Stretch nonwoven fabric and tapes
A technology of non-woven fabrics and thermal shrinkage rate, applied in textiles, bandages, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve problems that have not been fundamentally solved, have not yet been developed, and achieve the effect of high scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
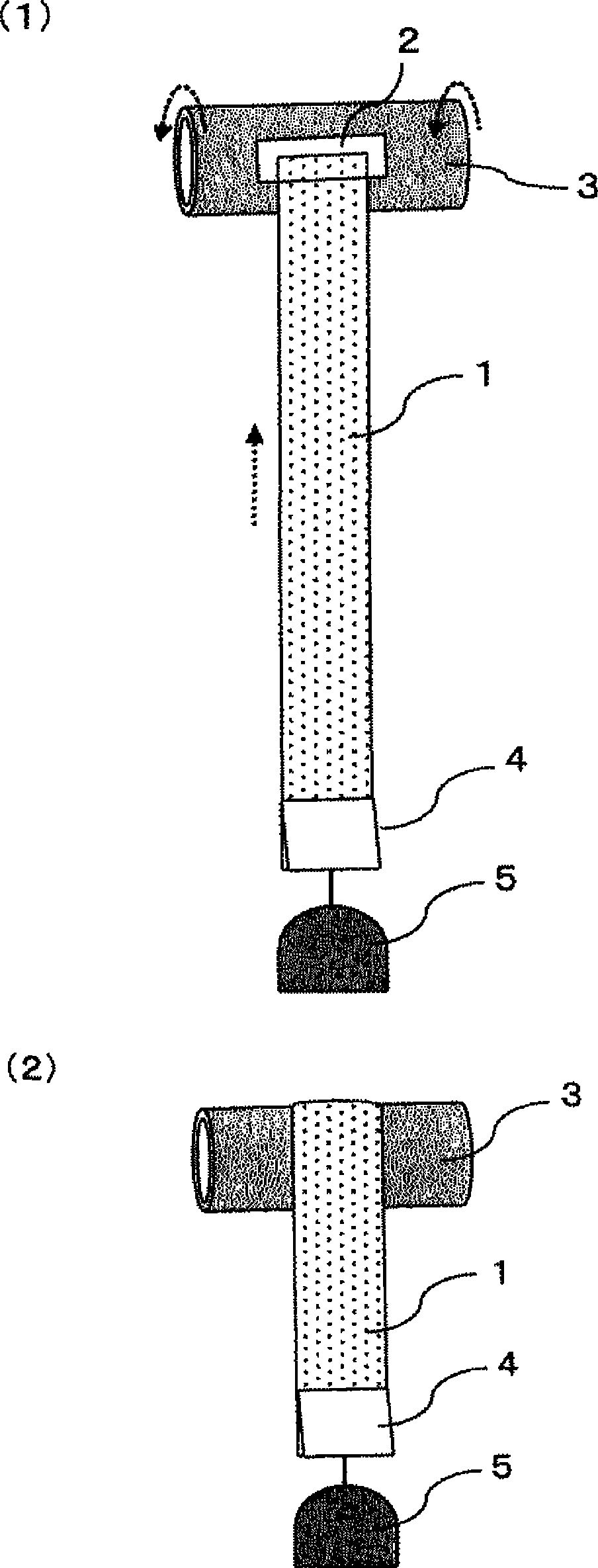
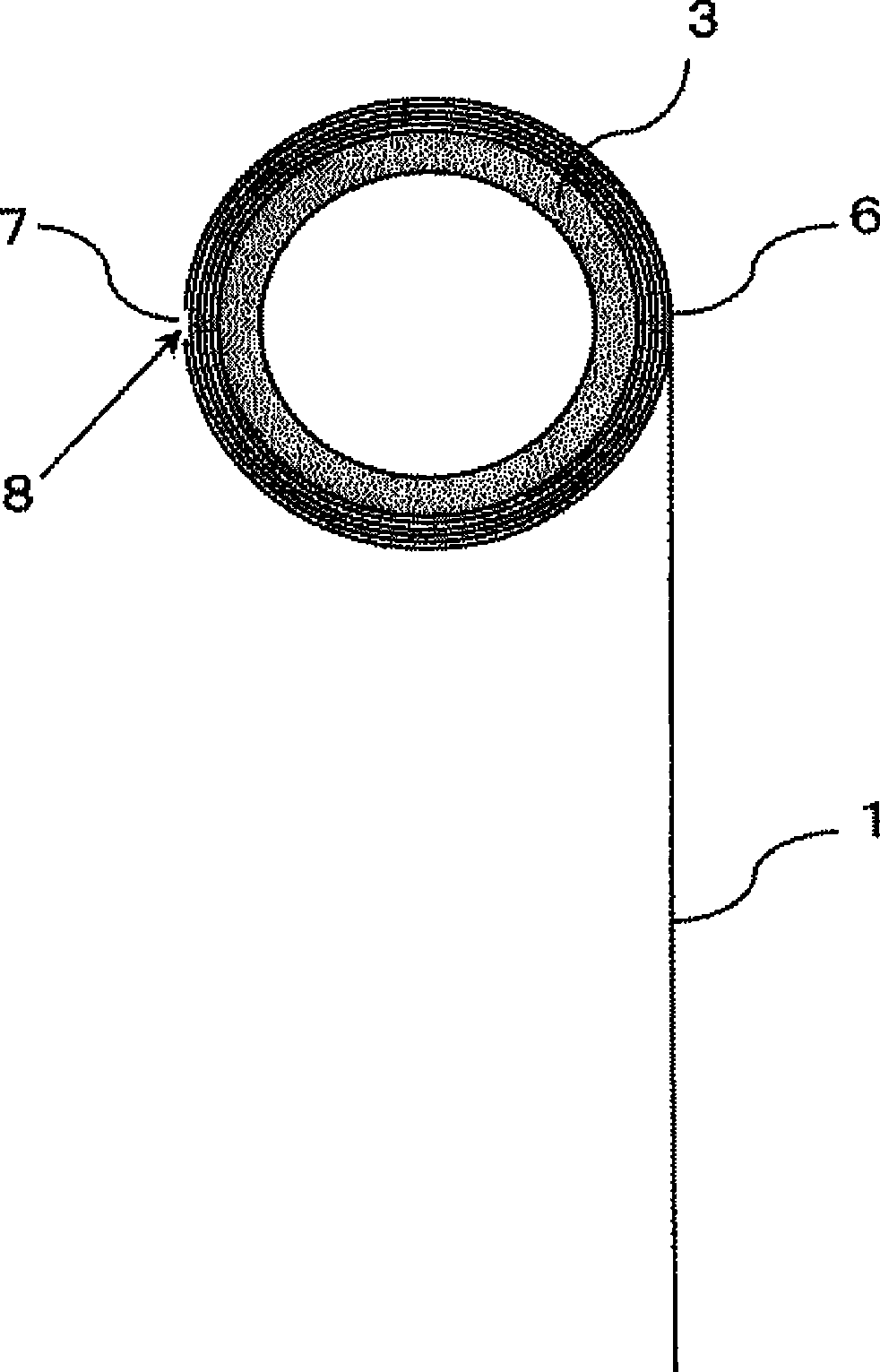
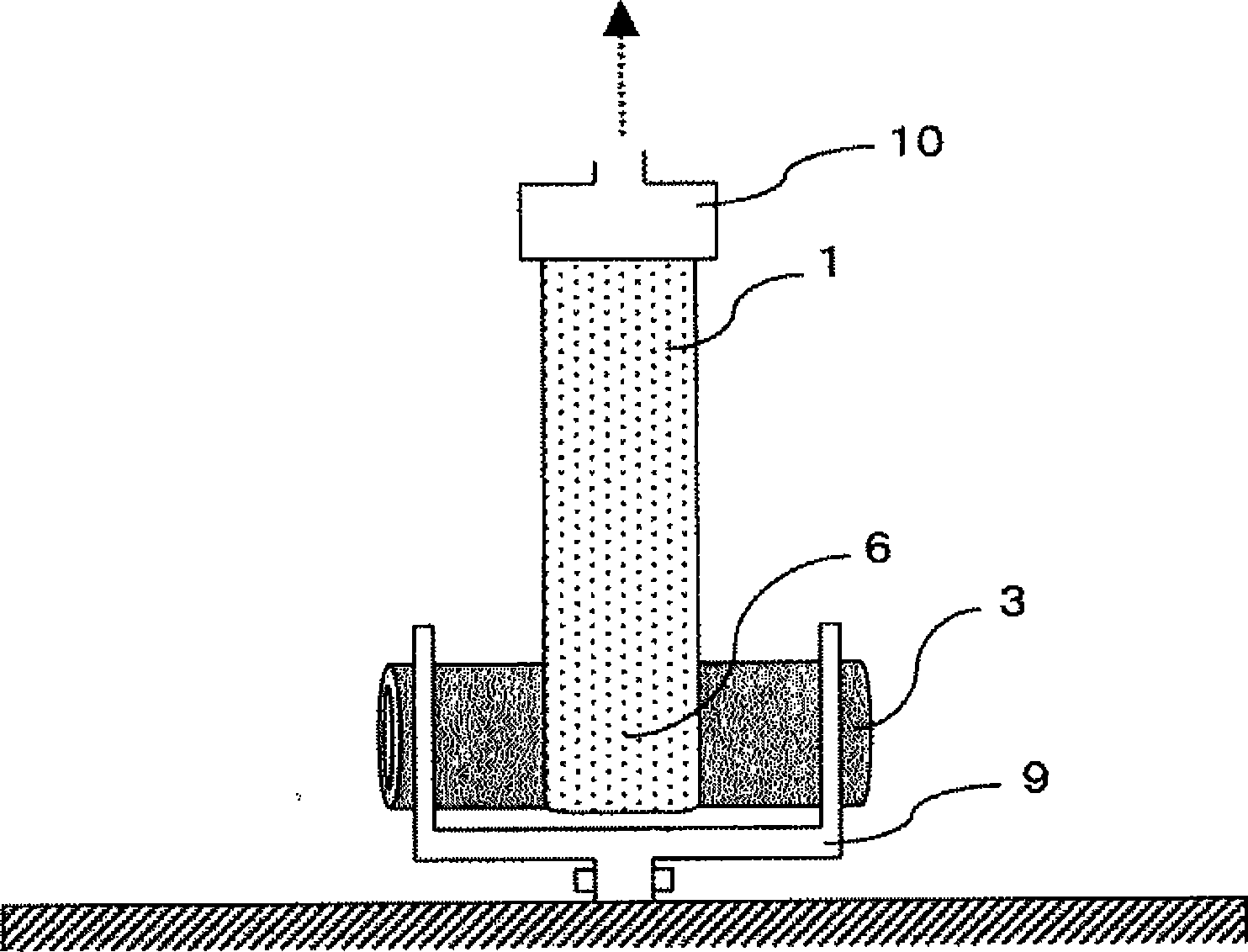
[0138] As a latent crimping fiber, prepare a polyethylene terephthalate resin (component A) containing an intrinsic viscosity of 0.65, and a modified polyethylene terephthalate resin obtained by copolymerizing 20 mol% of isophthalic acid and 5 mol% of diethylene glycol. Side-by-side composite short fibers of ethylene diformate resin (component B) (manufactured by Kuraray, "PN-780", 1.7dtex x 51mm long, number of mechanical crimps 12 / 25mm, heat treatment at 130°C x 1 minute The final crimp number is 62 / 25mm). Using 100% by mass of the above side-by-side composite short fibers, the weight per unit area is 32.1 g / m by carding 2 carded fiber web.
