Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Surface electrocardiogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a record of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It was invented by Willem Einthoven. It is done by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device outside the body. An electrocardiogram is used to monitor your heart.
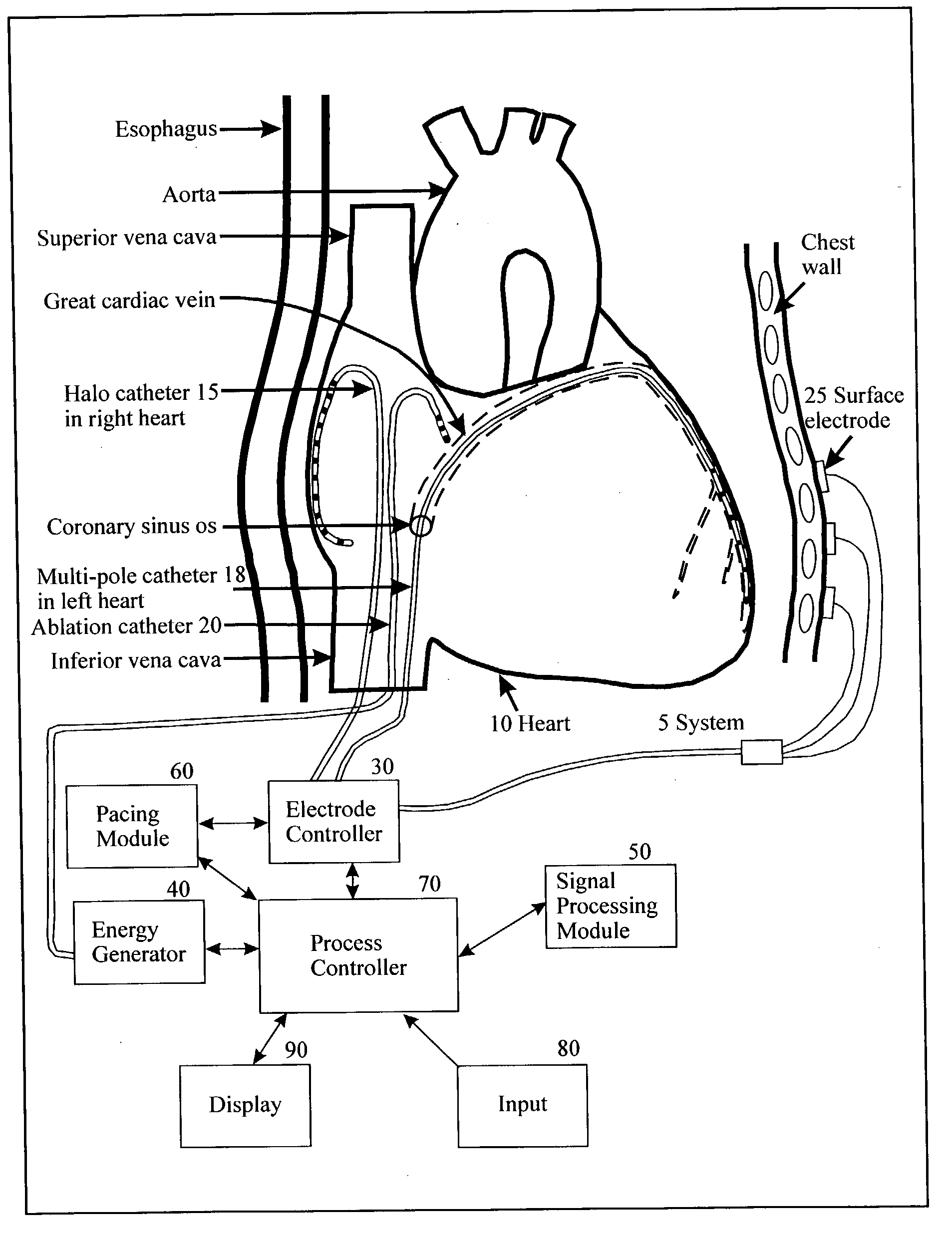
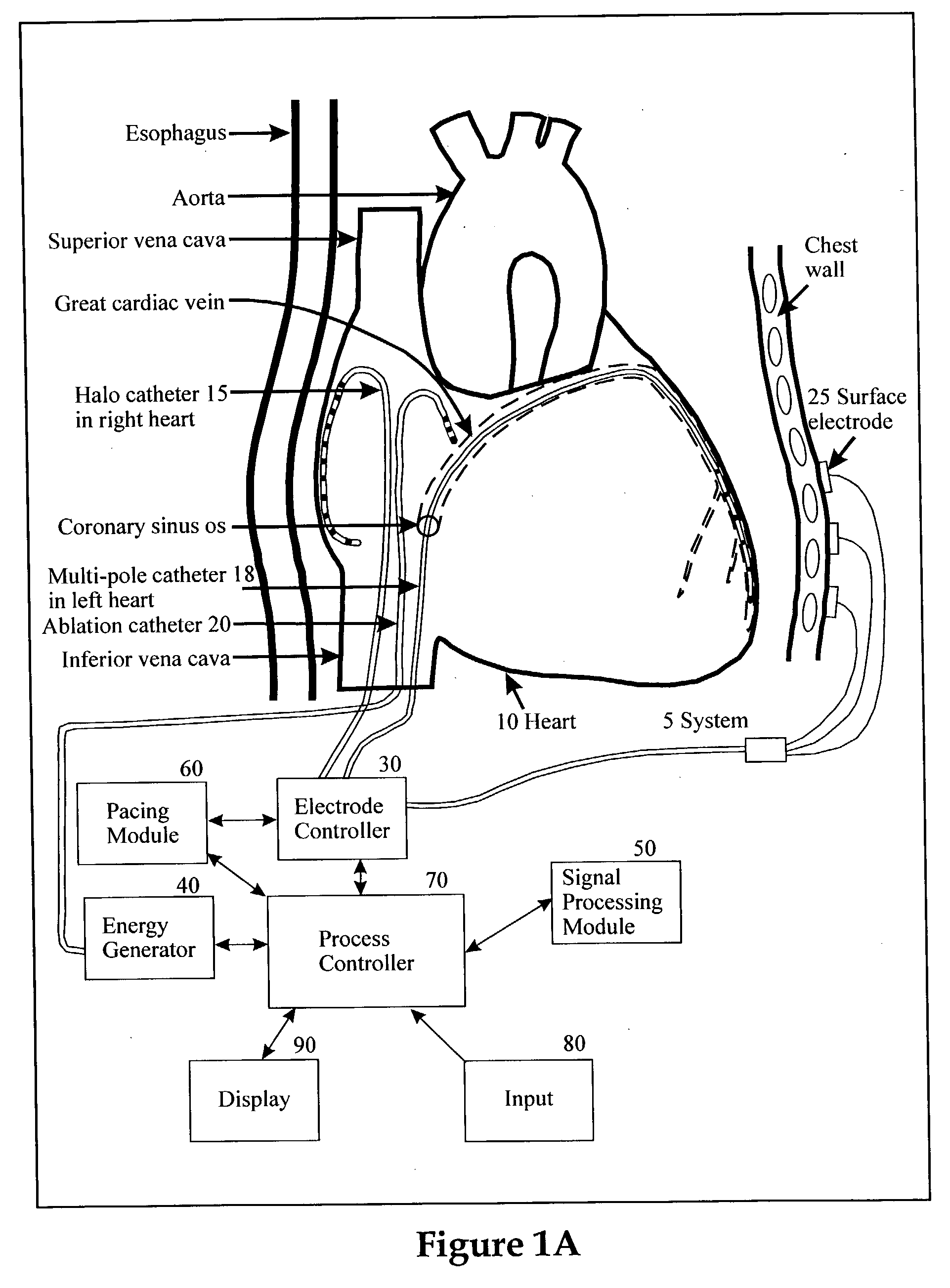
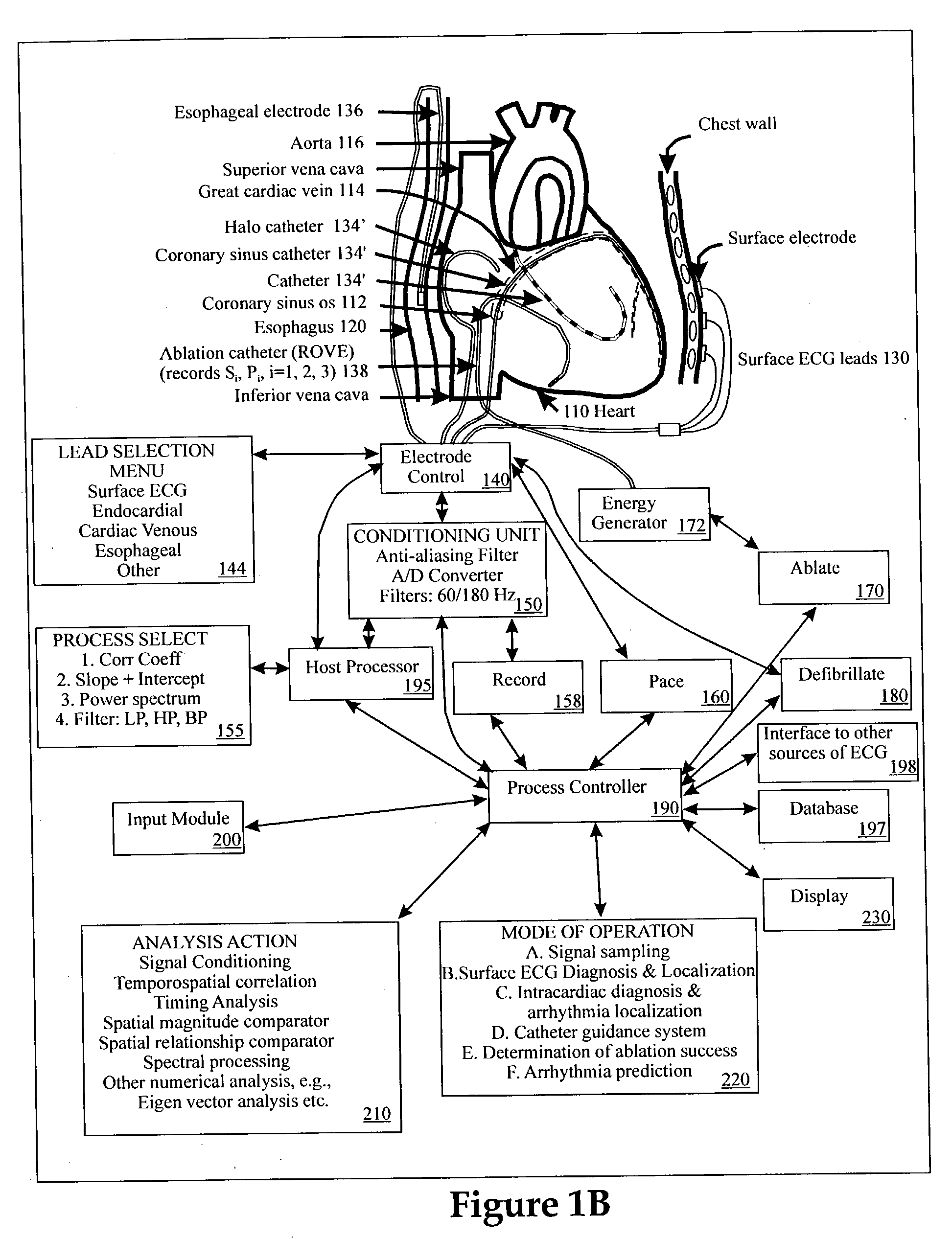
Method and apparatus for classifying and localizing heart arrhythmias
Analyzes surface electrocardiographic and intracardiac signals to identify and separate electrical activity corresponding to distinct but superimposed events in the heart. Assesses the spatial phase, temporal phase, rate, spectrum and reproducibility of each event to determine uniformity of activation in all spatial dimensions. Uses numerical indices derived from these analyses to diagnose arrhythmias. Uses these indices to determine the location of an arrhythmia circuit, and to direct the movement of an electrode catheter to this location for ablation or permanent catheter positioning. Subsequently, uses these indices to determine whether ablation has successfully eliminated the circuit. Uses variability in these indices from the surface electrocardiogram to indicate subtle beat-to-beat fluctuations which reflect the tendency towards atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Emergency heart sensor patch
InactiveUS20060030781A1Easy and intuitive to useInexpensive and suitable for disposable useElectrocardiographySensorsCardiac arrest- pulseless electrical activityPulseless electrical activity
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for the non-invasive detection and indication of a heart condition during a medical emergency. The patch is placed on the chest area for sensing and analyzing a surface electrocardiogram (ECG). The heart condition is rapidly indicated via an indicator integrated in the patch. The disposable smart patch is inexpensive and simple to use by a layperson assisting or living with the person experiencing the medical crisis. The patch is activated automatically upon its removal from the package and placement on the chest. The detection and indication occurs rapidly and within 90 seconds of placement on the chest. In another embodiment of the invention, a vibration sensor element is incorporated for detecting cardiovascular vibrations and for ruling out pulseless electrical activity.
