Ethionine resistance Candida utilis and application thereof
A technology of Candida utilis and ethionine, which is applied in fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effects of broad growth nutrition spectrum, low ethanol production, and good industrial application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
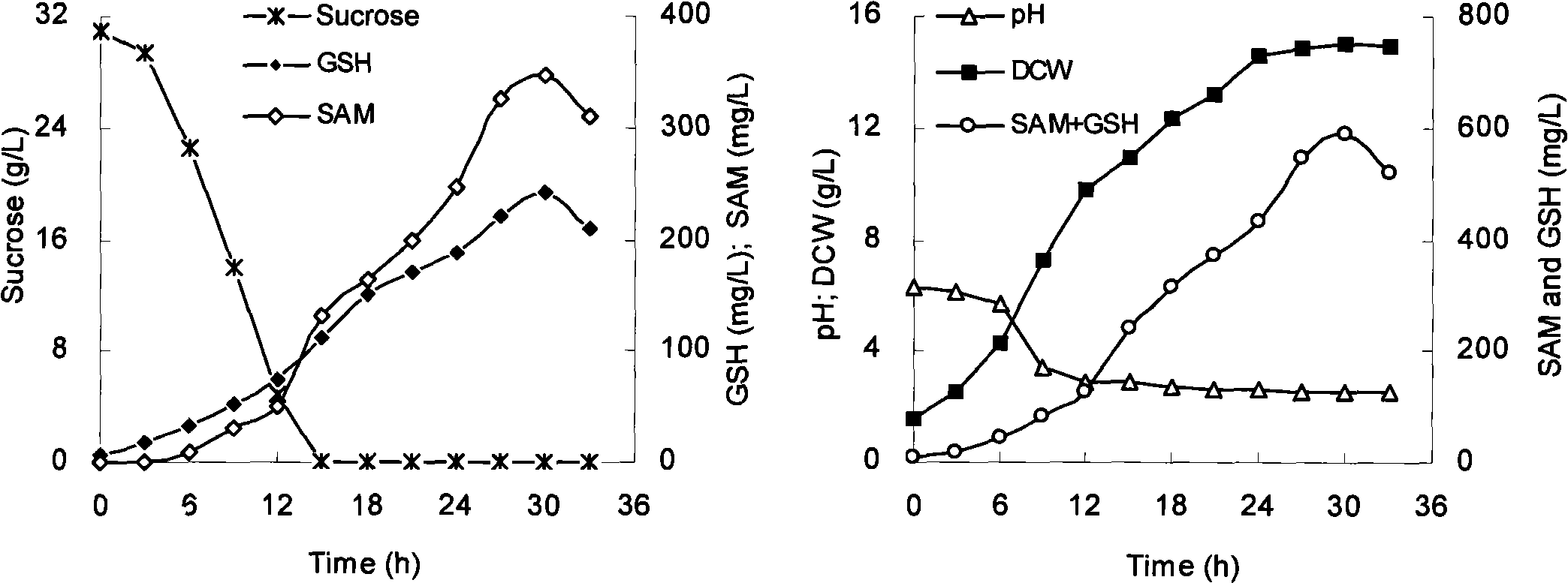
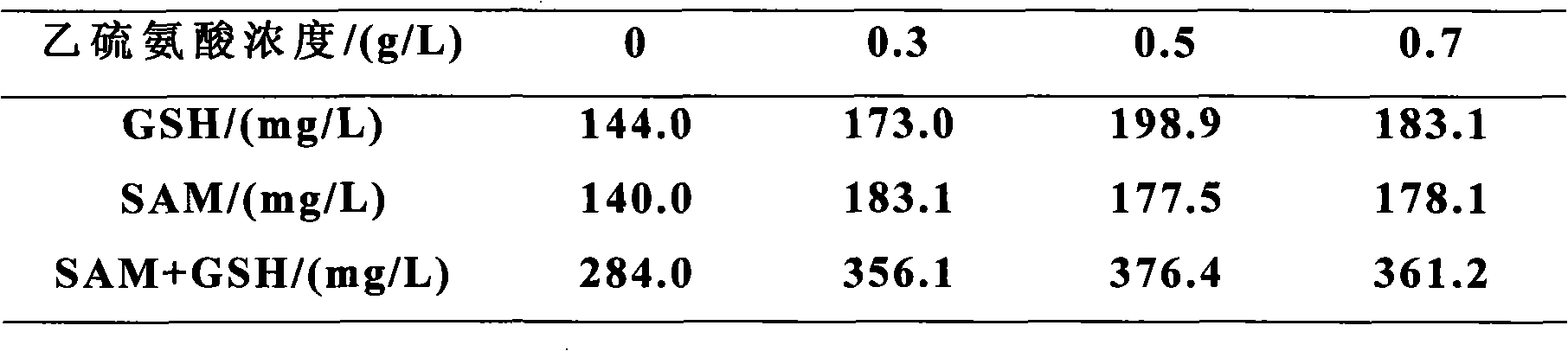
[0029] Example 1, co-production fermentation of SAM and GSH, and determining the optimal concentration of ethionine
[0030] (1) strain
[0031] The starting strain was Candida utilis (Candida utilis) SZU 07-01, which was preserved by the Industrial Microbiology Laboratory of Soochow University.
[0032] (2) culture medium
[0033] Slope and seed medium (g / L): glucose 20, peptone 20, yeast extract 10, pH 6.0;
[0034] Screening medium: add 0-0.7g / L ethionine to the seed medium;
[0035] Fermentation medium before optimization (g / L): glucose 30, ammonium sulfate 8, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3, magnesium sulfate 0.25, pH 5.5.
