Fuel cell vehicle and vehicle
A technology for fuel cell vehicles and fuel cell systems, which is applied in the fields of fuel cells, fuel cell additives, and transportation fuel cell technologies, and can solve the problems of not paying attention to the existence of electric vehicles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
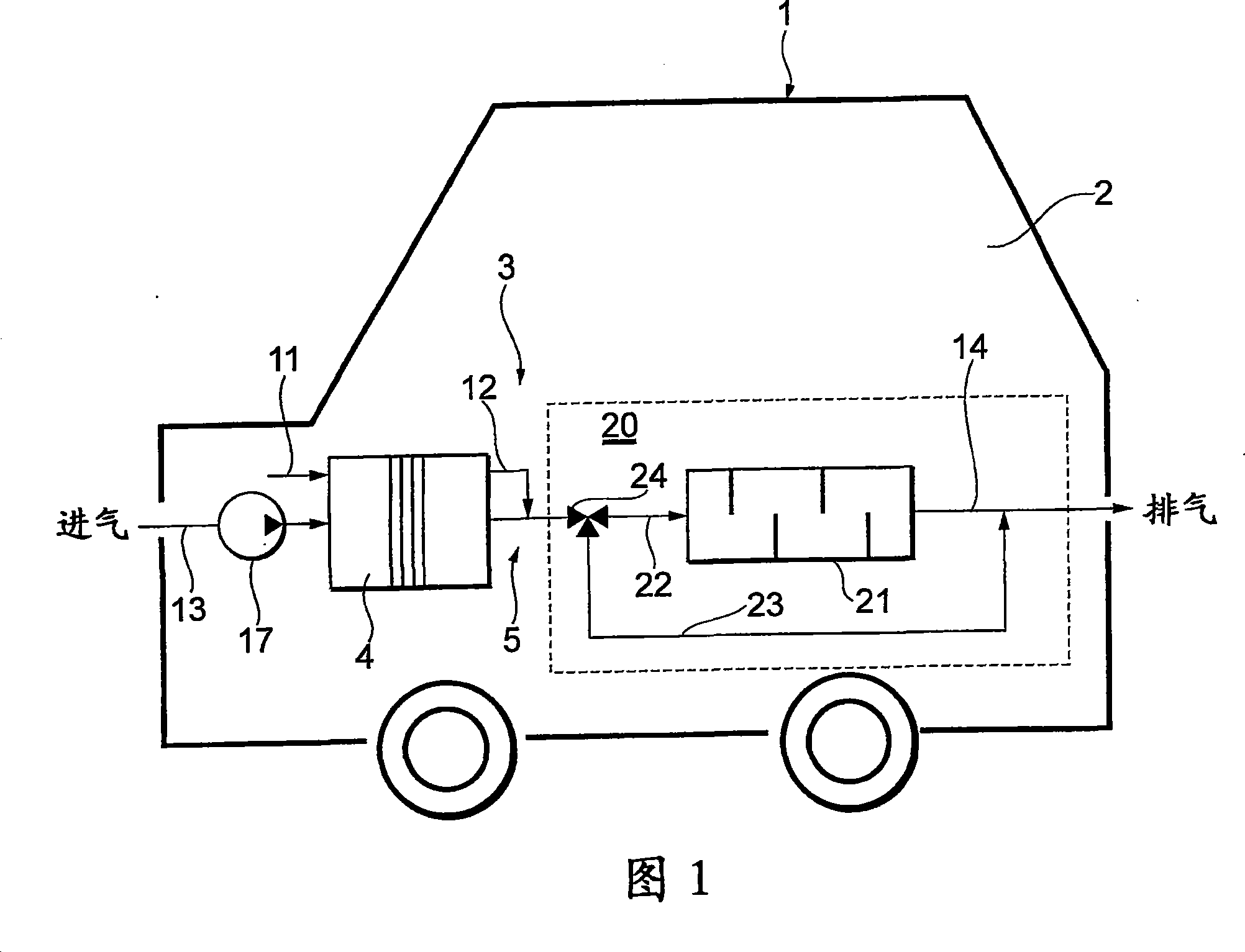
[0067] As shown in FIG. 1 , a fuel cell vehicle 1 is equipped with a fuel cell system 3 on a vehicle body 2 . The fuel cell 4 of the fuel cell system 3 is connected to an unillustrated drive motor via an unillustrated inverter, and the unillustrated drive motor rotates an unillustrated axle. Such a fuel cell vehicle is not limited to the four-wheeled fuel cell vehicle 1 shown in FIG. 1 , but may also be a two-wheeled vehicle, or may be an electric train, a bicycle, or the like.
