Semiconductor device
A semiconductor and transistor technology, applied in the field of preventing electrostatic damage, can solve the problems of PN junction damage, easy local concentration of surge current, etc., and achieve the effect of good ohmic contact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0044] Next, a first embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 to 9 .
[0045] First, a preferred example of the semiconductor device according to the embodiment will be described.
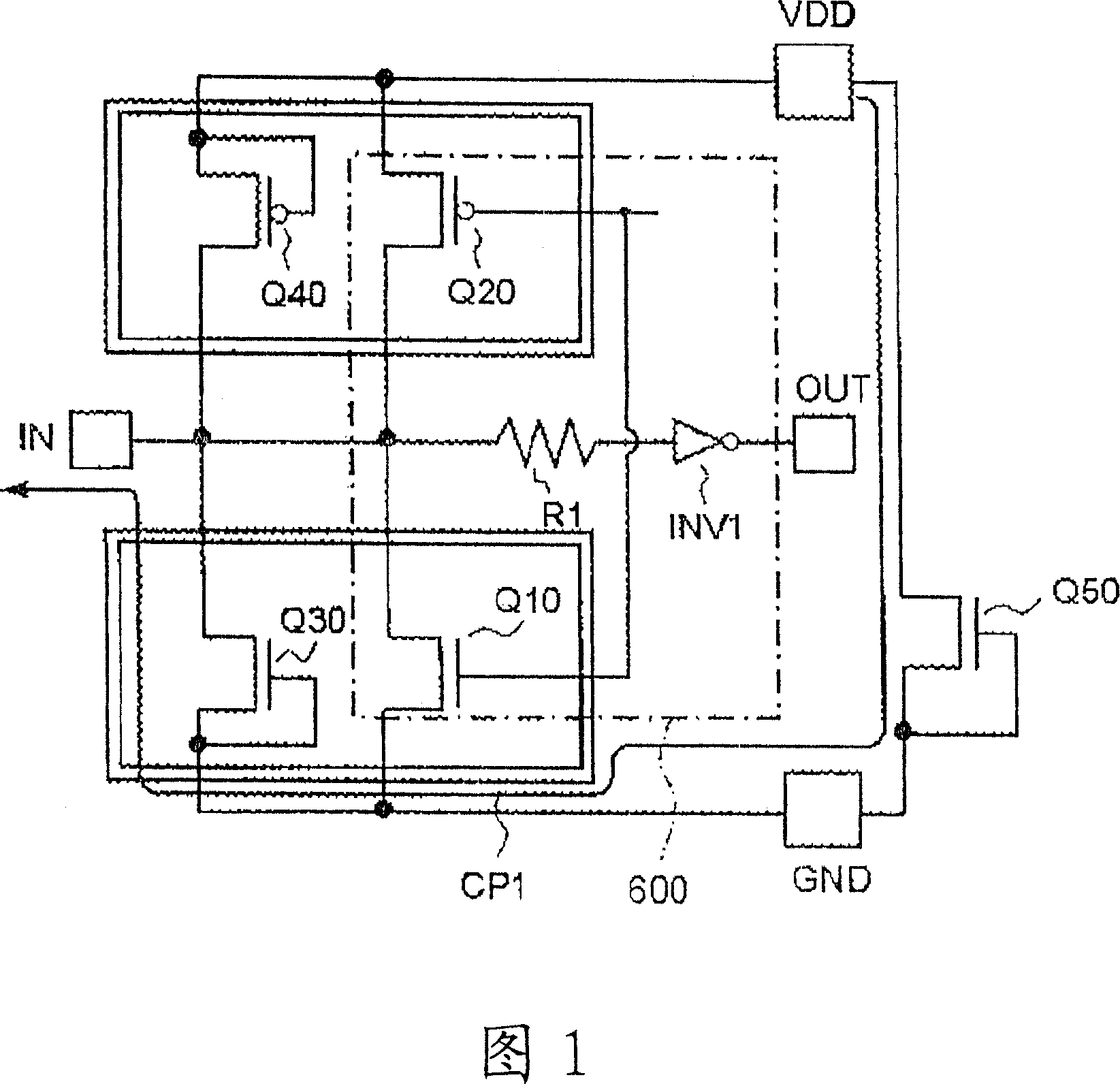
[0046] FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram of a semiconductor device 10 (input / output circuit) mounted with an ESD protection circuit. The semiconductor device 10 shown in FIG. 6 has: a CMOS output circuit 6 (output transistors Q1, Q2, current limiting resistor R1, inverter INV1) receiving a gate control signal; Transistors (Q3, Q4, Q5).
