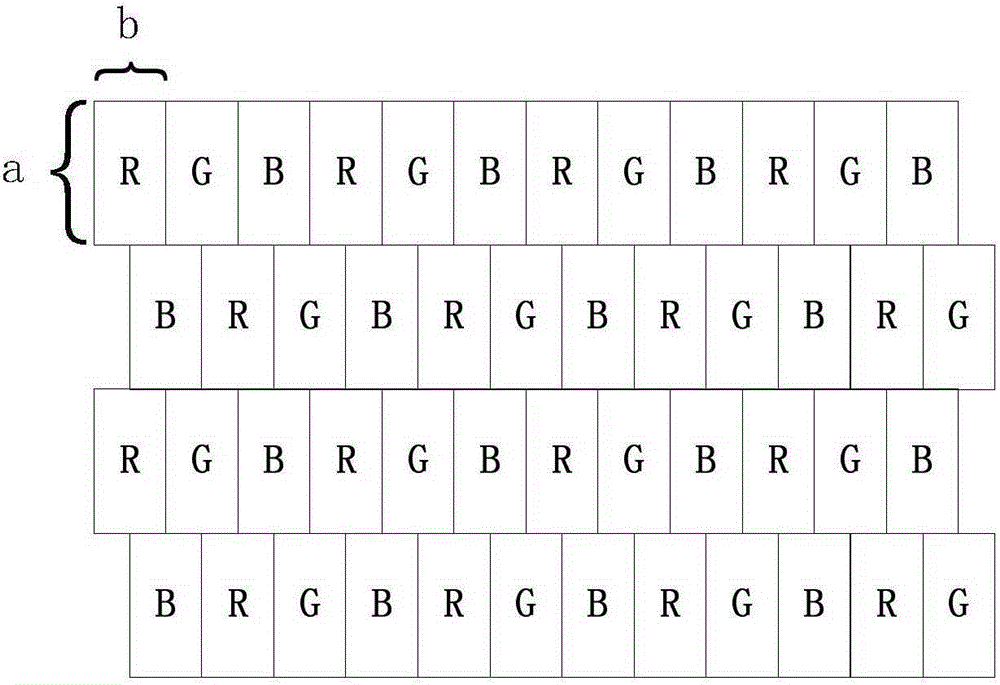
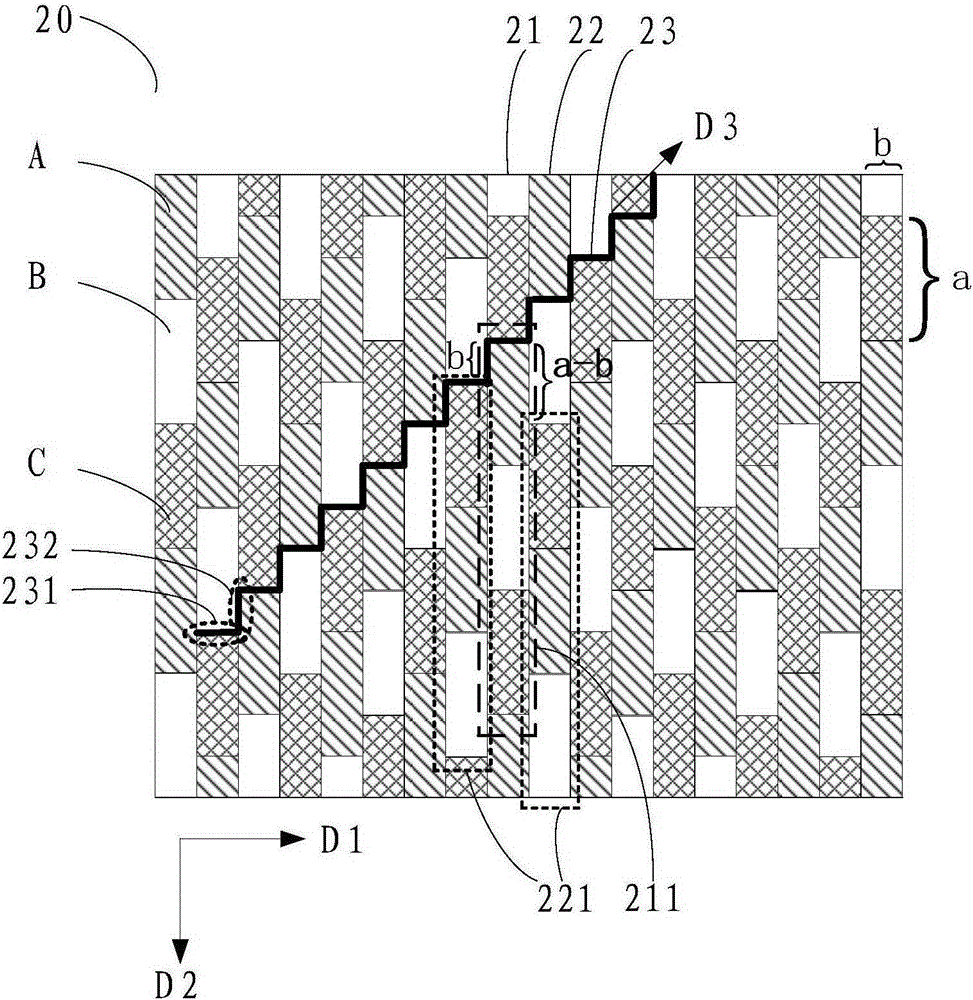
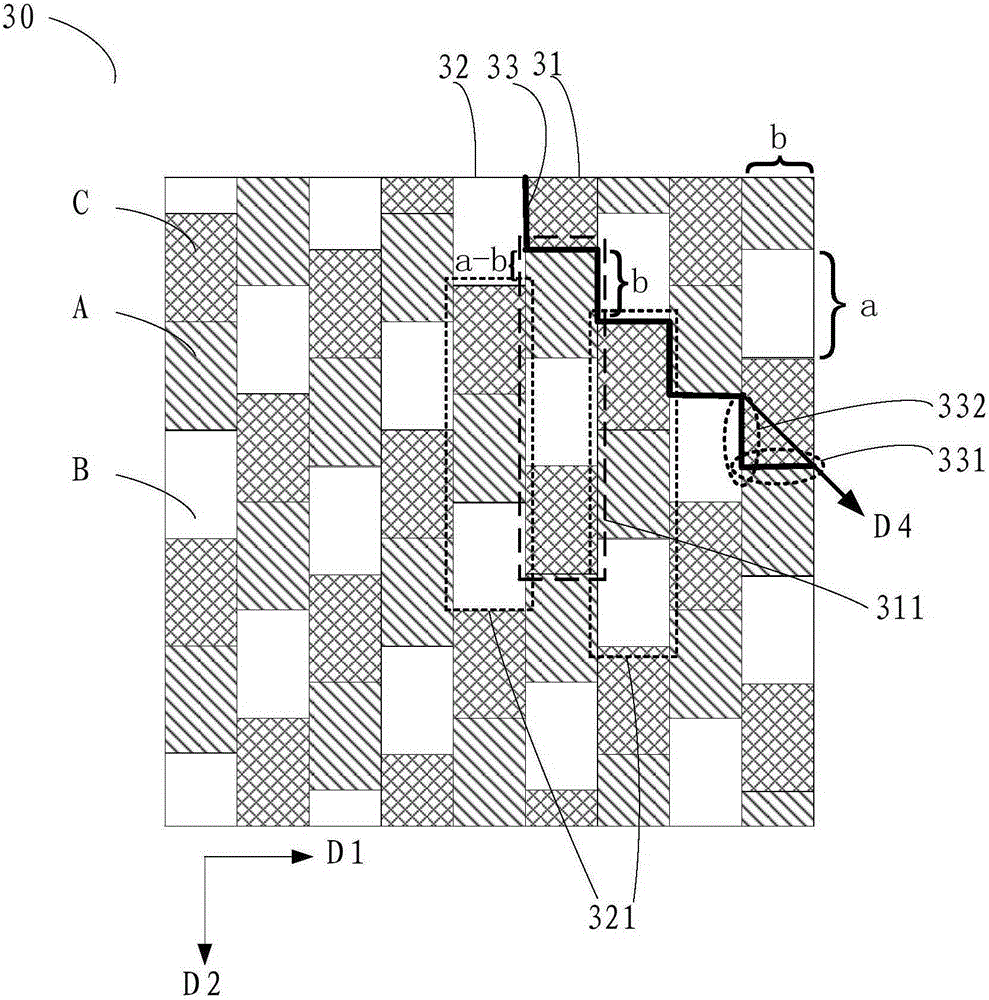
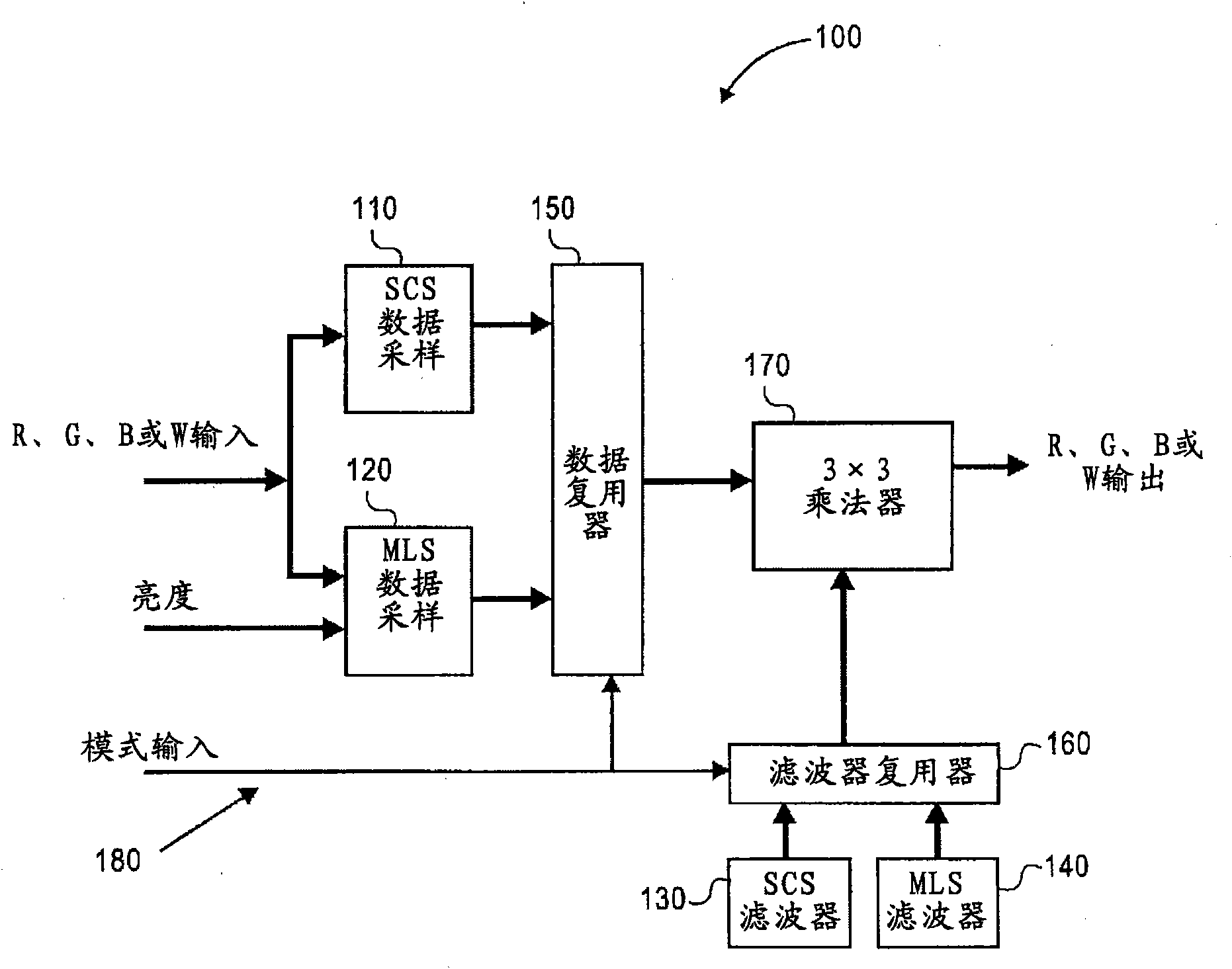
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Subpixel rendering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
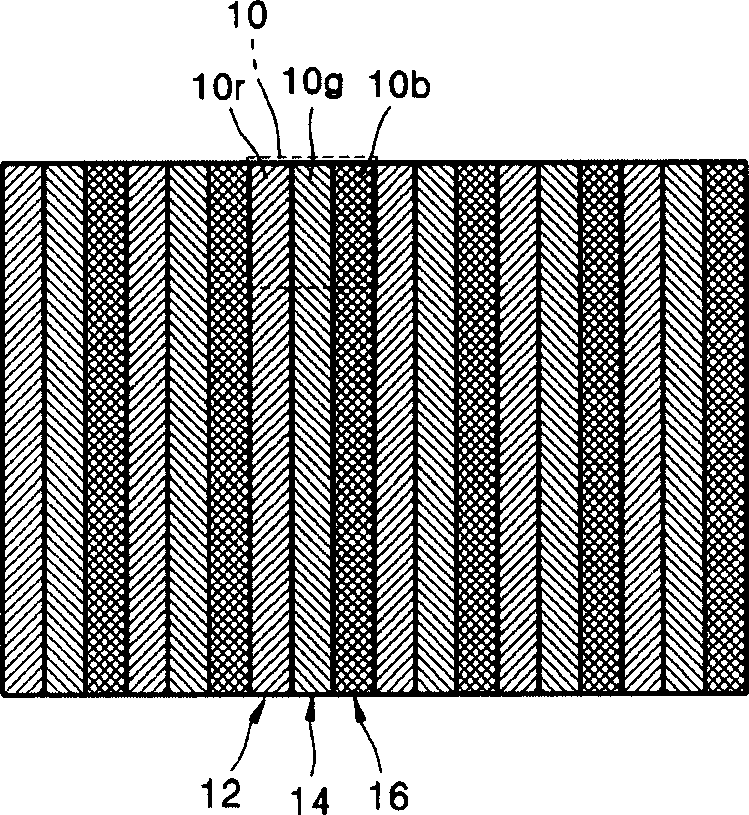
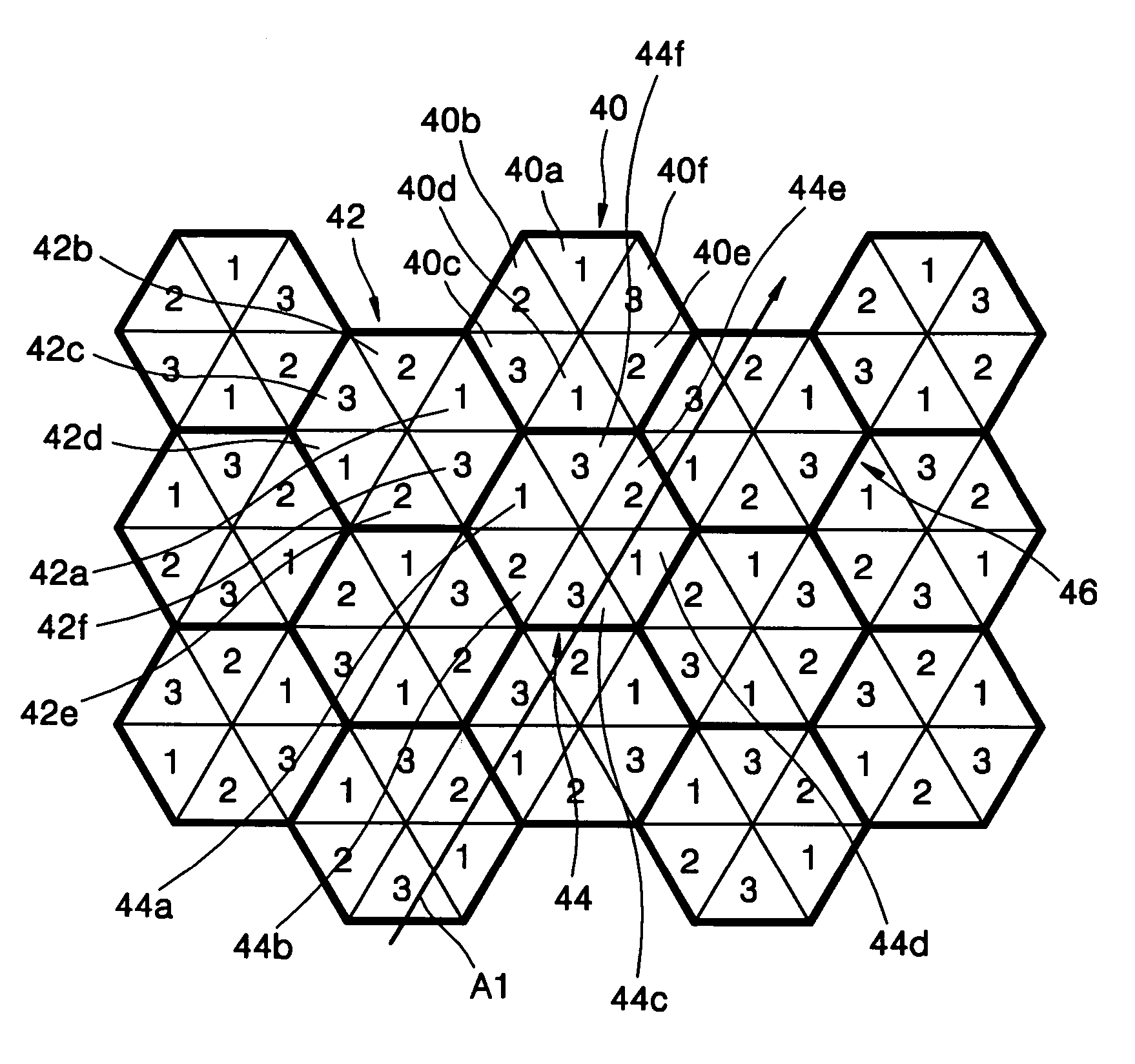
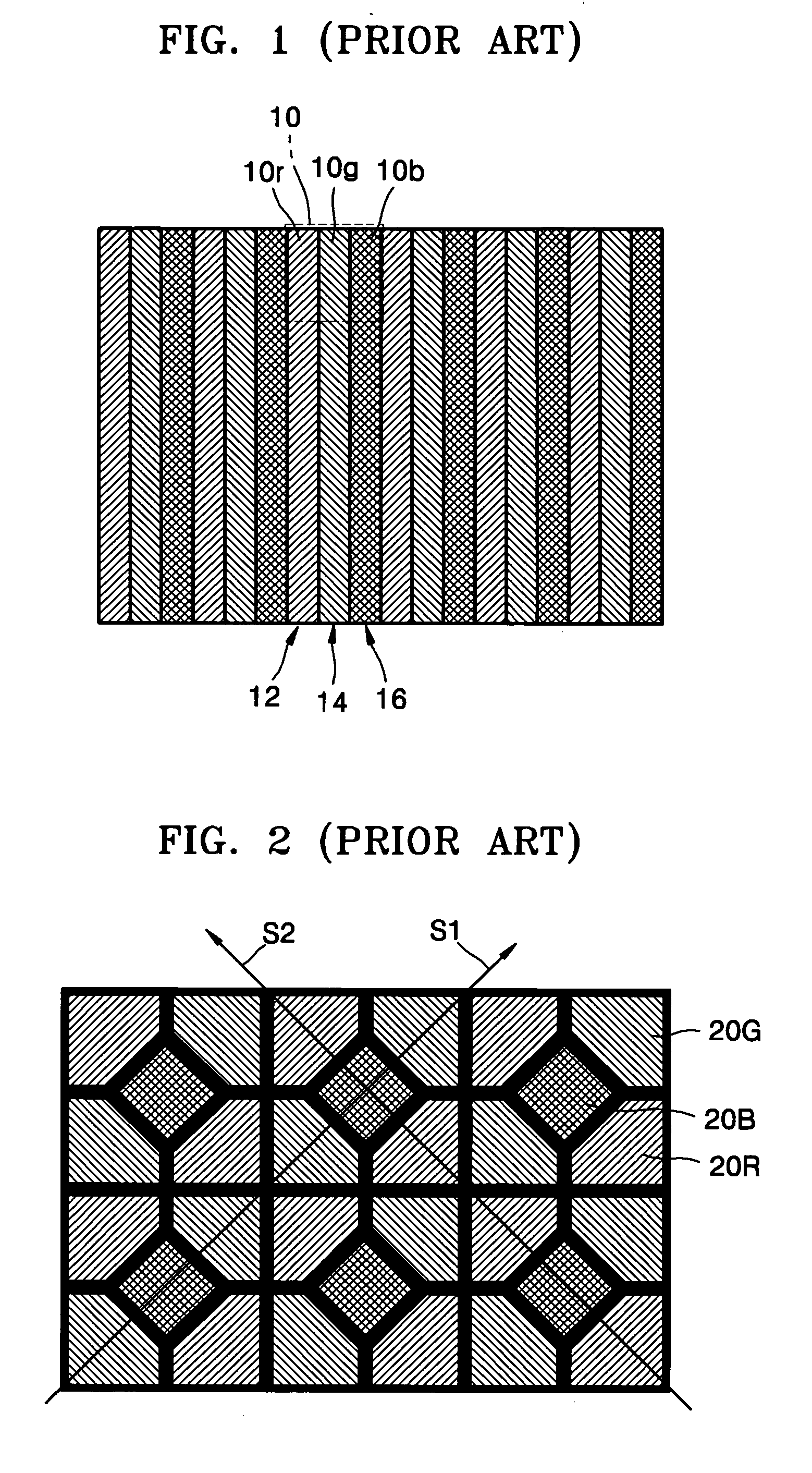