Owner:CARDIOVU
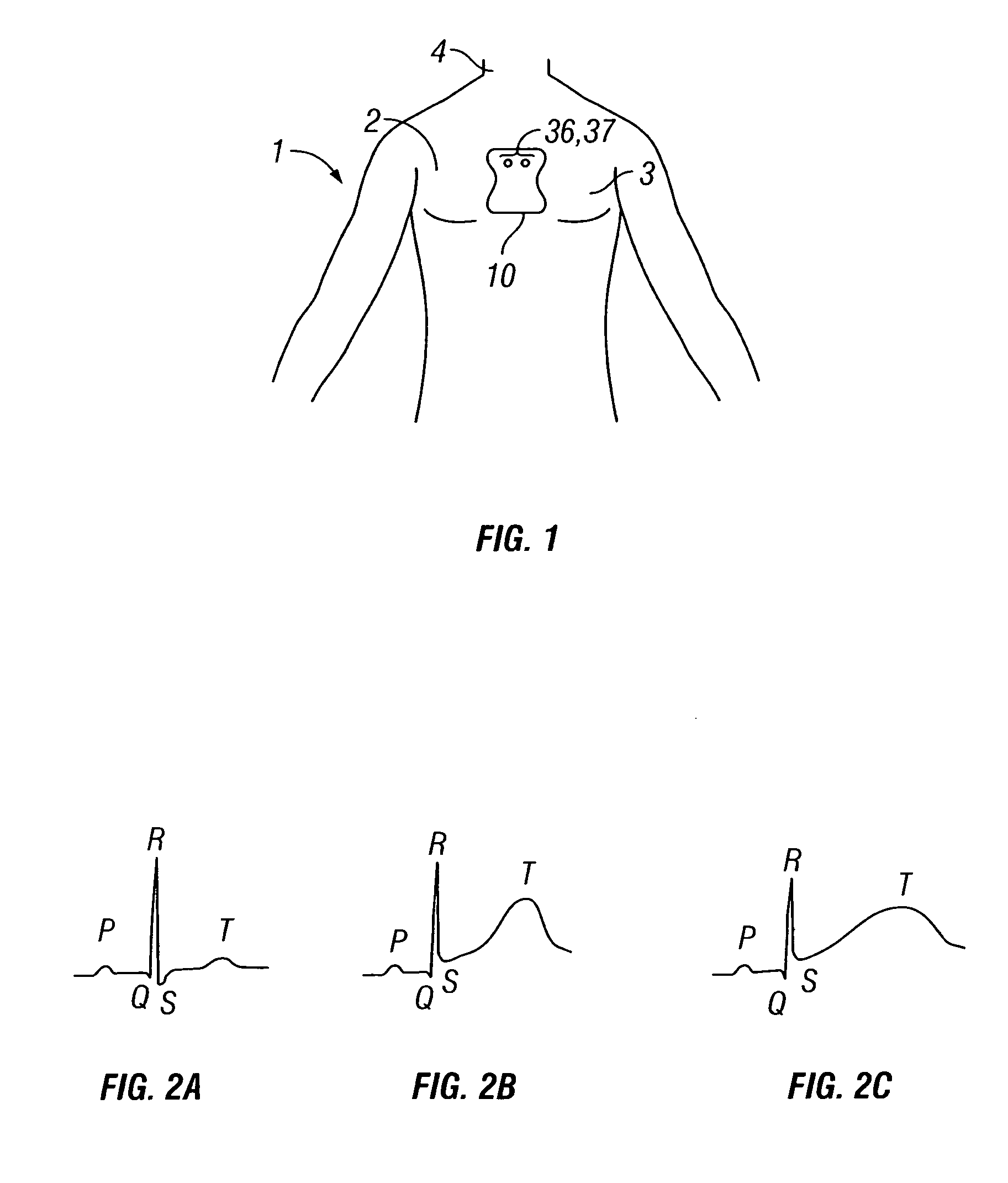
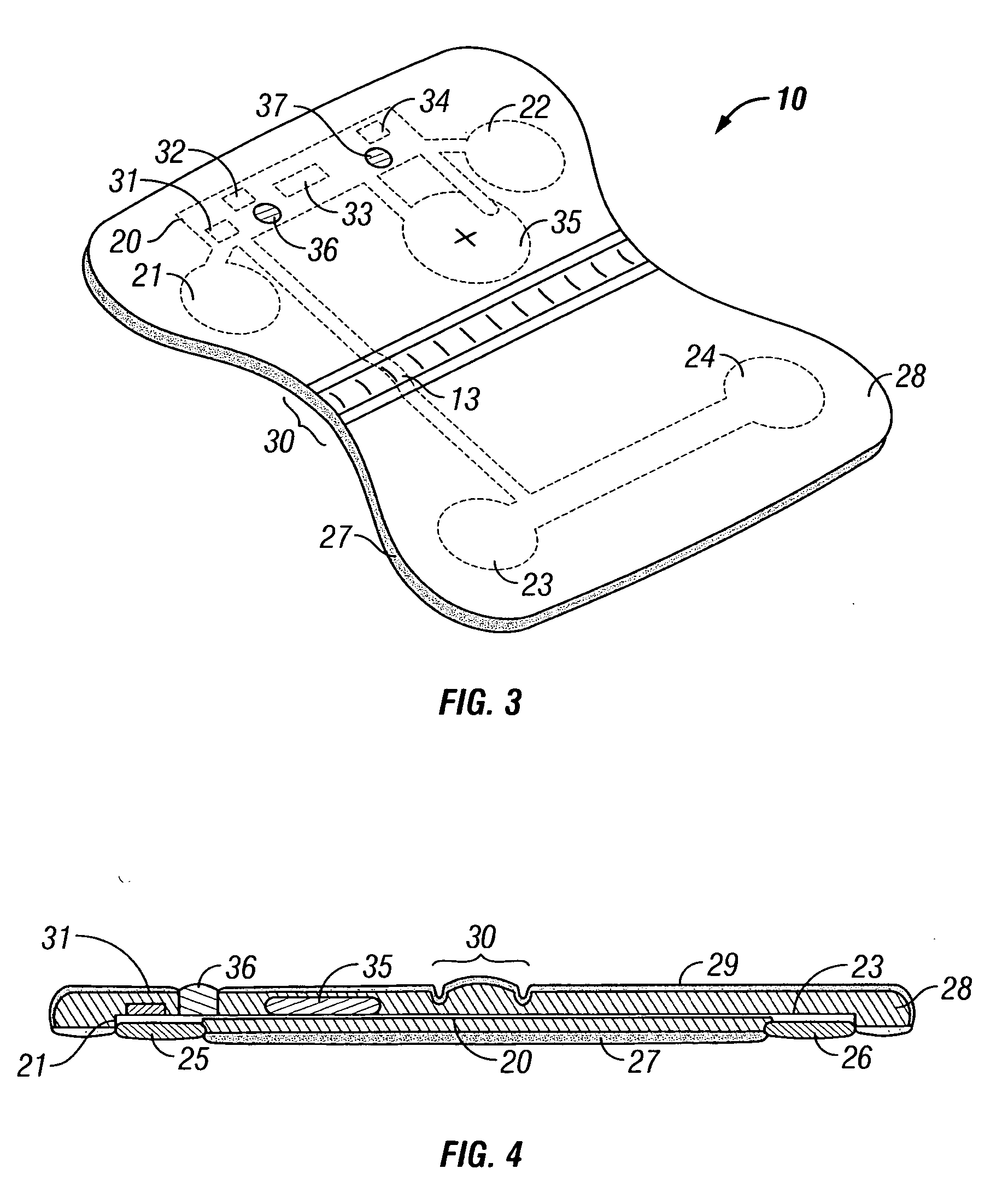
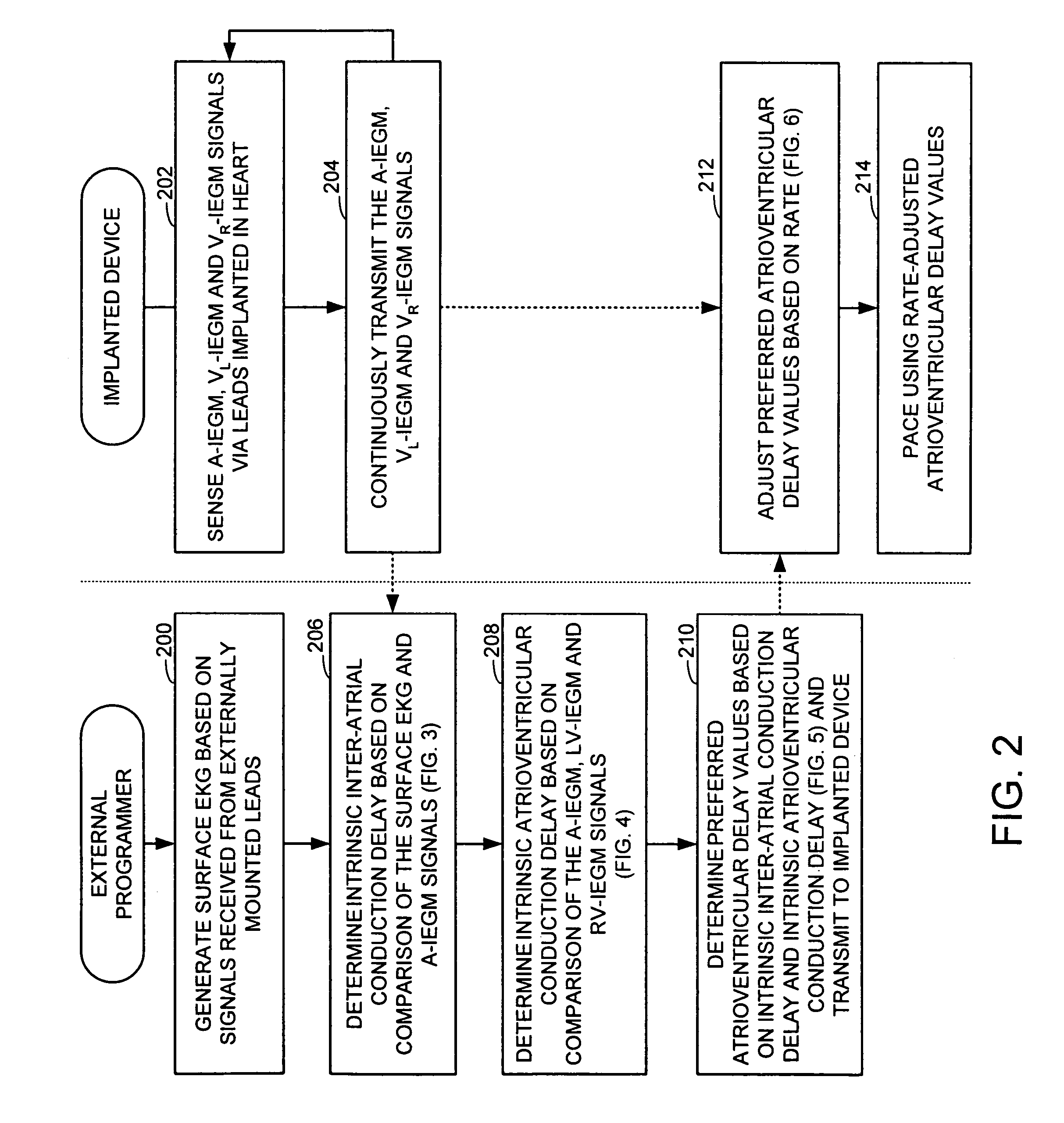
System and method for determining optimal atrioventricular delay based on intrinsic conduction delays
ActiveUS7248925B2ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationIntracardiac ElectrogramSurface electrocardiogram
A system and method for estimating optimal atrioventricular delay values for use in pacing the ventricles. Both the intrinsic inter-atrial conduction delay and the intrinsic atrioventricular conduction delay are determined for the patient and then the preferred atrioventricular pacing delay is derived therefrom. By taking into account intrinsic inter-atrial delay along with intrinsic atrioventricular delay, a more reliable estimate of the true optimal atrioventricular delay values for the patient can be achieved than with techniques that only take into account intrinsic atrioventricular delay values. In one example, the technique uses intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals and surface electrocardiogram (EKG) signals and hence can be performed by an external programmer without requiring Doppler echocardiography or other cardiac performance monitoring techniques. In another example, wherein the implanted device is equipped with a coronary sinus lead, the technique uses only IEGM signals and hence can be performed by the device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
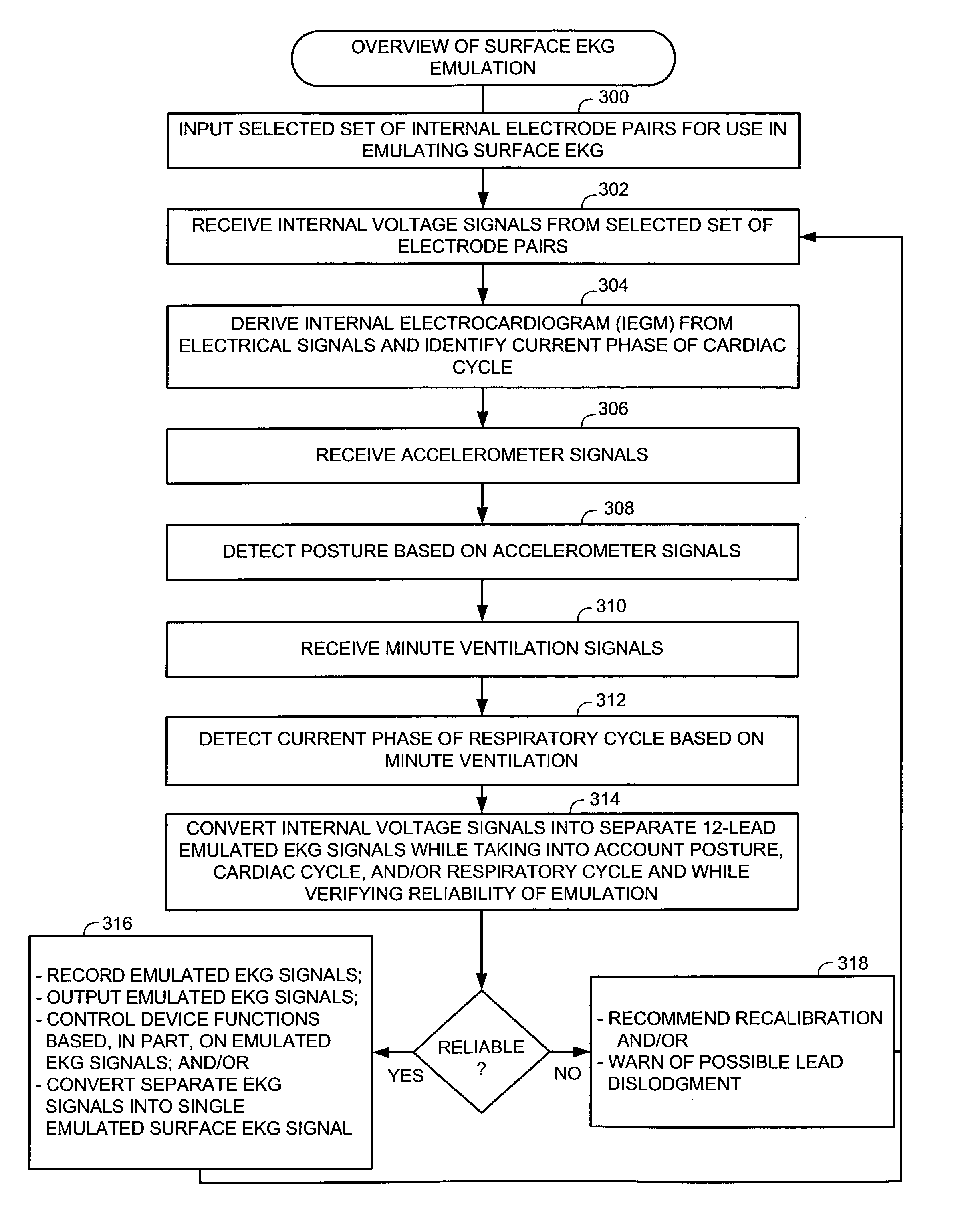
System and method for emulating a surface EKG using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS6993379B1Avoid less flexibilitySimulation is accurateElectrocardiographyEndoradiosondesImplanted deviceEngineering
A surface electrocardiogram (EKG) is emulated using signals detected by the internal leads of an implanted device. The emulation is performed using a matrix-based technique that separately emulates each of the individual signals of a multiple-lead EKG, rather than merely emulating a single combined EKG. In one example, each of the twelve signals of a standard 12-lead EKG are individually emulated, allowing for separate processing and display. The emulation technique takes into account factors affecting the relative locations of the internal leads, such as respiration and posture, to thereby provide a more accurate emulation. A calibration technique is provided for calibrating the EKG emulation for use with a particular patient and a verification technique is provided for automatically verifying the reliability of the emulation. Any significant loss in emulation reliability is likely caused by lead dislodgment and so automatic detection of possible lead dislodgment is also achieved.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Catheterization method and system for controlling tip displacement
