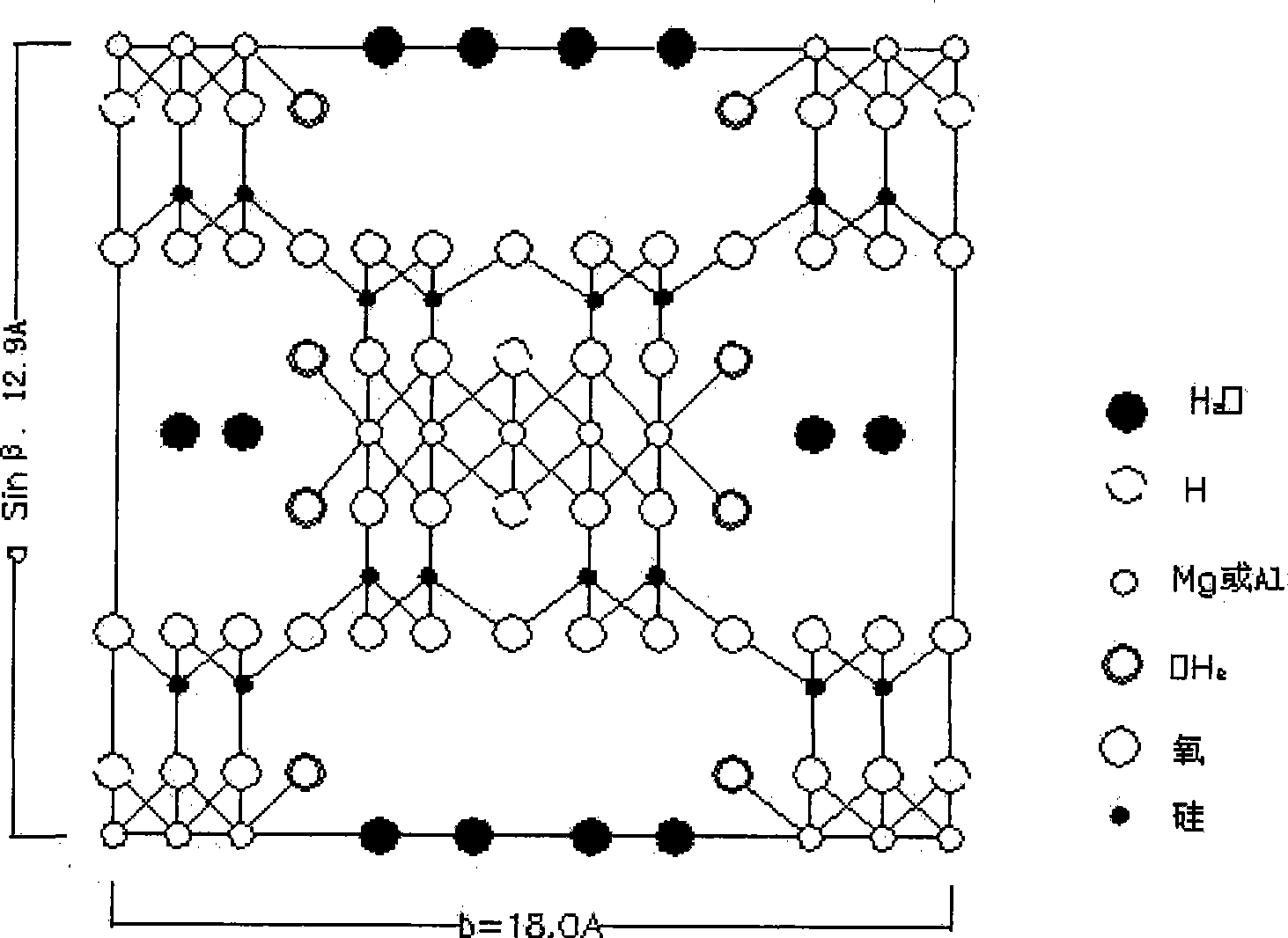
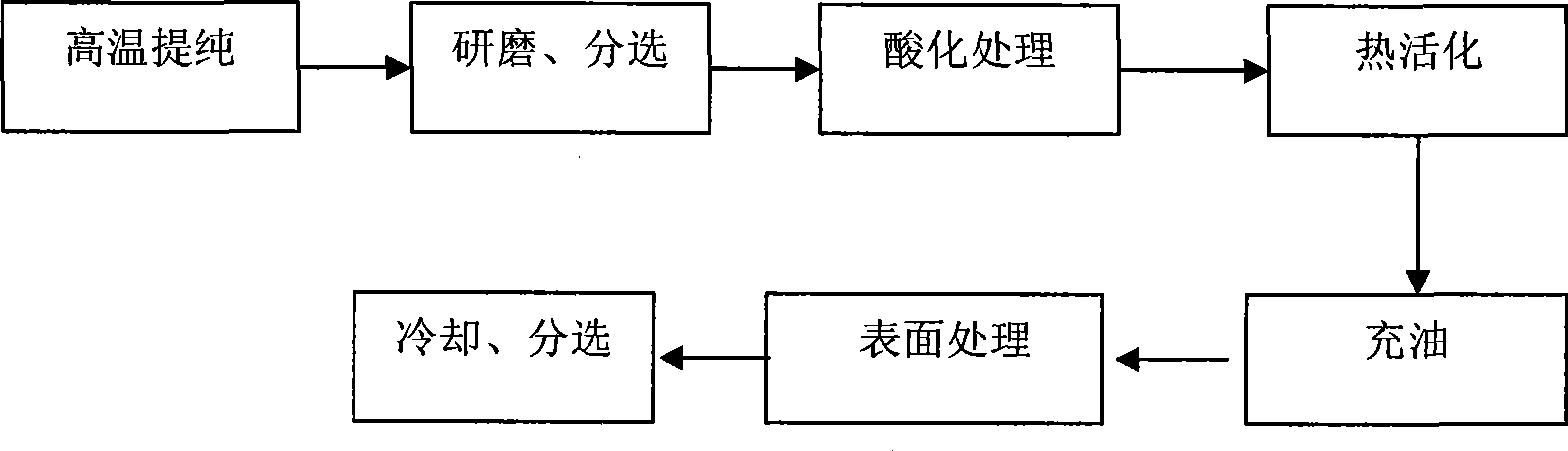
Inorganic high molecular plastics and rubber toughening agent
An inorganic polymer and toughening agent technology, applied in the field of processing aids for rubber and plastic products, can solve the problems of not being able to fully exert the toughening effect of attapulgite materials, affecting the physical properties of products, and poor processing fluidity, and achieve unique modification functions , better fluidity of particles, and improved toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] (1) Place the raw ore in a drying furnace and roast at a constant temperature of 600°C for 5 hours. Impurities such as adsorbed soil, oligomers and ores on the surface of the attapulgite clay are stripped, and then passed through a pipeline air separator to reduce the density to 0.75-0.80 g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sent into the storage bin, and the stirring is started for cooling.
[0068] (2) Grind the cooled attapulgite clay with a Raymond machine, and use an airflow sorting unit to grind the attapulgite clay after the grinding process to a fineness of 850-1200 mesh and a density of 0.75-0.80g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sorted into the storage bin and the fine impurities are collected with cloth bags.
[0069] (3) Prepare a solution of 6mol / L hydrochloric acid to acidify the attapulgite clay. The mass-volume ratio of attapulgite clay to hydrochloric acid was 1:10 in g / ml. After stirring at 50°C for half an hour, dehydration was carried out with a centrifuge. ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] (1) Place the raw ore in a drying furnace and roast at a constant temperature of 400°C for 4 hours. Impurities such as adsorbed soil, oligomers and ores on the surface of the attapulgite clay are stripped, and then passed through a pipeline air separator to reduce the density to 0.75-0.80 g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sent into the storage bin, and the stirring is started for cooling.