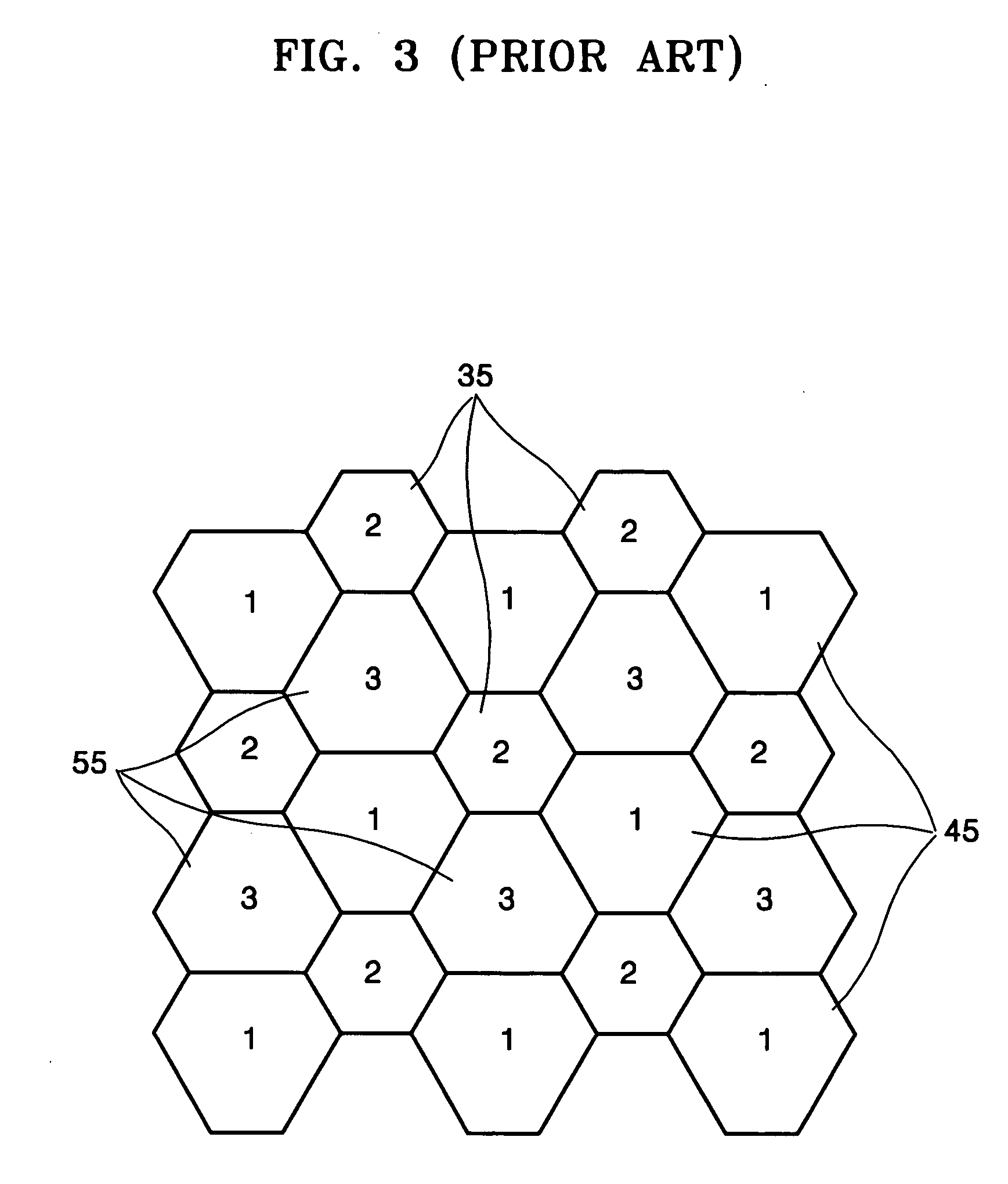
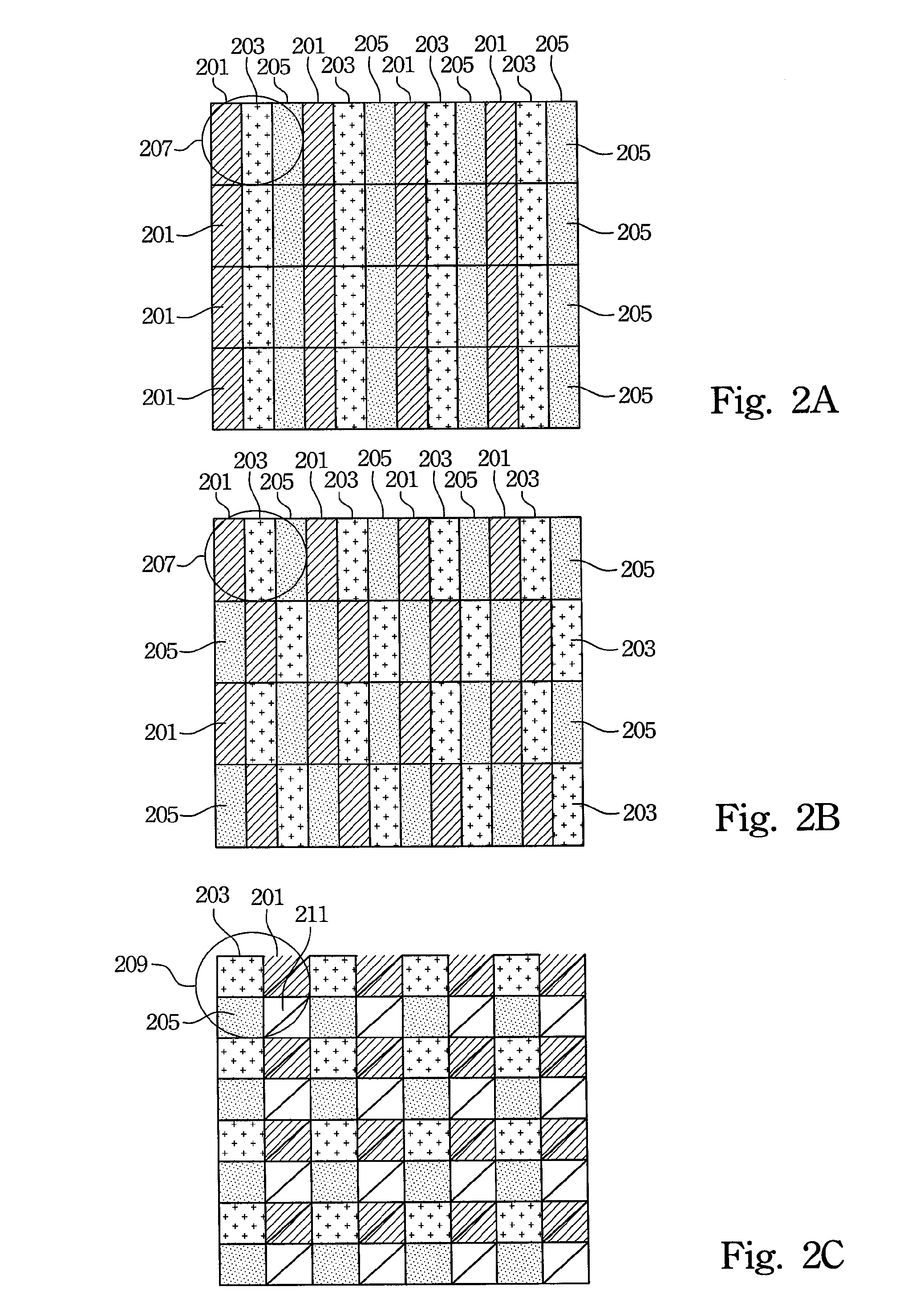
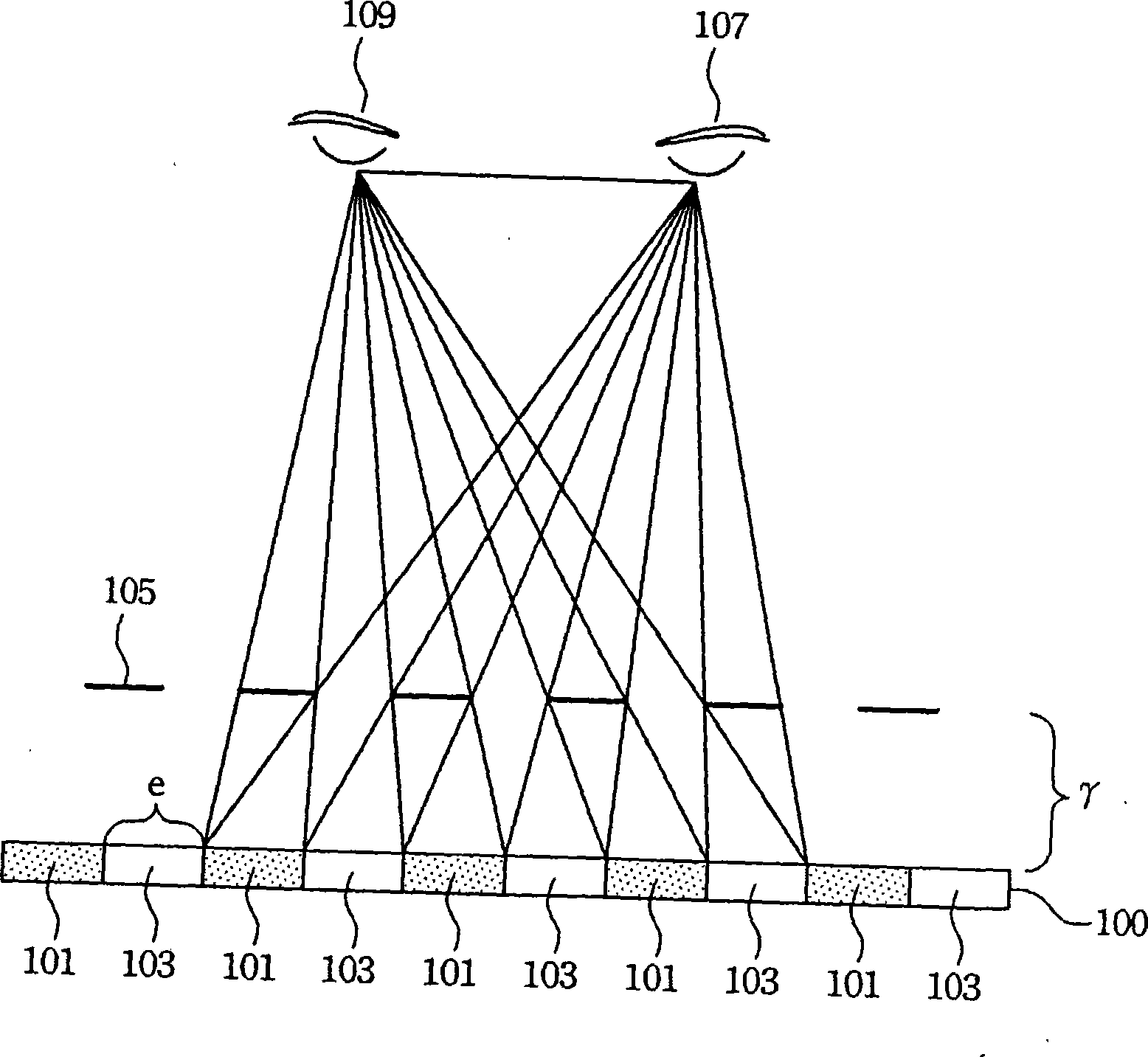
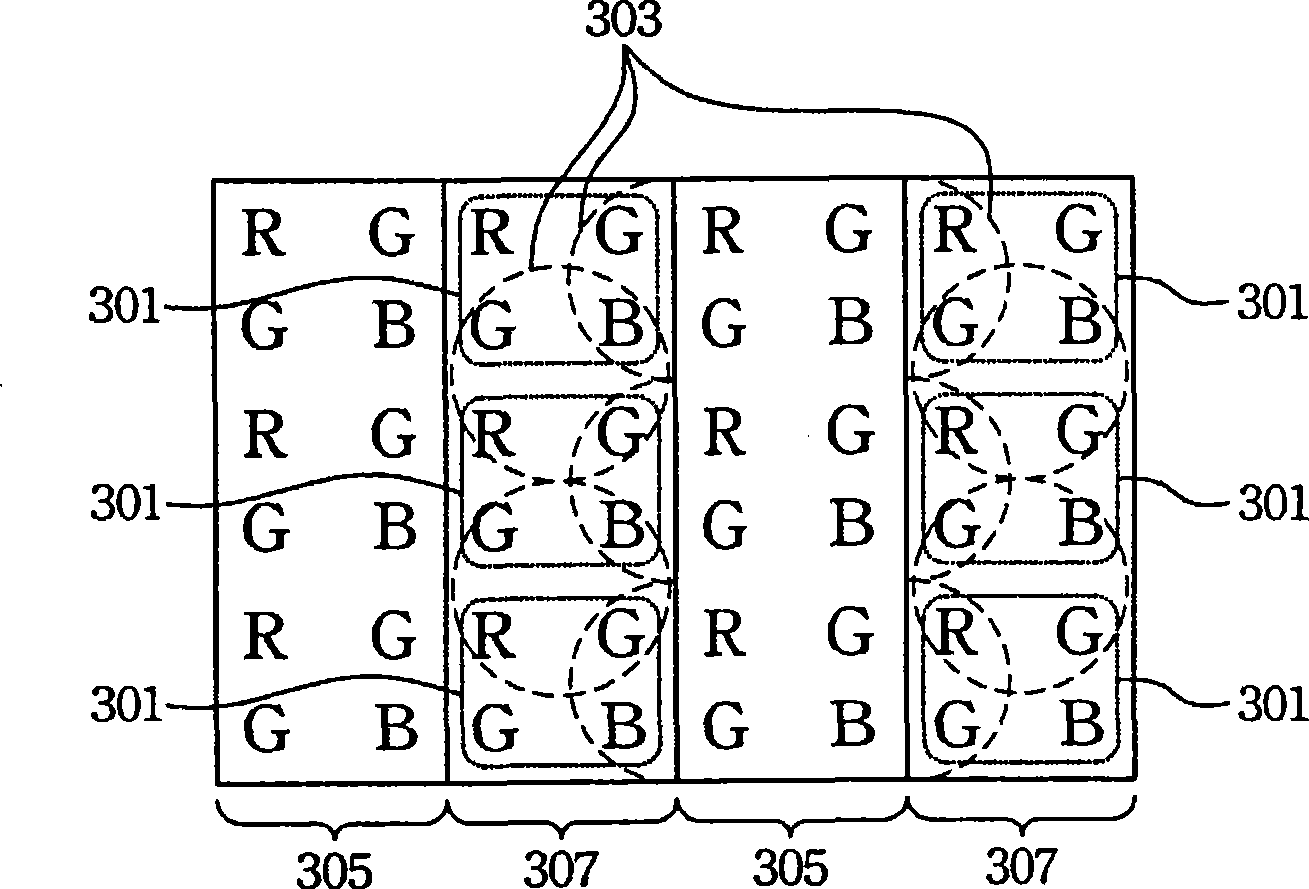
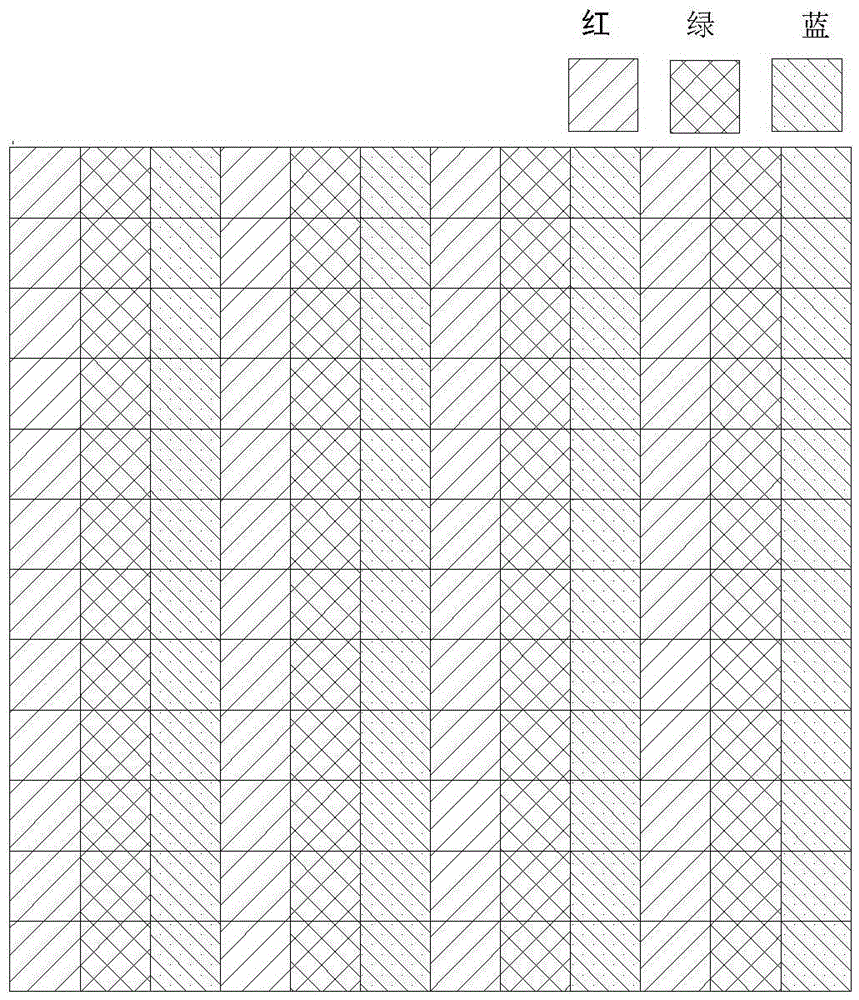
Subpixel rendering is a way to increase the apparent resolution of a computer's liquid crystal display (LCD) or organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display by rendering pixels to take into account the screen type's physical properties. It takes advantage of the fact that each pixel on a color LCD is actually composed of individual red, green, and blue or other color subpixels to anti-alias text with greater detail or to increase the resolution of all image types on layouts which are specifically designed to be compatible with subpixel rendering.
