EphB receptor-binding peptides
A technology of receptors and amino acids, applied in the direction of peptides, specific peptides, drug combinations, etc., can solve problems such as unclear how EphA2-binding peptides activate EphA2
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
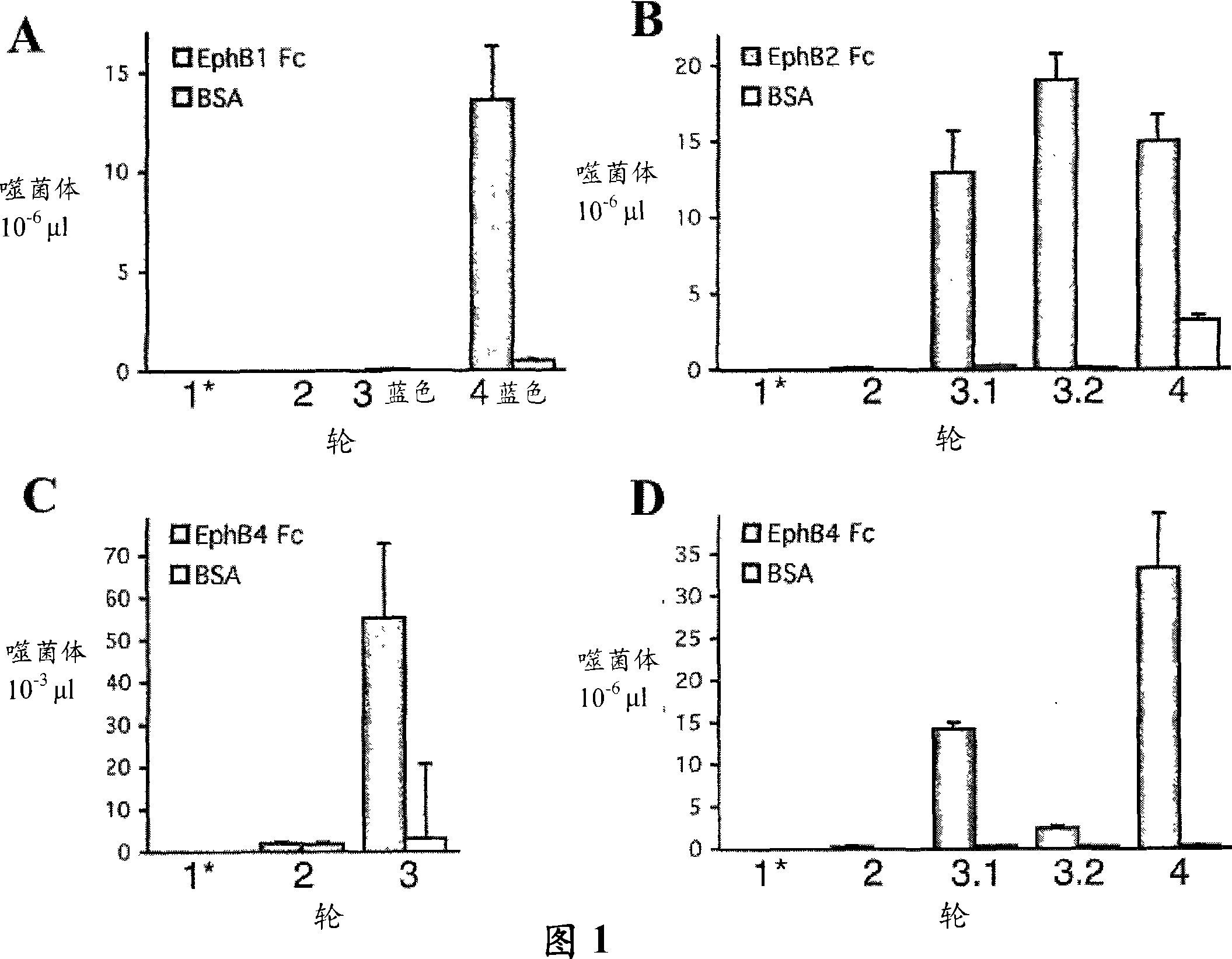
[0188] Identification of peptides that bind to different EphB receptors
[0189] To identify EphB receptor-binding peptides, immunoscreens displaying random peptides 12 amino acids long based on EphB1, EphB2, or EphB4 ectodomains fused to human Fc and immobilized on nickel-coated wells by carboxy-terminal hexahistidine tagging M13 phage library (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) (Figure 1). Anti-phage antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (M13 Phage Detection Kit, Amersham Biosciences) was used with 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) as substrate Phage bound to Ni-NTA wells coated with 1 μg / ml Eph receptor Fc fusion protein was quantified. Background subtracted from assay values was determined in the absence of EphB4Fc. Histidine-tagged EphB ectodomain Fc fusion protein was incubated overnight at 4°C in nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA)-coated ELISA wells in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) (150 mM NaCl , 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5) at a concentration o...