[0047] The NMOS transistor Q5 is provided between a power supply terminal VDD (second reference potential) and a ground terminal GND (first reference potential). The NMOS transistor Q3 is provided between the input terminal IN and the ground terminal GND, and the PMOS transistor Q4 is provided between the input terminal IN and the power supply terminal VDD.
[0048] As schematically shown in FIG. 6, th...
no. 2 approach
[0081] Next, a second embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 10 to 12 . In addition, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same parts as those of the semiconductor device of the first embodiment, and repeated explanations are omitted.
[0082] As already described, in the semiconductor device 10 according to the first embodiment, since no silicide is formed on the side facing the transistor formation region 20, the surge current is less likely to be locally concentrated as compared with the prior art. The purpose of the semiconductor device 11 of the present embodiment is to prevent the local concentration of the surge current more reliably by its structure.
[0083] First, the structure of the semiconductor device 11 of the embodiment will be described.
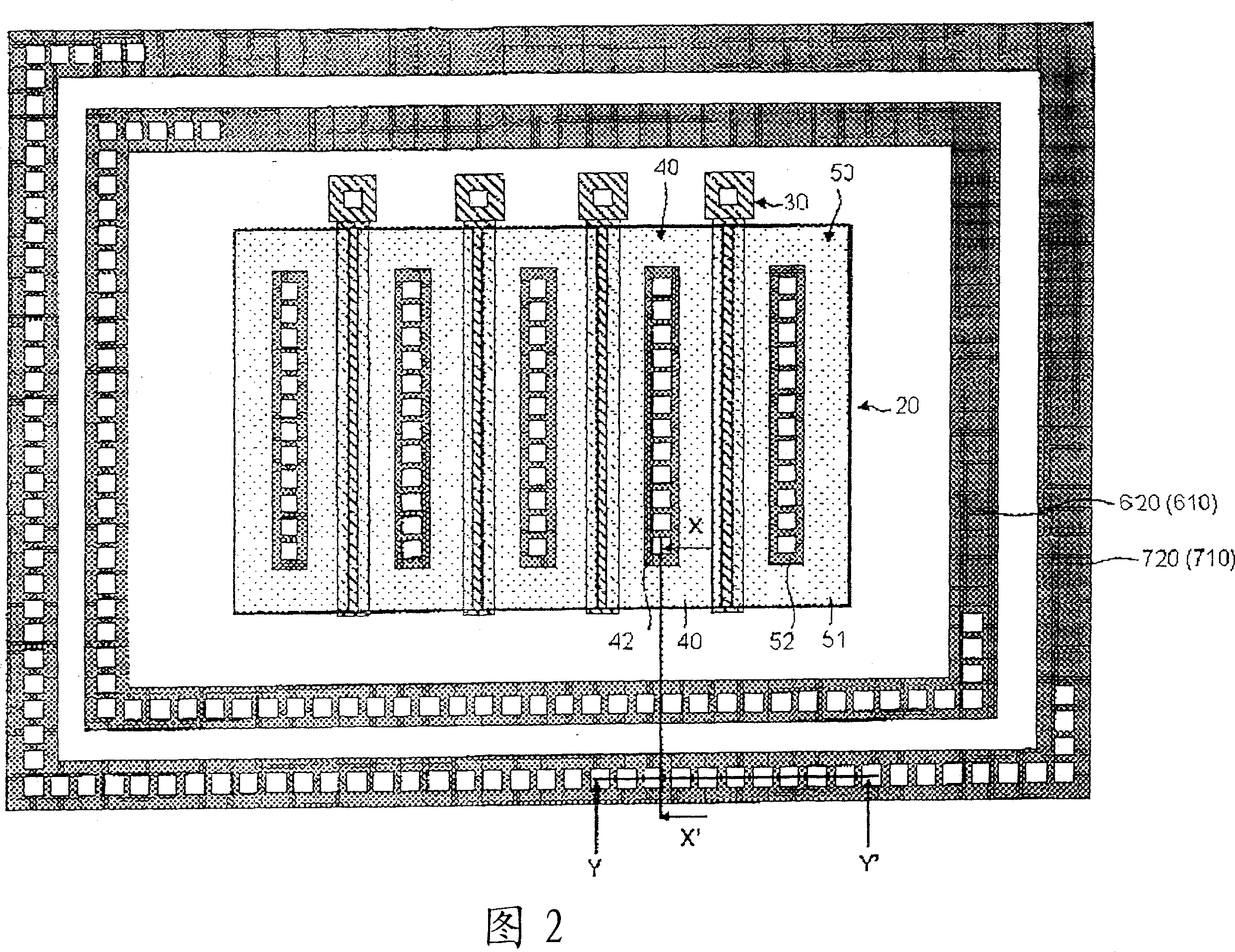
[0084] FIG. 10 is a plan view of a semiconductor device 11 according to the second embodiment. Fig. 11 is a sectional view taken along line B-B' ...
no. 3 approach
[0095] Next, a third embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 13 to 16 . In addition, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same parts as those of the semiconductor device of the first embodiment, and repeated explanations are omitted.