[0036] (3) UV mutagenesis
[0037] Irradiation was carried out under Philips ZWSSJD-30 ultraviolet lamp, the irradiation power and wavelength were 30W, 253.7nm, respectively, and the irradiation distance was 30cm. The specific operation steps are: absorb 1 mL of seed culture solution after 20 hours of cultivation, centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment two, determine optimal carbon source
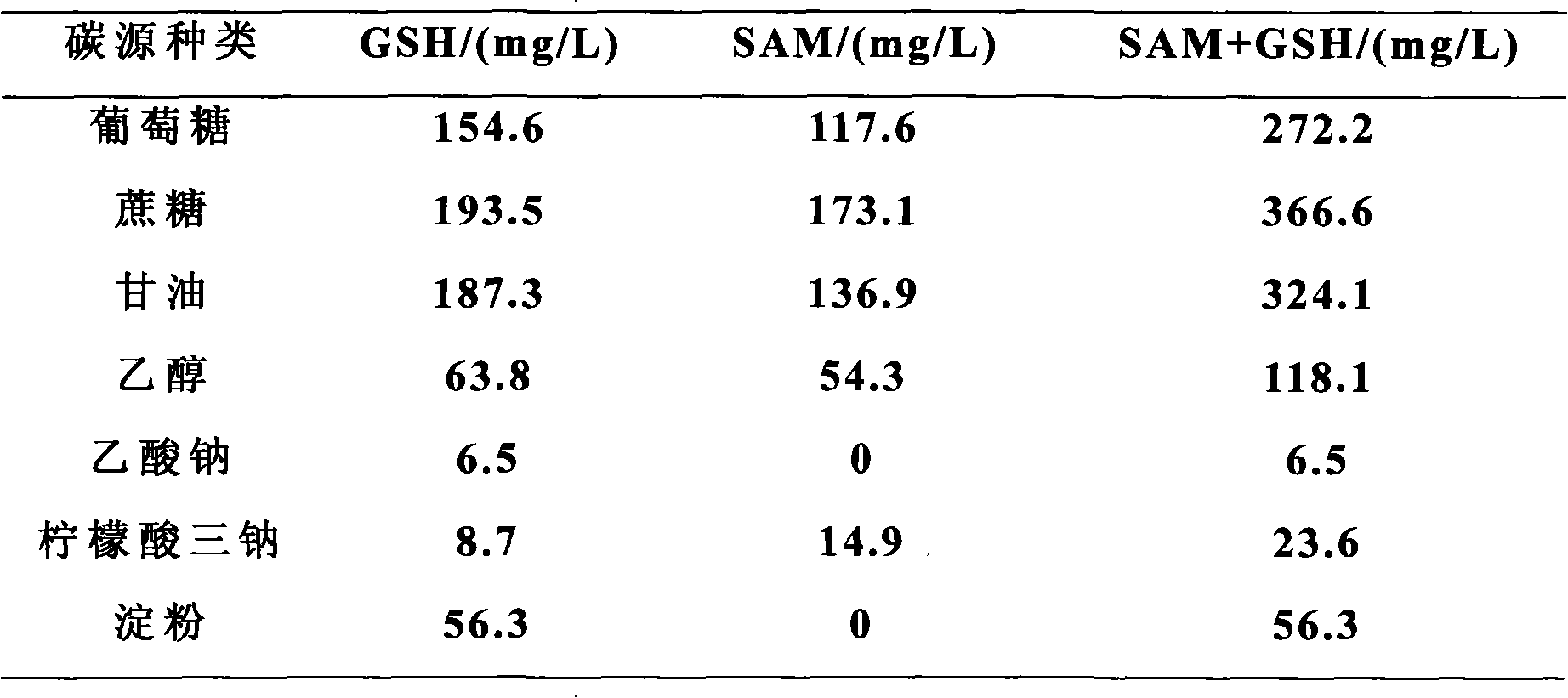
[0065] Carry out operation according to embodiment one, difference is: take the fermented medium before optimization as benchmark, investigate different carbon source (carbon source is respectively glucose, sucrose, glycerol, ethanol, sodium acetate, sodium citrate and starch) to SAM and GSH The impact of co-production fermentation, on this basis, the experimental results of co-production fermentation to prepare SAM and GSH, the results are shown in Table 2:
[0066] SAM output: 0~173.1mg / L; GSH output: 6.5~193.5mg / L;
[0067] The total co-production of SAM and GSH is 6.5-366.6mg / L;
[0068] Among them, the best carbon source is sucrose.
[0069] Table 2 Effects of carbon source types on co-production fermentation of SAM and GSH
[0070]
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment three, determine optimal nitrogen source
[0072] Carry out operation according to embodiment one, difference is: take the fermented medium before optimization as benchmark, investigate different nitrogen sources (nitrogen sources are respectively yeast extract, beef extract, peptone, potassium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, urea and ammonium nitrate) to SAM The influence of co-production fermentation with GSH, on this basis, the experimental results of co-production fermentation to prepare SAM and GSH, the results are shown in Table 3:
[0073] SAM output: 41~146mg / L; GSH output: 57.5~167.7mg / L;
[0074] The total co-production of SAM and GSH is 90.5-308.7mg / L;
[0075] Among them, the best nitrogen source is ammonium sulfate.
[0076] Table 3 Effects of nitrogen source types on co-production fermentation of SAM and GSH
[0077]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com