Thermo-responsive blends and uses thereof
A blend, heat-sensitive technology, applied in biochemical devices and methods, one-component synthetic polymer rayon, immobilized on/in an organic carrier, etc., capable of addressing prolonged, damaging exposure, cellular difficulties, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] c. Preparation of blends
[0037] The blends described herein can be prepared by known techniques. In one aspect, the blends can be prepared by a high temperature combination process. Heat-sensitive and non-heat-sensitive / water-insoluble polymers are mixed at high temperature so that the blend can be obtained by extrusion. For example, poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (heat-sensitive polymer) is stable above 270°C, which has advantages over the thermal stability (280°C) of polystyrene (non-heat-sensitive / water-insoluble polymer) . As described below, the blend can be molded into shaped products by existing injection molding machines. The amount of thermosensitive polymer and non-thermosensitive / water-insoluble polymer used to prepare the blend will vary depending on the polymer chosen and the desired pattern of cellular release. By varying the amount of each polymer, cell adhesion can be increased or decreased, as well as cell release can be fine-tuned by varying the temp...
Embodiment 1
[0123] The preparation of embodiment 1 polystyrene and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) blend
[0124] Copolymers of polystyrene and poly(N-isoacrylamide) (PolyNIPAAm; Mn=20000-25000, see Aldrich 535311) were prepared by mixing the polymers in solution and evaporating off the solvent to obtain a solid blend. mixture. Other mixing techniques such as extrusion can also be used when the thermal properties (eg thermal stability) of the two polymers are very similar. Under these conditions, existing polystyrene forming techniques such as injection molding are not significantly affected by the additive polyNIPAAm.
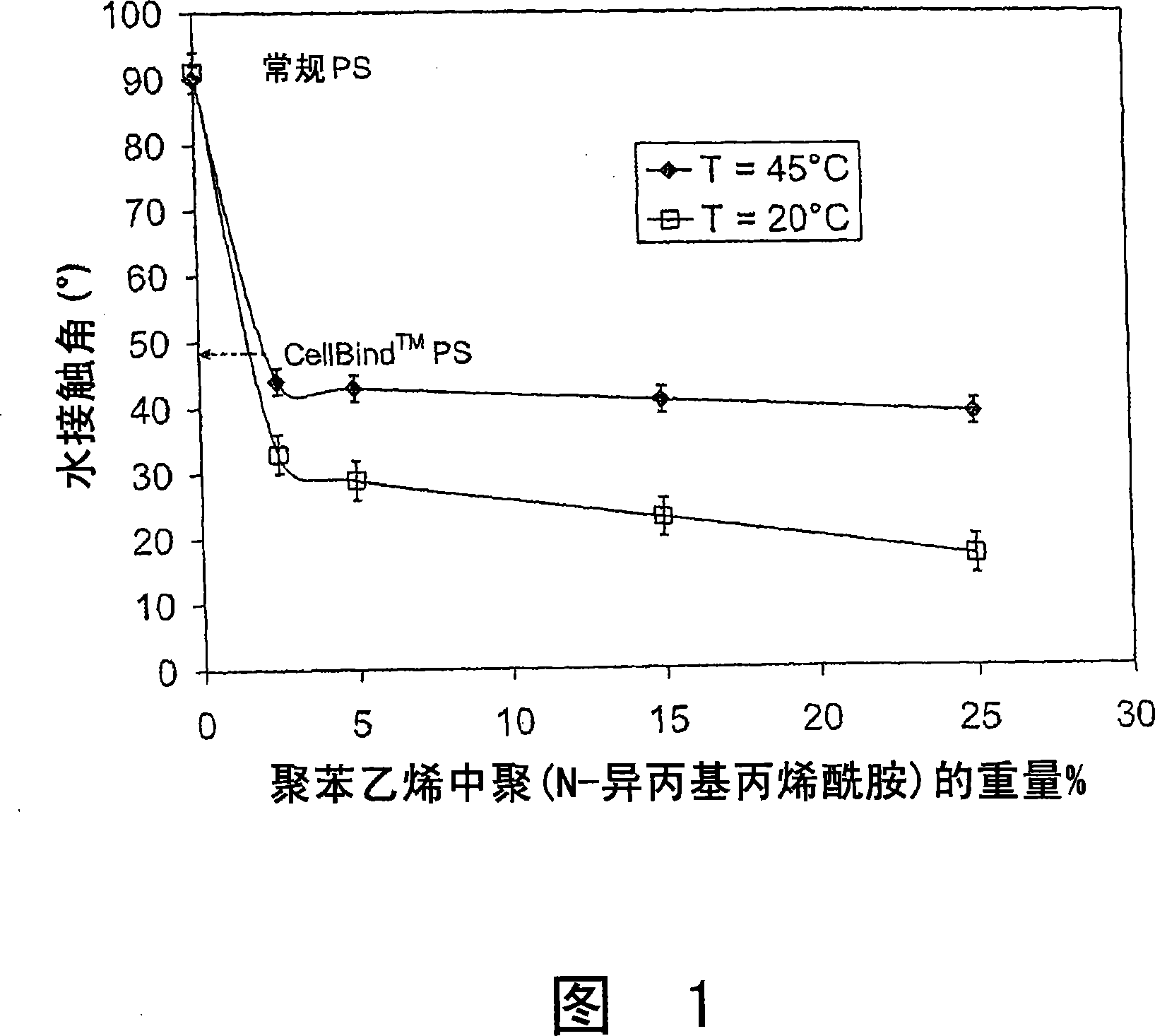
[0125] The change of water contact angle of the blend composed of polystyrene and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) is shown in Fig. 1 . The water contact angles of blends of different compositions were measured at two different temperatures, with the amount of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) varying from 0 to 25 wt%. The polystyrene / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) blend is significantl...
