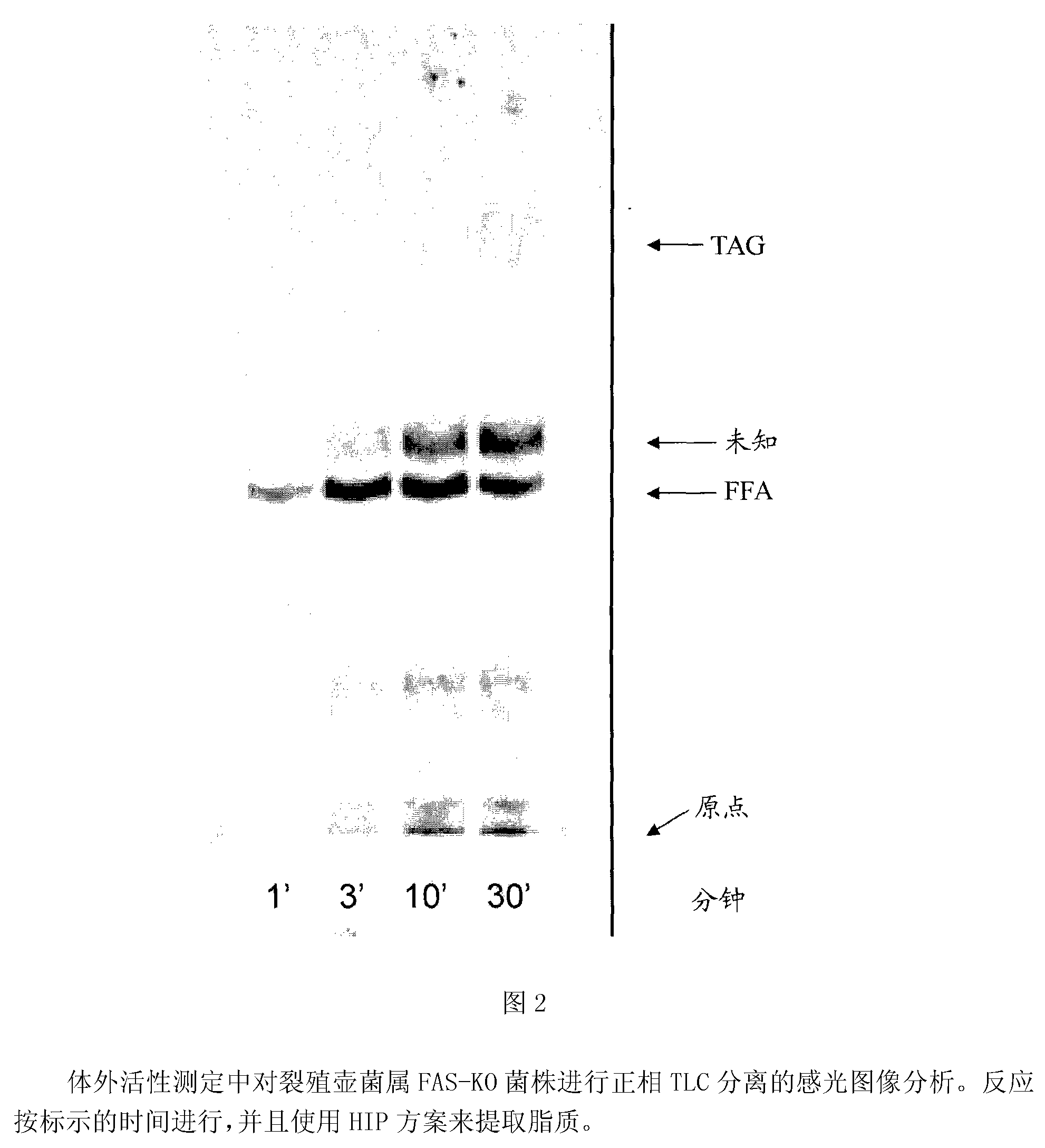Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
A technology for synthesizing enzymes and free fatty acids, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, which can solve problems such as inaccurate mechanism definition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0434] This example describes the generation of a FAS knockout strain of Schizochytrium for biochemical studies.
[0435] Schizochytrium contains a large gene encoding the FAS enzyme responsible for the production of short chain saturated fatty acids (described in US Patent Application Publication No. 20050191679 A1). Using the method described in US Pat. No. 7,001,772, a Schizochytrium FAS knockout (FAS-KO) construct was obtained. The EcoRV fragment of about 10.0 kB in genomic DNA containing most of the FAS Orf (from about 728 bp downstream of the putative ATG start codon to about 680 bp downstream of the stop codon) was cloned into Stratagene Bluescript In the vector (pBSK), the vector is located in the EcoRV site of the polycloning region. The approximately 3.5 kB internal BglII fragment was removed from the cloned Schizochytrium DNA and replaced with the approximately 1.1 kB BamHI fragment from pTubZeo11-2, which contains a Zeocin resistance cassette (see above US patent ...
Embodiment 2
[0437] The following examples describe general protocols for the preparation of cell-free extracts of the following strains: Schizochytrium Ac66, PUFA synthase KO strain derived from Schizochytrium Ac66, and Schizochytrium Ac66-derived FAS-KO strain.
[0438] An example of a protocol for preparing a cell-free homogenate (CFH) from a cell wall deficient strain of Schizochytrium is as follows. Cells were grown in A50-3 medium and then diluted into M2B medium. The medium used to grow the KO strains was supplemented with appropriate fatty acids. Cells were grown in M2B medium to an OD600nm of >about 2.5 and <about 5. Cells in 50 mL of medium were collected by centrifugation in 50 mL plastic tubes (benchtop centrifuge, approximately 1200 rpm x 4 min). The supernatant was decanted and the cells were resuspended in 5 mL of Buffer A (100 mM phosphate (pH 7.2), 10% (w / v) glycerol, 1 mM EDTA and 2 mM DTT), then as before. Centrifuge as described. Discard the supernatant and resuspe...
Embodiment 3
[0440] This example describes general conditions for in vitro assays of FAS and PUFA synthetase activity.
[0441] Examples of protocols for in vitro activity assays for FAS and PUFA synthase activity are as follows. Mix the enzyme preparation and Buffer A (both components in a volume of 90 μL) and the following components (added as a cocktail (10 μL)) to make a final volume of 100 μL to give the indicated in parentheses Final concentration: Malonyl-CoA (50 μM - non-radioactive malonyl-CoA and malonyl-2- 14 A mixture of C-CoA with a final concentration of radiolabeled at 0.65 μCi / mL), NADH (1 mM), NADPH (1 mM) and acetyl-CoA (10 μM). These and additional components can be adjusted based on the needs of a particular experiment. The assay reactions were performed in glass tubes in a room temperature (about 21°C) water bath. The time of incubation depends on the needs of the experiment. The reaction was stopped using one of two work-up protocol based methods. For the use of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com