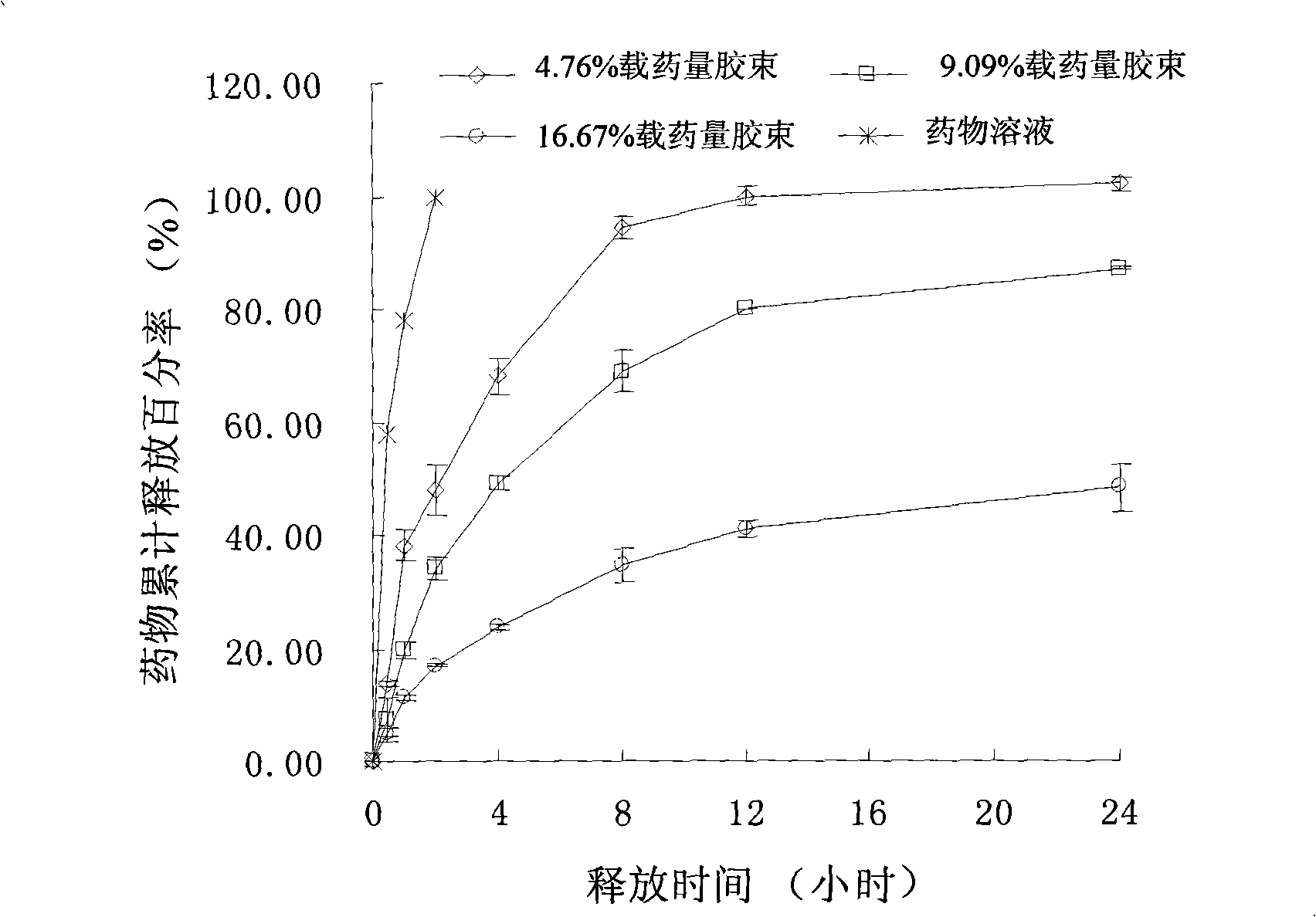
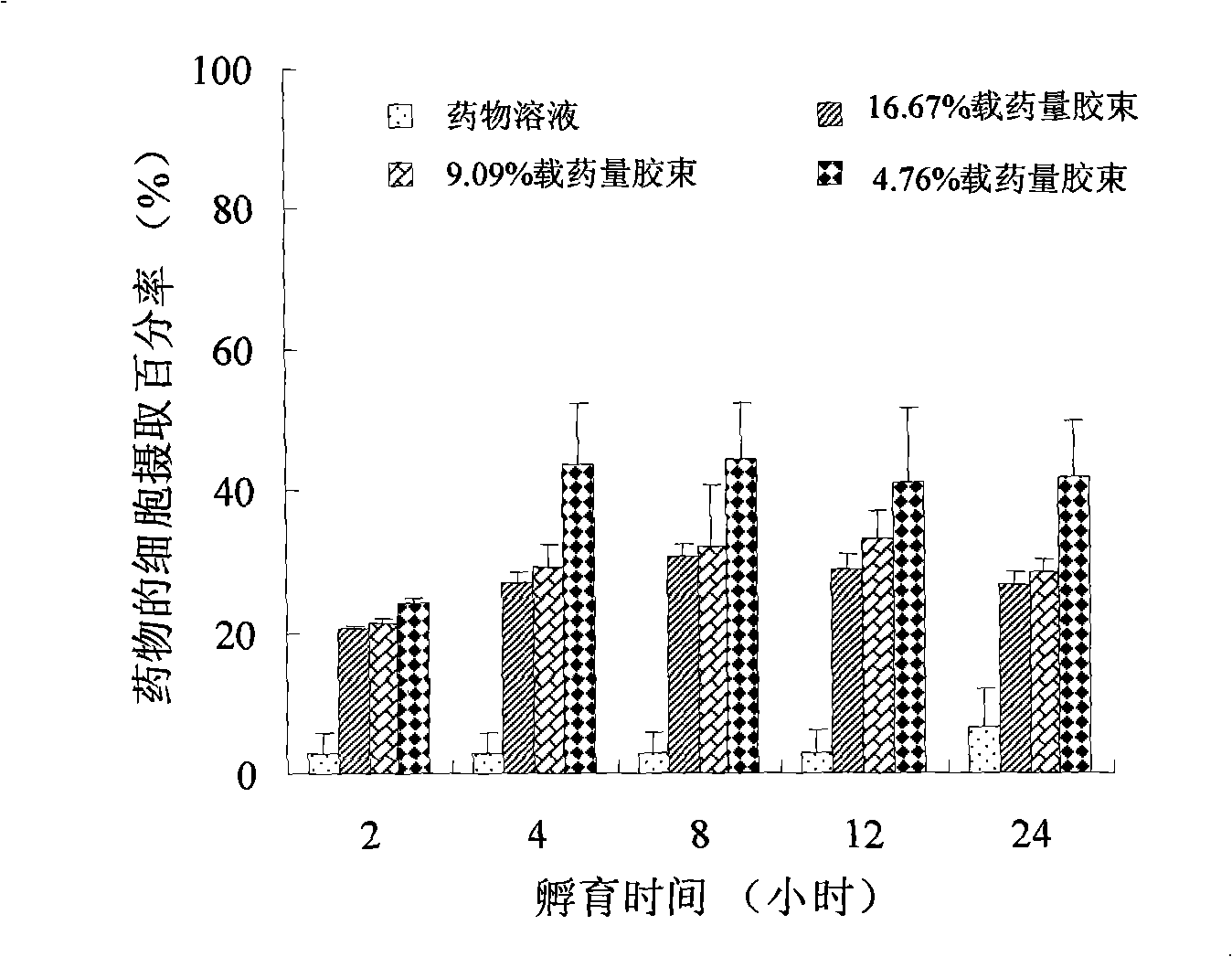
Chlorin e6 chitosan-stearic acid graft micelle
A technology of chlorin and stearic acid, applied in the field of targeted preparations, can solve the problems of lack of specificity, toxic and side effects, skin phototoxicity, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing drug concentration and reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0019] Take 90g of commercially available chitosan with a molecular weight of 450kDa (degree of deacetylation: 95%), add it to 3000mL 1.25% (v / v) hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, swell at 55-60°C for 2 hours, Add 5% cellulase (w / w) and degrade at a temperature of 55-60°C. Control the reaction temperature and time to obtain low molecular weight chitosan. The resulting degradation reaction solution is classified by ultrafiltration using 50Kda and 10Kda ultrafiltration membranes (Biomax-10, Millipore Co., USA), and then the ultrafiltrate with a molecular weight of 10-50Kda is freeze-dried. The molecular weight of chitosan was determined by gel permeation chromatography using TSK-gel G3000SW chromatographic column, 0.1mol / L sodium acetate (pH 6.0) as the mobile phase, and the molecular weight of 0.73, 5.9, 11.8, 47.3, 212.0, 788.0Kda An elution curve was prepared from the glycan standard, and the molecular weight of chitosan ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0037] Take 90g of commercially available chitosan with a molecular weight of 450kDa (degree of deacetylation 95%), add it to 3000mL 1.25% (v / v) hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, swell at 55-60℃ for 2 hours, Add 5% cellulase (w / w), and degrade at a temperature of 55-60°C. Control