An improved process for heap leaching of nickeliferous oxidic ores
A technology for ore and heap leaching, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, which can solve the problems of high capital and maintenance costs of leaching equipment, increased acid consumption, and low nickel recovery.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0056] Australian laterite ore samples from arid regions were crushed and screened such that all ore samples were smaller than 25mm. The analysis of the ore is shown in Table 2.
[0057] Table 2.
[0058] %Al
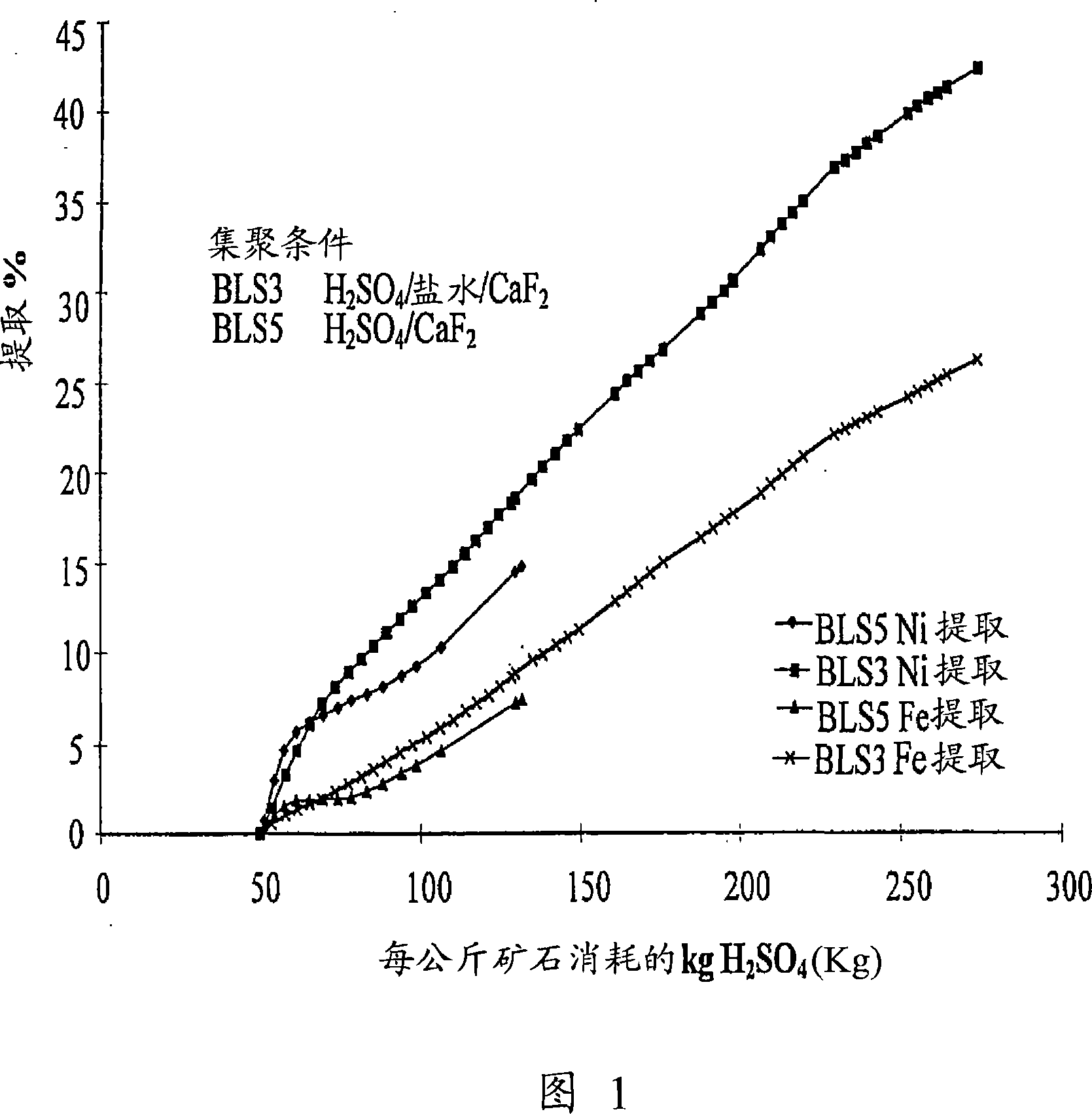
[0059] Eight columns (100 mm diameter x 1.86 m high) containing about 10 kg of agglomerated ore were set up to simulate heap leaching and test the leaching kinetics of hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid systems. Some of the columns had fluorspar added during the aggregation process.
[0060] To compensate for the leachate, a synthetic hypersaline solution was prepared to simulate the subsurface brine in the orebody region. The hypersaline solution strength was 140,000 ppm total dissolved solids, including 129 gpl sodium chloride. Table 3 summarizes the conditions for each column.
[0061] Table 3. Test column conditions
[0062]
[0063] The test results are shown in Table 4.
[0064] Table 4. Extracted data
[0065] Column test numb...
