Biocompatibility nanoparticle and application thereof as drug conveying carrier
A nanoparticle, drug-loaded technology, applied in drug combinations, medical preparations with inactive ingredients, antitumor drugs, etc., can solve the problems of low stability, easy dissociation, and inability to improve drug availability and efficacy. , to achieve the effect of enhanced circulation and stability, good hydrophilicity, good biocompatibility and biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1, the synthesis of related compounds
[0050] 1. Synthesis of COP
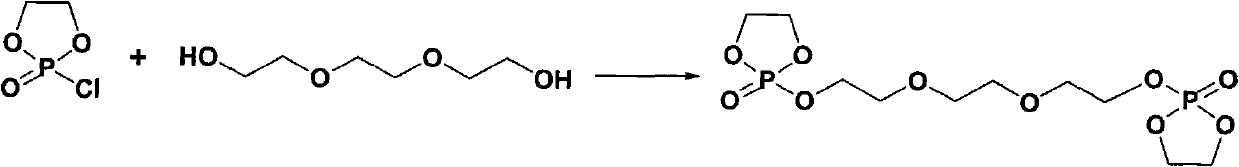
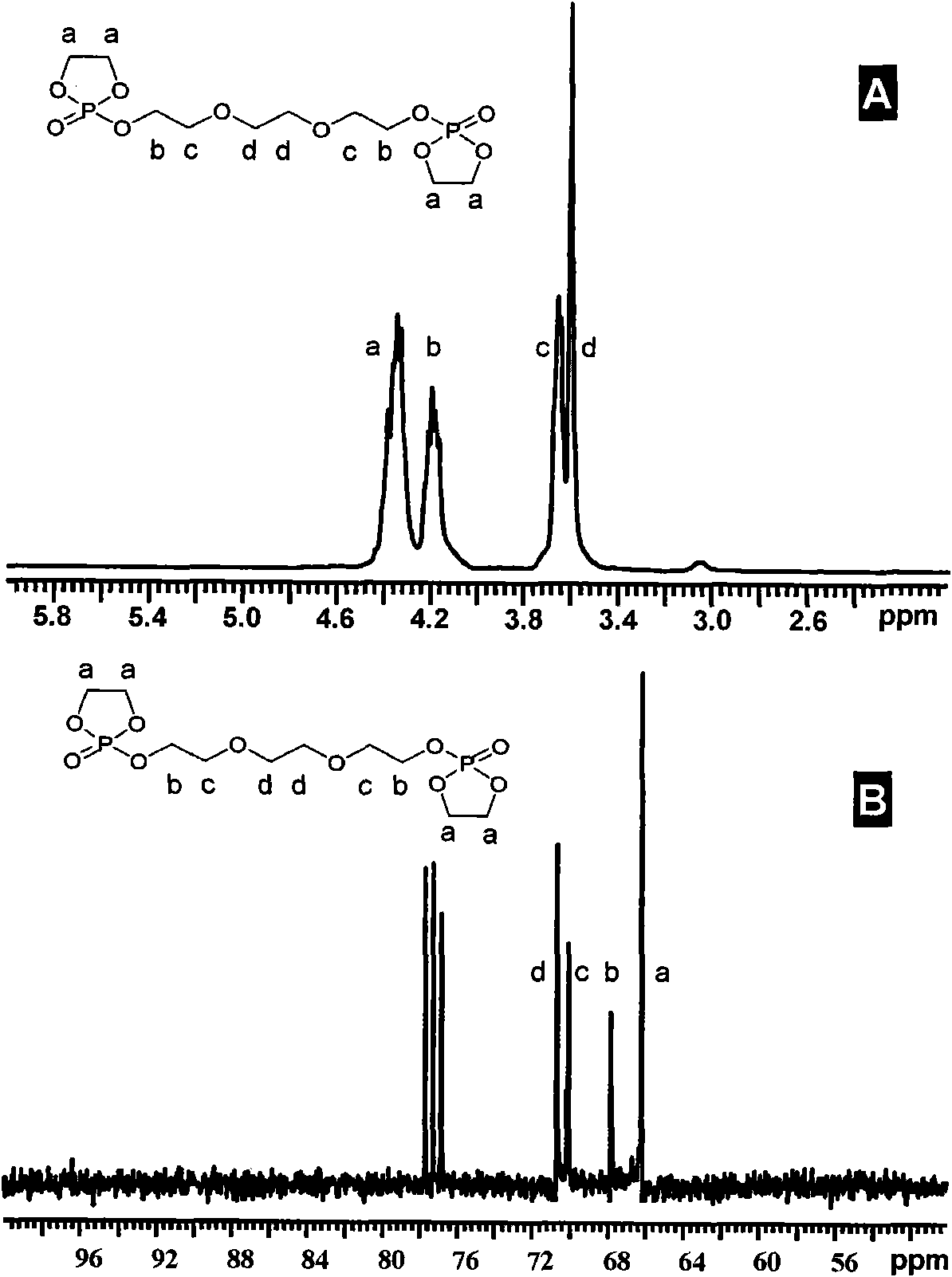
[0051] Synthesis of 2-chloro-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane (2-chloro-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane, COP) by reaction of phosphorus trichloride with ethylene glycol ), the specific synthesis method is as follows: in a 1000mL three-necked round-bottomed flask, phosphorus trichloride (3.0mol) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane (500mL), and slowly dropped into ethylene glycol through a constant pressure dropping funnel (3.0mol), after all the drops were finished, the reaction was continued for 0.5 hours, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the product was evaporated by continuous vacuum distillation twice (50°C, 200Pa). Dissolve the product in benzene and pass through O 2 Reaction for 48 hours, the solvent benzene was evaporated under reduced pressure, and then the product (COP) was evaporated twice by continuous distillation under reduced pressure (88~89°C, 20Pa), and...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, synthesis and characterization of mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles
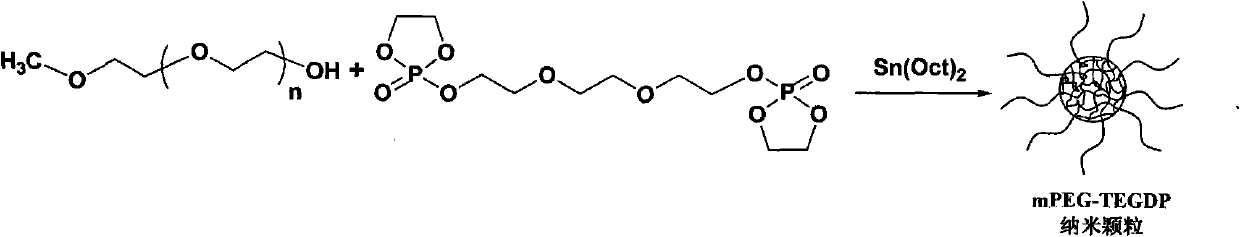
