Method for reprocessing spent nuclear fuel and centrifugal extractor therefor
一种提取装置、核燃料的技术,应用在核燃料的再加工领域,能够解决溶剂放射线劣化变大、提取用溶剂寿命变短等问题,达到抑制效果良好的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0055] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the 1st Embodiment of the reprocessing method of the used nuclear fuel of this invention.
[0056]The method for reprocessing used nuclear fuel in this embodiment is based on the pleux method. The pleux method is to dissolve the used nuclear fuel taken out of the nuclear reactor in an aqueous solution of nitric acid, and dissolve the fuel obtained by the dissolution by solvent extraction. The atomic nuclides contained in the liquid are separated and recovered.
[0057] figure 1 It is a flow chart showing the reprocessing process performed by this reprocessing method, and each process of this reprocessing method is demonstrated below.
[0058] Step S1 is a step of storing and cooling the used nuclear fuel taken out of the nuclear reactor in a storage pool until it reaches a predetermined radioactive level (storage and cooling of used nuclear fuel).
[0059] Step S2 is a step of cutting the used nuclear fuel (fuel assembly) cooled an...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
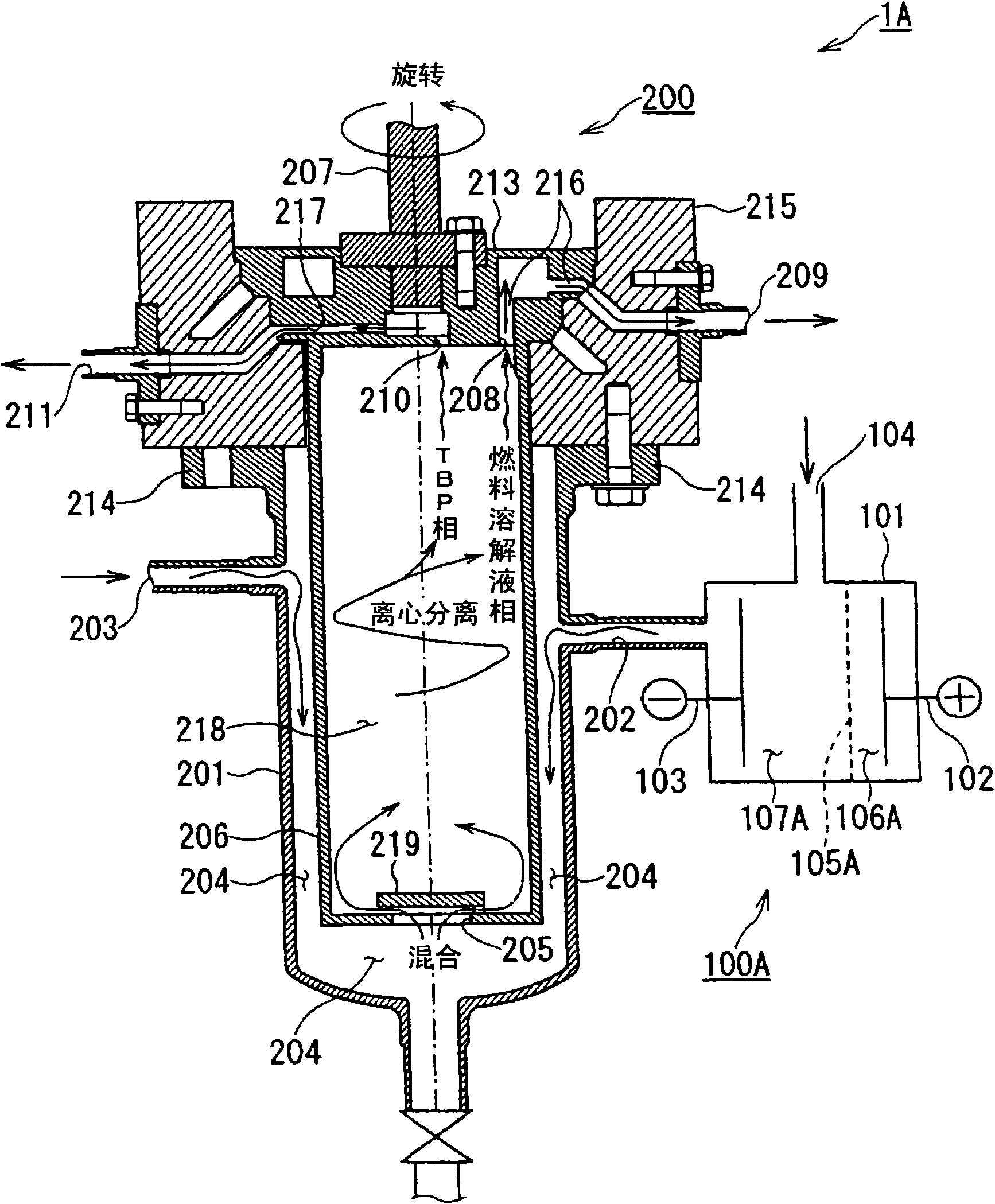
[0101] image 3 It is a figure (longitudinal sectional view) which shows 2nd Embodiment of the centrifugal extraction apparatus of this invention.
[0102] This embodiment is an example in which the configuration of the electrolytic reduction unit 100 of the centrifugal extraction device 1 of the first embodiment is modified. Note that the same configurations as those of the first embodiment are assigned the same symbols and their descriptions are omitted, and the configurations of the first embodiment that are modified or newly added will be described by adding “A” at the end of the symbols.
[0103] Such as image 3 As shown, the centrifugal extraction device 1A of this embodiment has an electrolytic reduction unit 100A. The electrolytic reduction cell 101 of this electrolytic reduction unit 100A has a diaphragm 105A inside, and an anode chamber 106A and a cathode chamber 107A in which an anode 102 and a cathode 103 are provided via the diaphragm 105A. In addition, in the...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0109] Figure 4 It is a figure which shows the 3rd embodiment of the centrifugal extraction apparatus of this invention, Figure 4 (A) is a longitudinal sectional view of the centrifugal extraction device, Figure 4 (B) is Figure 4 (A) III-III sectional view.
[0110] This embodiment is an example in which the configuration of the electrolytic reduction unit 100 of the centrifugal extraction device 1 of the first embodiment is modified. Note that the same configurations as those of the first embodiment are given the same symbols and their descriptions are omitted, and the configurations of the first embodiment that are modified or newly added will be described by adding “B” at the end of the symbols.
[0111] Such as Figure 4 As shown in (A), the centrifugal extraction device 1B of this embodiment has electrolytic reduction units ( 102B, 103B, 202B, 204B). That is, the centrifugal extraction device 1 of the present embodiment is a device in which the centrifugal extrac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com