Display Device
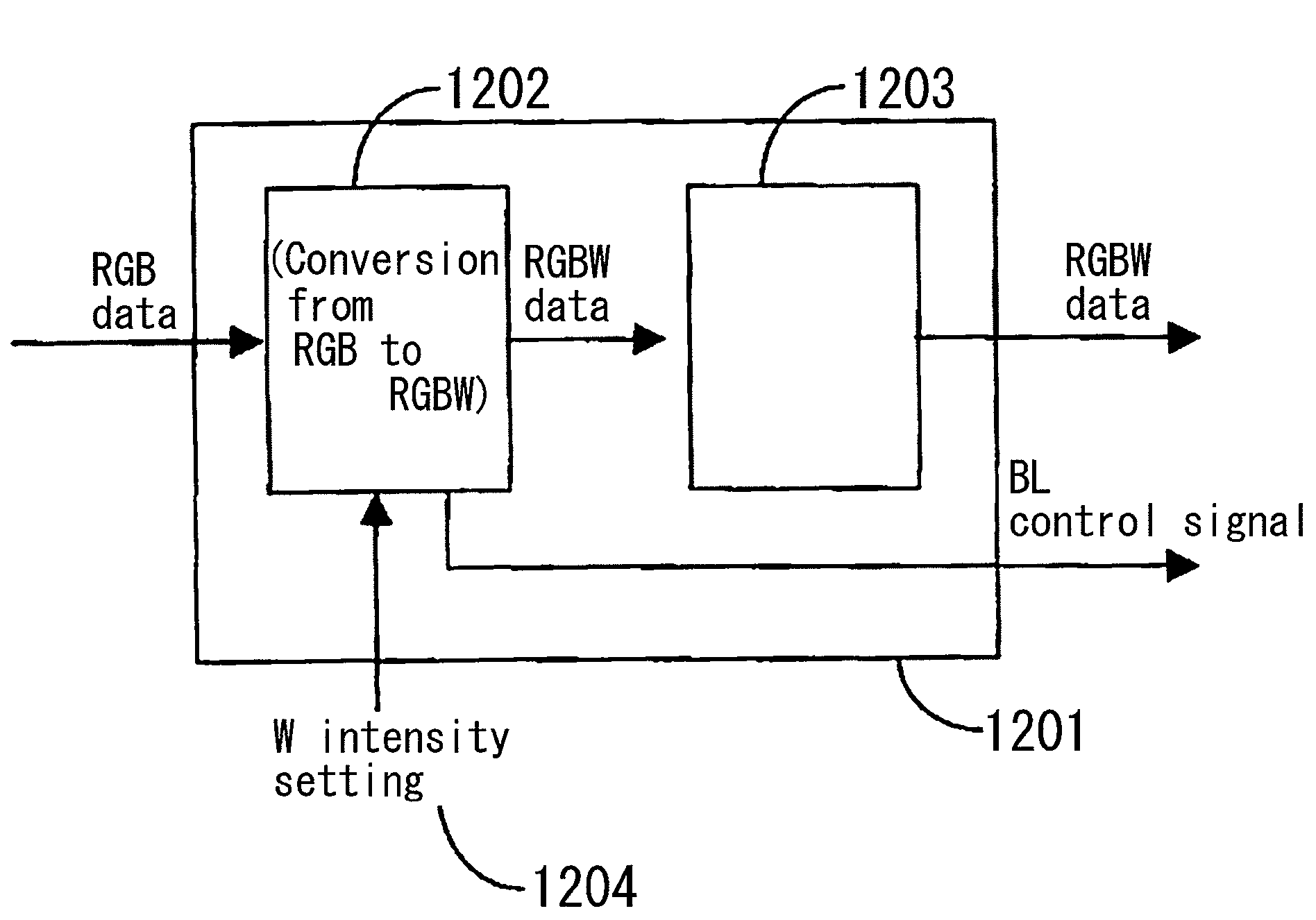
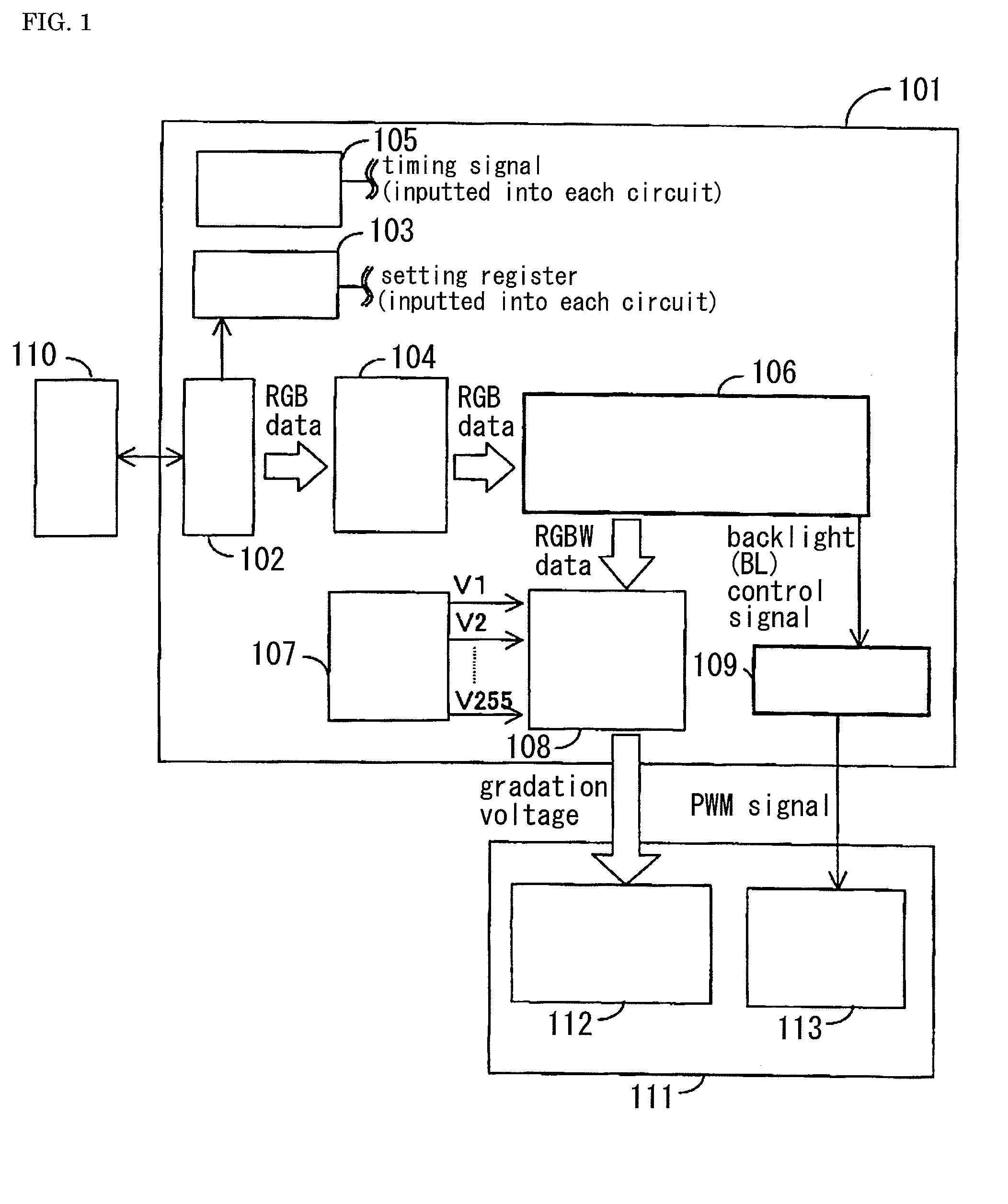
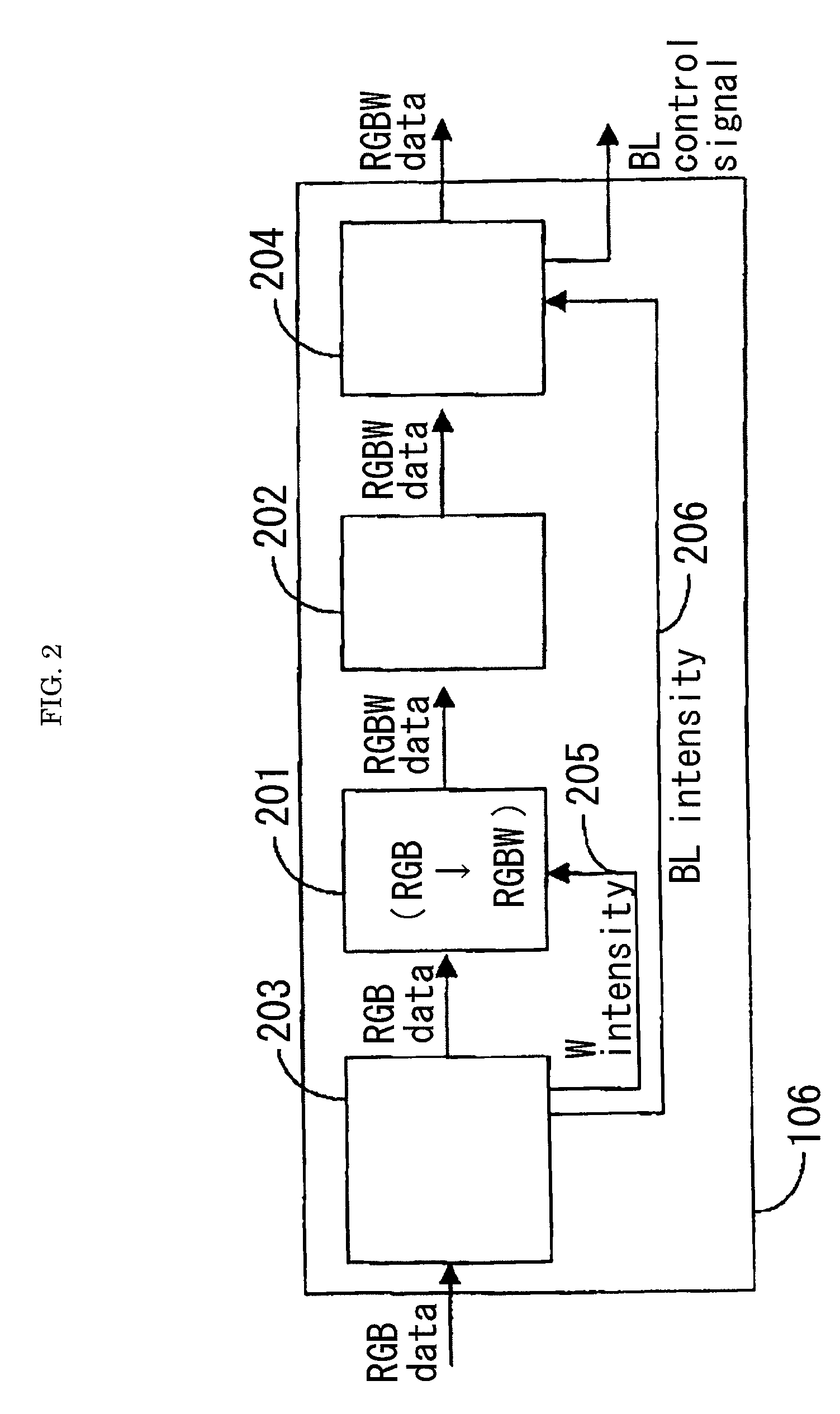
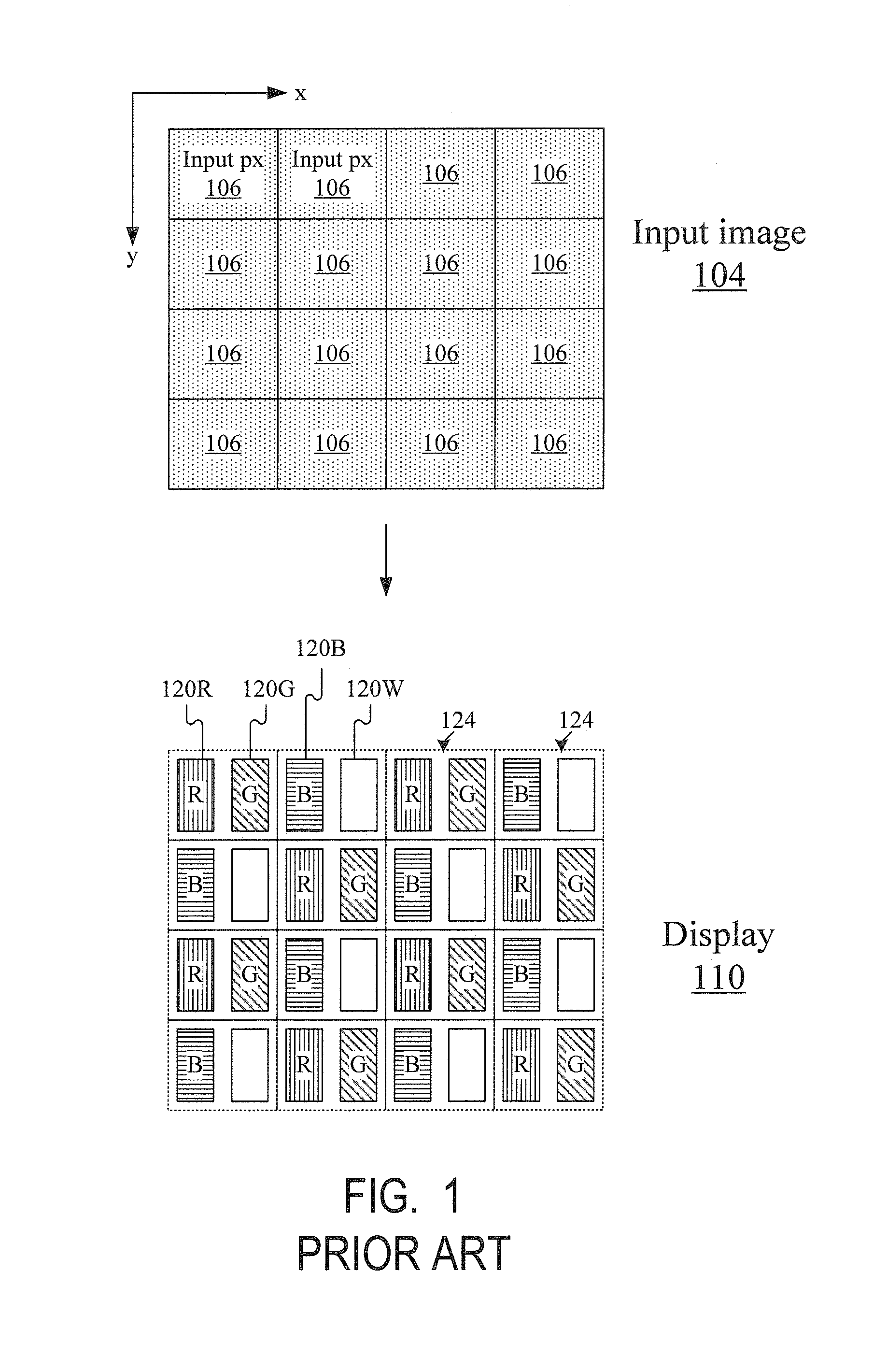
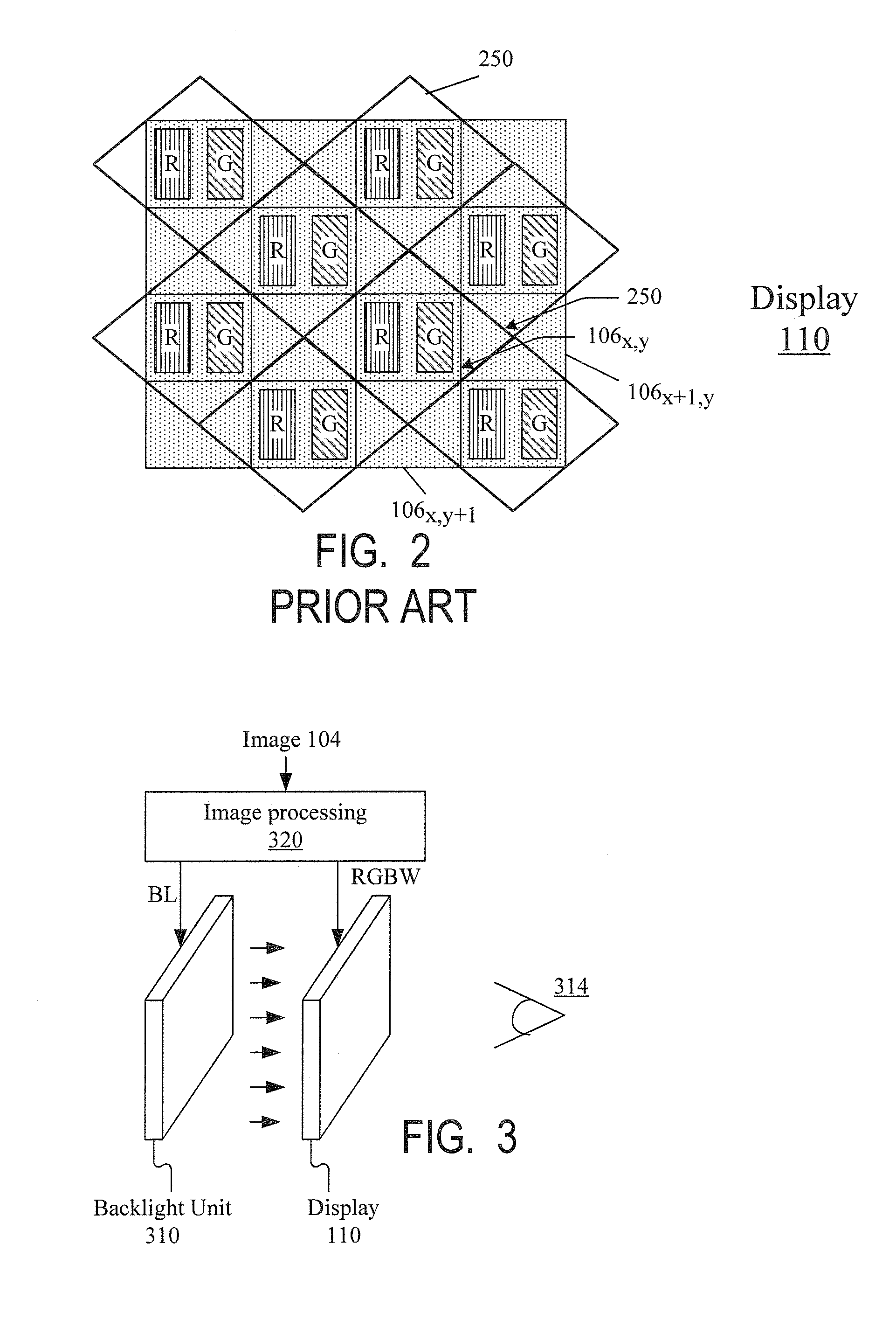
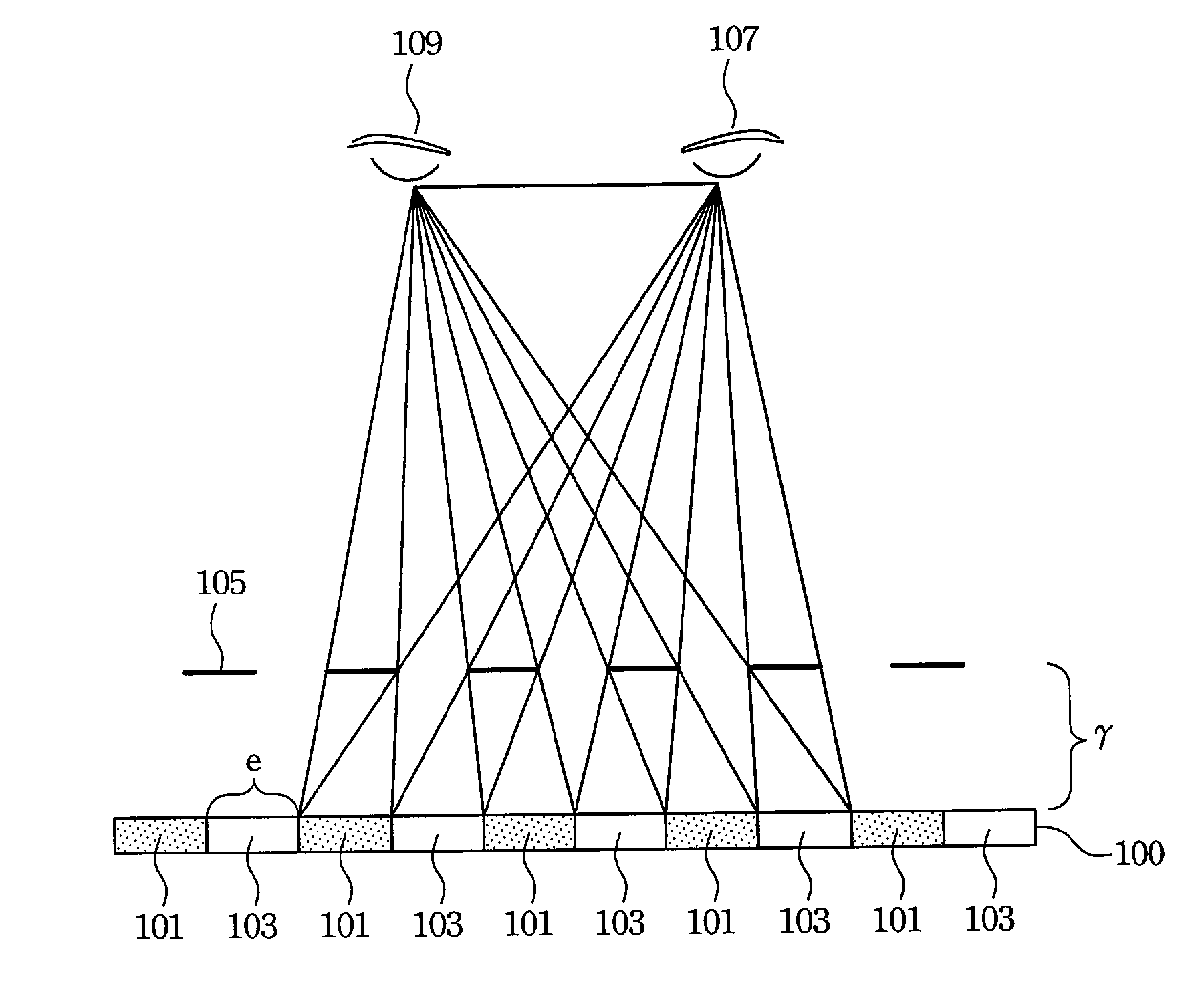
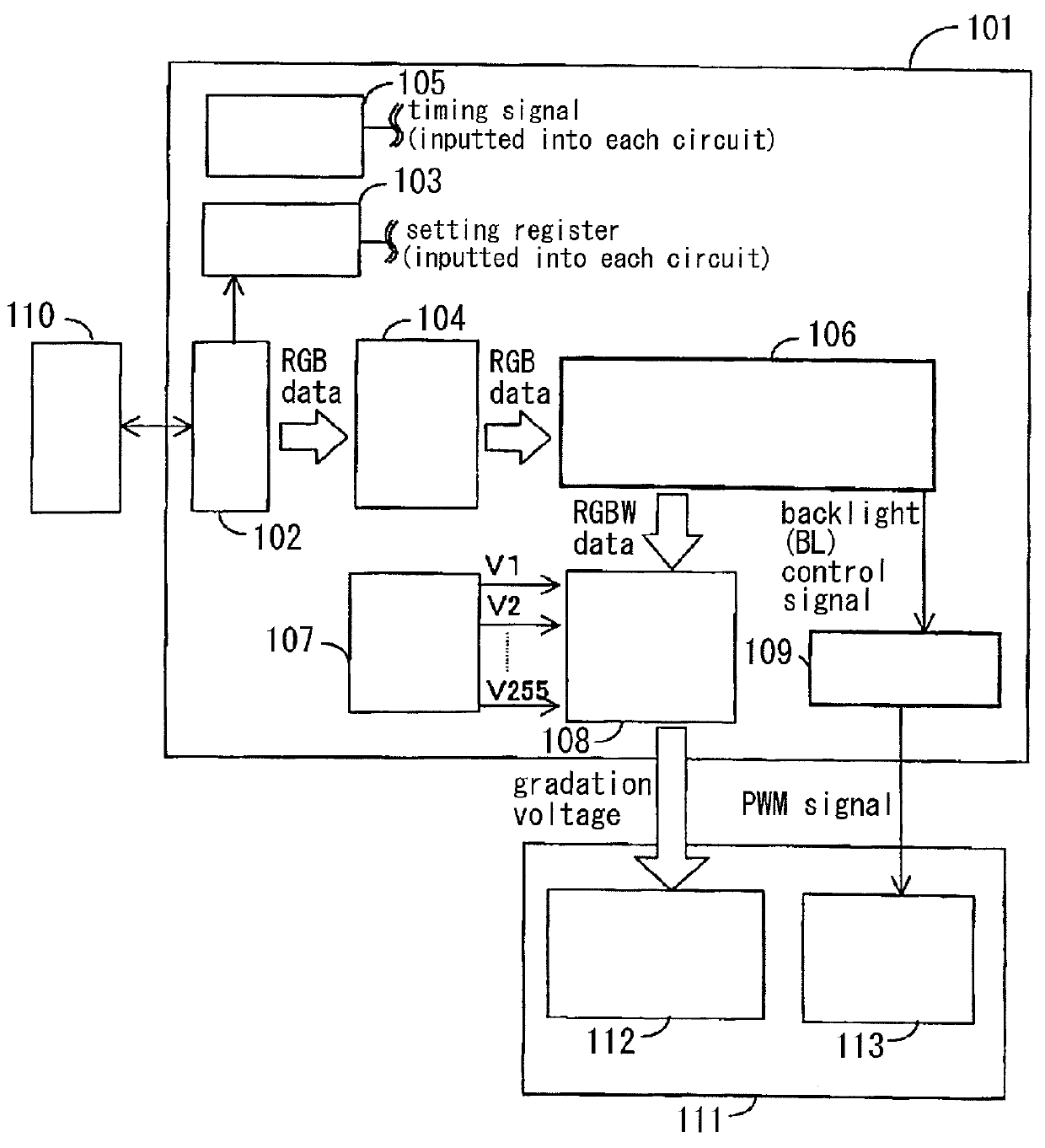
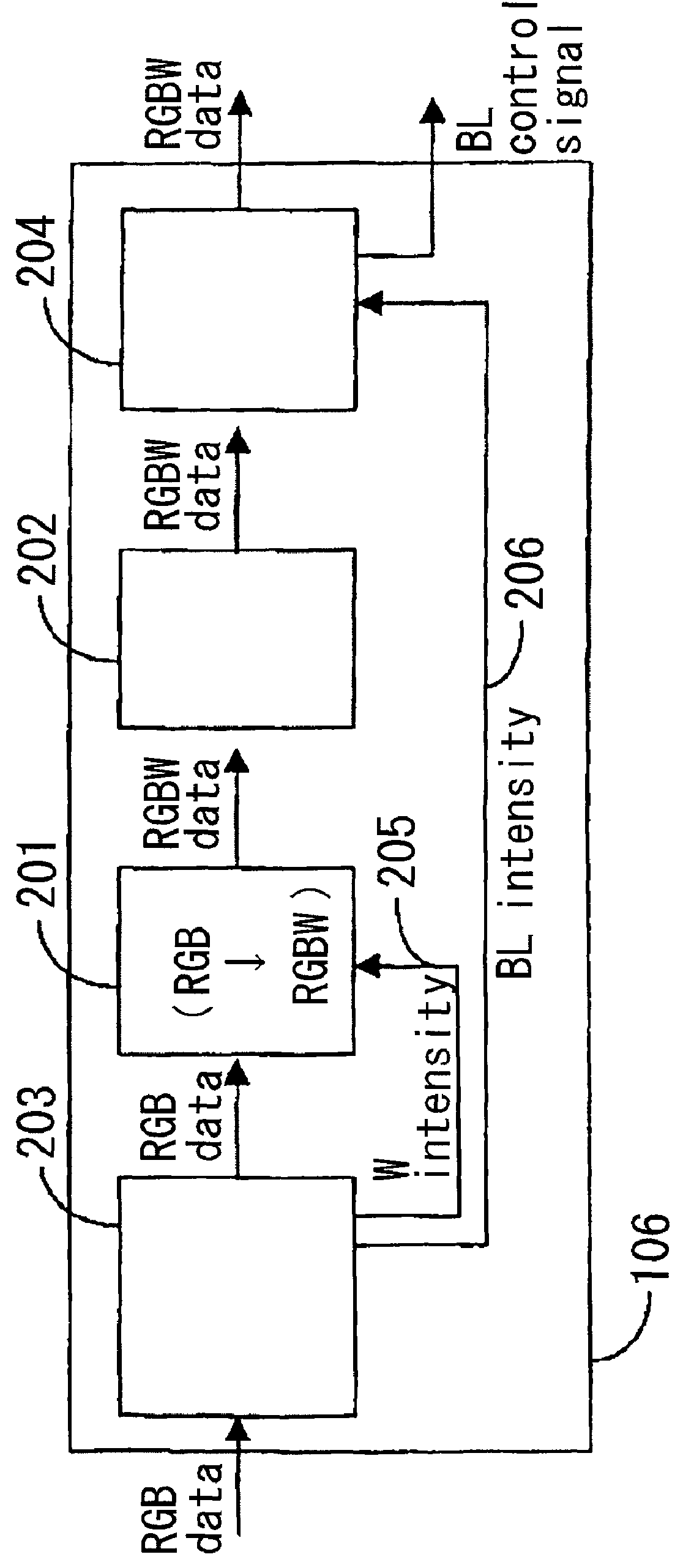
ActiveUS20090207182A1Reduce the required powerDeterioration of image qualityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsData expansionControl signal
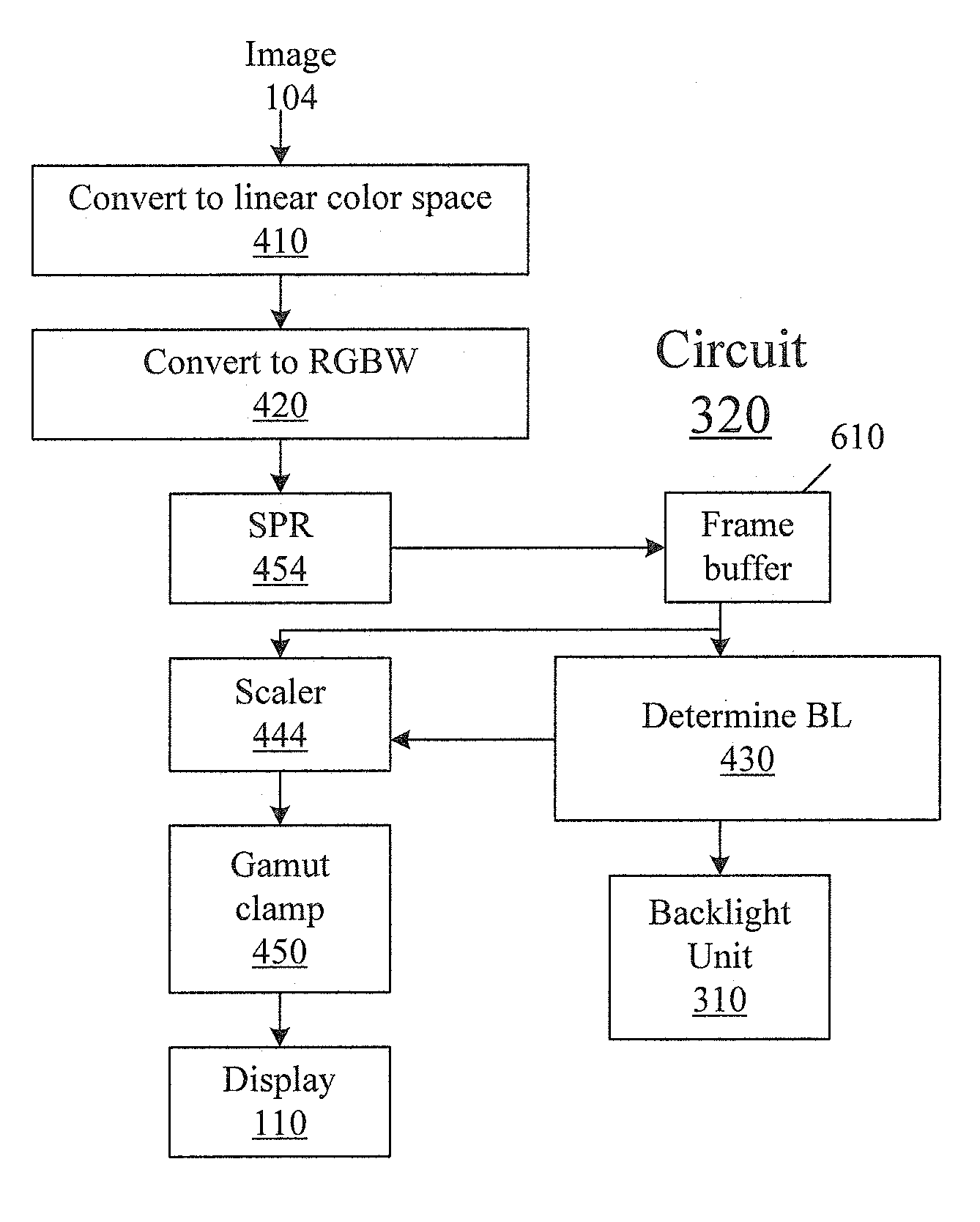
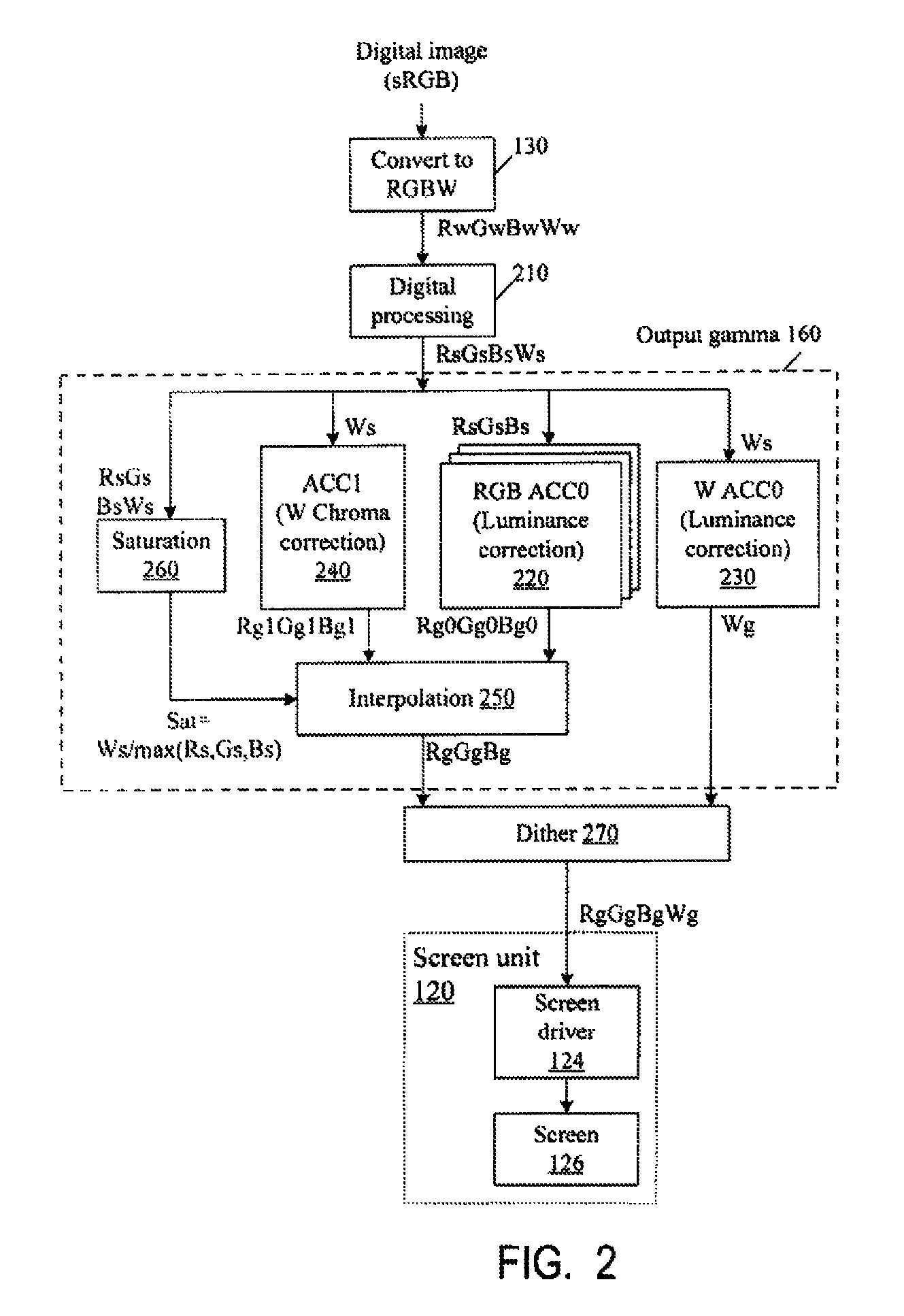
The deterioration (darkness) of image quality due to a reduction in the brightness of a single color as a result of the conversion from RGB pixels to RGBW pixels is prevented and a reduction in the power is achieved. A processing portion for conversion from RGB to RGBW 106 is formed of a W generating circuit 201, which is the same as in the prior art, a sub-pixel rendering circuit 202, a W intensity calculating portion 203 which transmits a W intensity setting value 205 to a W generating circuit 201, and a low power backlight control circuit 204 which expands data on the basis of the RGBW pixels generated by the sub-pixel rendering portion 202 and lowers the backlight in accordance with the amount by which the data is expanded. The inputted RGB data is used as the RGBW data with the W intensity calculated by the W intensity calculating portion 203. A backlight control signal is generated in accordance with the amount of data expansion in the sub-pixel rendering portion 202.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
High density multi-view image display system and method with active sub-pixel rendering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Picture element structure for panel display device
The present invention provides a pixel structure for a flat panel display apparatus displaying images using a plurality of pixels, each of the pixels including six or more sub-pixels. The flat panel display apparatus including the pixel structure is free from a color fringe error, and the pixel can include three or more primary colors. Thus, a color representation range of the flat panel display apparatus can be widened. In addition, since the sub-pixels of the pixel can be controlled by sub-pixel rendering, a resolution of the apparatus can be improved. Moreover, high resolution can be obtained in every direction on the display due to superior rotational symmetry of the pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of sub-pixel rendering for a delta-triad structured display