Embodiment 2
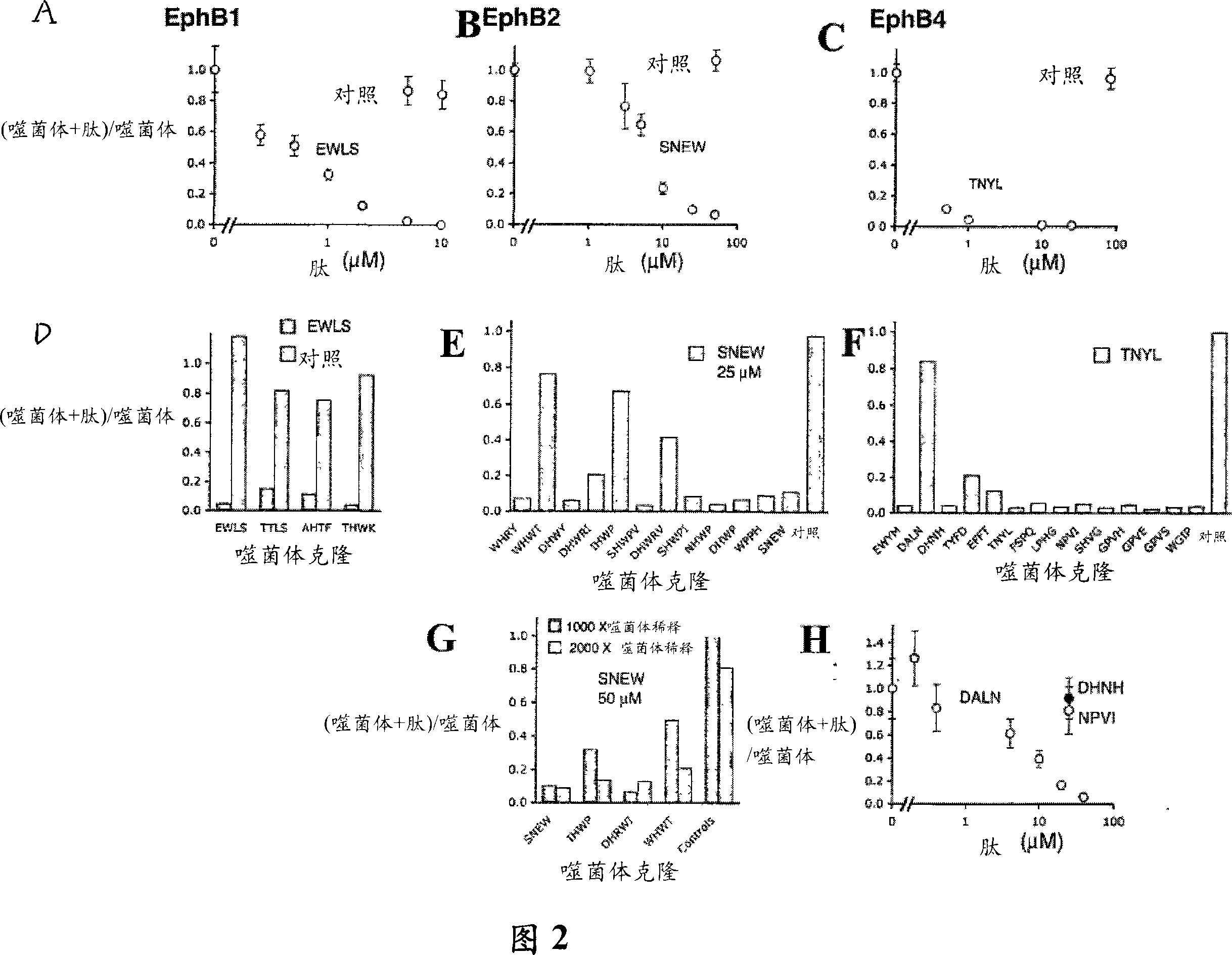
[0193] Different peptides compete with each other for binding to the EphB receptor for their isolation
[0194] To determine whether different phage clones target overlapping Eph receptor binding sites, EWLS EphB1-binding peptides and TNYL EphB4-binding peptides were chemically synthesized. These peptides were chosen because they contain motifs found in Ephrin and bind specifically to EphB1 or EphB4, respectively, when they are displayed on phage (Table 1). The peptide was synthesized using Fmoc (N-(9-fluorenyl)methoxycarbonyl) chemistry and purified by high pressure liquid chromatography. Biotinylated peptides were synthesized with a carboxy-terminal GSGSK linker with biotin attached to the side chain of a lysine, or with a carboxy-terminal N-biotinyl-N'-Fmoc-ethylenediamine (Novabiochem ) carboxy-terminal GSGS sequence. Correct peptide synthesis and purity were confirmed using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The stock solution o...