[0080] (2) Grind the cooled attapulgite clay with a Raymond machine, and use an airflow sorting unit to grind the attapulgite clay after the grinding process to a fineness of 850-1200 mesh and a density of 0.75-0.80g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sorted into the storage bin and the fine impurities are collected with cloth bags.
[0081] (3) Prepare a solution of 7mol / L benzoic acid to acidify the attapulgite clay. The mass-to-volume ratio of attapulgite clay to benzoic acid was 1:15 in g / ml. After stirring at 45° C. for 4 hours, dehydration was performed using a centrifuge. Then dry a...
Embodiment 3
[0091] (1) Place the raw ore in a drying furnace and roast at a constant temperature of 800°C for 2.5 hours. Impurities such as adsorbed soil, oligomers and ores on the surface of the attapulgite clay are stripped, and then passed through a pipeline air separator to separate the particles with a density of 0.75- 0.80g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sent into the storage bin, and the stirring is started for cooling.
[0092] (2) Grind the cooled attapulgite clay with a Raymond machine, and use an airflow sorting unit to grind the attapulgite clay after the grinding process to a fineness of 850-1200 mesh and a density of 0.75-0.80g / cm 3 The attapulgite clay is sorted into the storage bin and the fine impurities are collected with cloth bags.
[0093] (3) Prepare a solution of 10 mol / L acetic acid to acidify the attapulgite clay. The mass-volume ratio of attapulgite clay to acetic acid was 1:15 in g / ml. After stirring at 50° C. for 1 hour, dehydration was performed using a centri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com