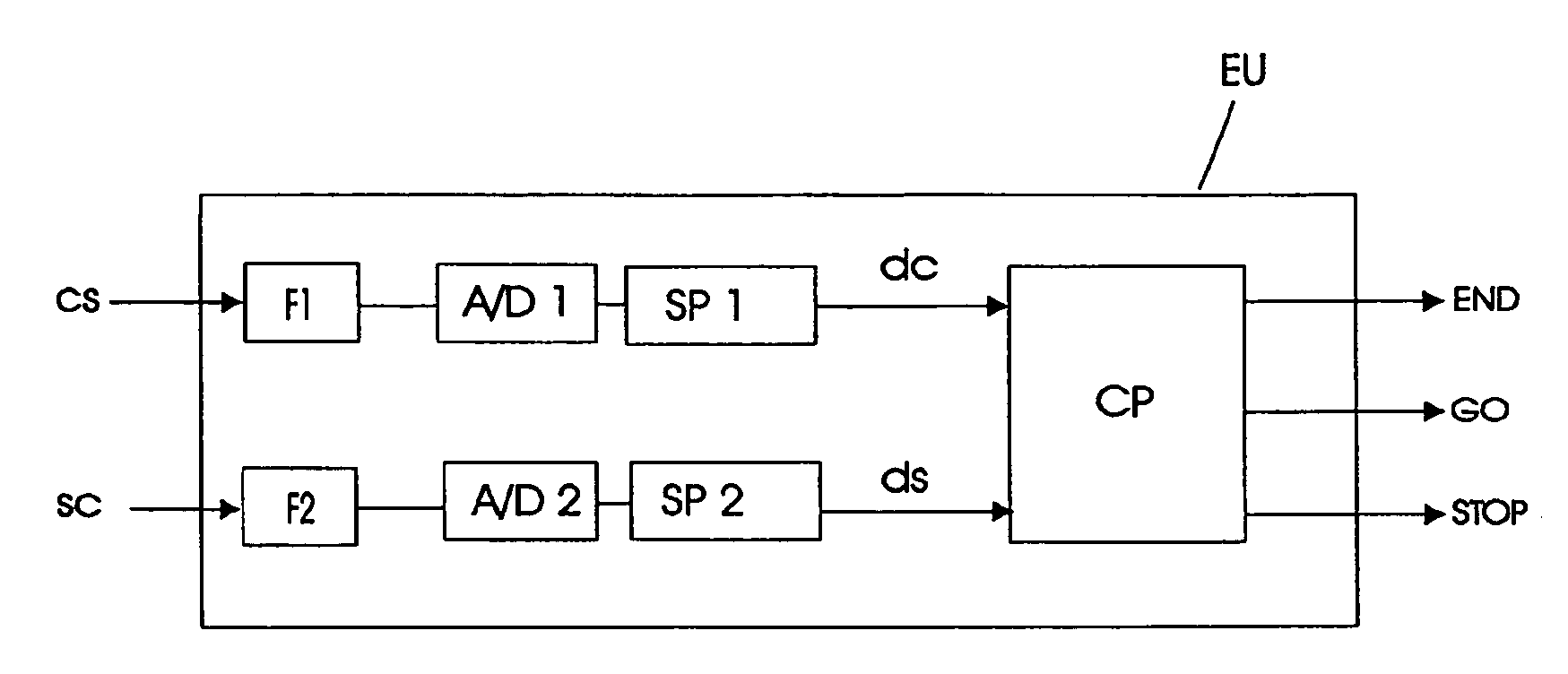
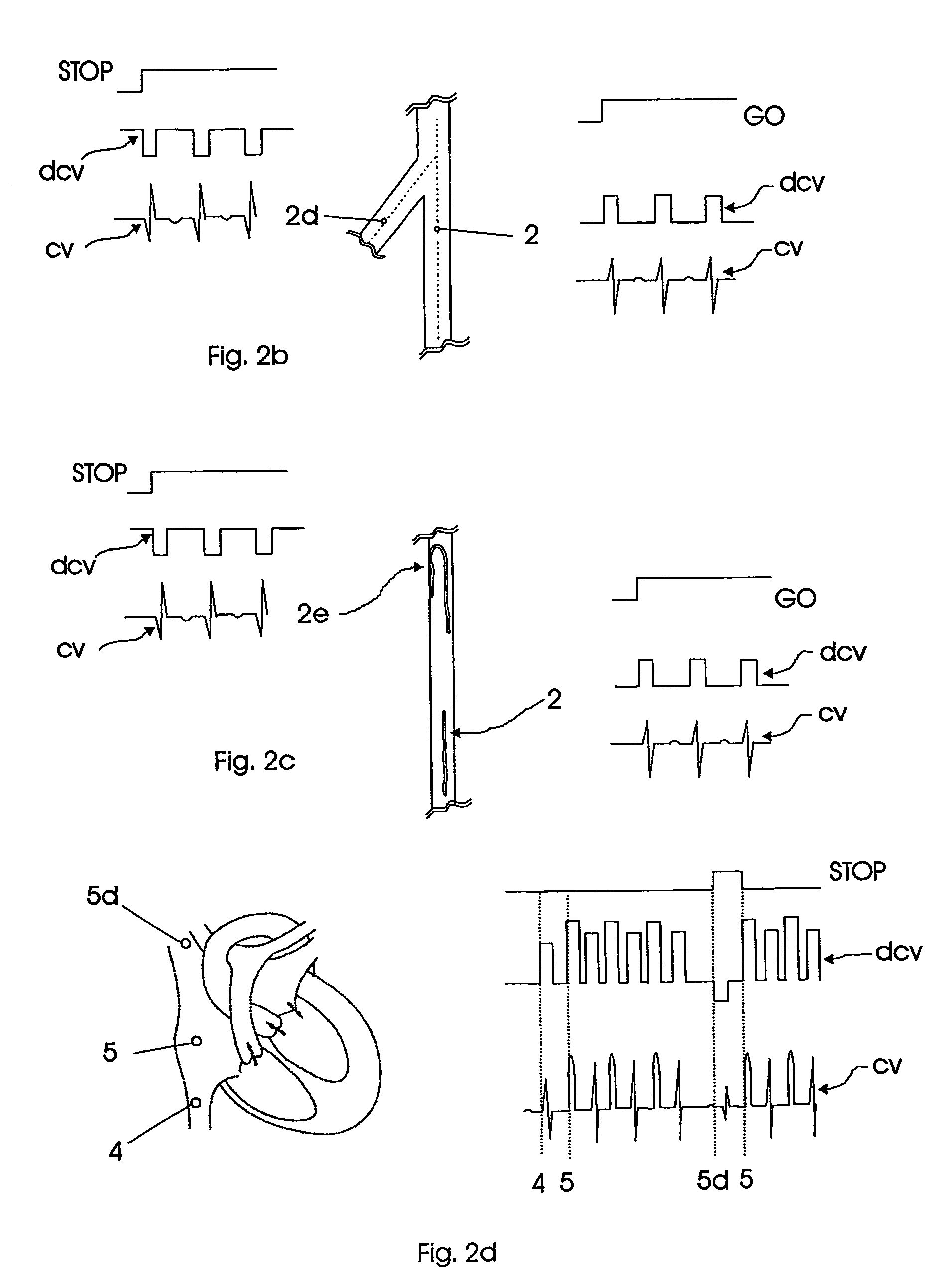
ActiveUS7640053B2Effectively avoid drawback and limitation of X-rayRapidly catheterizationElectrocardiographyEar treatmentControl signalSignal on
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
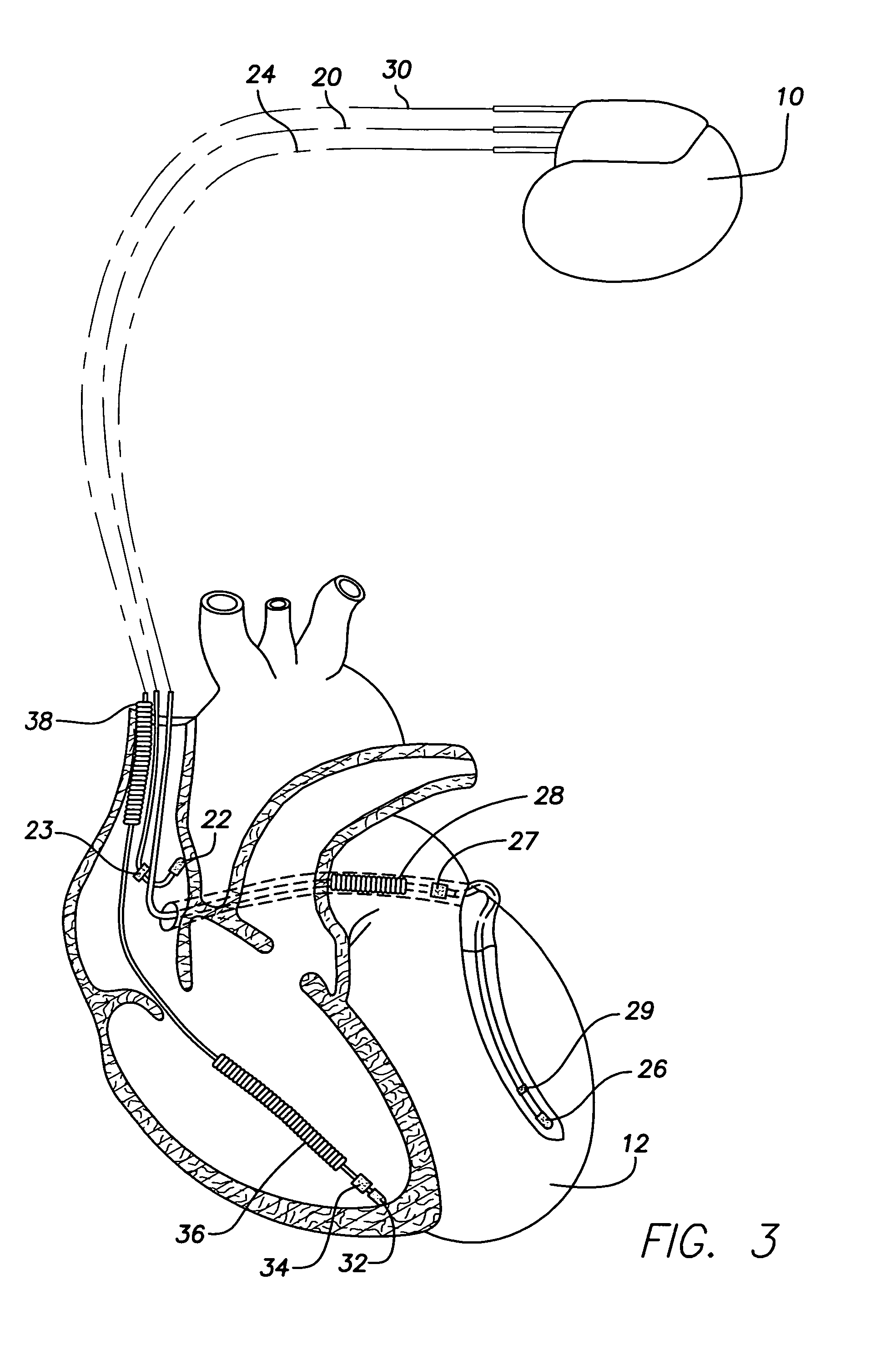
Subcutaneous defibrillation system and method using same
A medical system includes a housing configured for implantation within a patient's subclavicular region. Detection circuitry provided in the housing is configured to detect cardiac electrical activity. Energy delivery circuitry provided in the housing is configured to deliver therapy to treat a detected tachycardia or fibrillation episode. A lead is coupled to the housing, detection circuitry, and energy delivery circuitry. The lead is configured for subcutaneous, non-intrathoracic placement within the patient, and extends from the subclavicular region to just below the patient's ribs or the subxiphoid process. A defibrillation electrode is provided at a distal end of the lead body. A pair of sensing electrodes is provided on the lead body at locations consistent with positions V2-V5 of surface electrocardiogram electrodes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
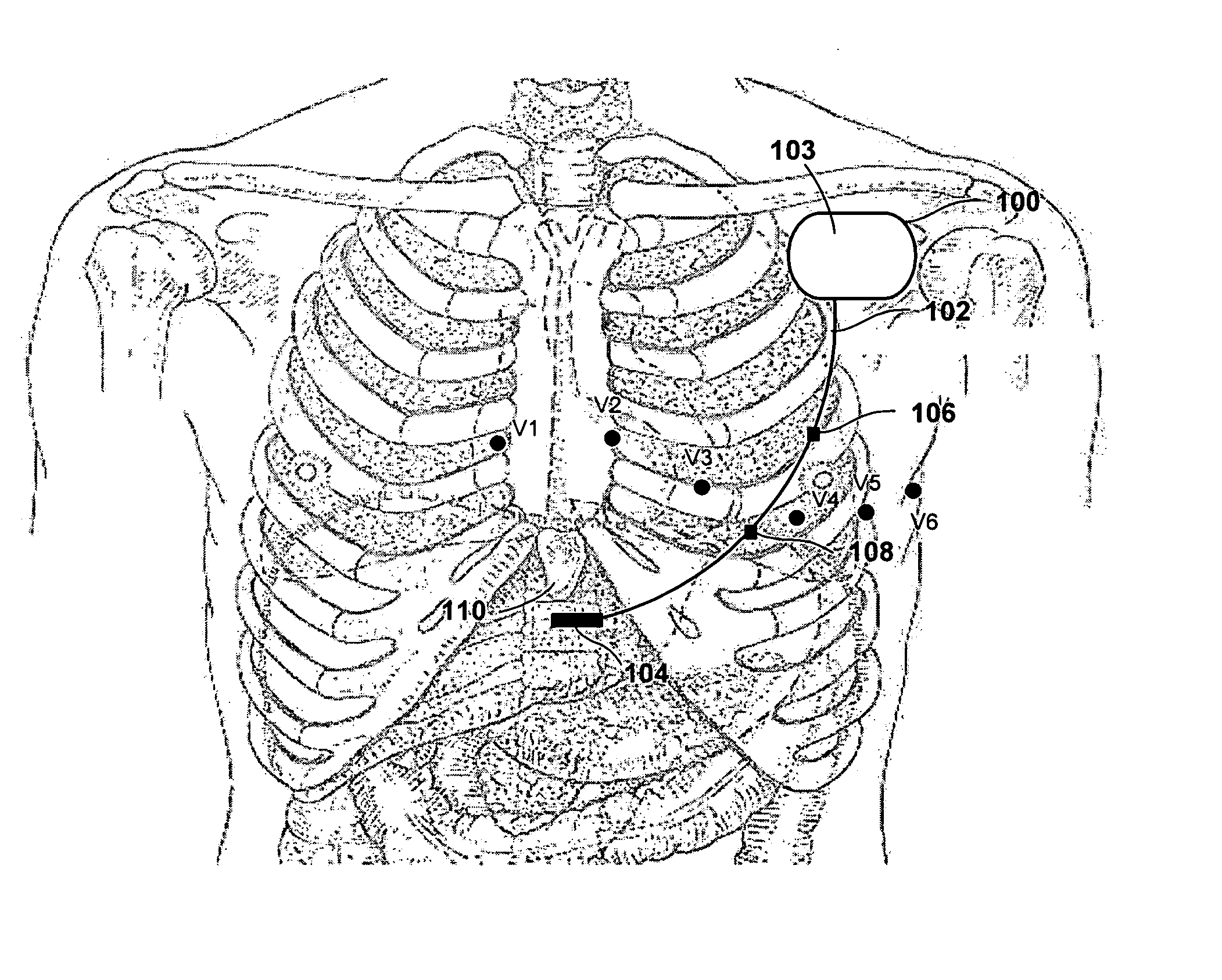
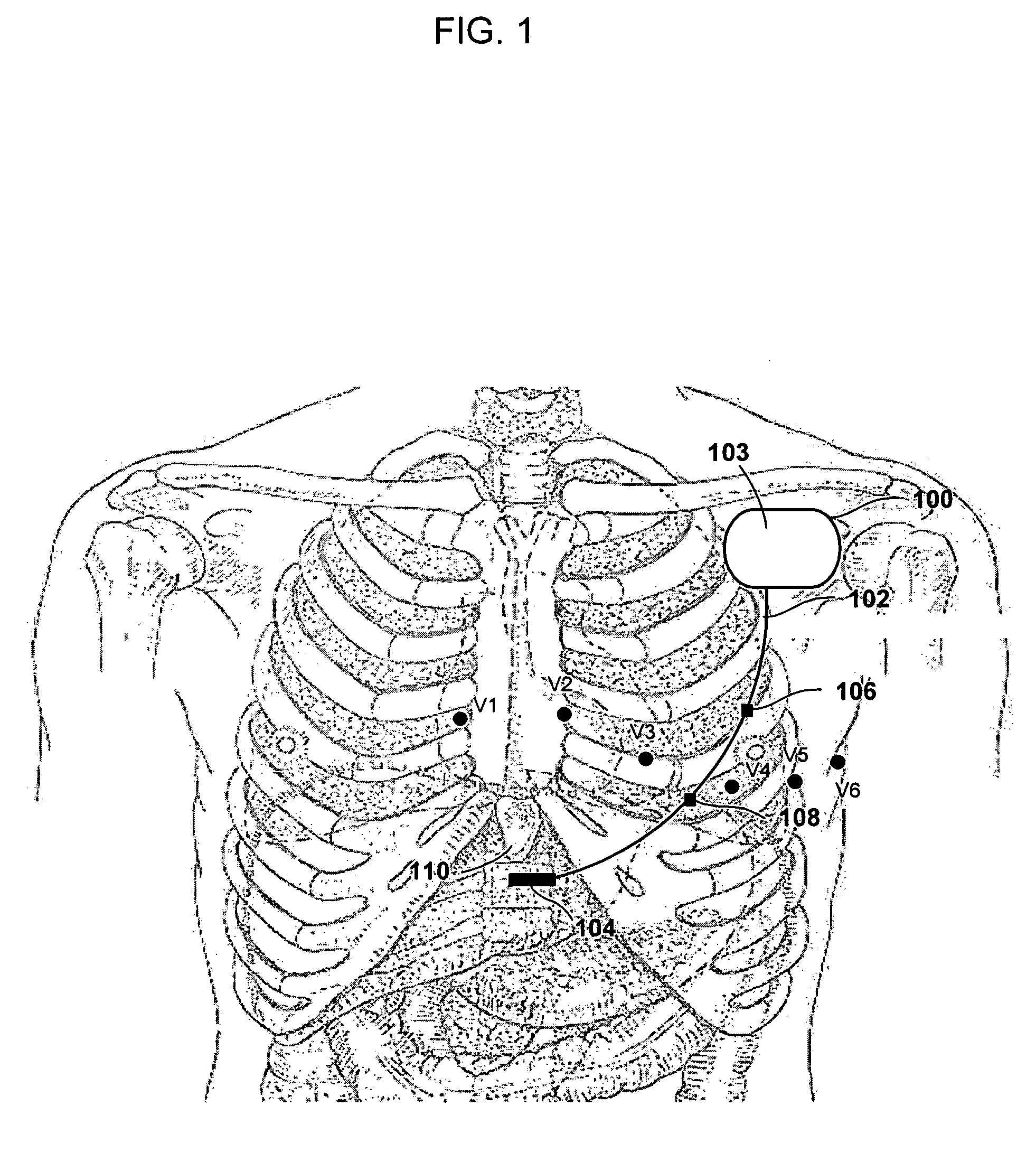
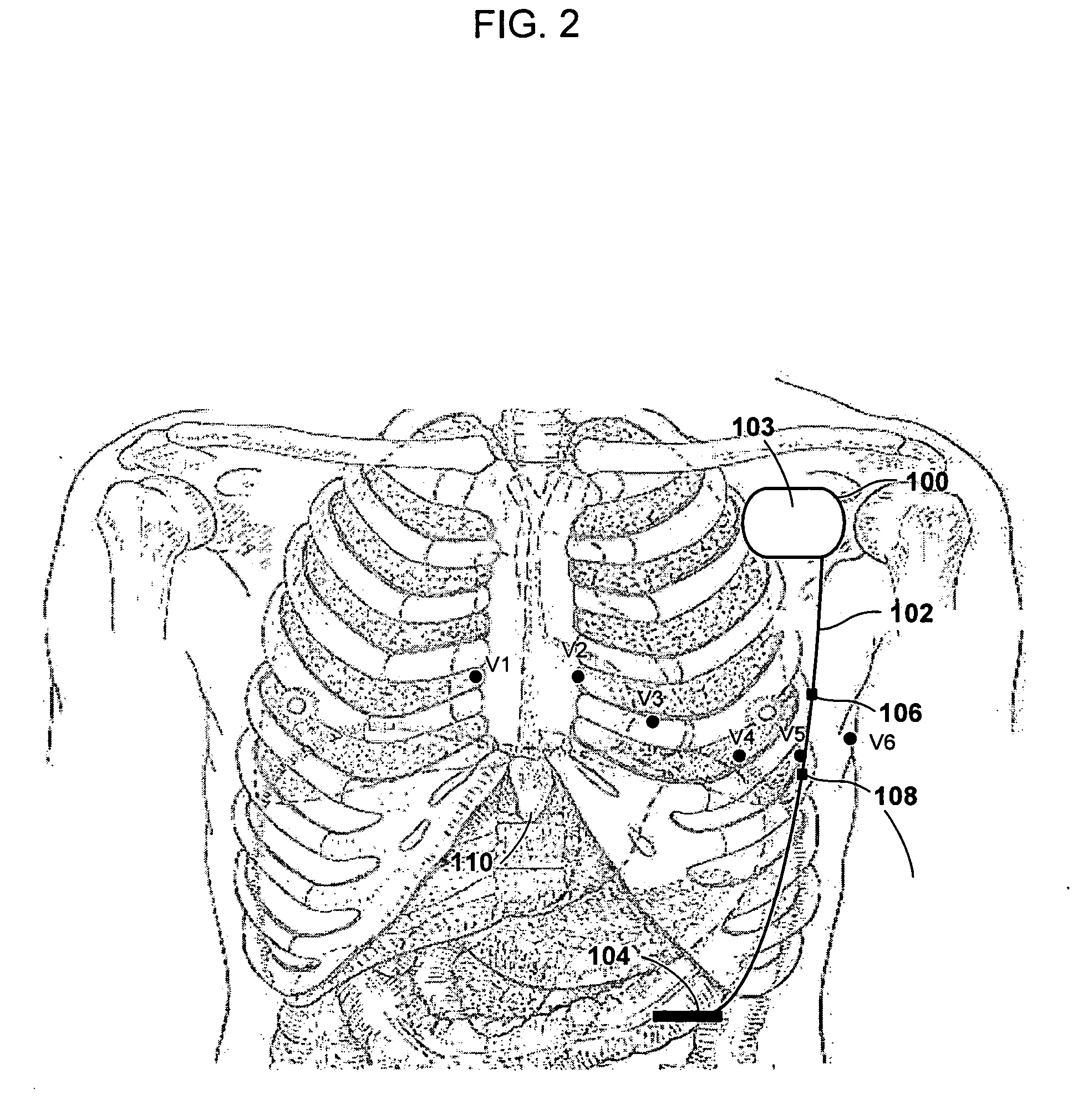
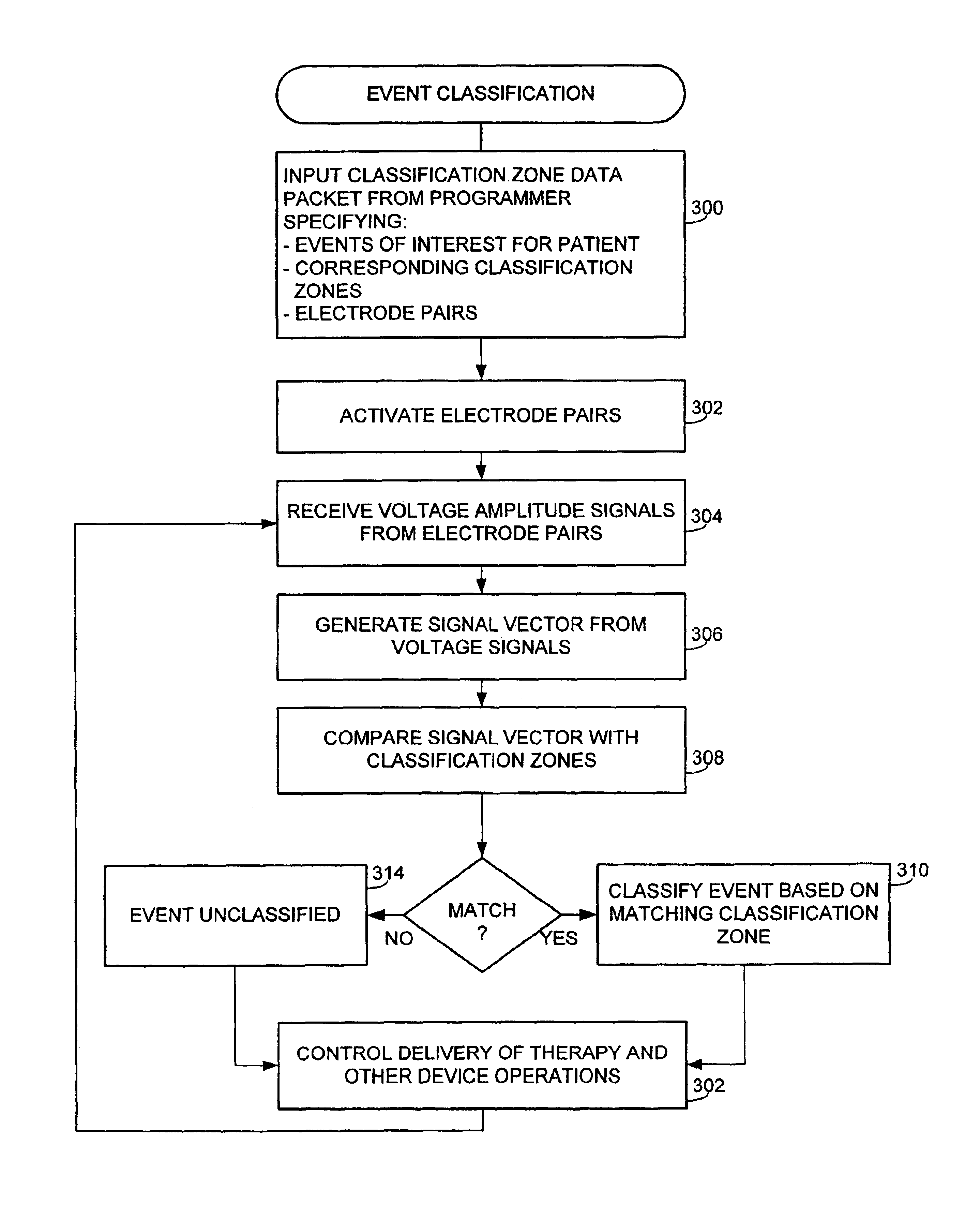
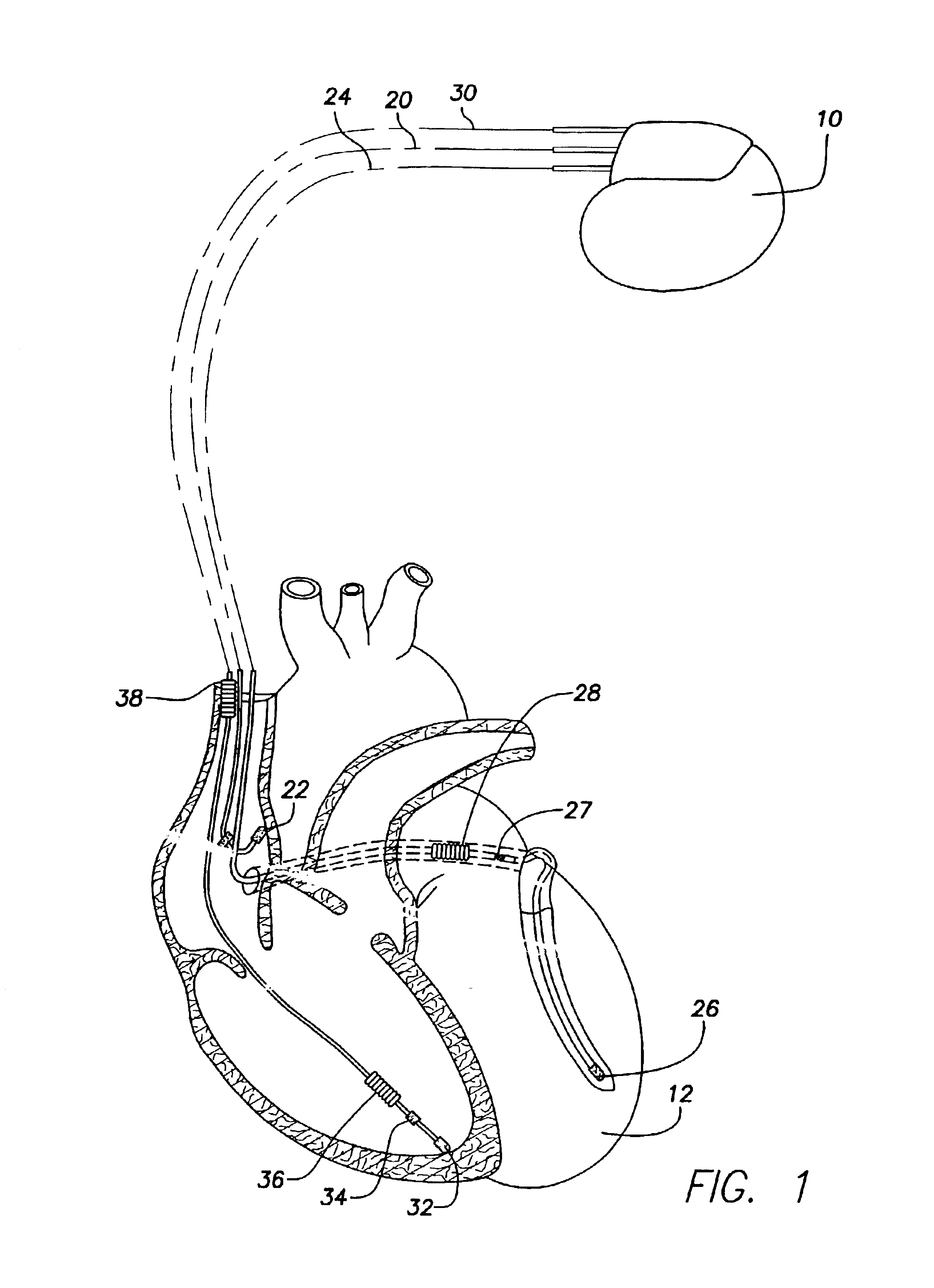
Implantable medical device and method for detecting cardiac events without using of refractory or blanking periods
Cardiac electrical events are detected by comparing signal vectors with pre-determined classification zones representative of different cardiac events. The signal vector is generated by sensing the voltages between various combinations of electrodes, such as A-tip to V-tip, A-tip to A-ring, and A-ring to V-ring. The signal vector is compared with a set of classification zones corresponding to different events, such as P-waves, R-waves, T-waves, A-pulses, and V-pulses, to determine whether the vector lies within any of the classification zones. In this manner, cardiac events are detected using only the voltages received from the electrodes and no refractory periods or blanking periods are required to distinguish one event from another. The classification zones vary from patient to patient and a technique is provided herein for generating a set of vector classification zones for a particular patient. Signal vectors corresponding to various unknown cardiac events are generated by the implanted device and are transmitted to an external device programmer. ECG signals, generated by a surface ECG detector, are simultaneously received by the external programmer. The external programmer identifies the cardiac electrical event corresponding to each signal vector based on the ECG signals and then generates classification zones for each event type using only the signal vectors corresponding to the event.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