Embodiment 3
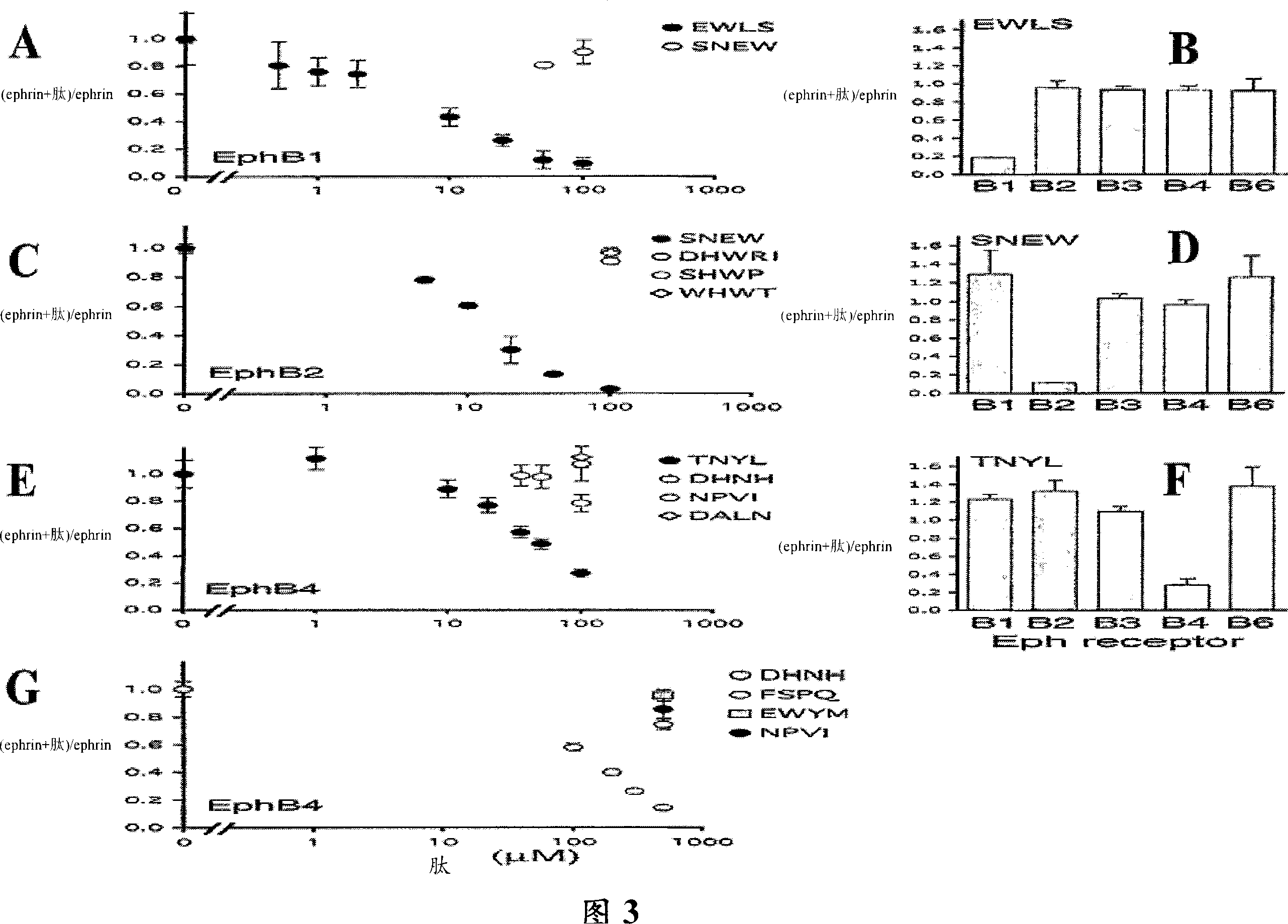
[0202] Peptides that selectively antagonize the binding of Ephrin to EphB1, EphB2, and EphB4 receptors
[0203] Peptides that bind to the same receptor region as Ephrin are expected to inhibit Eph receptor-Ephrin binding if they interact with sufficient affinity. A number of synthetic peptides were tested for their ability to inhibit the binding of alkaline phosphatase-tagged Ephrin-B2 (Ephrin-B2-AP) to the EphB receptor (Figure 3). Most peptides were synthesized biotin-labeled and immobilized on streptavidin plates to demonstrate their ability to capture the EphB ectodomain for their isolation.
[0204] Binding of Ephrin-B2AP to the indicated extracellular domains of immobilized EphB receptors was assayed in the presence of the indicated peptides and detected by measuring alkaline phosphatase activity. Among the peptides tested for their ability to inhibit the binding of Ephrin to the EphB receptor, EWLS and AHTF inhibited the binding of Ephrin to EphB1; SNEW (but not DHWRI,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com