FISH method of one piece and multiple target of cotton
A multi-target, cotton technology, applied in the field of molecular cytogenetics, can solve the problem that the probe and the target DNA have no homologous sequence and are difficult to tell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 FISH experiment of a piece of cotton with multiple targets
[0020] Experimental materials: diploid cotton species Raymond cotton, Thurber cotton, Davidson cotton and tetraploid cotton species sea island cotton, yellow brown cotton and Darwin cotton were all from the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
[0021] Experimental reagents: cellulase Onazuka R-10 and pectinase Pectolyase Y-23 were purchased from Solarbio; probe labeling kits Bio-Nick Translation Mix and DIG-Nick Translation Mix were purchased from Roche.
[0022] 1. Cotton genomic DNA extraction
[0023]Preheat nuclear lysis buffer at 60°C (add 2% β-mercaptoethanol v / v before the experiment), take about 2g of young leaves, put them into a frozen mortar immediately, add liquid nitrogen to the mortar and quickly grind them into powder . Quickly put it into a 7mL centrifuge tube, add about 3mL of extraction buffer preheated in a 60°C water bath, and shake well. ...
Embodiment 2
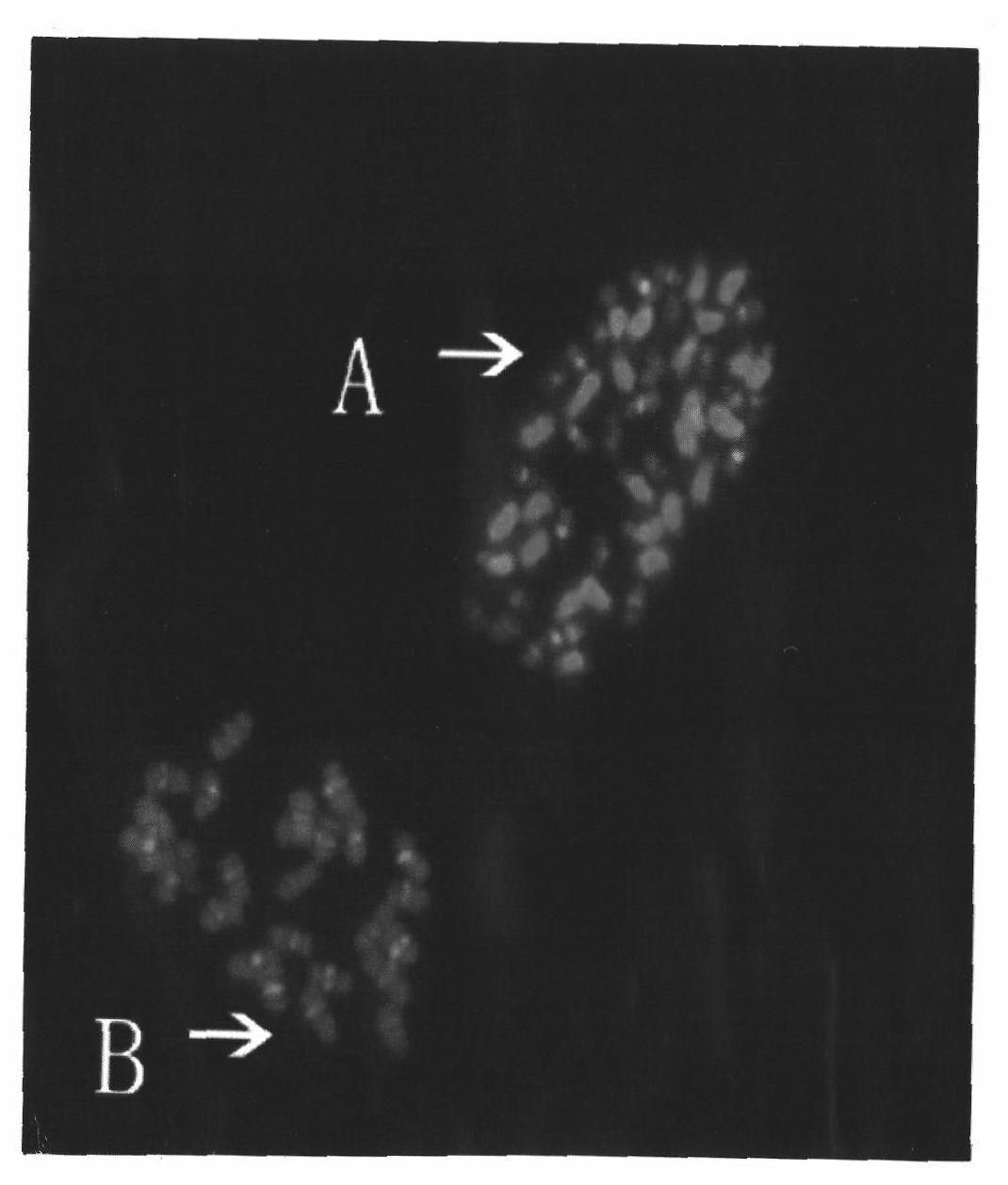
[0038] The preparation used in Example 1 was hybridized with the 428k20 sequence and the 150D24 sequence as a double-purpose probe, and the hybridization result obtained was as follows figure 2 Shown: The red signal of the 150D24 sequence appears in all chromosomes of Raymond cotton ( figure 2 -B) and the centromere region of the smaller chromosome (subgroup D) of sea-island cotton, because it overlaps with the green signal produced by the 428k20 sequence in the centromere region of the smaller chromosome (subgroup D) of sea-island cotton, so sea-island cotton is relatively Centromeric regions of small chromosomes (subgroup D) are seen as synthetic signals in yellow ( figure 2 -A), it can also be confirmed that the 150D24 sequence is from its donor species Raymond cotton, but it is inconsistent with the 428k20 sequence.