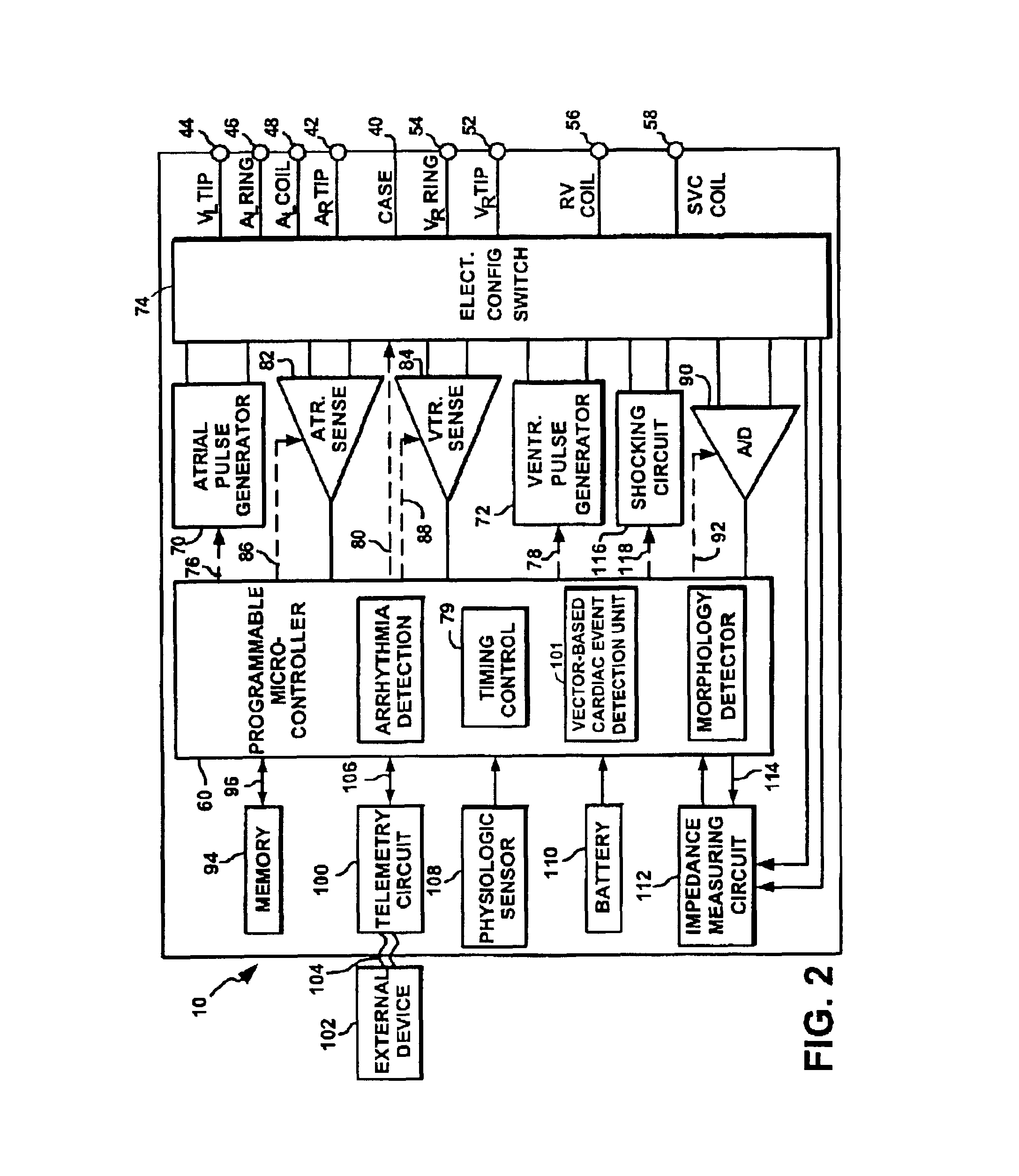
Device, method and computer-readable storage medium for enhanced sense event classification in implantable devices by means of morphology analysis
ActiveUS20090240157A1Accurate classificationEffective calculationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalCardiac pacemaker electrode
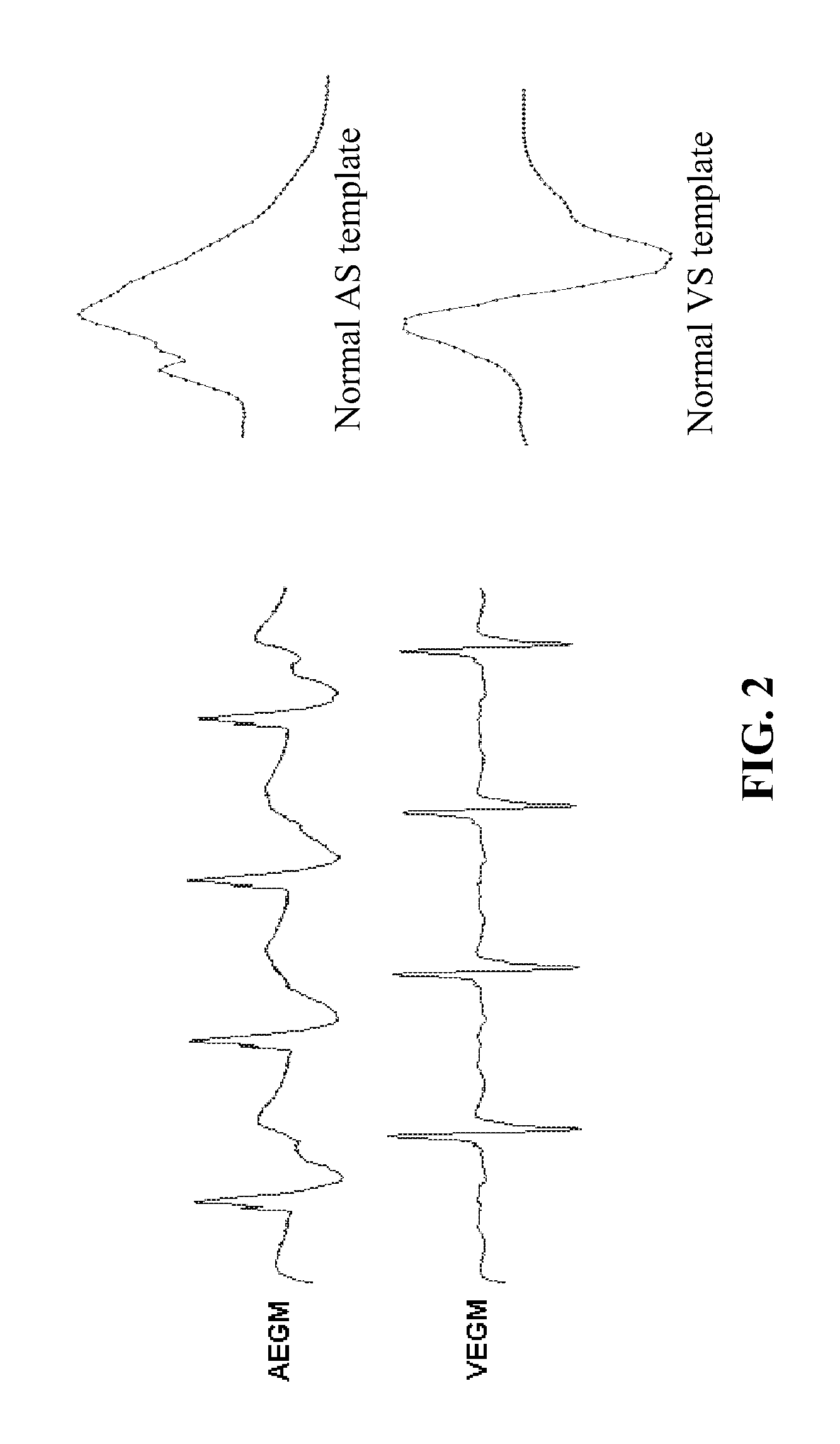
An implantable cardiac device, e.g., a pacemaker, defibrillator, cardioverter or biventricular pacing device, that can sense cardiac electrical signals and accurately classify the sensed events. The device provides a template signal and a test signal originated from an electrogram. The device further transforms at least the test signal into a representation of the test signal for example in numerical format where the sample values of the test signal take the form of integers. The device further determines a correlation between the template and test signals, and classifies the sense events based on the correlation. The electrogram may be an intracardiac electrogram (IEGM), atrial electrogram (AEGM), ventricular electrogram (VEGM), surface electrocardiogram (ECG) or subcutaneous electrogram.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method for generating three standard surface ECG leads derived from three electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the torso
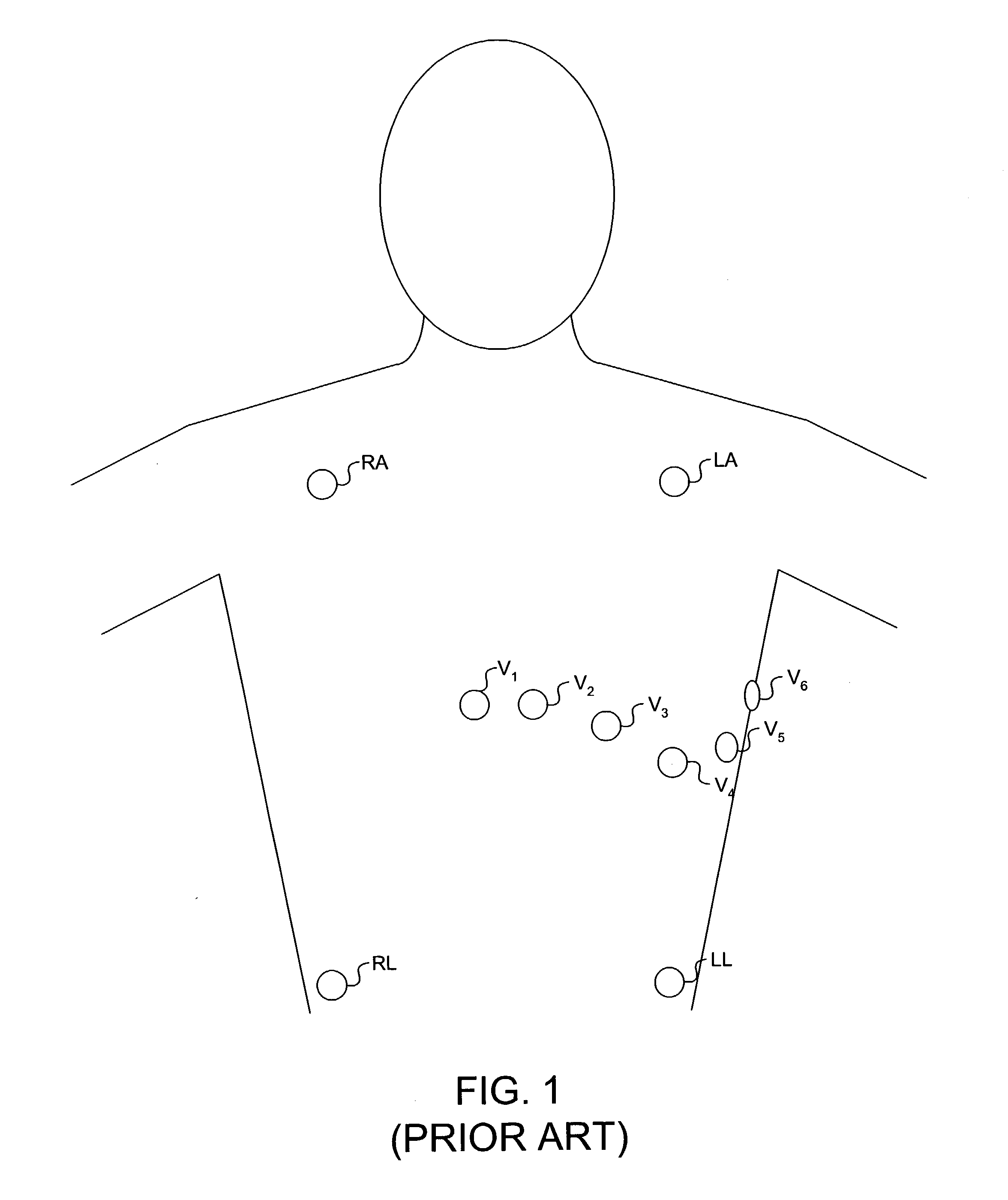
A method for a 3-lead electrocardiographic (ECG) recording comprising three signal electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the human torso and the calculation of the standard leads I, II and III. Such electrodes are placed in-line as in a chest belt instead of the traditional positioning of electrodes in the upper and low parts of the frontal plane of the torso.
Owner:MISCZYNSKI DALE J +3
System and method for determining optimal atrioventricular delay based on intrinsic conduction delays
Techniques are provided for estimating optimal atrioventricular delay values for use in pacing the ventricles. Both the intrinsic inter-atrial conduction delay and the intrinsic atrioventricular conduction delay are determined for the patient and then the preferred atrioventricular pacing delay is derived therefrom. By taking into account intrinsic inter-atrial delay along with intrinsic atrioventricular delay, it is believed that a more reliable estimate of the true optimal atrioventricular delay values for the patient can be achieved than with