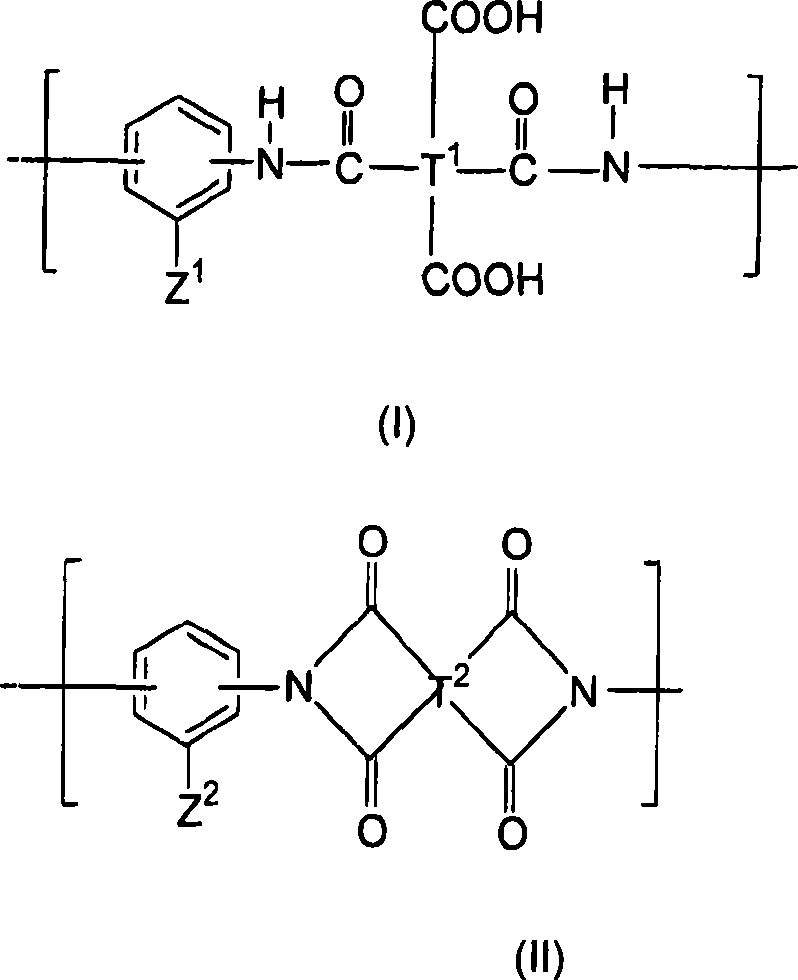
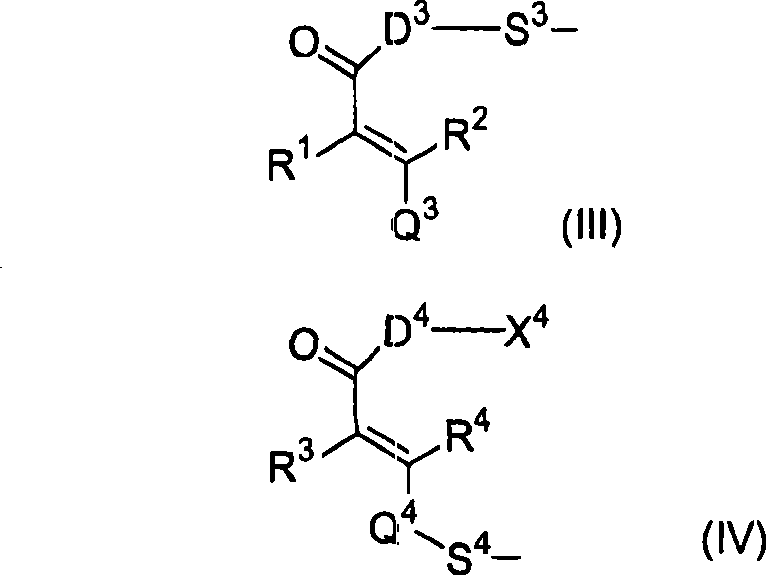
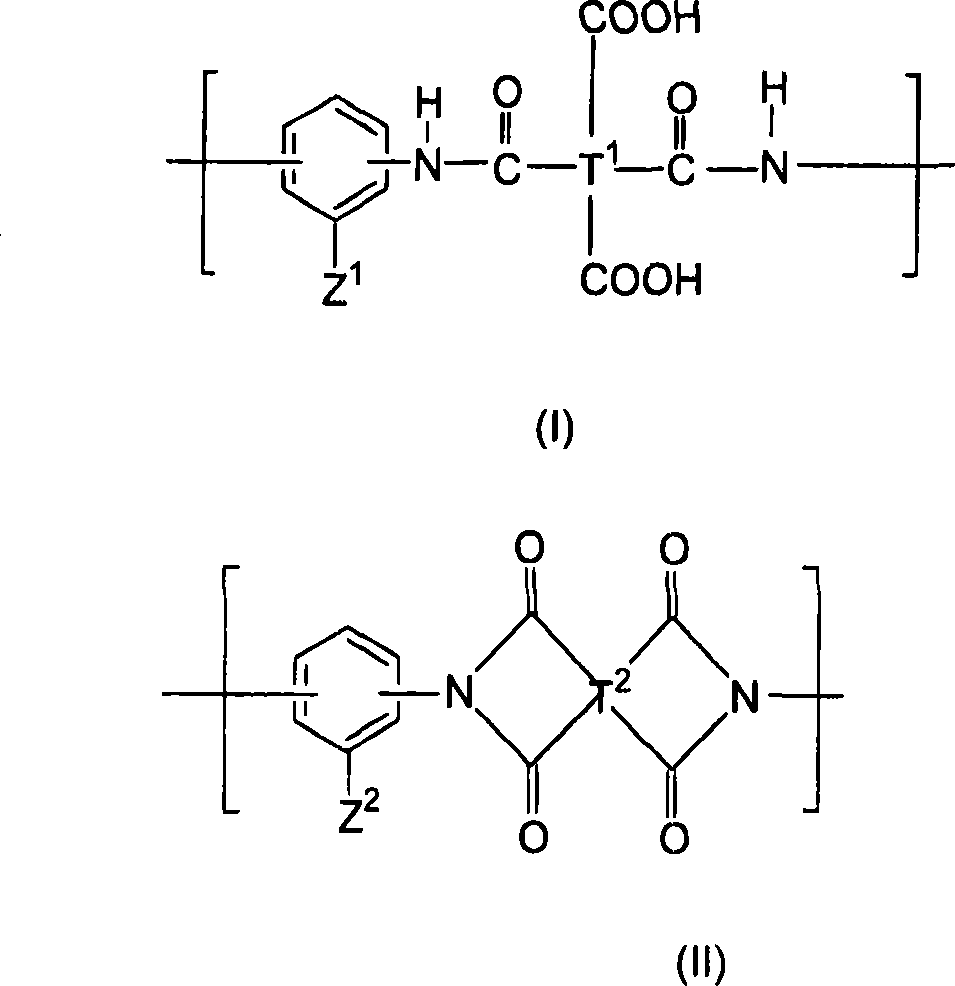
Liquid crystal aligning agent, liquid crystal aligning film, liquid crystal display element and optical components
A technology of liquid crystal alignment agent and liquid crystal alignment film, which is applied in optics, liquid crystal materials, nonlinear optics, etc., and can solve the problems of unstable liquid crystal alignment ability and large amount of radiation exposure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0096] Although the present invention will be specifically described below by way of examples, the present invention is not limited to these examples.
[0097] [Measuring method of imidization rate of imidized polymer]
[0098] After the imidized polymer was dried under reduced pressure at room temperature, it was dissolved in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide, and measured at room temperature with tetramethylsilane as the standard substance 1 H-NMR is obtained by the formula represented by the following formula (i).
[0099] Imidization rate (%) = (1-A 1 / A 2 ×α)×100 (1)
[0100] A 1 : Peak area of proton derived from NH group (10ppm)
[0101] A 2 : Peak area derived from other protons
[0102] α: In the precursor of the polymer (polyamic acid), the ratio of the number of other protons to one proton of the NH group.
[0103] [solution viscosity]
[0104] The solution viscosity (mPa·s) of the polymer is measured at 25° C. using an E-type rotational viscometer for a solu...
Synthetic example 1
[0106] Polymerization of polyamic acid
[0107] Dissolve 0.1 mole (22 g) of 2,3,5-tricarboxycyclopentylacetic dianhydride and 0.1 mole (27 g) of 3,5-diaminobenzyl cinnamate in 300 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, The reaction was carried out at 60°C for 6 hours to obtain about 340 g of a polyamic acid solution (hereinafter referred to as "polymer 1a") having a solution viscosity of 50 mPa·s at a solid content concentration of 10% by weight.