[0056] Schematic diagram of the synthesis of mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles image 3 shown. Pre-dosed mPEG, TEGDP and Sn(Oct) in a dry round bottom flask 2 , the molar feed ratio of the three and the parameters of the reaction system are shown in Table 1. After the system was reacted for 12 hours, a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 15,000 was dialyzed in ultrapure water for 72 hours, and a white powder product (mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticle) was obtained after lyophilization.
[0057] Table 1 Synthesis conditions of mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles
[0058]
[0059] The composition of the nanoparticles was determined using elemental analysis methods. Table 2 shows the elemental analysis results of mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles, indicating that nanoparticles with different compositions can be obtained by adjusting the synthesis conditions.
[0060] Table 2 Elemental analysis of mPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles
[...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Preparation and characterization of embodiment 3, mPEG-laPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles
[0066] The schematic diagram of the synthesis of mPEG-laPEG-TEGDP nanoparticles is shown in Image 6 shown.
[0067] 1. mPEG-N 3 Preparation of PEG-TEGDP nanoparticles
[0068] mPEG2000, N 3 PEG3400, TEGDP and Sn(Oct) 2 They were added to dry round bottom flasks (see Table 3 for the molar feed ratio). After reacting in dimethyl sulfoxide for 12 hours, dialyze in ultrapure water for 72 hours with a molecular weight of 15,000, and freeze-dry to obtain the surface azide group-functionalized nanoparticles mPEG-N 3 PEG-TEGDP.
[0069] mPEG-N 3 The element ratios of PEG-TEGDP nanoparticles and the calculation results of each component ratio are listed in Table 3. As can be seen from Table 3, N 3 The proportion of PEG in the total amount of initiator increased from 0.9 / 0.1 to 0.5 / 0.5, and its content in nanoparticles also increased, from 0.9 / 0.039 to 0.5 / 0.235. This result indicates tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com