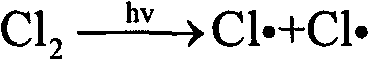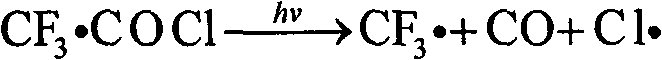Method for preparing trifluoroacetyl chloride from 2,2-dichloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane
A technology of trifluoroacetyl chloride and trifluoroethane, which is applied in the field of compound preparation and can solve problems such as corrosion of ultraviolet lamps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
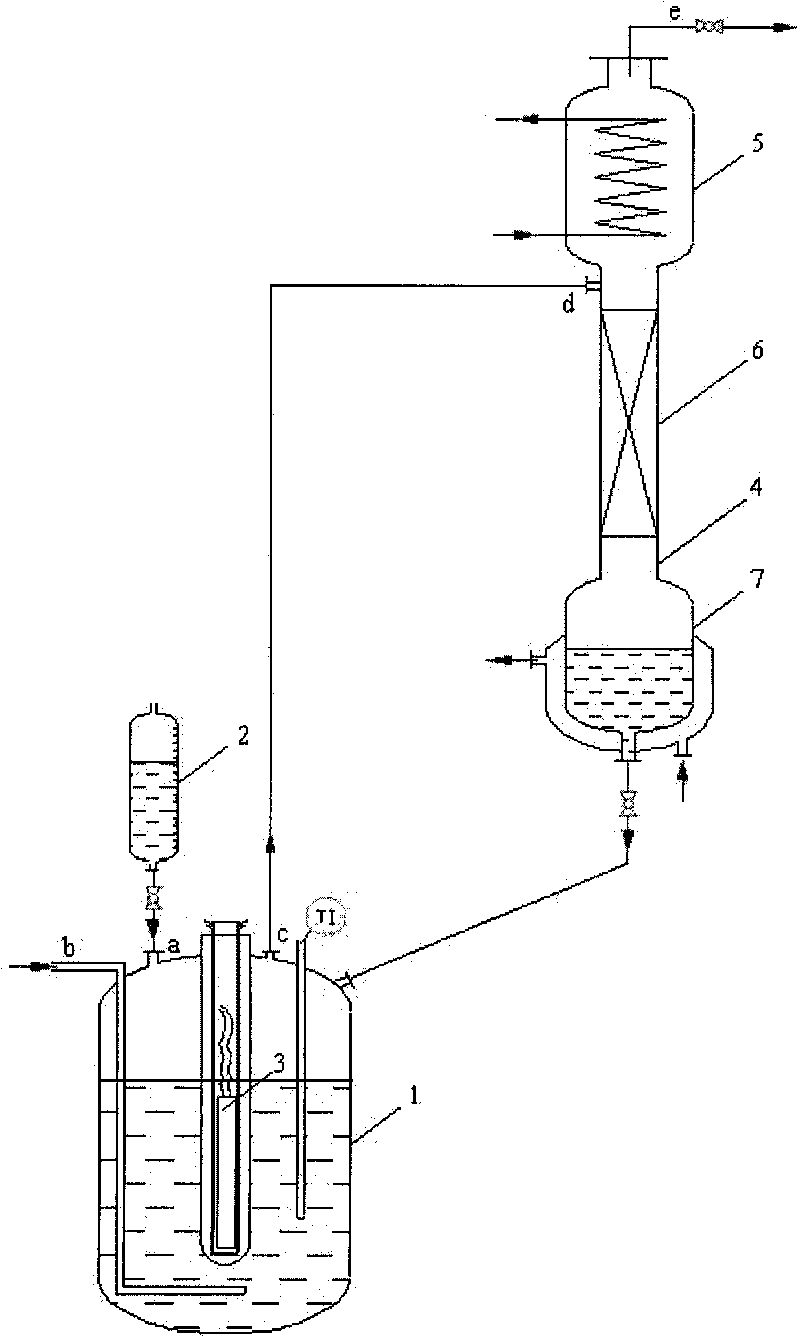
[0029] Add 1L of HCFC-123 into a 1L special glass flask. The middle interface on the top of the flask is a mercury lamp installation port. Place a 500w mercury lamp, quartz cold hydrazine, and quartz sleeve in sequence from the inside to the outside. The sleeve and the interface are sealed. Continuously feed oxygen and chlorine under stirring, flow rate is respectively 75ml / min and 15ml / min, open mercury lamp after 15 minutes, carry out photochemical oxidation reaction by mercury lamp radiation, react at normal pressure, material bubble point temperature (about 28°C). The reactant is continuously discharged from the gas phase outlet on the upper part of the reactor in the form of gas phase, and the liquid level in the reactor is kept constant by continuously adding HCFC-123 through the dropping funnel, and the supplementary speed is determined by the reaction rate; the continuously discharged reactant includes HCFC vaporized during the reaction -123, product TFAC, by-product h...
Embodiment 2
[0033]The difference between the reaction of Example 2 and Example 1 is that an ice water bath is added outside the flask in Example 2 to control the reaction temperature in the flask to be 10°C, and other conditions are the same as in Experiment 1, except for HCFC-123, oxygen, and chlorine in the gas phase products TFAC accounts for 94% with hydrogen chloride gas, and generates 0.78mol TFAC in total. The content of HCFC-123 in the bottom liquid is 95.21%, and the by-product CFC-113a is 4.74%. After several batches of continuous reaction, corrosion was found in the glass of the reactor, quartz tube, and reflux condenser.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Reaction in embodiment 3 is different from experiment 1 in that the reaction pressure of embodiment 3 is 0.05MPa, and reaction temperature is the bubble point temperature (about 10 ℃) of material in the reactor, and other conditions are identical with experiment 1, except that HCFC-123, oxygen, chlorine and hydrogen chloride gas accounted for 98% of TFAC, and a total of 0.80mol TFAC was generated. The content of HCFC-123 in the bottom liquid is 95.11%, and the by-product CFC-113a is 4.77%. After several batches of continuous reaction, no corrosion phenomenon was found in glass such as reactor, quartz tube and reflux condenser tube.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com