[0108] imidization reaction
[0109] 210 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, 7.9 g of pyridine, and 10.2 g of acetic anhydride were added to 175 g of polymer 1a, followed by dehydration and ring closure at 120° C. for 4 hours. After the imidization reaction, replace the solvent in the system with new N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (this operation removes pyridine and acetic anhydride used in the imidation reaction from the system) To obtain a solid content concentration of about 10% by weight, a solution viscosity of about 55 mPa·s (N-methyl-2-pyrroli...
Synthetic example 2
[0111] Polymerization of polyamic acid
[0112]Solid content was obtained in the same manner as in Synthesis Example 1, except that 0.1 mol (25 g) of 2,4-diaminophenylcinnamate was used instead of 0.1 mol (27 g) of 3,5-diaminobenzylcinnamate. About 340 g of a polyamic acid solution (hereinafter referred to as "polymer 2a") having a solution viscosity of 45 mPa·s at a concentration of 10% by weight.
[0113] imidization reaction
[0114] Except for using 176 g of polymer 2a instead of 175 g of polymer 1a, the same operation was performed as in Synthesis Example 1 to obtain a solid content concentration of about 10% by weight and a solid content concentration of 10% by weight (N-methyl-2- pyrrolidone solution) having a solution viscosity of about 50 mPa·s and an imidization rate of about 47% of an imidized polymer solution (hereinafter referred to as "polymer 2b") was about 210 g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Solution viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solution viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com