[0068] The fuel cell 4 has a stack structure in which a plurality of single cells (single cells) are stacked. The fuel cell 4 generates electric power (driving energy) by receiving air as an oxidizing gas and hydrogen as a fuel gas. As the fuel cell 4, there are various types such as phosphoric acid type, but here it is composed of a solid polymer electrolyte type. As a method of supplying hydrogen to the fuel cell 4, a method of converting raw fuel such as natural gas into hydrogen on the vehicle b...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
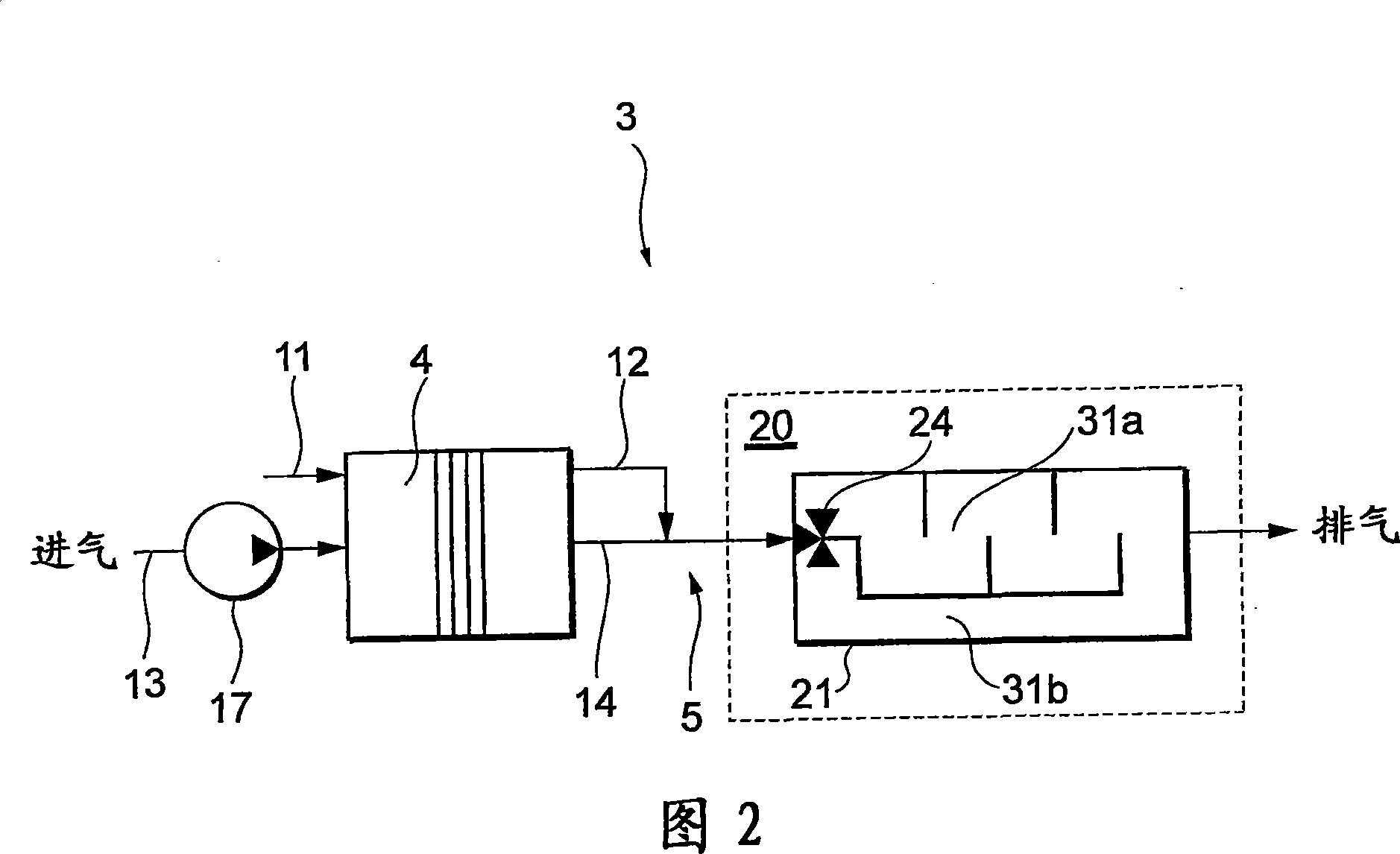
[0086] Next, referring to FIG. 2 , a fuel cell vehicle 1 according to a second embodiment will be described focusing on differences from the first embodiment. FIG. 2 shows a fuel cell system 3 mounted on a fuel cell vehicle 1 . The difference from the first embodiment is the structure of the muffler 20 .
