Spun laced fabric and processing method thereof
A processing method and technology of spunlace cloth, applied in the field of non-woven fabrics, can solve the problem that spunlace cloth cannot directly become a durable material, etc., and achieve the effect of obvious price advantage, free design and high mechanical weaving characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
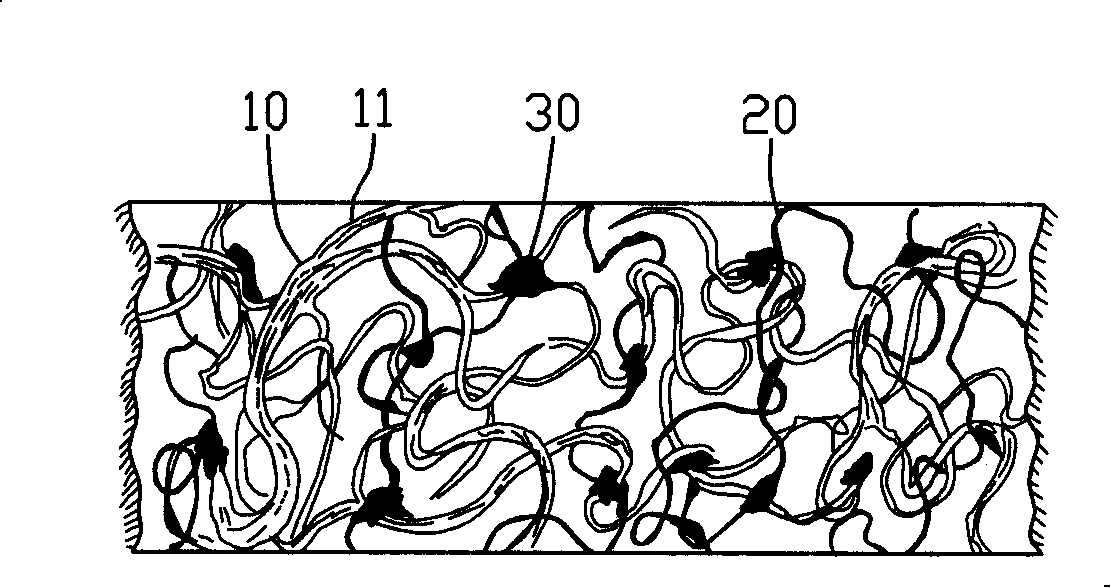
[0029] Embodiment one, select untanned animal gray skin and leftover material thereof for use. In parts by weight, take 80%-99% of collagen fiber bundles; 1%-20% of chemical textile fibers, 1-5% of interstitial fibers; a small or trace amount of elastic fibers, reticular fibers, sweat glands, lipids in raw hides Glands, blood vessels, and other non-fibrous substances and a small amount of non-fibrous substances artificially added in the pre-tanning process are ignored.
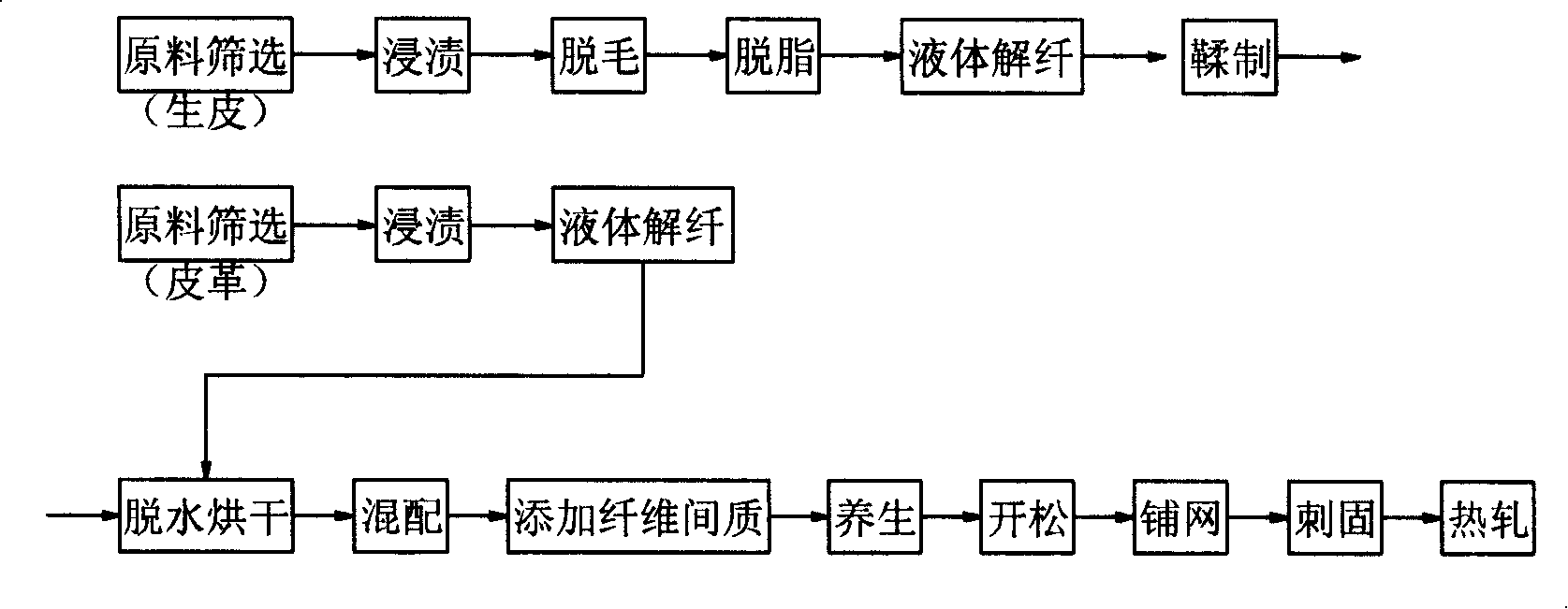
[0030] Technological process: raw material screening - impregnation - hair removal - degreasing - liquid defibrillation - tanning - dehydration and drying - mixing - adding fiber matrix - health - opening - carding - paving Net - stabbed - hot rolled.
[0031] Process description:
[0032] 1. Raw material screening: select at least one animal skin from cattle, sheep, pigs, horses, dogs, deer, rabbits, crocodiles and snakes or untanned gray leather corners.
[0033] 2. Dipping: Dipping in the liquid for 1 to...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment two, by weight, collagen fiber bundle 30%~80%; Cotton, fiber crops, wool, silk natural textile fiber 20~70%, fiber interstitial 3~10%; Inherent trace elastic fiber in the original leather , reticulated fibers and other non-fibrous substances and artificially added non-fibrous substances in the tanning process are ignored.
[0049] Technological process: raw material screening - impregnation - liquid defibrillation - dehydration and drying - mixing - adding fiber matrix - health care - opening - carding - net laying - stabbing - hot rolling .
[0050] The technological process of this embodiment is different from embodiment one in that:
[0051] 1. Raw material screening: select all kinds of leather tanned by tanning process and its leftover materials and waste leather.
[0052] 2. Immerse in a liquid at 15°C to 60°C for more than 10 hours, and the rest of the process is the same as Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment three, by weight, collagen fiber bundle 90~99%, fibrous interstitium 1~10%; Inherent micro elastic fiber, reticular fiber and other non-fibrous substances and other residues in the original leather and the tanning process Artificially added non-fibrous matter is ignored.
[0054] The process flow and process description of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com