InactiveUS20130106891A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingColor imageDisplay device
A method of rendering a color image on a delta-structured color display. The display has a plurality of first sub-pixel groups and a plurality of second sub-pixel groups interlacing with each other. Each first sub-pixel group includes a first sub-pixel of a first color. Each second sub-pixel group includes a second sub-pixel of a second color and a third sub-pixel of a third color. In one embodiment, the method includes inputting the color image, analyzing the color image to estimate one or more patterns of the image, determining one or more color template indexes, each color template indexes corresponding to a respective one of the one or more patterns, generating an intensity map, including an intensity for each first sub-pixel, second sub-pixel, and third sub-pixel of the display, according to the color template indexes, and outputting a plurality of electrical signals according to the intensity map to the display.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Pixel structure for flat panel display apparatus
A pixel structure for a flat panel display apparatus displaying images using a plurality of pixels, each of the pixels including six or more sub-pixels. The flat panel display apparatus including the pixel structure is free from a color fringe error, and the pixel can include three or more primary colors. Thus, a color representation range of the flat panel display apparatus can be widened. In addition, since the sub-pixels of the pixel can be controlled by sub-pixel rendering, a resolution of the apparatus can be improved. Moreover, high resolution can be obtained in every direction on the display due to superior rotational symmetry of the pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Supbixel rendering suitable for updating an image with a new portion
ActiveUS20110043533A1Reduce memory requirementsReduce degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Subpixel rendering
In an image update, a display apparatus receives only a new portion (1110) of an image for display but does not receive the remaining, unchanged portion of the image. The display apparatus performs a subpixel rendering (SPR) operation (454) for the new portion but does not redo the SPR for the whole image. Efficient techniques are provided to achieve good appearance at the edges between the new portion and the rest of the image. Other features are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image device