[0087] The muffler 20 includes a muffler 21 that introduces the mixed gas in the oxidizing gas discharge line 14 to muffle the noise. The inside of the muffler 21 is divided into two silencing spaces 31a and 31b having different silencing capabilities. On the gas inlet side inside the muffler 21, a directional control valve 24 for switching between the two muffler spaces 31a, 31b is provided as a passage for introducing the mixed gas. The directional control valve 24 has the same structure as that of the first embodiment. The directional control valve 24 is mechanically operated based on the running condition of the fuel cell vehicle 1, and is switched to either of the tw...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
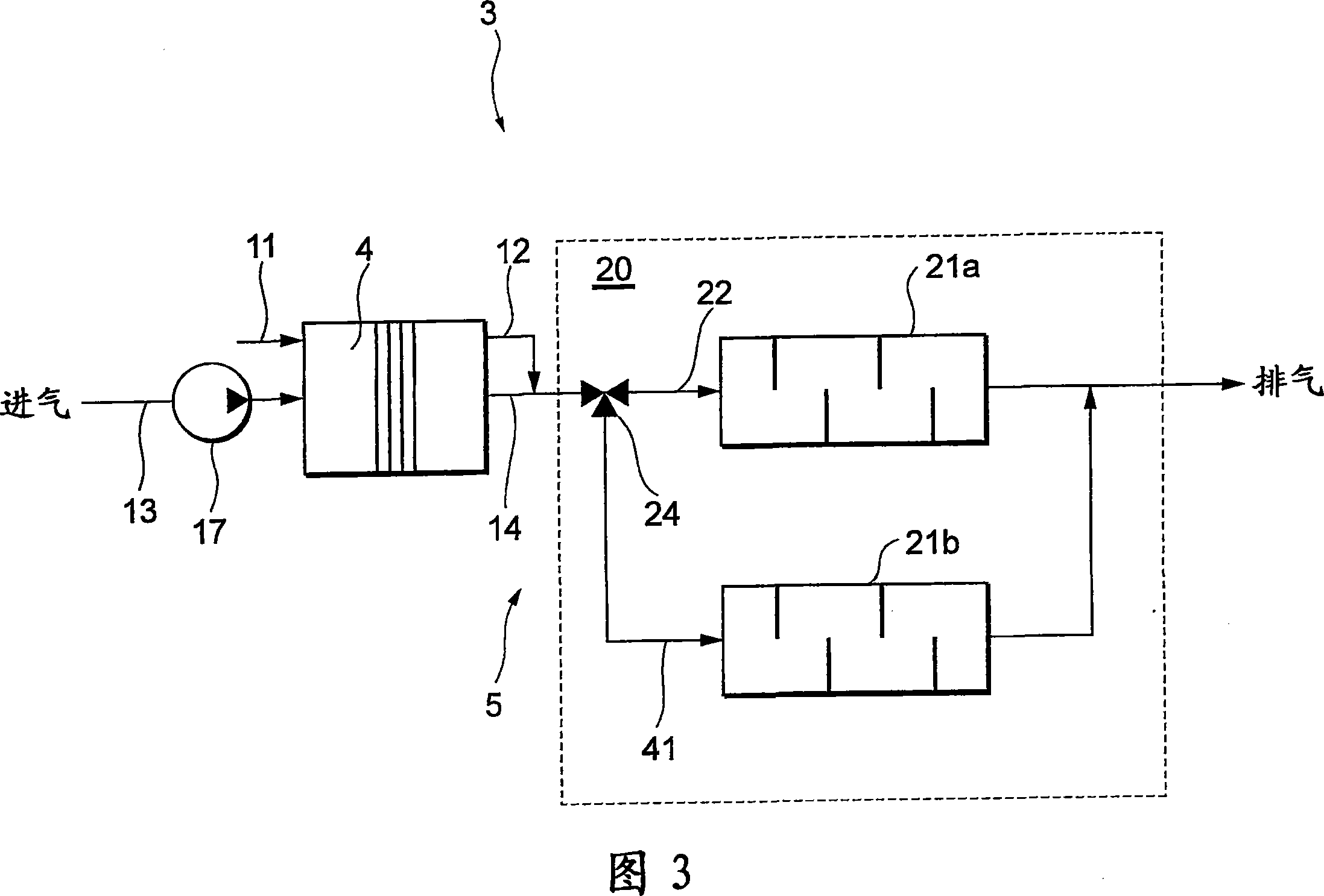
[0095] Next, a fuel cell vehicle 1 according to a third embodiment will be described focusing on differences from the first embodiment with reference to FIG. 3 . FIG. 3 shows a fuel cell system 3 mounted on a fuel cell vehicle 1 . The difference from the first embodiment is the structure of the muffler 20 .
[0096] The muffler unit 20 includes two mufflers 21a, 21b that introduce the mixed gas of the oxidizing gas discharge line 14 to muffle the noise, and a directional control valve 24 that switches to either of the two mufflers 21a, 21b.
[0097] One muffler 21 a is provided in the main airflow passage 22 , and the other muffler 21 b is provided in a branch passage 41 provided in parallel with the main airflow passage 22 . The upstream end of the branch passage 41 is connected to the directional control valve 24 , and the downstream end thereof is connected to the downstream side of the muffler 21 a of the main flow passage 22 . The directional control valve 24 is mechani...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com