Embodiment 2
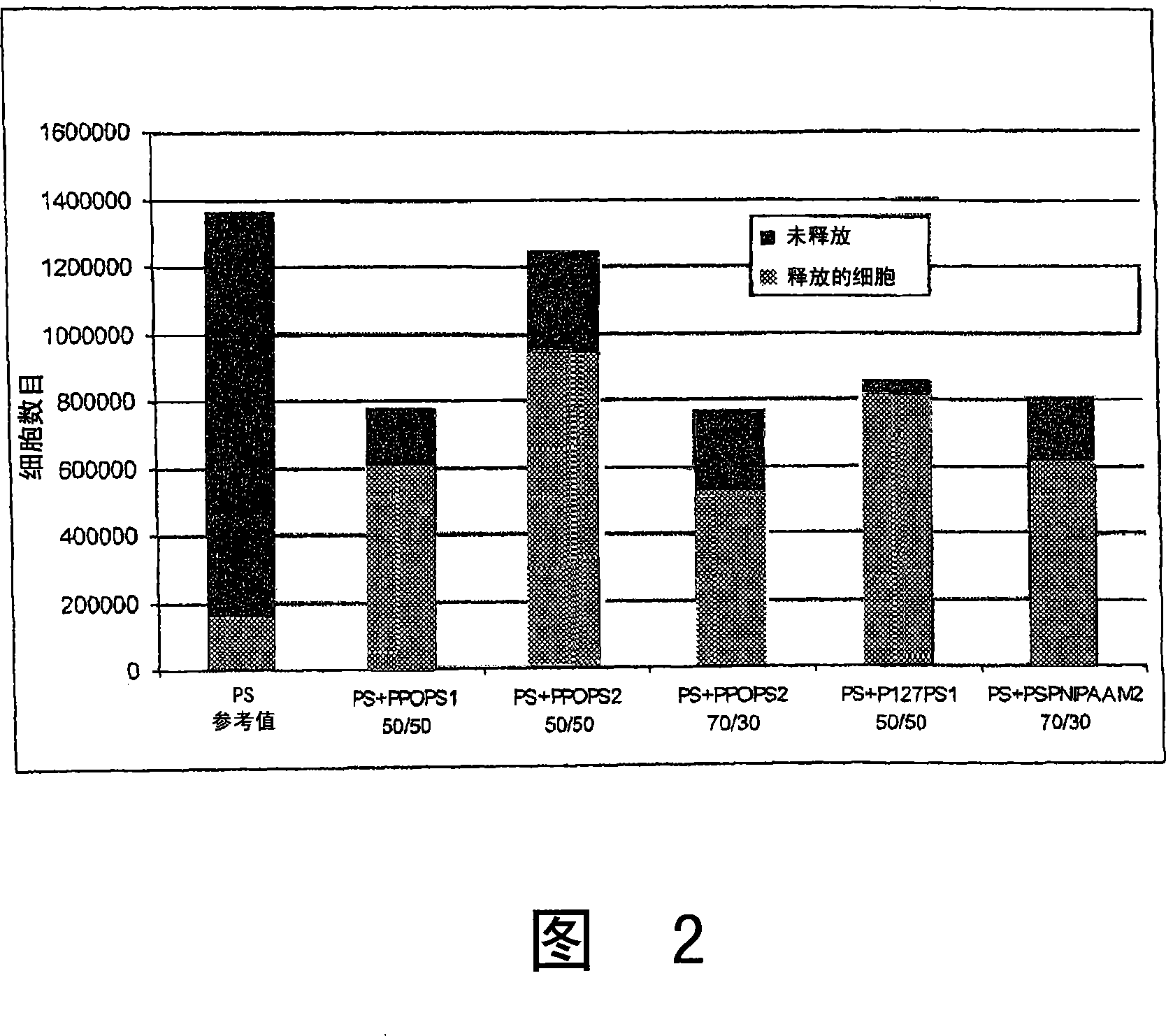
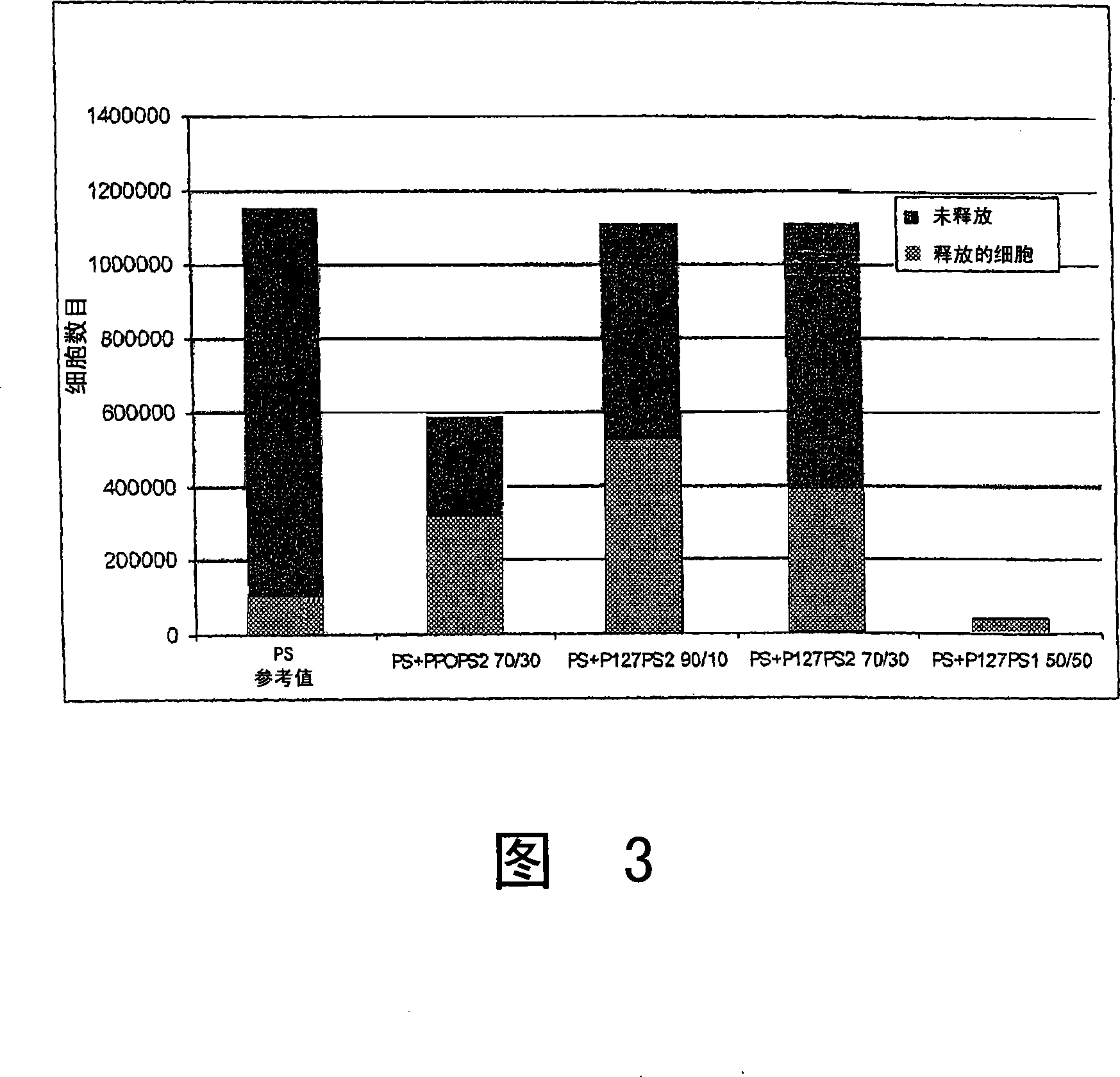
[0127] Example 2 Preparation and characterization of blends composed of copolymers
[0128] The heat-sensitive properties of polymer blend surfaces were studied using the following heat-sensitive segments: (polyN-isoacrylamide) (PolyNIPAAm-LCST 32°C), polypropylene oxide (PPO-LCST 10-15°C) Aldrich Ref. 202355, Mn 4000 g / mol and F Pluronic 127(R) (Sigma Ref. P2443), a block copolymer of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) (P127-LCST27 ℃), Mn12600g / mol. Polystyrene (PS)-PNIPAAm block copolymer (PSPolyNIPAAm2) was prepared by continuous atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), that is, dimethyl dibromopimelate was used as the initiator at 80 °C and the Copper bromide / pentamethyldiethylenetriamine as a catalyst to polymerize styrene; then use copper chloride / tris[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amine as a catalyst to polymerize N-isoacrylamide at 25°C . , the above preparation is carried out using the technique described in US Patent 5763548, which is inc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com