techniques that only take into account intrinsic atrioventricular delay values. In one example, the technique uses intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals and surface electrocardiogram (EKG) signals and hence can be performed by an external programmer without requiring Doppler echocardiography or other cardiac performance monitoring techniques. In another example, wherein the implanted device is equipped with a coronary sinus lead, the technique uses only IEGM signals and hence can be performed by the device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
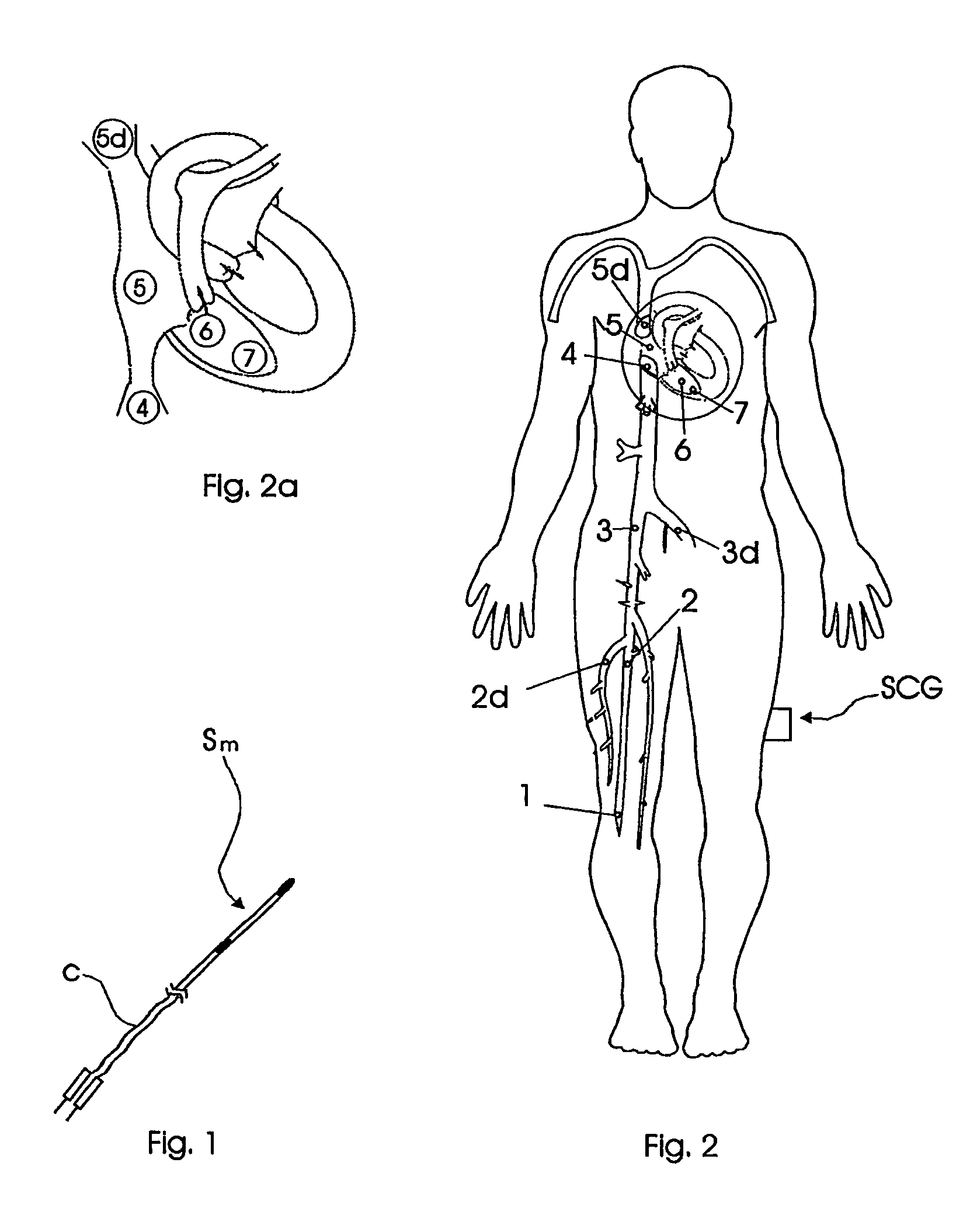
ActiveUS20120035459A1Improve accuracyIncrease computing speedElectrocardiographyCatheterAnatomical structuresContinuation
Reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. On the set of surface electrocardiograms for each discrete moment of the cardiocycle, values of the heart electric field potential at points of ECG-recording are determined, and a value of the electric field potential at each point of the chest surface is calculated by interpolation. Based on data of any visualization methodology, boundaries of chest and lungs surfaces and of the heart epicardial surface are determined. Further, a continuation of the electric field potential over the whole chest surface up to the heart epicardial surface with taking into account differences in electroconductivity of large anatomical structures of the chest is performed by computational way based on solution of the Cauchy problem for the Laplace equation in a piecewise-homogenous medium.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Reconstruction of a Surface Electrocardiogram From Far Field Signals Extracted of an Endocardial Electrogram
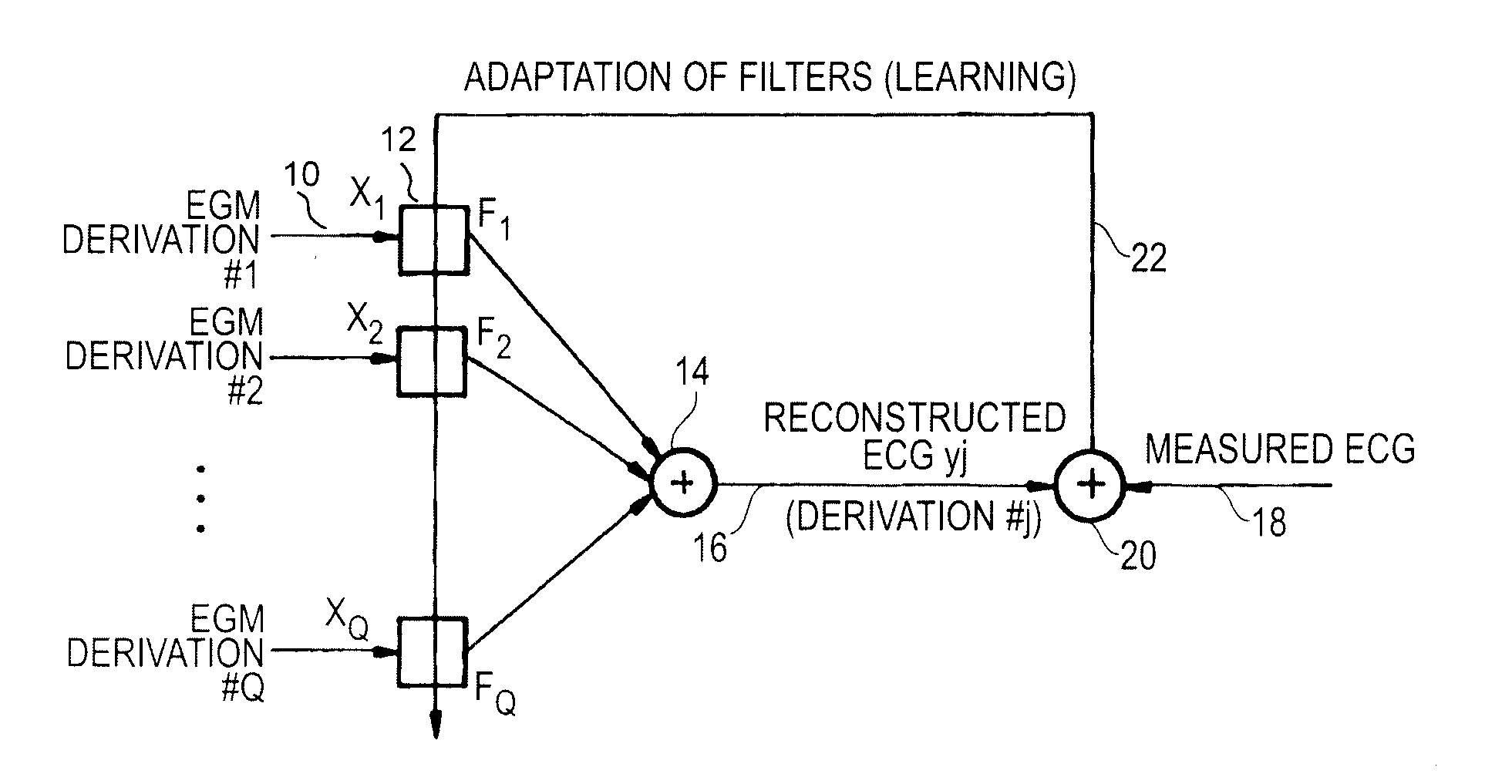
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from far field signals extracted from an endocardial electrogram in an active medical device is disclosed. The device collects a ventricular EGM signal (EGMV) and an atrial EGM signal (EGMA), and extracts a ventricular far field signal component (FFV) and an atrial far field signal component (FFA). The ventricular and atrial far field signal components are combined to deliver as an output a reconstructed surface electrogram ECG signal (ECGj*). The ventricular and atrial far field signals are respectively extracted from the collected ventricular and atrial EGM signals (FFV, FFA). The reconstruction of the ECG is operated by ventricular (18) and atrial (16) far field signal estimator filters. According to one embodiment, the far field signal estimator filters are linear or nonlinear filters, receiving as input the far field signal components. An adder (20) adds the filtered signals and delivers as output the reconstructed ECG signal (ECGj*).
