
Embodiment 3
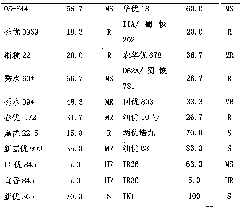
[0038] Embodiment 3 Under the condition of natural occurrence and the comparison of using the method of the present invention to identify rice insect resistance
[0039] Respectively in the situation of brown planthopper occurring naturally and utilizing the implementation of the present invention, monitoring varieties TN1, IR26 and IR36 are to the resistance of brown planthopper, and the results show that IR26 is 9 grades to brown planthopper resistance, which is the same as the susceptible variety TN1, showing that IR26 is to brown planthopper Has completely lost resistance. The resistance level of IR36 was 3, which was slightly higher than that of 5 in the case of natural occurrence, indicating that IR36 still had a moderate level of resistance to N. lugens. Illustrate that adopting the method of the present invention is consistent with the results of identifying rice insect resistance under natural conditions (table 3), but under natural conditions, the identification is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com