Embodiment 3
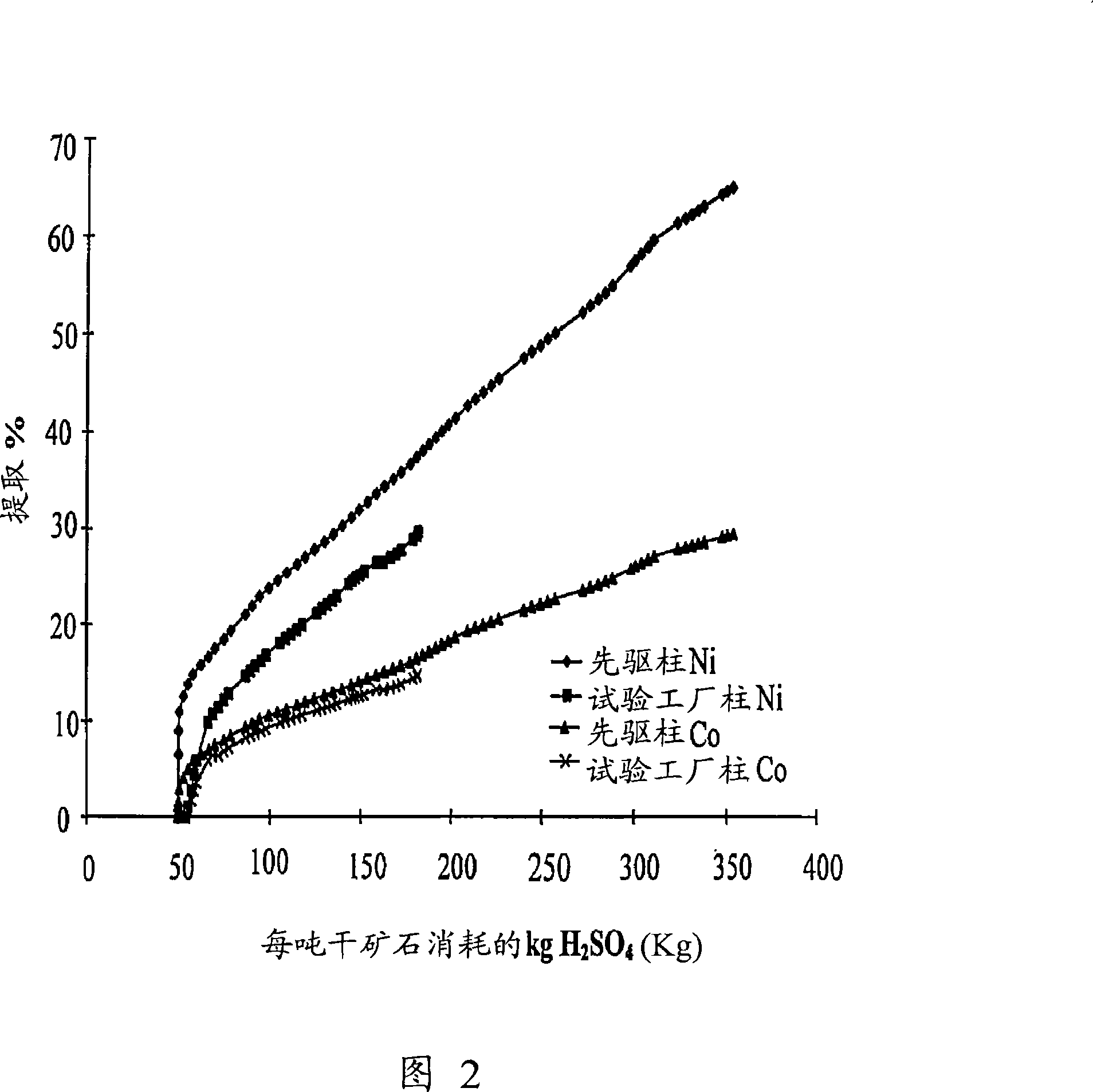
[0068] A pilot plant heap run was established based on the test BLS2 (pioneer column) in Example 2. The pilot plant consisted of a 762kg loaded heap leaching column (diameter 0.93m x height 2.48m) and an ISEP pilot ion exchange unit filled with 30 liters of Dow 4195 ion exchange resin for nickel and cobalt recovery. The aggregation conditions are summarized in Table 5. Permeate flow rate is 5 liters / m 2 / hr, corresponding to a flow rate of 80 liters per day.
[0069] Table 5: Large-scale heap accumulation conditions
[0070] Dry ore mass (kg)
Ore moisture (%)
kg H 2 SO 4 / T ore
Salt water (liter / T)
762
27
54.4
106.5
[0071] 62% nickel extraction, 30% cobalt extraction and 366kg / t ore acid consumption over 74 days for 100mm pioneer column. For the 762kg test heap, nickel extraction was 29.6% cobalt extraction was 17.0% and acid consumption was 181.8kg / t ore over a period of 53 days. Figure 2 shows that the two columns hav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com