[0139] The carded web is moved onto a conveyor net so that it passes between the conveyor and a perforated plate drum having a diameter of Holes (circular) arranged in a zigzag pattern with a pitch of 2 mm face the fiber web and the mesh belt conveyor from the inside of the perforated plate drum, and a spray-like water flow is spraye...
Embodiment 2
[0145] The carded fiber web used in embodiment 1 is passed between the perforated plate drum and the mesh belt (net) the same as in embodiment 1, except that the water pressure of the water jet sprayed out at this time is 1.2MPa, adopt and embodiment 1 The same method is used to obtain non-woven fabrics. The weight per unit area of the gained non-woven fabric is 68.3g / m 2 , the non-woven fabric stretches well in the MD and CD directions, and after being stretched by hand to such an extent that it does not tear, it quickly returns to its original shape when the stress is released. The results are shown in Table 1. This nonwoven fabric was torn in the longitudinal direction with a width of 5 cm, and wound up into a roll to obtain the bandage of the present invention. This bandage was wound around the finger for about 3 weeks and then pulled strongly, resulting in a break, and the broken end could be fixed to the nonwoven fabric wrapped around the finger.
[0146] As a resul...
Embodiment 3
[0148] 95% by mass of the side-by-side composite short fibers used in Example 1 and 5% by mass of polyethylene terephthalate fibers (1.6dtex × 51mm long, 15 mechanical crimps / 25mm) were mixed, and were mixed with a carding Method to form a weight per unit area of 34.3g / m 2 carded fiber web. This fiber web was transferred to a belt conveyor, and a nonwoven fabric was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the fiber web was oversupplied by about 120%.
[0149] The resulting non-woven fabric has a weight per unit area of 62.7 g / m due to shrinkage 2 , It stretches well in both MD and CD directions, and after being stretched by hand to the extent that it does not break, it will quickly return to its original shape if the stress is released. The results are shown in Table 1. This non-woven fabric was torn in the longitudinal direction with a width of 5 cm, and rolled into a roll to obtain the stretchable self-adhesive bandage of the present invention. This b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| loose density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com