Prokaryotic cell non-fusion soluble expression system
A prokaryotic cell and expression system technology, applied in the field of prokaryotic cell non-fusion soluble expression system, can solve the problems such as low yield of inclusion body denaturation/renaturation biological activity and increased production cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
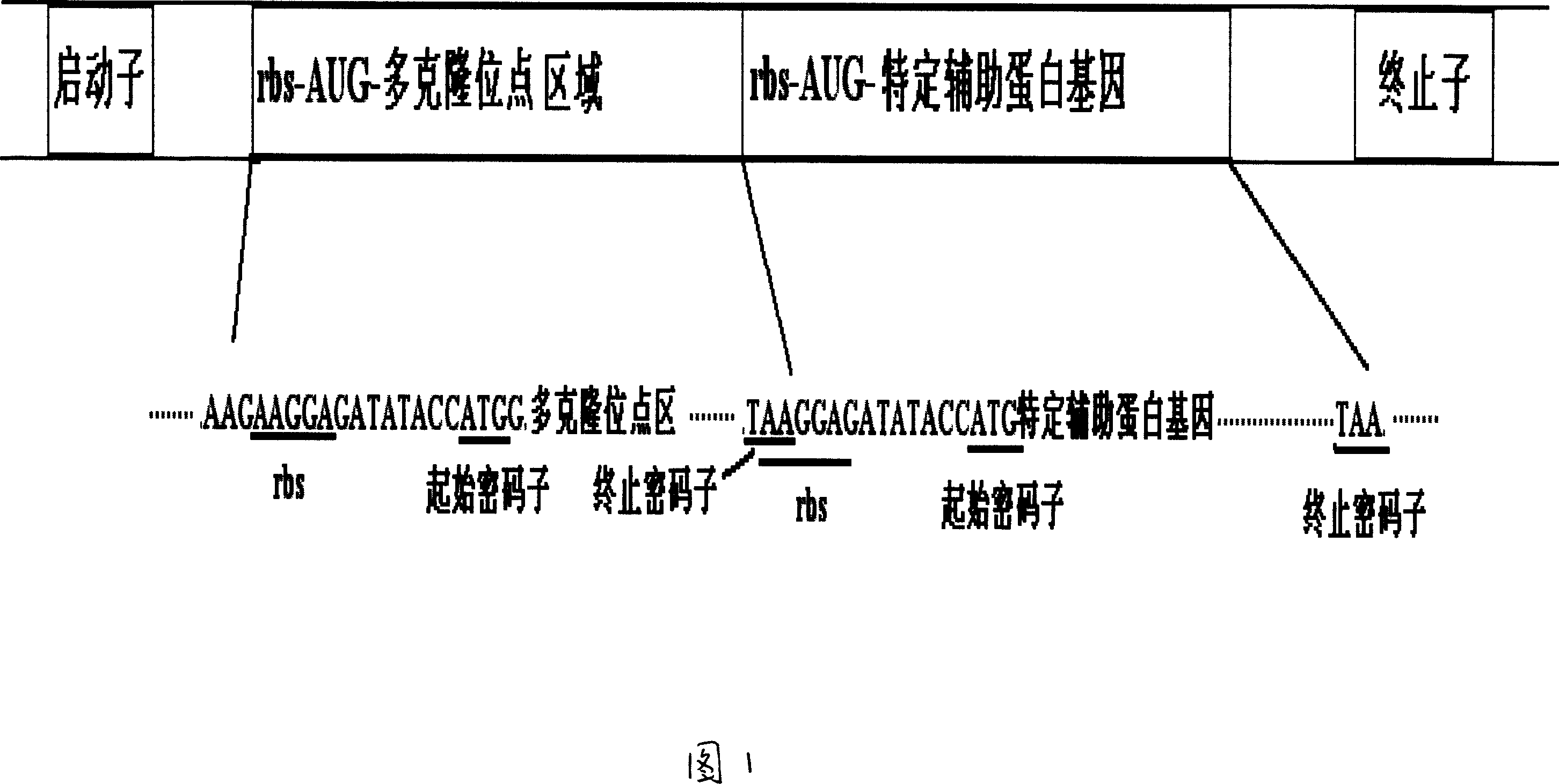
[0028] According to the measures and principles of the above-mentioned object of the present invention, the non-fusion expression plasmid pSYPU-1 in prokaryotic cells is produced by T 7 -lac (lactose) double promoter and T 7 Transcription unit regulated by terminators. The translation of each gene in the transcription unit is regulated by prokaryotic SD sequence, translation initiation codon and translation termination codon respectively. The most upstream of the transcription unit is a multiple cloning site region with independent translation regulation, which is used for recombination (cloning) of various exogenous target genes pre-expressed, and its purpose is to enable the high-efficiency expression of exogenous target genes. Immediately following this region is a thioredoxin reductase TrxA gene with independent translational regulation. The construction measures and principles are implemented according to the model of transcription unit I above. The transcription unit ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] According to the above measures and principles of the present invention, the construction of prokaryotic cell non-fusion expression plasmid pSYPU-1a is the same as pSYPU-1 in principle and form, the difference is that the antibiotic resistance gene is ampicillin.
[0032] The exogenous target gene expressed is analgesic-antitumoral peptide I (AGAP I), AGAP I is composed of 74 amino acid residues, with a molecular weight of 7820Da, containing eight cysteine residues, forming four pairs of disulfides key. The AGAP I gene is recombined in the multi-cloning site region of the prokaryotic cell non-fusion expression plasmid pSYPU-1a, the AUG start codon is added before the AGAP I gene, and the translation stop codon is added at the end of AGAP I expression. The obtained recombinant pSYPU-1a-AGAP I expression plasmid was transformed into prokaryotic cell expression host cell BL21(DE3), and the bacterial cells were collected after IPTG-induced expression (37°C culture inducti...
Embodiment 3
[0034] According to the above measures and principles of the present invention, the construction of prokaryotic cell non-fusion expression plasmid pSYPU-1b is the same as pSYPU-1 in principle and form, the difference is that the antibiotic resistance gene is chloramphenicol.
[0035] The recombinant pSYPU-1b-ANEP II expression plasmid was transformed into the E. coli expression host cell BL21(DE3), and the expression was induced by IPTG (induction at 37°C for 3 hours). The bacteria were collected and lysed by ultrasonication, and centrifuged to obtain two parts of the supernatant and the precipitate. . Cell lysates, ultrasonic supernatants, and precipitates were analyzed by small molecule Tricine-SDS-PAGE. The imaging system analysis showed that the expression product of ANEP II accounted for more than 12% of the total bacterial protein, and ANEP II was mainly present in the supernatant of ultrasonically lysed bacteria, accounting for more than 90% of the total expression.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com