Owner:SORIN CRM
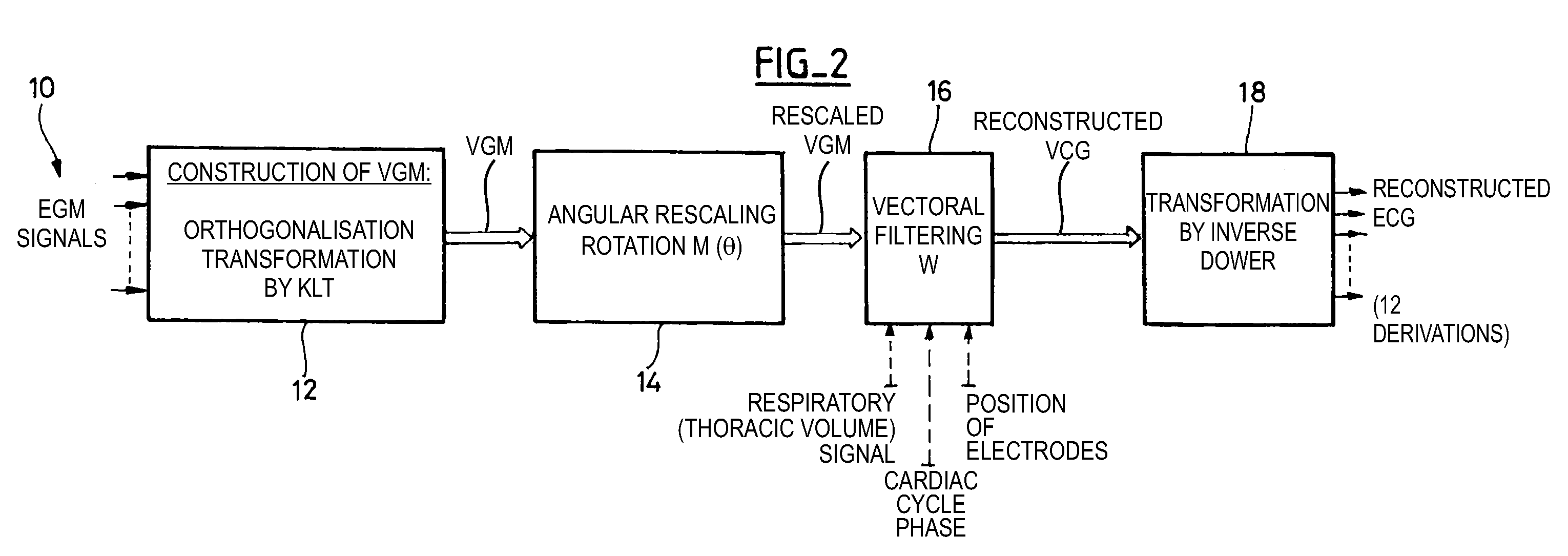
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram
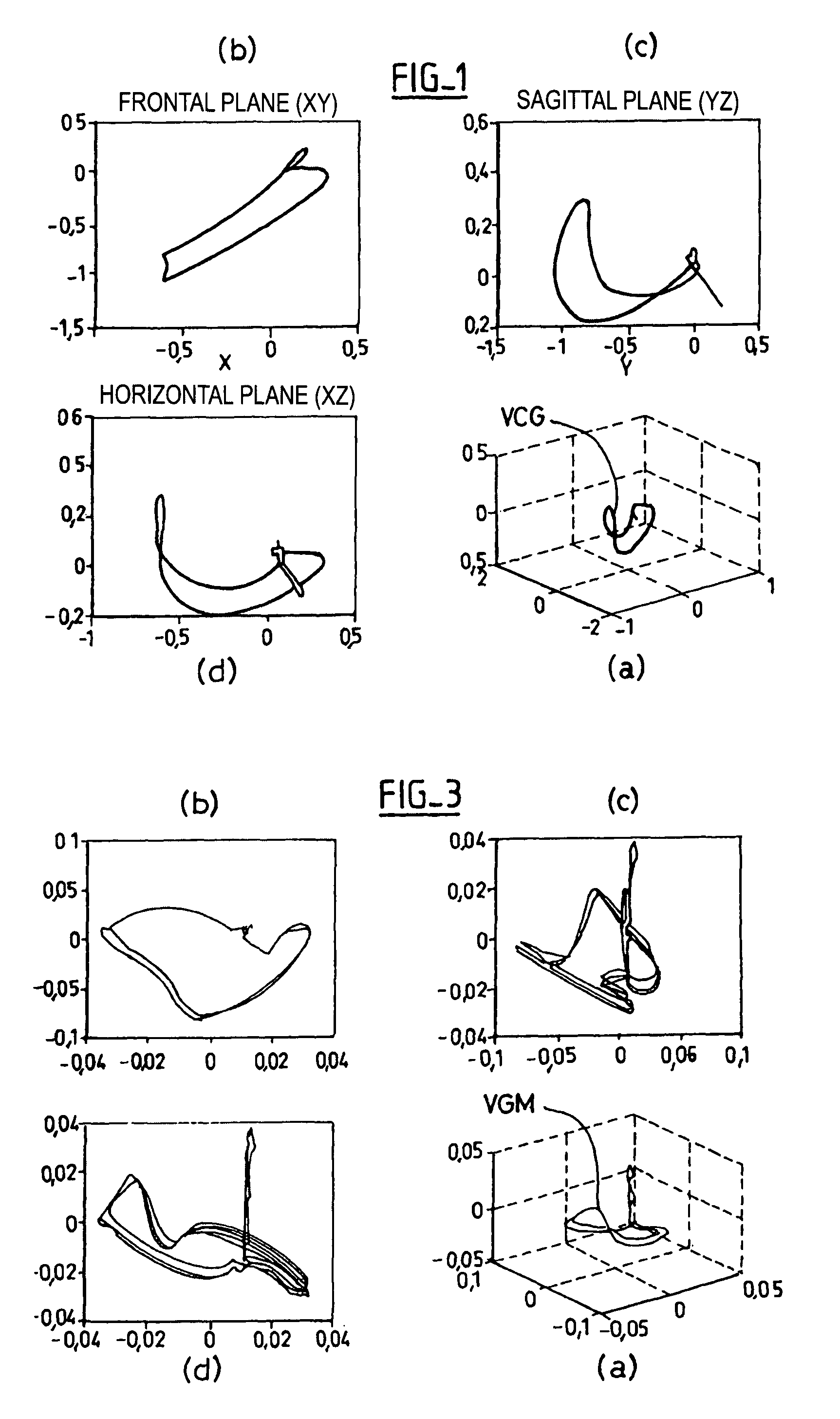
The reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram. This method includes: (a) acquisition (10) of a plurality of endocardial electrogram signals (EGM) through a plurality of endocardial derivations defined based upon endocardial electrodes; (b) calculation (12), by combining the endocardial electrogram (EGM) signals acquired at step (a), of the corresponding endocardial vectogram (VGM); (c) angular resealing (14) of the orthonormated mark of the endocardial vectogram (VGM) with that of the surface vectocardiogram (VCG); (d) estimation (16), based upon the endocardial vectogram (VGM) calculated at step (b), of a reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed); and (e) calculation (18) of the surface electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to said reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed).
Owner:SORIN CRM
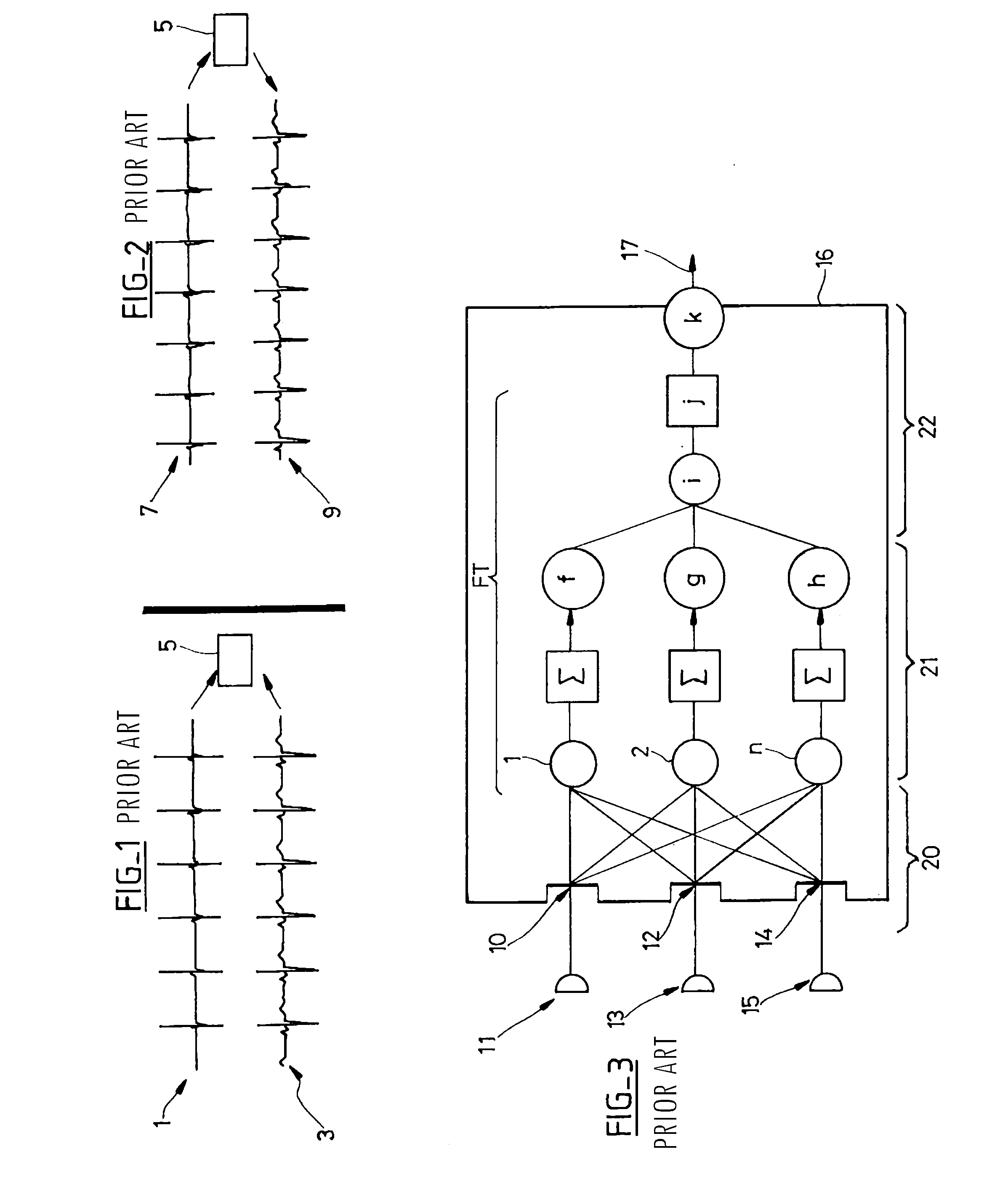
Non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface Electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram
InactiveUS20100249623A1Quality improvementElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalLinear filter
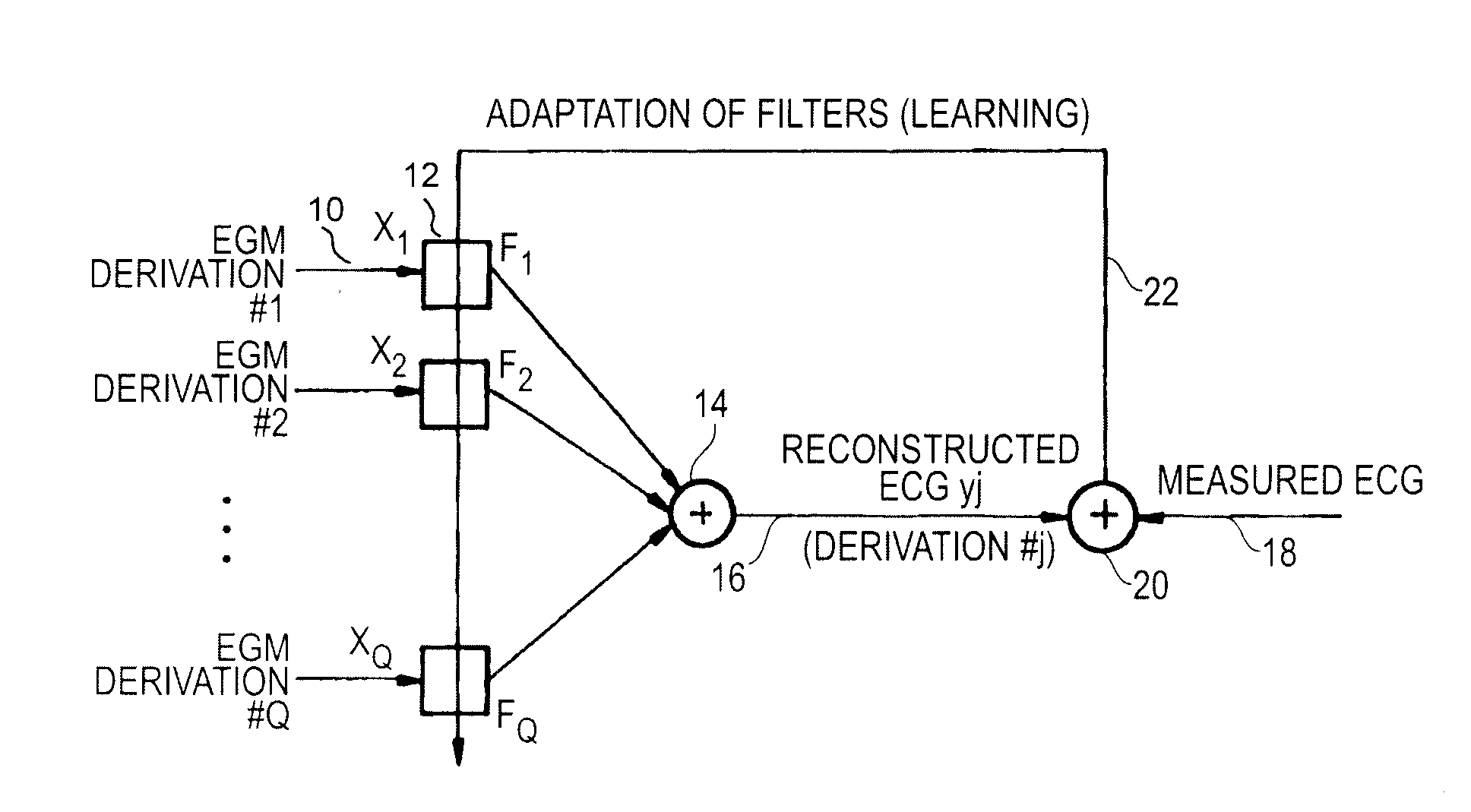
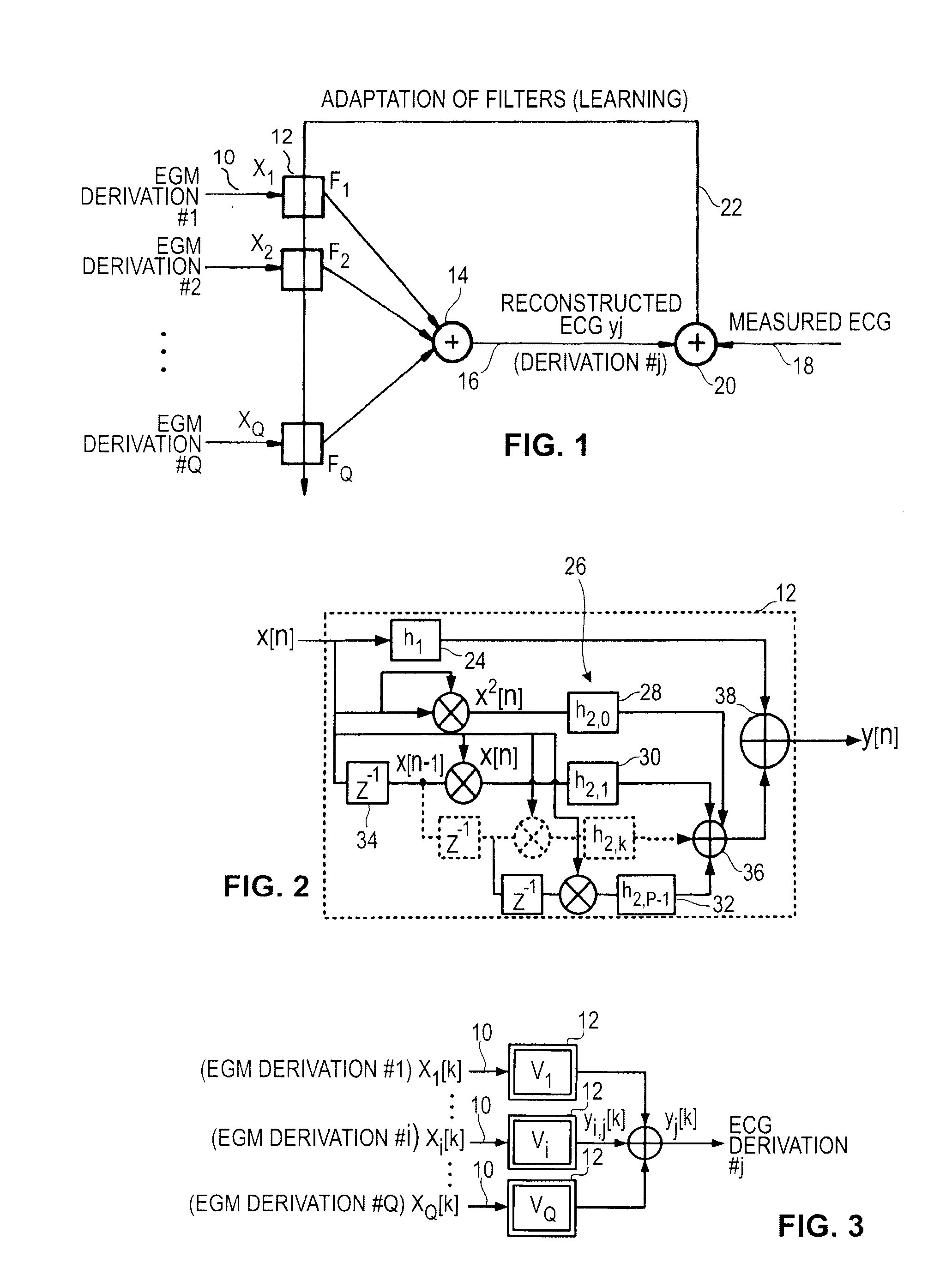
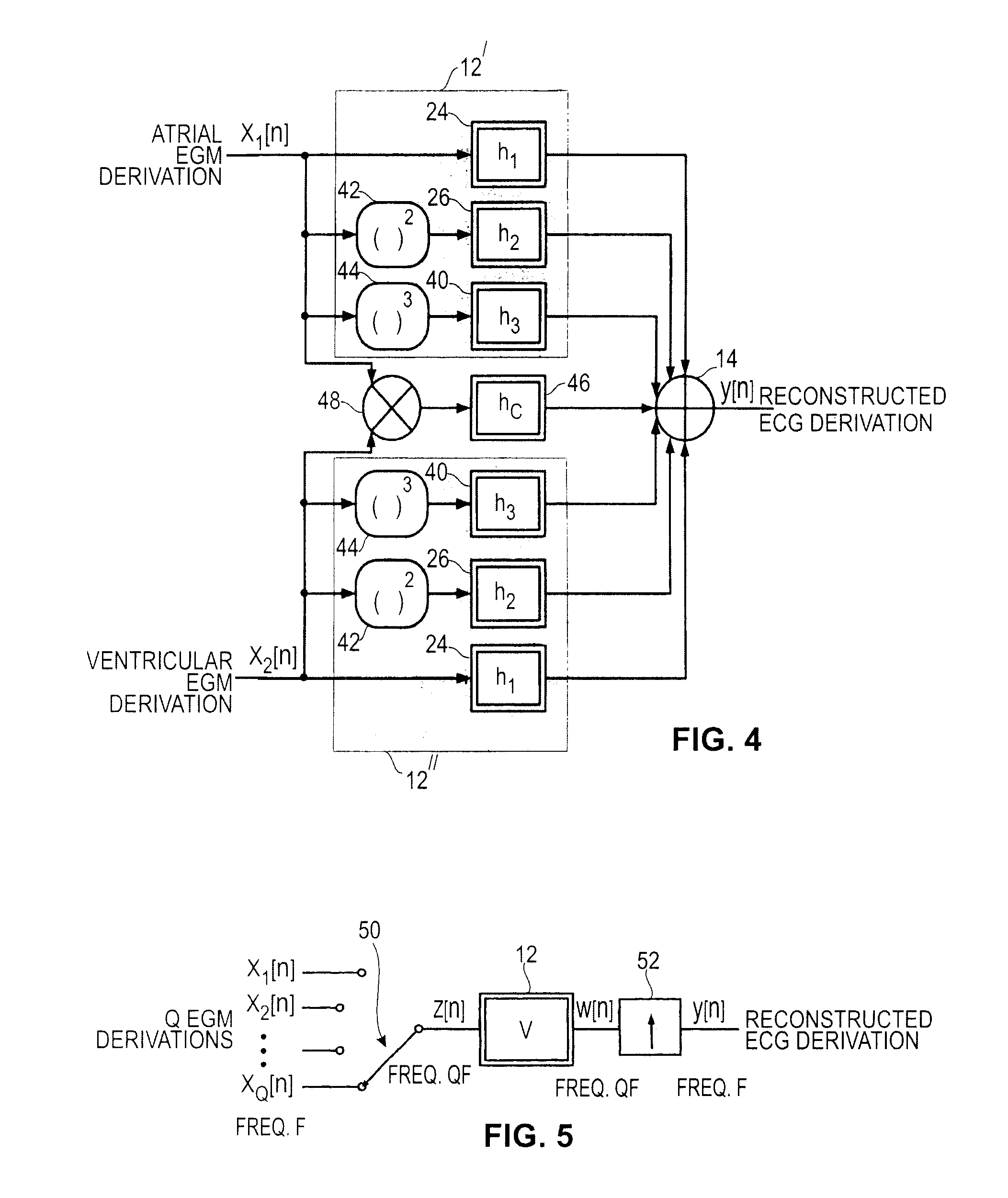
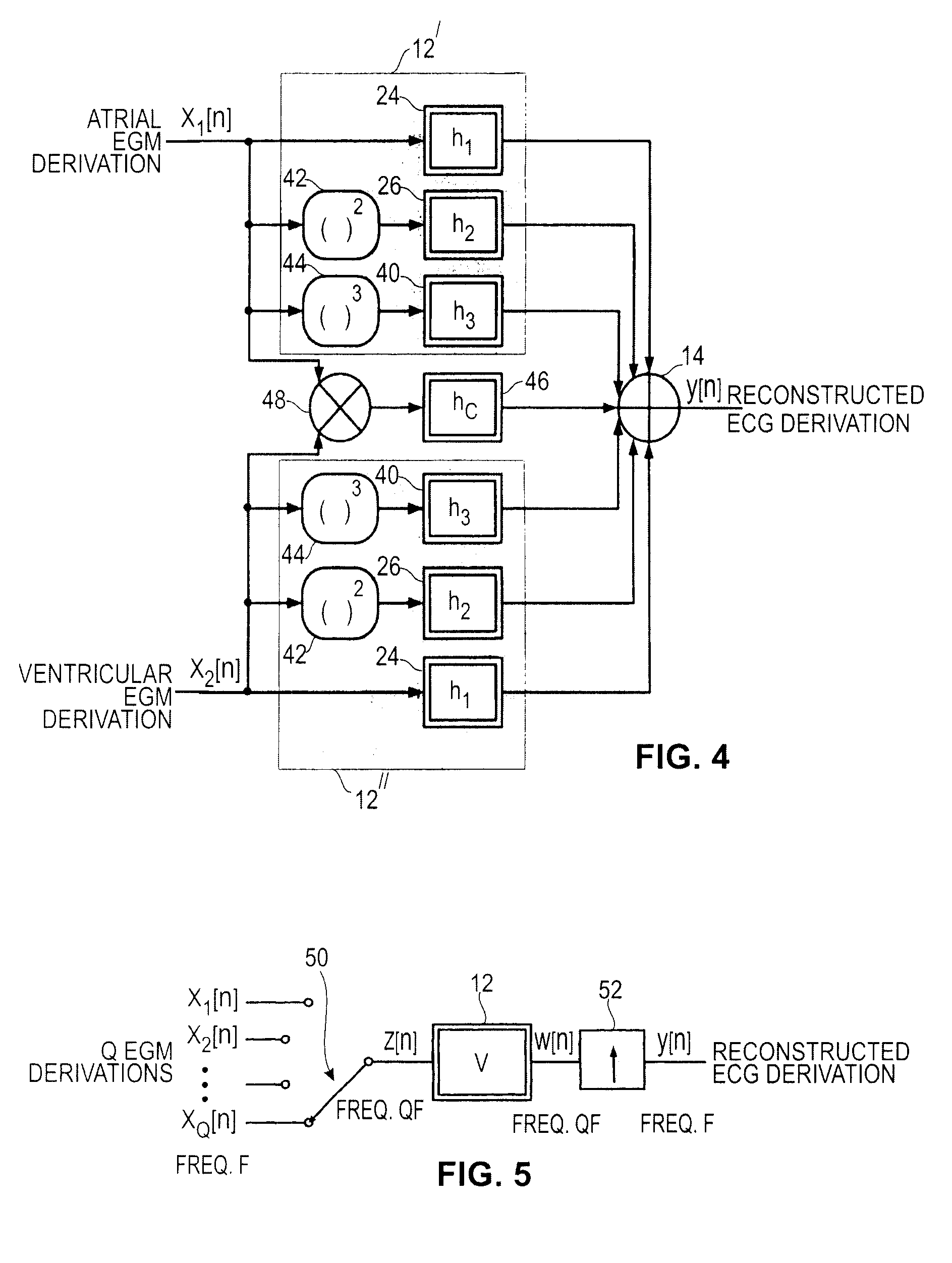
An active medical device using non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) from an endocardial electrogram (EGM) is disclosed. The device for the reconstruction of the surface ECG comprises: a plurality of inputs, receiving a corresponding plurality of EGM signals