Amino acid copolymer-calcium sulfate composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material, amino acid technology, applied in the field of polyamino acid copolymer-calcium sulfate composite material and its preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6
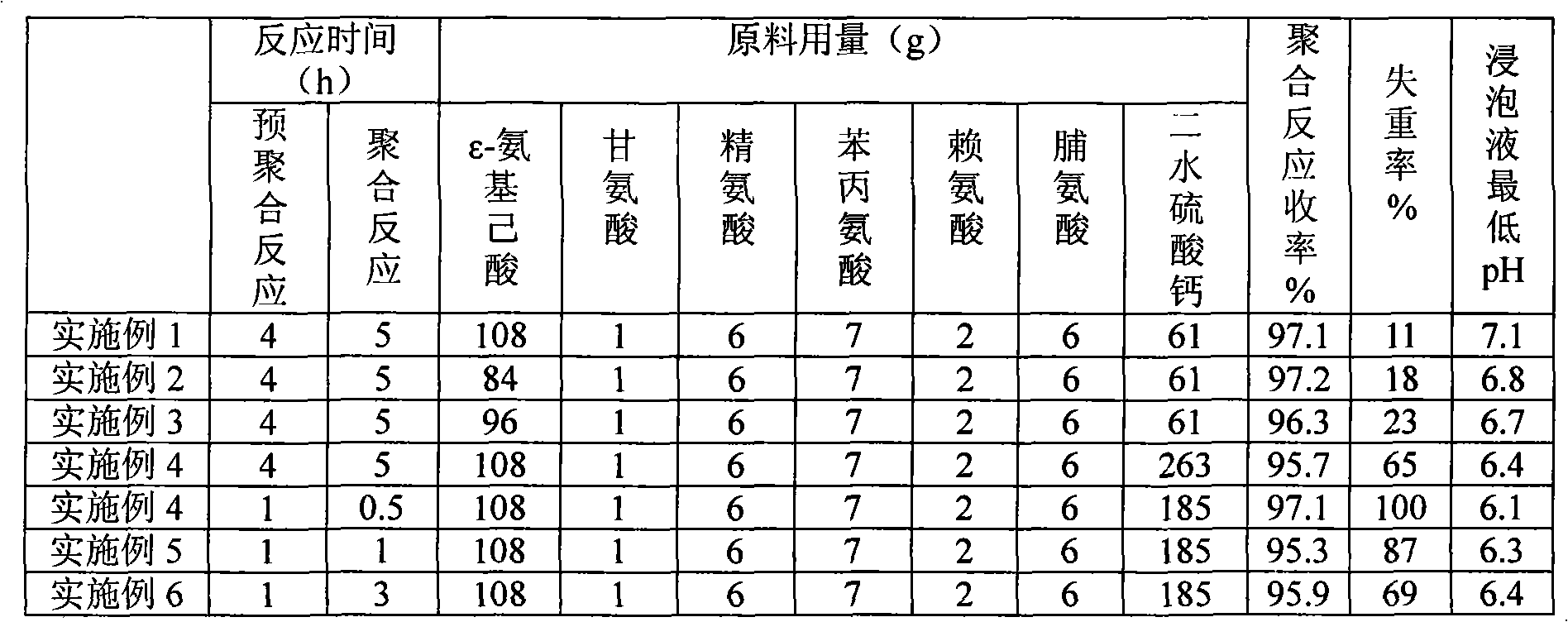
[0017] The raw materials are calcium sulfate dihydrate, ε-aminocaproic acid, glycine, arginine, phenylalanine, lysine, and proline, and the amounts used in each embodiment are shown in Table 1 respectively.
[0018] Put the raw materials into a 250ml three-necked bottle, add 100ml of water, and dehydrate at 150-160°C (until the amino acid starts to melt). After dehydration, the temperature was raised to 220°C, pre-polymerization was carried out in a molten state, and then the temperature was raised to 230°C to carry out polymerization reaction. The time of the two steps of pre-polymerization and polymerization reaction are shown in Table 1 respectively. The yield and degradation performance index of each case of polymer composite products are shown in Table 1. The weight loss rate of the degradation of the polymer composite product after soaking in the simulated body fluid for 12w is also shown in Table 1 respectively.
[0019] Table 1 Example 1 to Example 6
[0020]
Embodiment 7
[0022] The raw material is 45g of calcium sulfate hemihydrate, the dosages of ε-aminocaproic acid, glycine, arginine, phenylalanine, lysine, proline, alanine, threonine, and serine are 91g, 1g, respectively. 3g, 5g, 5g, 2g, 5g, 6g, 2g, 1g. Put the raw materials into a 250ml three-neck bottle, add 100ml of water, and dehydrate at 150-160°C (you can judge whether the dehydration process has been completed by observing whether the amino acid starts to melt, etc.). After the dehydration is completed, the temperature is raised to 220° C., pre-polymerization is carried out for 3 hours in a molten state, and then the temperature is raised to 230° C. for 3 hours of polymerization reaction. The yield of the composite material was 96.5%; the simulated body fluid soaked for 12w, the weight loss rate was 43%, and the lowest pH value of the soaking solution was 6.7.
Embodiment 8
[0024] The raw material is 55g of anhydrous calcium sulfate, and the dosages of ε-aminocaproic acid, phenylalanine, lysine, proline, alanine, threonine, and serine are 84g, 2g, 3g, 5g, 5g, 2g, 5g, 6g. Put the raw materials into a 250ml three-neck bottle, add 100ml of water, and dehydrate at 150-160°C (you can judge whether the dehydration process has been completed by observing whether the amino acid starts to melt, etc.). After the dehydration is completed, the temperature is raised to 220° C., pre-polymerization is carried out for 2.5 hours in a molten state, and then the temperature is raised to 230° C. for 3.5 hours of polymerization reaction. The yield is 97.8%; the simulated body fluid soaks for 12w, the weight loss rate is 53%, and the pH value of the soaking solution is the lowest at 6.5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com