Embodiment 3
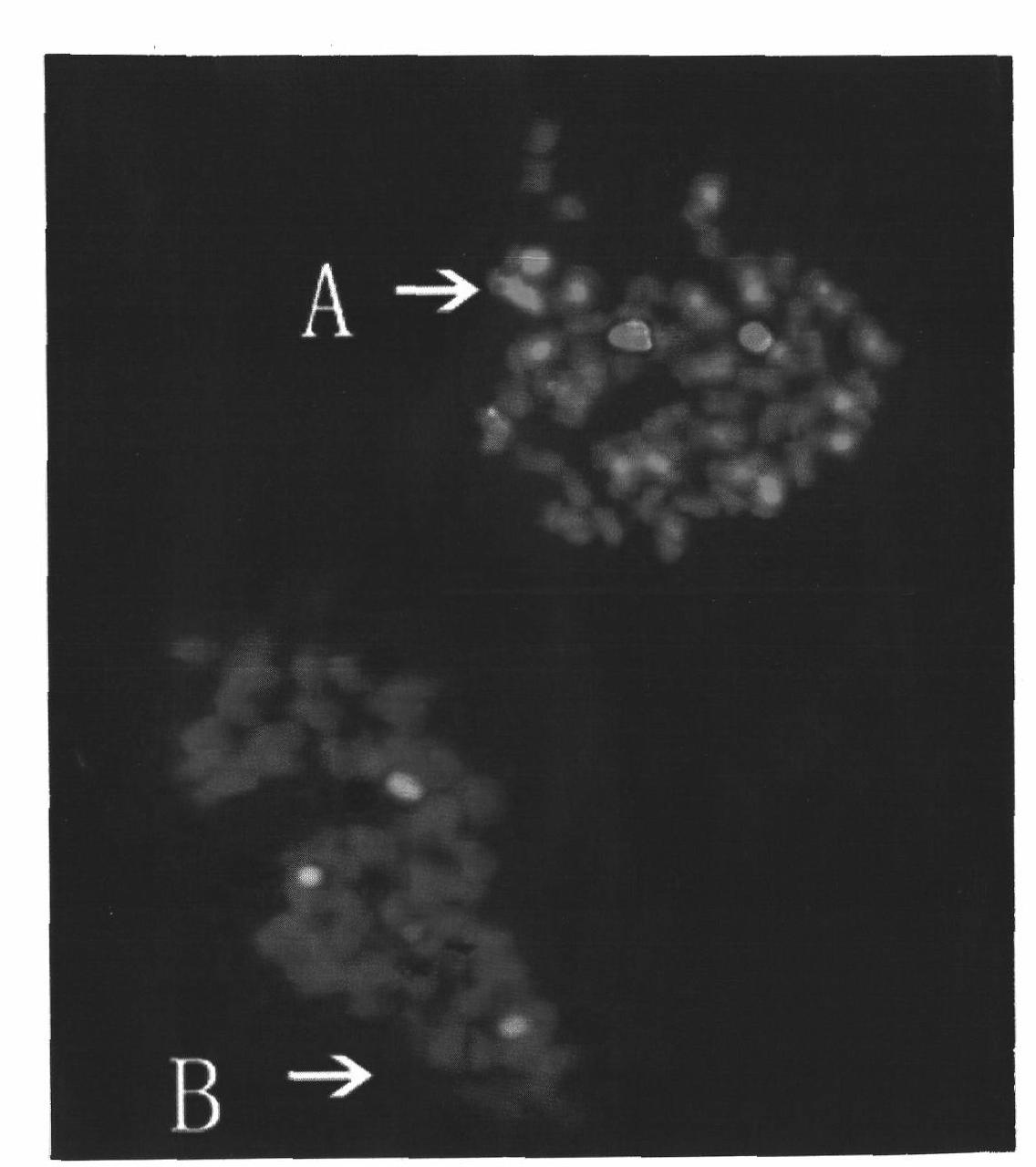
[0040] The yellow-brown cotton and Darwin cotton are both tetraploid cotton species, both of which have 52 chromosomes, and the recognition probe 45S is added. There are 3 pairs of 45S rDNA loci in the yellow-brown cotton, one of which is very large and almost covers the entire cotton. The short arm of the chromosome, while the other two pairs are very small; the three pairs of 45S rDNA loci in Darwin cotton are basically identical. The target probes are diploid D group Thurber's genome and Davidson's cotton genome respectively, and salmon sperm DNA is used as blocking, and the intensity of hybridization signal is used to compare the Thurber's cotton and Darwin's cotton respectively. What is the ratio of cotton gDNA to Davidson cotton gDNA.
[0041] The mitotic metaphase chromosomes of the yellow-brown cotton and Darwin cotton produced in the same slice were probed with Thurber's cotton gDNA, and the hybridization results were as follows: image 3 Shown: From the recognition ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com