from endocardial or epicardial electrogram (x1[n], x2[n]) each collected on a respective EGM derivation of a plurality of EGM derivations, and at least one output delivering a reconstructed surface ECG electrocardiogram signal (y[n]), related to an ECG derivation, and a non-linear digital filter (12′, 12′, 14) with a transfer function that determines the reconstructed ECG signal based on said plurality of input EGM signals. The non-linear digital filter includes a Volterra filter type (12, 12′, 12″) whose transfer function includes a linear term (h1) and at least one quadratic (h2) and / or cubic (h3) term(s).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Automated detection method of QRS wave groups of electrocardiosignals
ActiveCN107788969AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalTime domain
The invention provides an automated detection method of QRS wave groups of electrocardiosignals according to a time-domain difference threshold theory. The method comprises the concrete steps: S1, pre-processing electrocardiosignals; S2, calculating first-order time-domain fixed-point difference threshold of electrocardiosignals; S3, calculating self-adaptive threshold value; S4, detecting R wavecrest value points by combining self-adaptive threshold value and differential signals; S5, carrying out an echo detecting test on detected R wave crest value points. The automated detection method ofQRS wave groups of electrocardiosignals can be used for instruments and equipment for automatic analysis and recognition of surface electrocardiograms. Therefore, sensitivity and accuracy of automatic detection of QRS wave groups of electrocardiosignals are improved. The algorithm operation efficiency is increased.