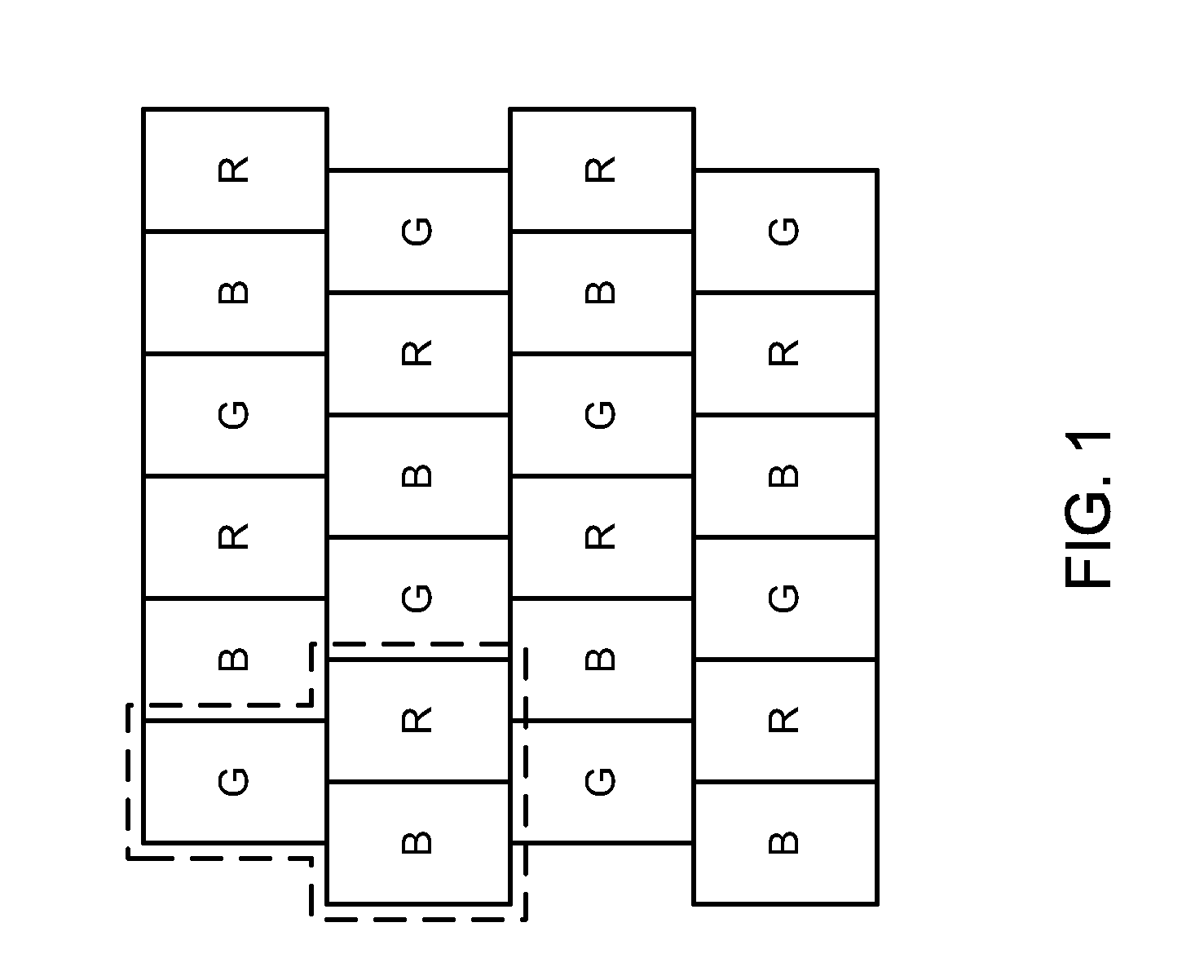
An image device includes a plurality of pixel groups. Each pixel group includes a plurality of dots arranged in a predetermined identical matrix form, and each pixel group has at least one first color dot, at least one second color dot, at least one third color dot and at least one fourth color dot. Any repeated sequence of consecutive color dots in a row direction and in a column direction comprise at least one first color dot, at least one second color dot, at least one third color dot, at least one fourth color dot. The advantage of the invention is to provide all multi-primary colors in a single row or column so that by using subpixel rendering method, black and white lines can be formed in rows or columns, thus reducing the number of columns in a multi-primary colors display.
Owner:VP ASSETAB
Sub-pixel rendering method and system
ActiveCN107331341AReduce the number of sub-pixelsReduce color distortionStatic indicating devicesComputer visionImaging data
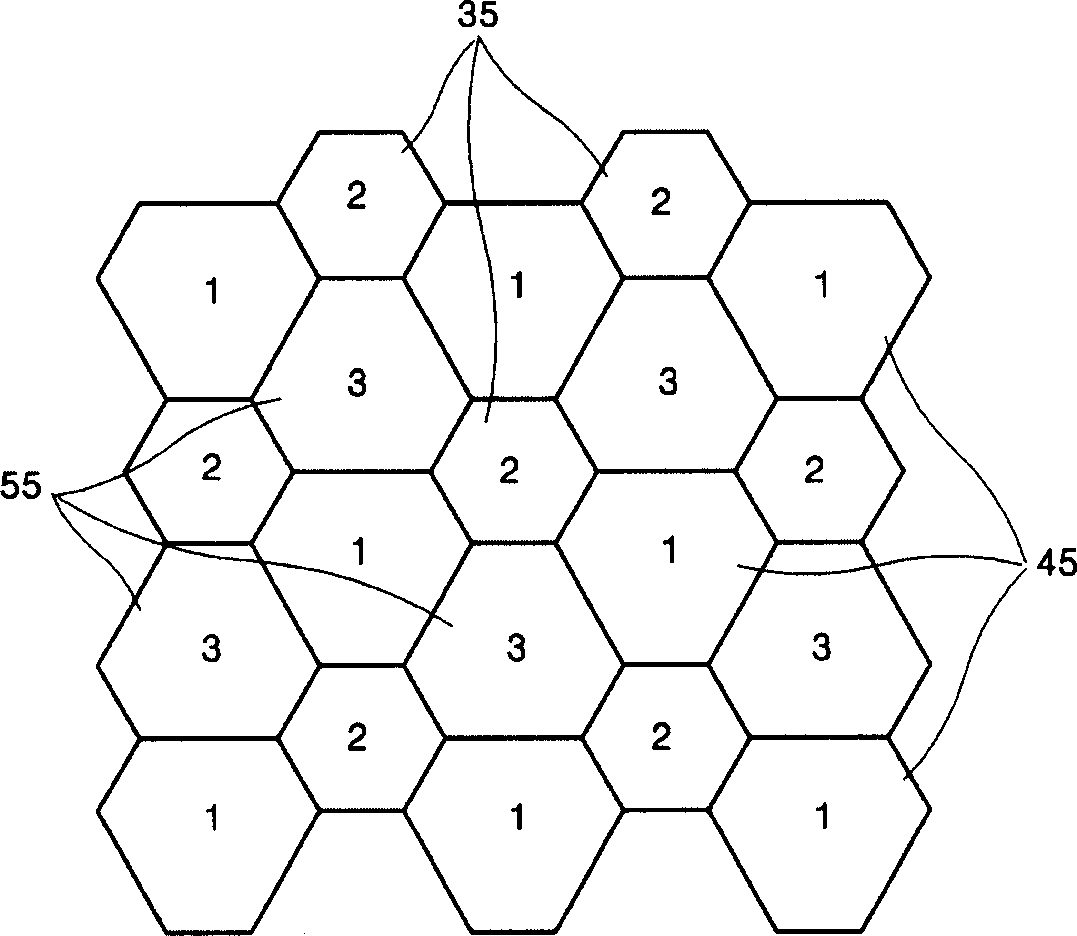
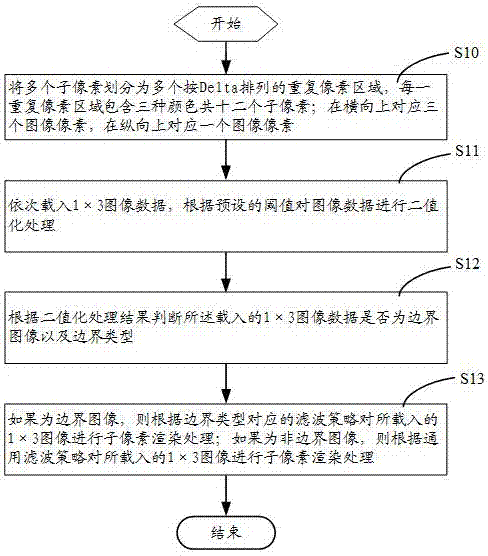
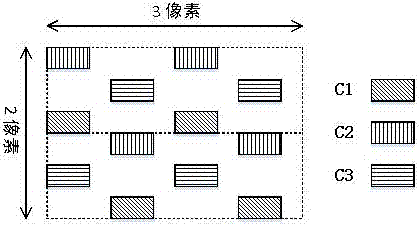
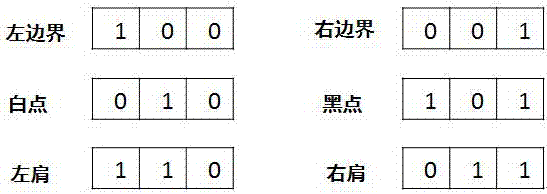
The embodiment of the invention discloses a sub-pixel rendering method which is used to render a Delta-type sub-pixel arrangement structure. The method comprises the steps that a number of sub-pixels are divided into a number of repeated pixel regions arranged in Delta, wherein each repeated pixel region comprises three colors and twelve sub-pixels, is corresponding to three image pixels in the horizontal direction and two image pixels in the vertical direction; 1*3 image data are sequentially loaded and binarized according to a preset threshold; whether the loaded 1*3 image data are a boundary image and the boundary type is determined according to the binarization processing result; and if the determination result is a boundary image, sub-pixel rendering is carried out on the loaded 1*3 image data according to a filter policy corresponding to the boundary type. The invention further discloses a corresponding system. According to the embodiment of the invention, the problem of distortion is improved when the image boundary region is displayed.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
High density multi-view image display system and method with active sub-pixel rendering
