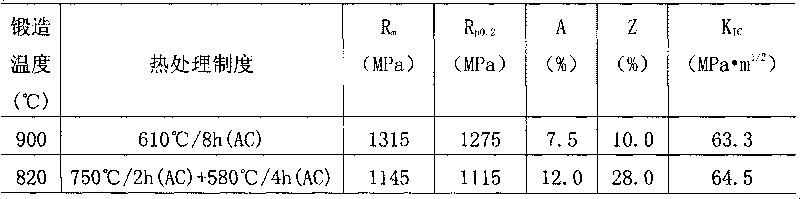Novel high strength and toughness titanium alloy
A technology of tough titanium alloy and titanium alloy, which is applied in the field of high-strength and high-toughness titanium alloy, can solve the problems affecting alloy performance and poor fracture toughness, and achieve the effects of low phase transition point, strong hardenability and good structural stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
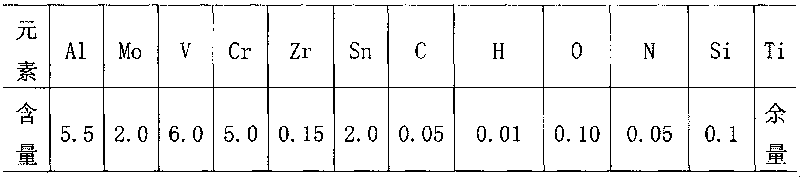
[0042]According to the determined alloy composition, the following alloy materials are selected for batching: commercially available sponge titanium, sponge zirconium, metal chromium, metal aluminum beans, Ti-Sn master alloy, Ti-Mo master alloy, and Al-V master alloy are prepared into a single block Electrode, a single electrode is assembled and welded into a consumable electrode in a vacuum welding box, and the consumable electrode is melted three times in a vacuum consumable melting furnace to prepare an ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 1.
[0043] Chemical composition (wt%) of table 1 ingot
[0044]
[0045] The alloy is billet-forged at the phase transition point of 1150°C, and after forging at 820°C, it is made into a φ110mm billet. After the billet is heated to 900°C or 820°C, it is forged into a 36mm×67mm bar on a precision forging machine. After being treated by the heat treatment system listed in Table 2, the mechanical performance tes...
Embodiment 2
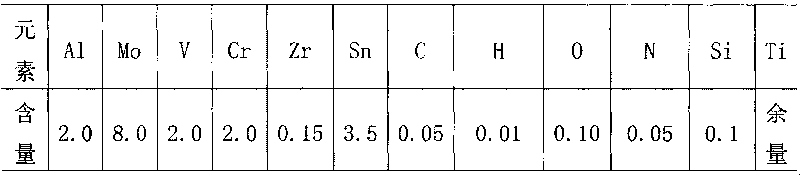
[0050] According to the determined alloy composition, the following alloy materials are selected for batching: commercially available sponge titanium, sponge zirconium, metal chromium, metal aluminum beans, Ti-Sn master alloy, Ti-Mo master alloy, and Al-V master alloy are prepared into a single block Electrode, a single electrode is assembled and welded into a consumable electrode in a vacuum welding box, and the consumable electrode is vacuum consumable smelted three times in a vacuum consumable melting furnace to prepare an ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 3.
[0051] Chemical composition (wt%) of table 3 ingot
[0052]
[0053] The alloy is billet-forged at the phase transition point of 1150°C, and after forging at 820°C, it is made into a φ110mm billet. After the billet is heated to 900°C or 820°C, it is forged into a 36mm×67mm bar on a precision forging machine. After being treated by the heat treatment system listed in Table 4, the mechan...
Embodiment 3
[0057] According to the determined alloy composition, the following alloy materials are selected for batching: commercially available sponge titanium, sponge zirconium, metal chromium, metal aluminum beans, Ti-Mo master alloy, and Al-V master alloy are prepared into monolithic electrodes. The consumable electrode was assembled and welded in the vacuum welding box, and the consumable electrode was smelted three times in the vacuum consumable melting furnace to prepare an ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 5.
[0058] Chemical composition (wt%) of table 5 ingot
[0059]
[0060] The alloy is billet-forged at the phase transition point of 1150°C, and after forging at 820°C, it is made into a φ110mm billet. After the billet is heated to 900°C or 820°C, it is forged into a 36mm×67mm bar on a precision forging machine. After being treated by the heat treatment system listed in Table 6, the mechanical properties were tested according to the requirements...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com