Owner:成都瑞迪康医疗科技有限公司
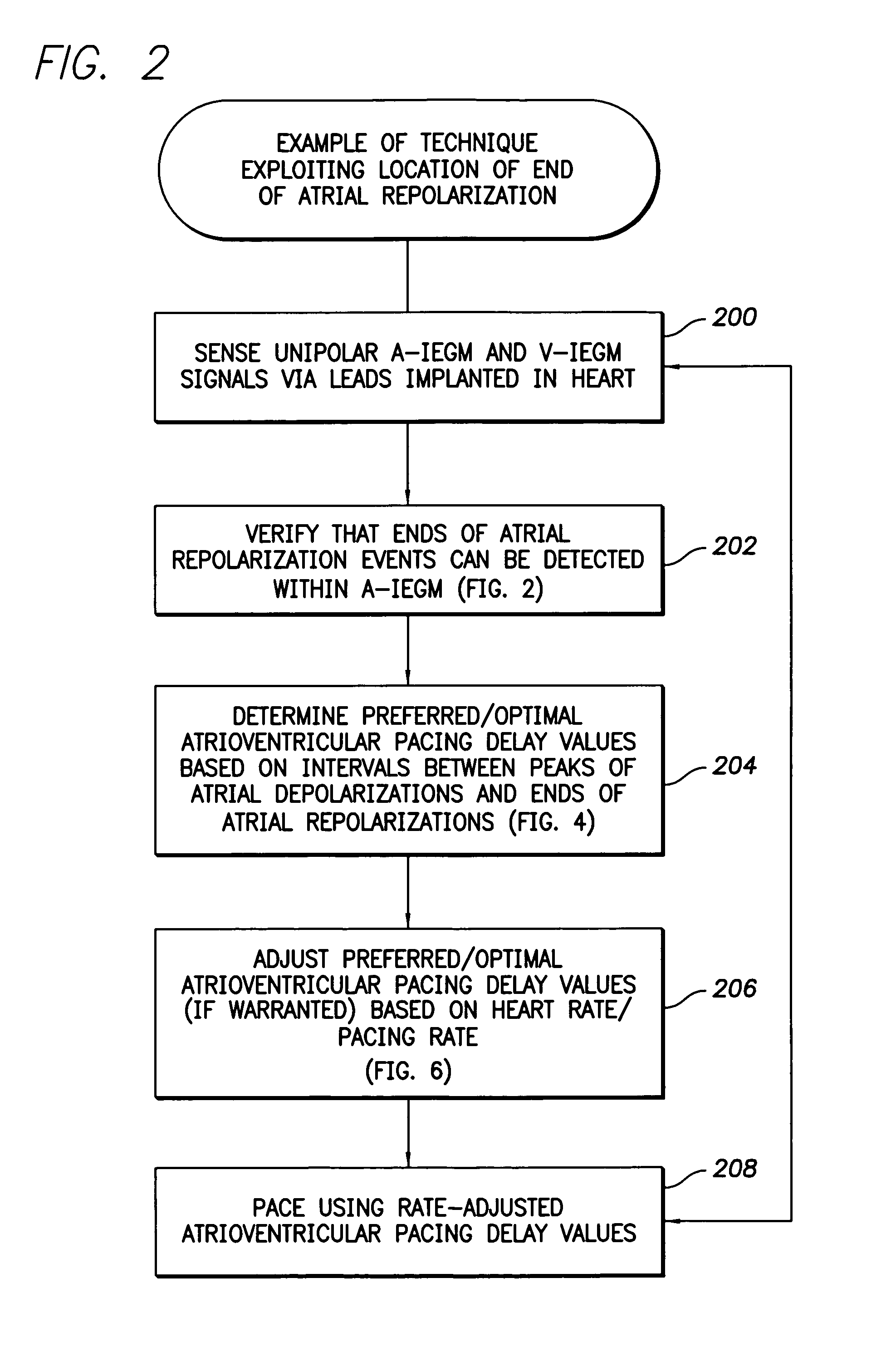
System and method for determining atrioventricular pacing delay based on atrial depolarization
ActiveUS7643878B1Maximize fillImprove ventricular fillingHeart stimulatorsDoppler echocardiographyIntracardiac Electrogram
Techniques are provided for estimating optimal atrioventricular pacing delay values for use in pacing the ventricles based on features of an intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signal. Briefly, atrioventricular pacing delay pacing values are set based upon the location of atrial repolarization events within the IEGM. In one example, the end of an atrial repolarization is identified, then the interval from the atrial depolarization to the end of the atrial repolarization is measured. The atrioventricular pacing delay is then set by subtracting an offset value from that interval so as to time delivery of V-pulses prior the end of atrial repolarization. In this manner, atrioventricular pacing delay values are set based only IEGM signals and hence can be set to optimal / preferred values by the device itself without requiring surface electrocardiogram (EKG) signals and Doppler echocardiography or other cardiac performance monitoring techniques.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram using non-linear filtering
The present invention relates to an active medical device that uses non-linear filtering for reconstructing a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram. At least one endocardial EGM electrogram signal is collected from of samples collected from at least one endocardial or epicardial derivation (71′, 72′, 73′), and at least one of a reconstructed surface electrocardiogram (ECG) signal through the processing of collected EGM samples by a transfer function (TF) of a neural network (60′). The neural network (60′) is a time-delay-type network that simultaneously processes said at least one endocardial EGM electrogram signal, formed by a first sequence of collected samples, and at least one delayed version of this EGM signal, formed by a second sequence of collected samples distinct from the first sequence collected samples. The neural network (60′) provides said reconstructed ECG signal from the EGM signal and its delayed version.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Device, method and computer-readable storage medium for enhanced sense event classification in implantable devices by means of morphology analysis
ActiveUS8090434B2Accurate classificationEffective calculationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalCardiac pacemaker electrode
An implantable cardiac device, e.g., a pacemaker, defibrillator, cardioverter or biventricular pacing device, that can sense cardiac electrical signals and accurately classify the sensed events. The device provides a template signal and a test signal originated from an electrogram. The device further transforms at least the test signal into a representation of the test signal for example in numerical format where the sample values of the test signal take the form of integers. The device further determines a correlation between the template and test signals, and classifies the sense events based on the correlation. The electrogram may be an intracardiac electrogram (IEGM), atrial electrogram (AEGM), ventricular electrogram (VEGM), surface electrocardiogram (ECG) or subcutaneous electrogram.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method and system for detecting premature ventricular contraction from a surface electrocardiogram
InactiveUS20070073176A1Reduce skin irritationElectrocardiographySensorsVentricular contractionSmall form factor
A system and method for automatically detecting abnormal heart contractions originating in the ventricles, in a way that is independent of signal morphology is provided. As an uninterrupted series of ventricular detections indicates a possible ventricular arrhythmia, all ventricular beats are detected including isolated premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) and the associated R-R intervals are corrected. Premature ventricular contractions (ectopic beats) in non-standard lead configuration in a noisy signal from an ambulatory subject from a low-cost sensor that may be a small form factor sensor with 1 inch lead separation and may be rotated through multiple placements to correct an R-R interval time series used to detect atrial fibrillation.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram
The reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram. This method includes: (a) acquisition (10) of a plurality of endocardial electrogram signals (EGM) through a plurality of endocardial derivations defined based upon endocardial electrodes; (b) calculation (12), by combining the endocardial electrogram (EGM) signals acquired at step (a), of the corresponding endocardial vectogram (VGM); (c) angular resealing (14) of the orthonormated mark of the endocardial vectogram (VGM) with that of the surface vectocardiogram (VCG); (d) estimation (16), based upon the endocardial vectogram (VGM) calculated at step (b), of a reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed), and (e) calculation (18) of the surface electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to said reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Method and system for detecting premature ventricular contraction from a surface electrocardiogram
InactiveUS7751876B2Reduce skin irritationElectrocardiographySensorsSmall form factorVentricular contraction
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
ActiveUS8529461B2Improve accuracyIncrease computing speedElectrocardiographyCatheterElectrophysiology studyAnatomical structures
Reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. On the set of surface electrocardiograms for each discrete moment of the cardiocycle, values of the heart electric field potential at points of ECG-recording are determined, and a value of the electric field potential at each point of the chest surface is calculated by interpolation. Based on data of any visualization methodology, boundaries of chest and lungs surfaces and of the heart epicardial surface are determined. Further, a continuation of the electric field potential over the whole chest surface up to the heart epicardial surface with taking into account differences in electroconductivity of large anatomical structures of the chest is performed by computational way based on solution of the Cauchy problem for the Laplace equation in a piecewise-homogenous medium.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
System and method for emulating a surface EKG for use with transtelephonic monitoring of an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7945314B1Easy to explainEasily emulatedElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsImplanted deviceEngineering
A surface electrocardiogram (EKG) is emulated using signals detected by internal leads of an implanted device. In one example, emulation is performed using a technique that concatenates portions of signals sensed using different electrodes, such as by combining far-field ventricular signals sensed in the atria with far-field atrial signals sensed in the ventricles. In another example, emulation is performed using a technique that selectively amplifies or attenuates portions of a single signal, such as by attenuating near-field portions of an atrial unipolar signal relative to far-field portions of the same signal. The surface EKG emulation may be performed by the implanted device itself or by an external programmer based on cardiac signals transmitted thereto. A transtelephonic monitoring network is also described, wherein the emulated surface EKG (or raw data used to emulate the EKG) is relayed from an implanted device to a remote monitor, typically installed in a physician's office.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System for Cardiac Pathology Detection and Characterization
InactiveUS20110054335A1Improve identificationEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyData processing applicationsDrugCardiac pathology
A system improves characterization and diagnosis of cardiac electrophysiological activities by analyzing and characterizing cardiac function signals (including surface ECG signals and intra-cardiac electrograms) based on cardiac electrophysiological energy mode and pattern identification and mapping. The system accurately determines a time stamp, location and severity of cardiac pathology and clinical events by calculating a cardiac signal energy mode and energy variation and distribution. The system identifies cardiac disorders, differentiates cardiac arrhythmias, characterizes pathological severity, predicts life-threatening events, and supports evaluation of administration of drugs.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram using non-linear filtering
Owner:SORIN CRM
Non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram
An active medical device using non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) from an endocardial electrogram (EGM) is disclosed. The device for the reconstruction of the surface ECG comprises: a plurality of inputs, receiving a corresponding plurality of EGM signals from endocardial or epicardial electrogram (x1[n], x2[n]), each collected on a respective EGM derivation of a plurality of EGM derivations, and at least one output delivering a reconstructed surface ECG electrocardiogram signal (y[n]), related to an ECG derivation, and a non-linear digital filter (12′, 12′, 14) with a transfer function that determines the reconstructed ECG signal based on said plurality of input EGM signals. The non-linear digital filter includes a Volterra filter type (12, 12′, 12″) whose transfer function includes a linear term (h1) and at least one quadratic (h2) and / or cubic (h3) term(s).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram
The reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram. This method includes: (a) acquisition (10) of a plurality of endocardial electrogram signals (EGM) through a plurality of endocardial leads defined based upon endocardial electrodes; (b) calculation (12), by combining the endocardial electrogram (EGM) signals acquired at step (a), of the corresponding endocardial vectogram (VGM); (c) angular resealing (14) of the orthonormalized mark of the endocardial vectogram (VGM) with that of the surface vectocardiogram (VCG); (d) estimation (16), based upon the endocardial vectogram (VGM) calculated at step (b), of a reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed), and (e) calculation (18) of the surface electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to said reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Electrocardiogram reconstruction from implanted device electrograms
A method of reconstruction of the standard 12-lead surface EKG given values of the electrical potential from an implanted medical device is described. This implanted device can be oriented in an arbitrary fashion and reconstruction technique is obtained through physical measurement of the orientation of the implanted device or correlation with a standard 12-lead EKG obtained from the patient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Noninvasive atrial activity estimation system and method
ActiveUS20150133808A1Wide applicationElectrocardiographySensorsNon invasiveSurface electrocardiogram
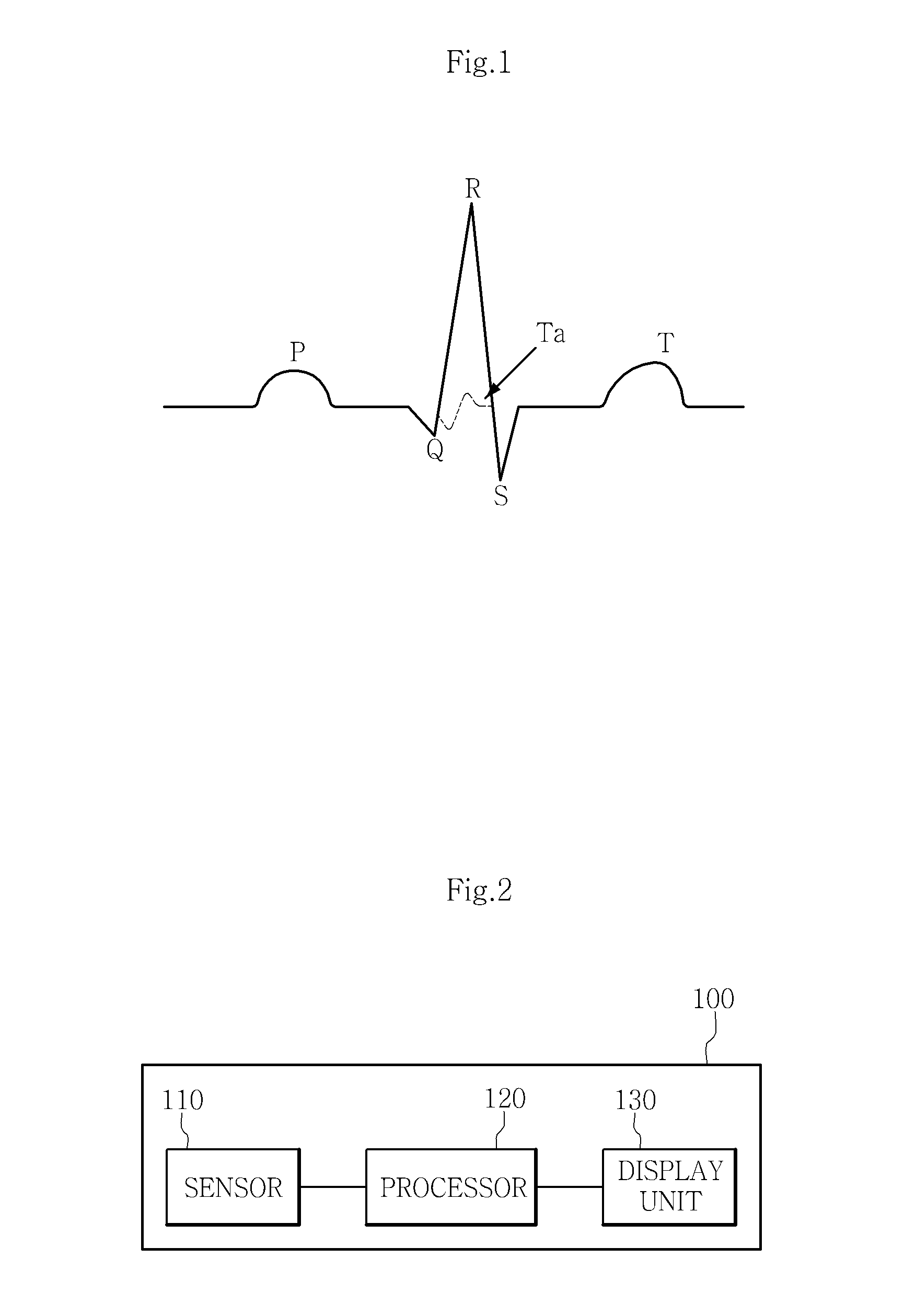
Provided is a non-invasive system for estimating an atrial signal, including a plurality of sensors to sense a surface electrocardiogram signal, a reference atrial signal generation unit to generate an estimated ventricular signal with respect to a R wave in an electrocardiogram signal from one sensor among the plurality of sensors, and to generate a reference atrial signal by subtracting the estimated ventricular signal from the electrocardiogram signal from the one sensor, and an atrial signal estimation unit to generate an estimated atrial signal by applying a constrained independent component analysis algorithm based on the reference atrial signal to the received surface electrocardiogram signal, and to estimate one of the estimated atrial signals as an actual atrial signal, and a method using the same.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from far field signals extracted of an endocardial electrogram
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from far field signals extracted from an endocardial electrogram in an active medical device is disclosed. The device collects a ventricular EGM signal (EGMV) and an atrial EGM signal (EGMA), and extracts a ventricular far field signal component (FFV) and an atrial far field signal component (FFA). The ventricular and atrial far field signal components are combined to deliver as an output a reconstructed surface electrogram ECG signal (ECGj*). The ventricular and atrial far field signals are respectively extracted from the collected ventricular and atrial EGM signals (FFV, FFA). The reconstruction of the ECG is operated by ventricular (18) and atrial (16) far field signal estimator filters. According to one embodiment, the far field signal estimator filters are linear or nonlinear filters, receiving as input the far field signal components. An adder (20) adds the filtered signals and delivers as output the reconstructed ECG signal (ECGj*).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com