Provided are a high density multi-view image display system and method based on active sub-pixel rendering. The image display system may perform a rendering with respect to a viewpoint image in a pixel unit, using a viewpoint varying based on a position of left / right eyes of a user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
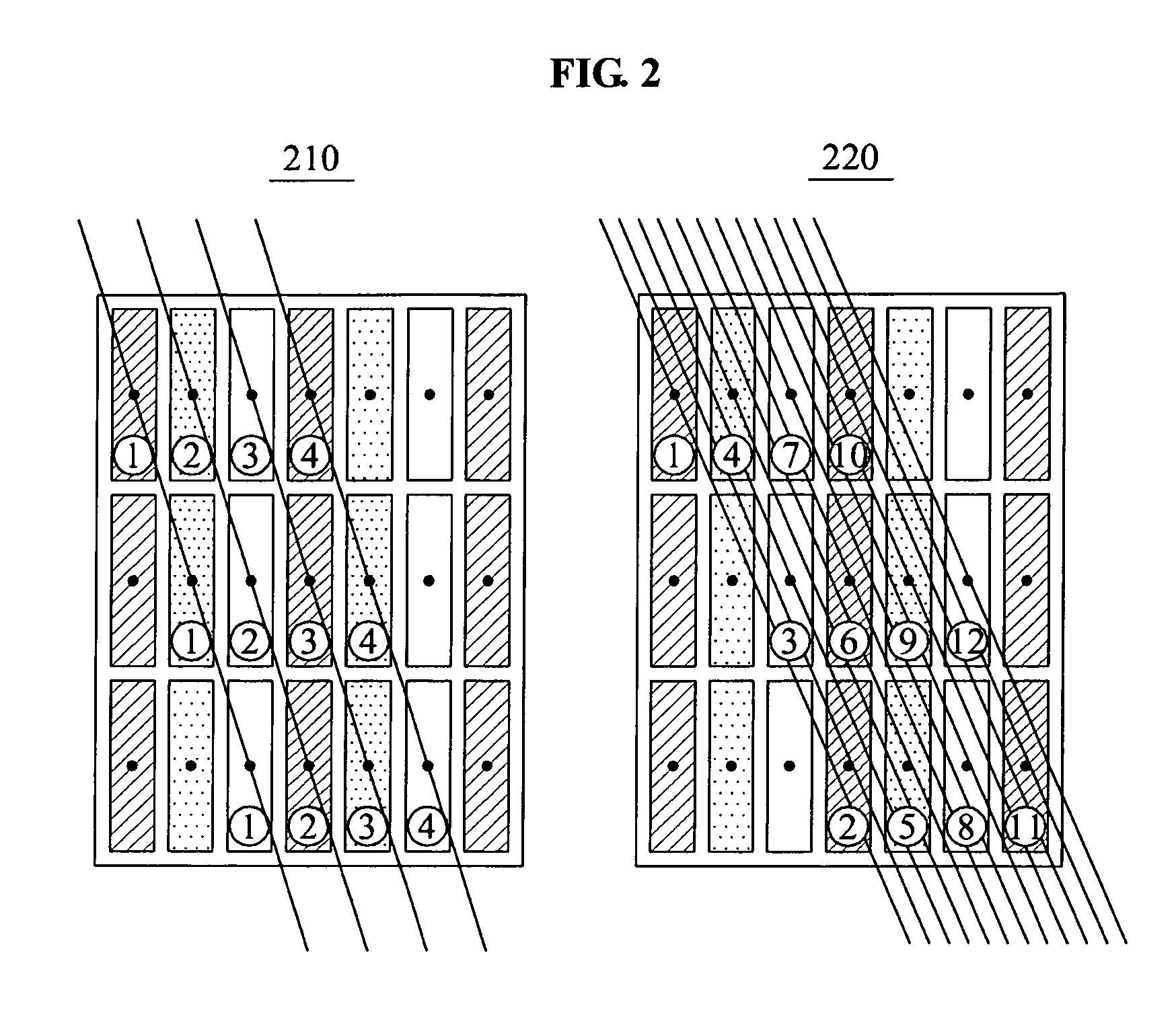
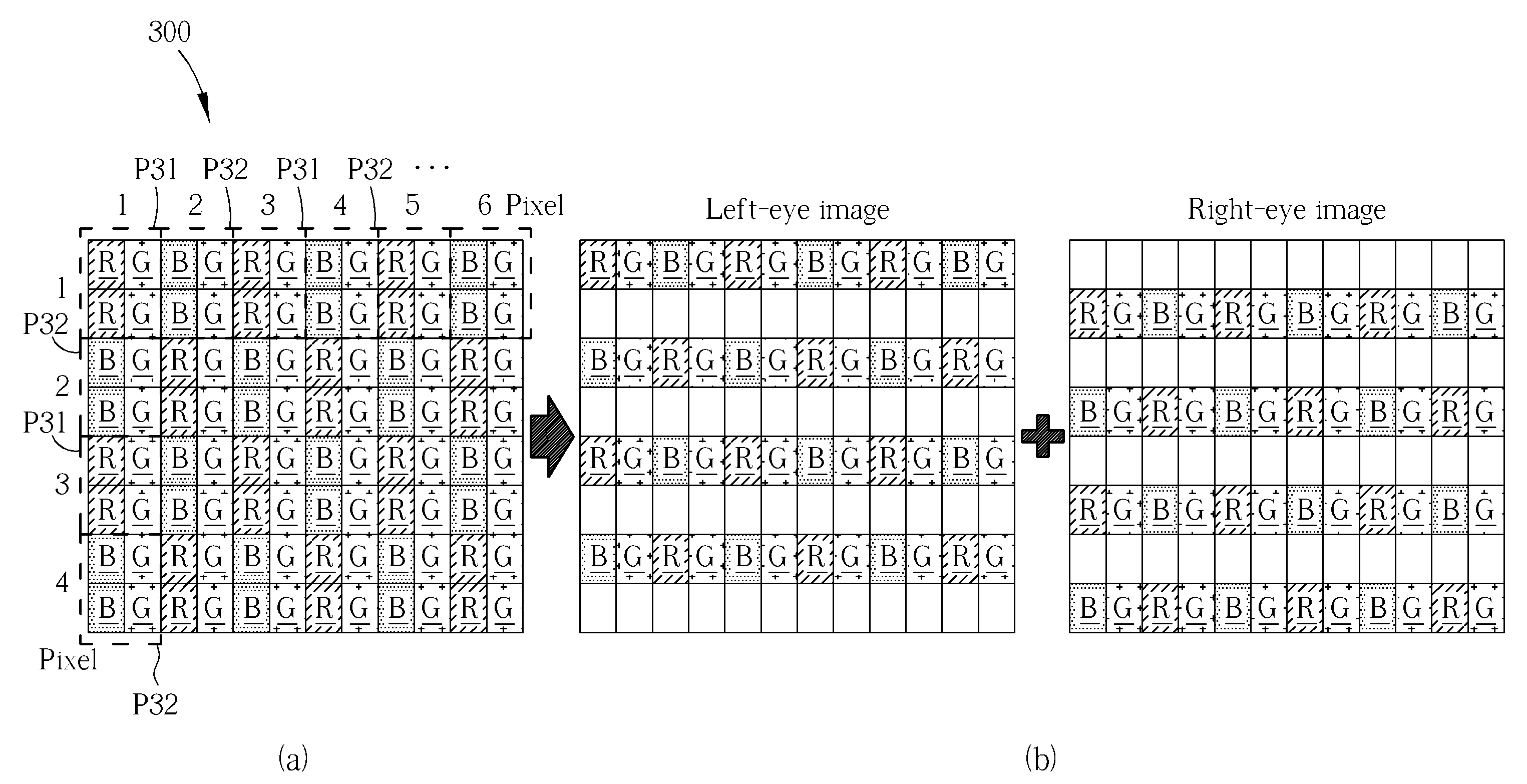
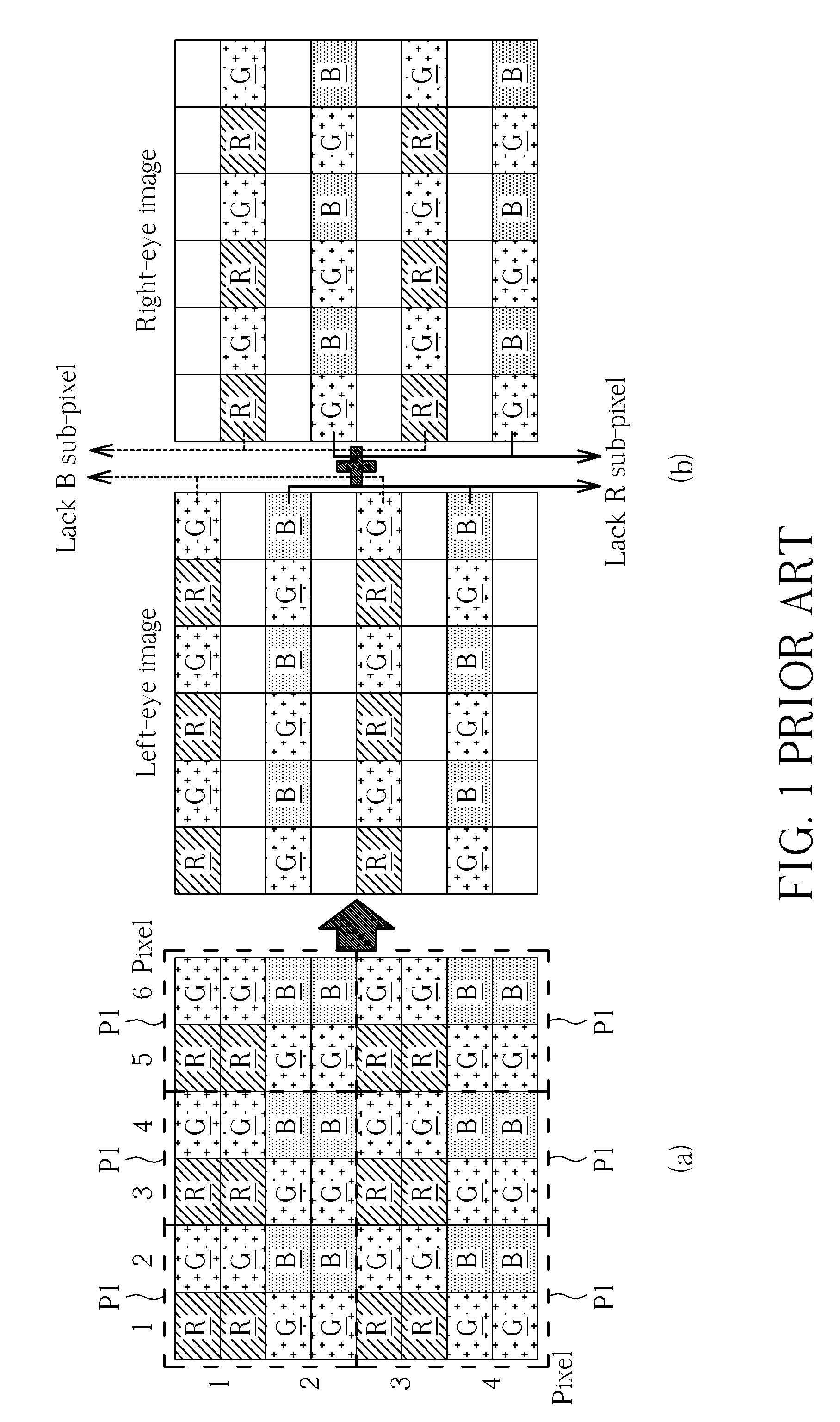
Layout method of sub-pixel renderings
ActiveUS20130021328A1Improve imaging resolutionImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsStereo imageSubpixel rendering
A layout method of sub-pixel renderings includes the following steps: providing an RGB pixel rendering, wherein each pixel of the RGB pixel rendering includes a plurality of sub-pixels, and the plurality of sub-pixels have different colors from each other; and when displaying a stereo image, dividing the RGB pixel rendering into a first sub-pixel rendering corresponding to a left-eye image and a second sub-pixel rendering corresponding to a right-eye image; wherein at least one of each row and each column of the first sub-pixel rendering includes R, G, and B sub-pixels, and at least one of each row and each column of the second sub-pixel rendering includes R, G, and B sub-pixels.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Subpixel rendering with color coordinates' weights depending on tests performed on pixels
ActiveUS20110043552A1Reduces replicate processingImprove local contrastCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPrimary colorSubpixel rendering
If a pixel (106) of an image is displayed in a subpixel area (124) which does not contain a primary color needed to display the pixel, and saturated colors are present in or adjacent to the subpixel area, then some of the pixel's luminance is shifted (850) to adjacent subpixel areas on one but not both sides of the pixel to avoid blurring the pixel. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Display device making use of sub-pixel rendering method and sub-pixel rendering method
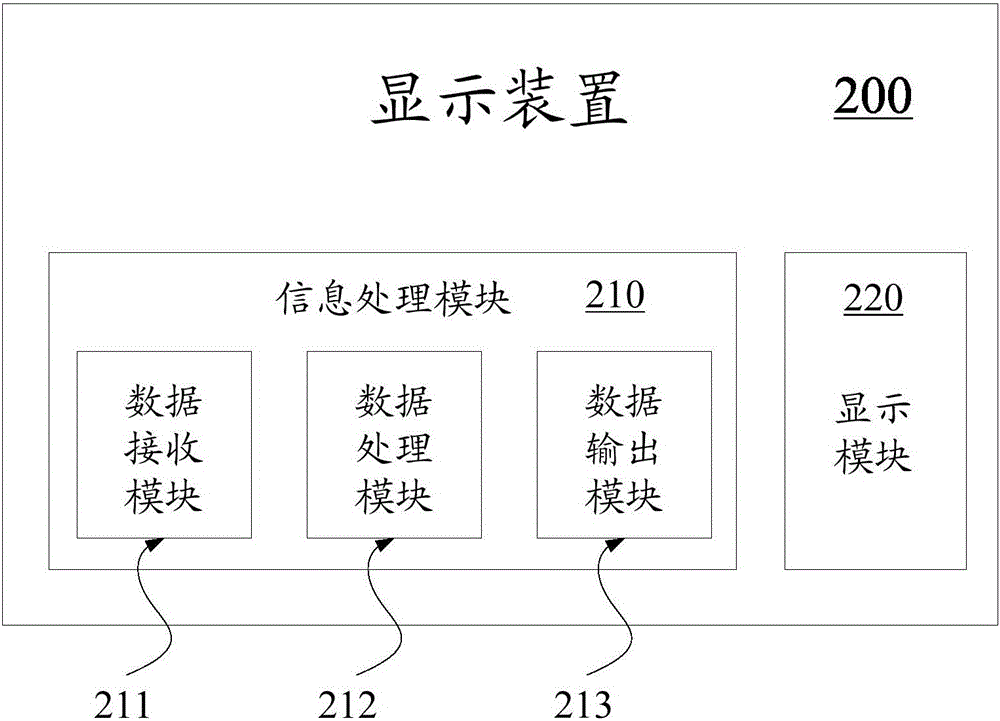
