Laser beam M* factor matrix measuring method and measuring instrument
A factor matrix and laser beam technology, applied in the field of laser beam quality analysis, can solve the problems of large difference in spot energy density, limiting measurement accuracy and application range, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
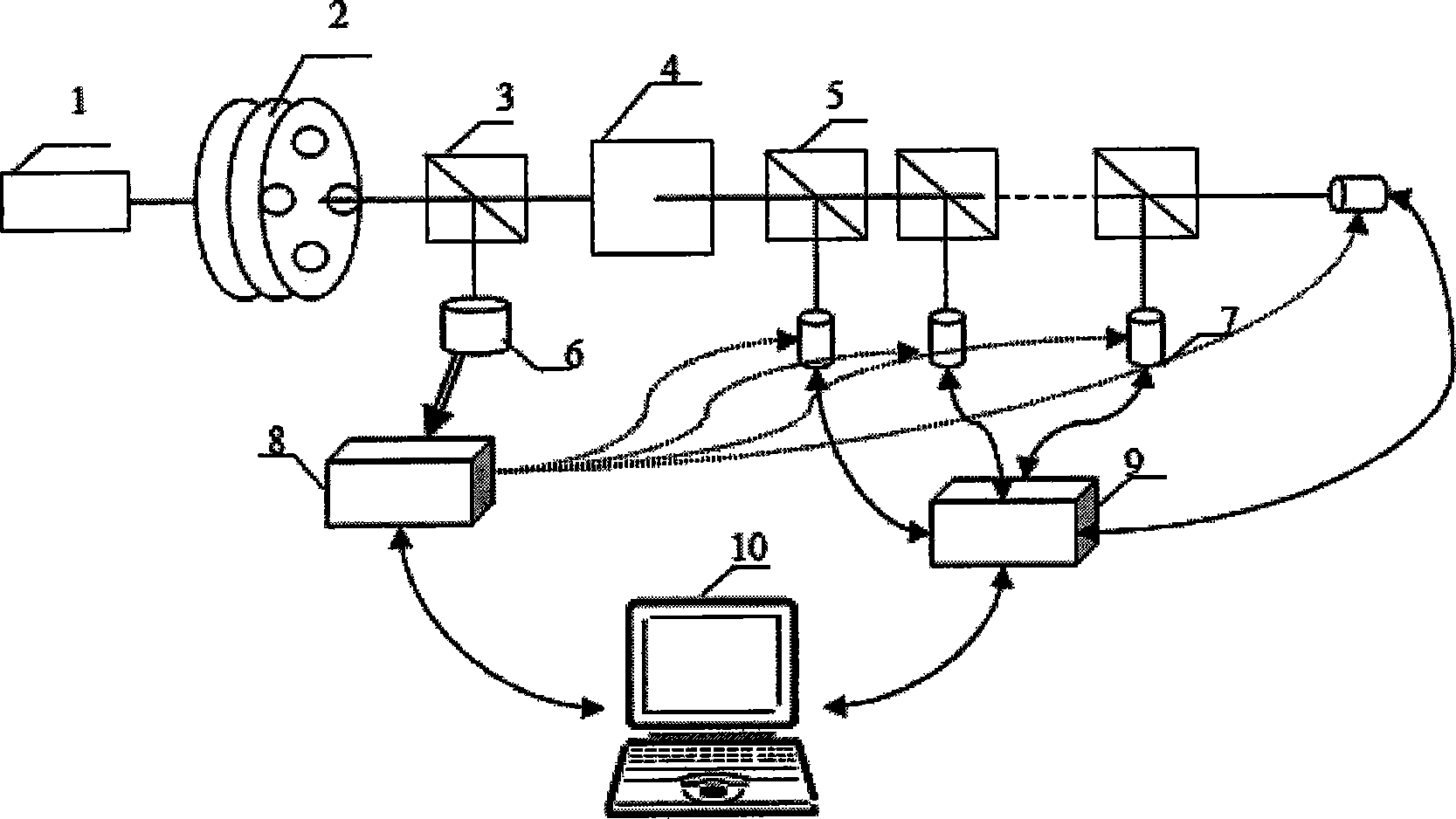
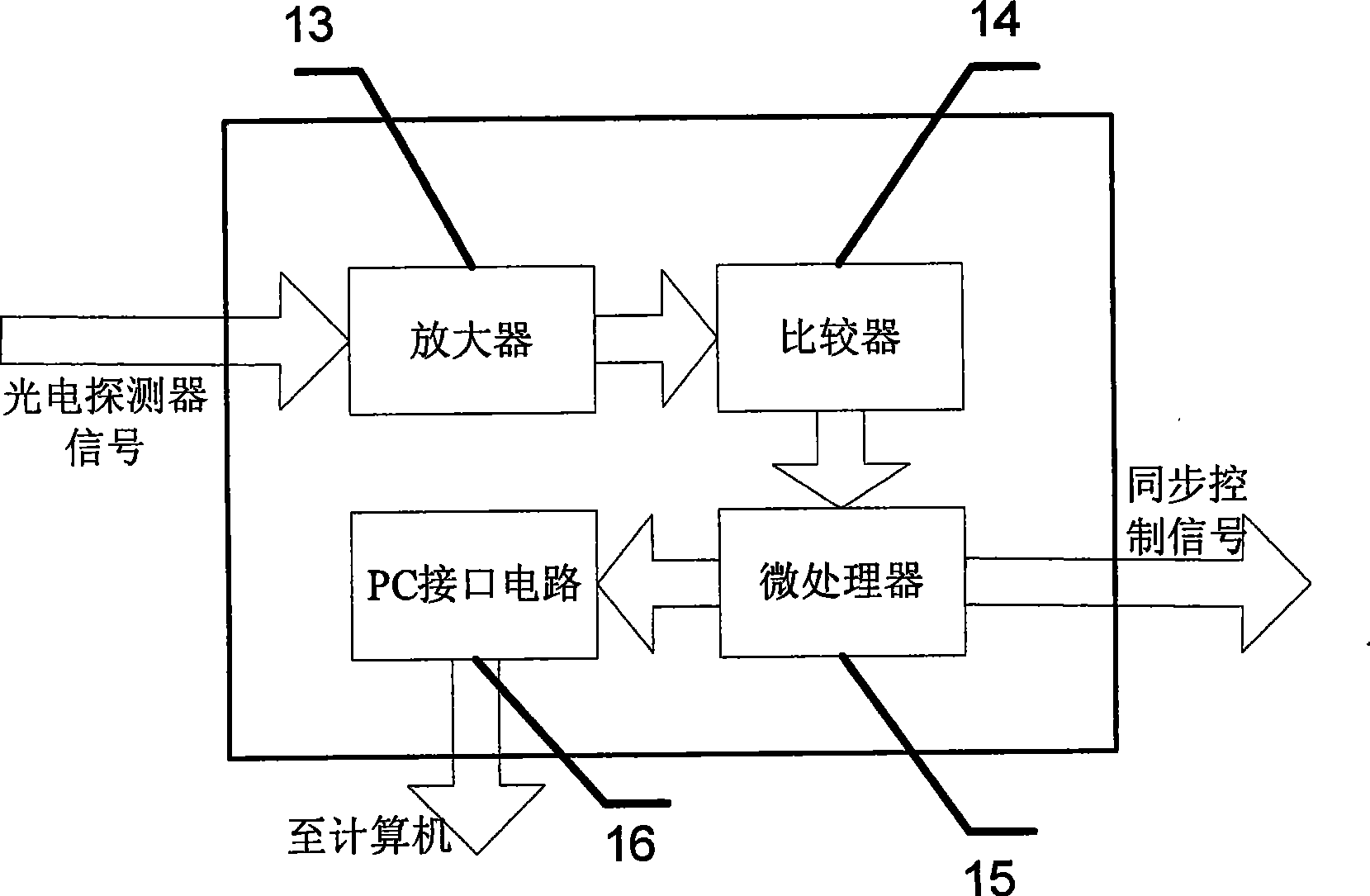
[0053] In this embodiment, the laser beam M 2 The structure of the factor matrix real-time measuring instrument is as figure 1 As shown, the linear attenuator with adjustable attenuation factor 2, the beam splitter 3, the focuser with adjustable focal length 4, the beam splitter group 5, the photodetector 6, the synchronization controller 8, the charge coupled device group 7, the router 9 and computer 10, there are 9 beam splitters in beam splitter group 5, and 10 charge coupled devices (CCD) in charge coupled device group 7.
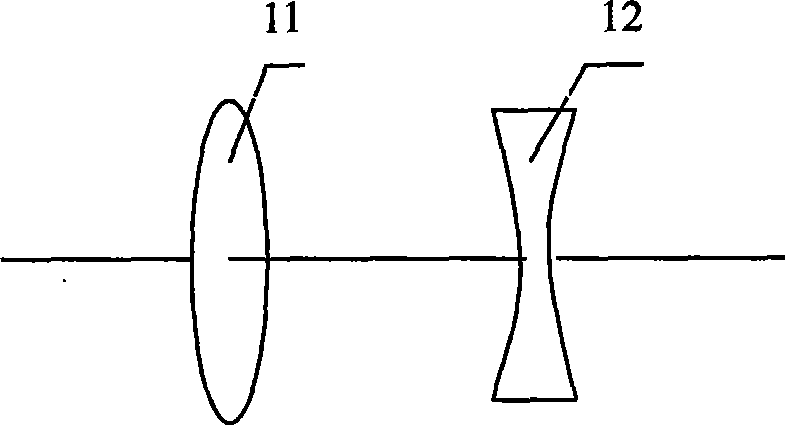
[0054] The linear attenuator 2 with adjustable attenuation multiple is selected as GCC-3010 (produced by Daheng Optoelectronics); the beam splitter 3 is a low-reflectivity mirror with a reflectivity of 5%; the focuser 4 with adjustable focal length is made of A convex lens 11 and a concave lens 12 are combined (such as image 3 As shown), the focal length of the convex lens and the concave lens are both 20cm (which can meet most measurement needs), and the...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This embodiment uses the laser beam M described in embodiment 1 2 The factor matrix real-time measuring instrument performs M on the laser output from laser 1 2 Factor matrix measurement. Laser beam M 2 The workflow of the factor matrix real-time measuring instrument Figure 4 , Laser beam M 2 For the procedure of the factor matrix measurement method, see Figure 5 .
[0065] 1. Warm-up and self-check
[0066]The preheating time is 5 minutes. After preheating, the measuring instrument is allowed to perform self-test.
[0067] 2. Input and prediction of initial parameters
[0068] The initial parameters are: the input wavelength is 652nm and the focal length of the focuser 4 is 20cm.
[0069] After predicting the amount, the program gives the reference adjustment parameters: the distance d between the convex lens and the concave lens in the focuser 4 is 10 cm, and the attenuation multiple of the linear attenuator 2 is 1000 times. The adjustment of the exposure time of each C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com