[0096] As already described, in the semiconductor device 10 according to the first embodiment, since no silicide is formed on the side facing the transistor formation region 20, the surge current is less likely to be locally concentrated as compared with the prior art. The purpose of the semiconductor device 12 of the present embodiment is to prevent the local concentration of the surge current more reliably by its structure.
[0097] First, the structure of the semiconductor device 12 of the embodiment will be described.
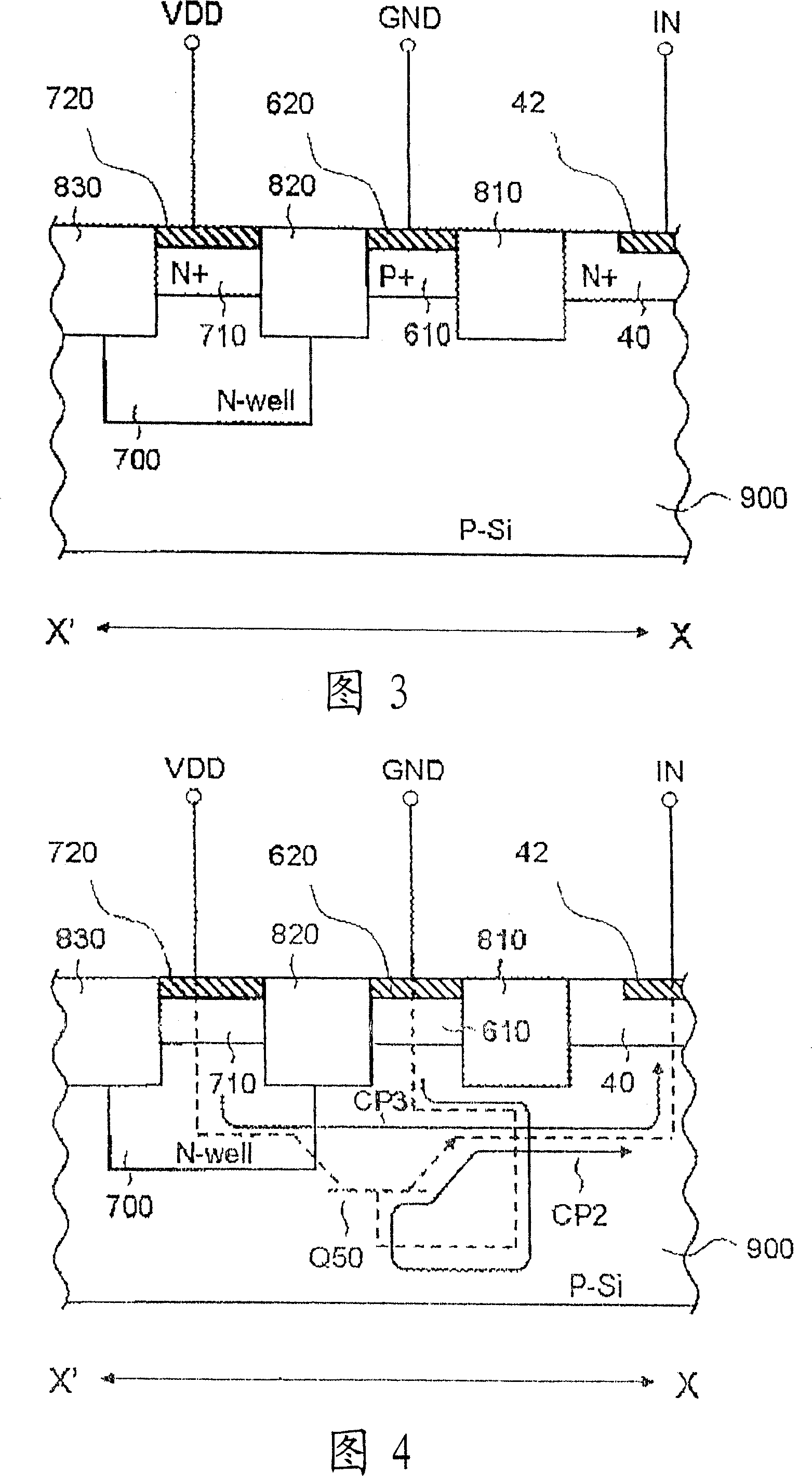
[0098] FIG. 13 is a plan view of a semiconductor device 12 according to the third embodiment. Fig. 14 is a sectional view taken along line C-C' of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com