Method of separating and purifying phosphatidyl choline from phospholipid by resin chromatography method
A technology for separation and purification of phosphatidylcholine, applied in the direction of edible phospholipid composition, application, protein food ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of low cost, short elution cycle, long elution cycle, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The screening of embodiment 1 resin
[0037] The adsorption capacity of phosphatidylcholine per unit mass of resin is an important parameter for equipment design. The adsorption performance of the resin is closely related to the polarity and size of the adsorbed molecules, as well as the polarity, specific surface area, and pore size of the adsorbent. 10 kinds of ion exchange resins were selected, and their static adsorption to phosphatidylcholine is shown in Table 1.
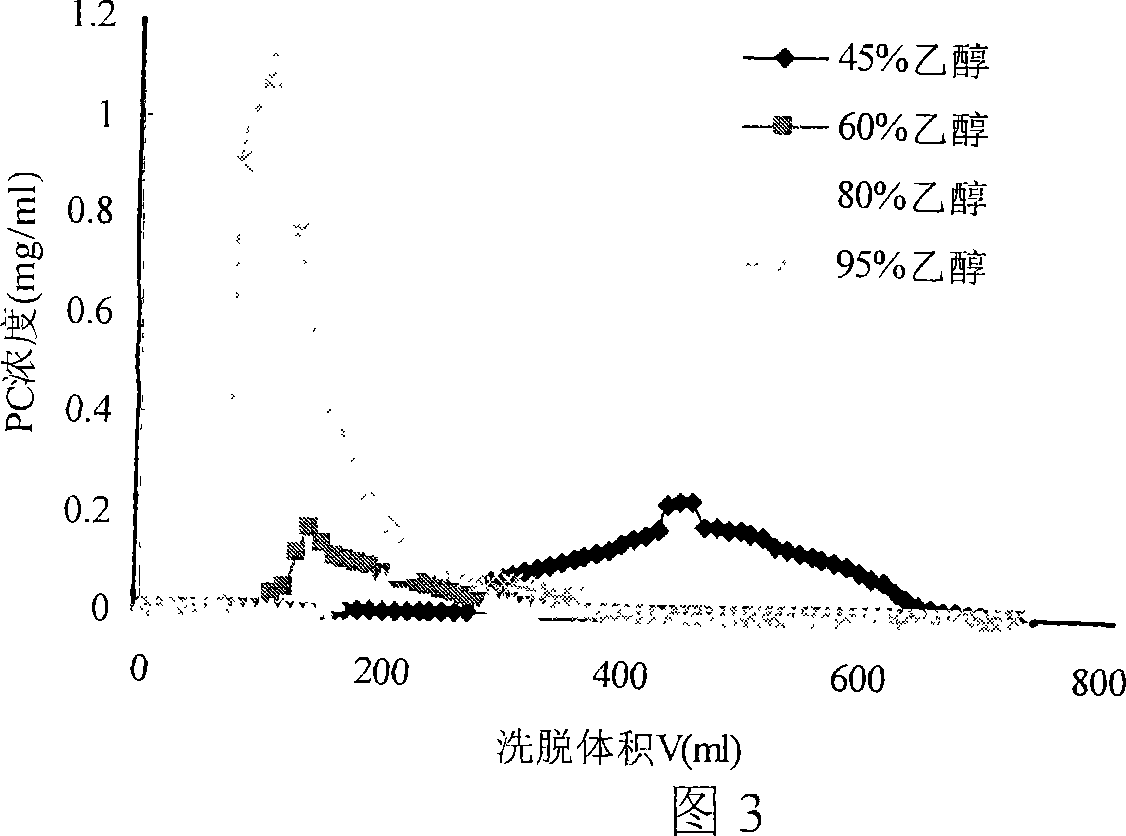
[0038] It can be seen from Table 1 that 201×7, 201×4, and D296 have higher adsorption rates, followed by D113-IIIFC, 001×7, and SQD-88, while the adsorption rates of D001, SQD-61, D301-III, and D318 smaller. According to the requirements of industrial applications, six kinds of resins with high adsorption rates, 201×7, 201×4, D296, D113-IIIFC, 001×7, and SQD-88, were selected for static desorption experiments. 100% ethanol was used for desorption, and the desorption test results are shown in Table 2. ...