the reaction temperature and time to obtain low molecular weight chitosan. The resulting degradation reaction solution is classified by ultrafiltration using 50Kda and 10Kda ultrafiltration membranes (Biomax-10, Millipore Co., USA), and the ultrafiltrate with a molecular weight of 10-50Kda is freeze-dried. The molecular weight of chitosan was determined by gel permeation chromatography, using TSK-gel G3000SW chromatographic column, 0.1mol / L sodium acetate (pH 6.0) as the mobile phase, and the molecular weight of 0.73, 5.9, 11.8, 47.3, 212.0, 788.0Kda An elution curve was prepared from the glycan standard, and the molecular weight of chitosan was c...
Embodiment 3
[0054] 1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0055] Take 90g of commercially available chitosan with a molecular weight of 450kDa (degree of deacetylation 95%), add it to 3000mL 1.25% (v / v) hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, swell at 55-60℃ for 2 hours, Add 5% cellulase (w / w), and degrade at a temperature of 55-60°C. Control the reaction temperature and time to obtain low molecular weight chitosan. The resulting degradation reaction solution is classified by ultrafiltration using 50Kda and 10Kda ultrafiltration membranes (Biomax-10, Millipore Co., USA), and the ultrafiltrate with a molecular weight of 10-50Kda is freeze-dried. The molecular weight of chitosan was determined by gel permeation chromatography, using TSK-gel G3000SW chromatographic column, 0.1mol / L sodium acetate (pH6.0) as the mobile phase, and the molecular weight of 0.73, 5.9, 11.8, 47.3, 212.0, 788.0Kda An elution curve was prepared from the glycan standard, and the molecular weight of chitosan was ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com