Embodiment 2
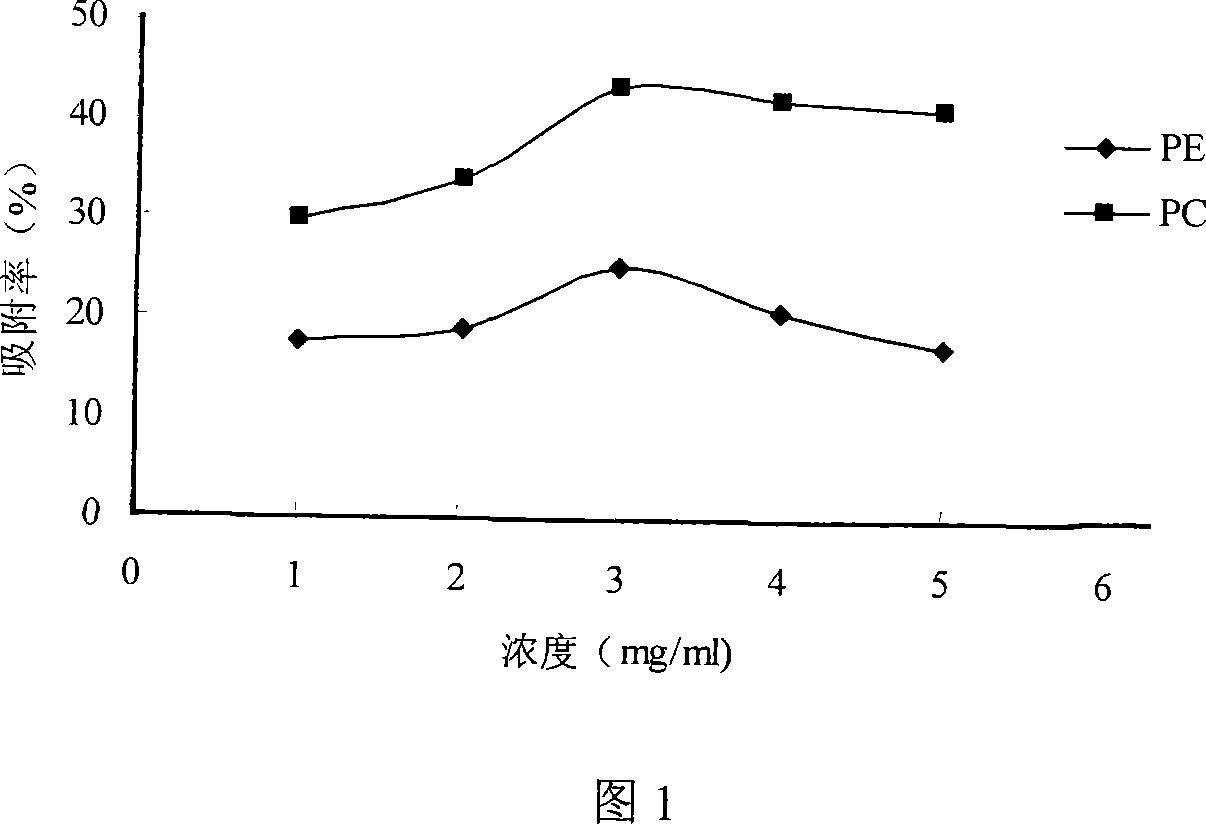
[0043] The influence of embodiment 2 sample solution concentration on adsorption effect
[0044] The dynamic adsorption experiment was carried out on alcohol-soluble phospholipid solutions with different concentrations, and the results are shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from Figure 1 that when the alcohol-soluble phospholipid concentration is 3-5 mg / mL, the adsorption rate of the resin to PC is relatively ideal. When the alcohol-soluble phospholipid concentration is 3mg / mL, the adsorption rate of the resin to PC is the largest, reaching 42.97%, so the best sample concentration is 3mg / ml.
Embodiment 3
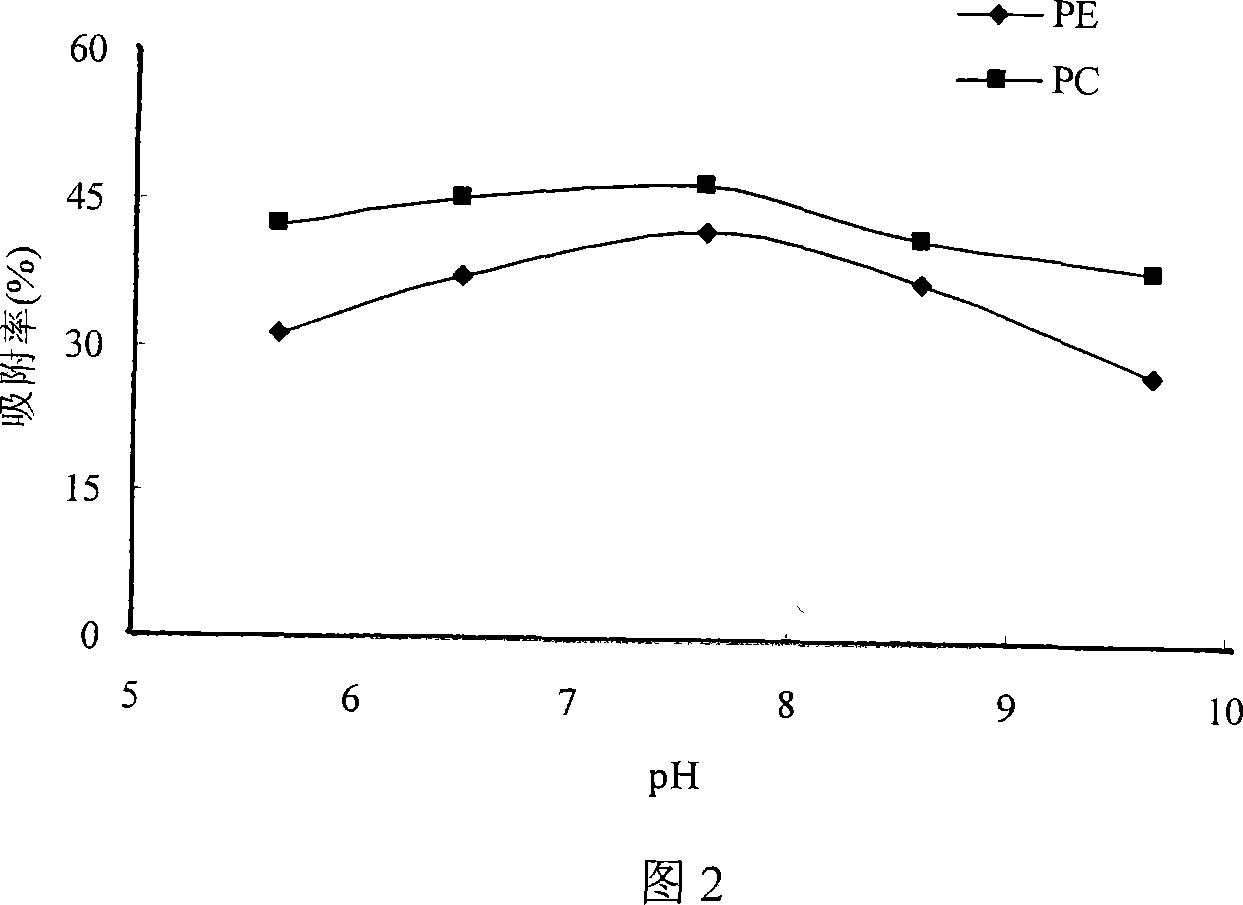
[0045] Example 3 Influence of sample liquid pH on adsorption effect
[0046] Adsorption experiments were carried out at different pH values, and the results are shown in Figure 2. The results show that the adsorption effects of PC and PE are relatively ideal under weakly alkaline conditions. When the pH value of the sample solution is about 7.5, that is, without changing the pH of the original solution, the adsorption rate of D113-IIIFC resin to PC is the largest. Continue to increase the pH, the adsorption rate decreased significantly. This is because the resin itself is a weakly acidic cation exchange resin, which is more conducive to ion exchange between PC and PE under weakly alkaline conditions, but when the pH is too high, due to a large amount of sodium ions and PC (or PE) Competitive adsorption, while too much alkalinity is not good for the resin itself, resulting in a decrease in the adsorption rate. Considering the adsorption effect and the simplicity of the proces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com