ActiveCN105096755AStatic indicating devicesIdentification meansInformation processingComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a display device making use of a sub-pixel rendering method and the sub-pixel rendering method. The display device comprises an information processing module and a display module, wherein the information processing module comprises a data receiving module which is used for receiving image data of a first pattern, a data output module for outputting image data of a second pattern, and a data processing module for mapping the first pattern to the second pattern by virtue of the sub-pixel rendering method. The second image is displayed by the display module, wherein each pixel of the first pattern corresponds to a virtual pixel of the second pattern; two adjacent virtual pixels of the second pattern share one or more sub-pixels; the data processing module is used for compensating the image data of the sub-pixel shared by the second pattern by virtue of a compensating coefficient; and the compensating coefficient is set in accordance with the image data of two adjacent pixels of the first pattern corresponding to the sub-pixel shared by the second pattern or is set as a constant.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS +1
Subpixel layouts and subpixel rendering methods for directional displays and systems
Display devices and systems are configured with display panels substantially comprising one of several embodiments of three primary color or multi-primary color subpixel repeating groups that are particularly suitable for directional display devices which produce at least two images simultaneously, such as autostereoscopic three-dimensional display devices or multi-view devices. Input image data indicating an image is rendered to a device configured with one of the illustrated subpixel repeating groups using a subpixel rendering operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Three-Dimensional Image Display Device and a Displaying Method Thereof
A three-dimensional image display device and a displaying method thereof. The display device includes a pixel array, a sub-pixel rendering device and a mask. The sub-pixel rendering device provides data signals to the sub-pixels to form the first frames and the second frames. The first frame and the second frame include a plurality of first pixel regions and a plurality of second pixel regions. The second pixel region and the adjacent first pixel regions have some sub-pixels in common. The mask projects the first frames and the second frames as a first image and a second image.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Display device
ActiveUS8232944B2Panel is improvedIncrease darknessDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsData expansionControl signal
The deterioration (darkness) of image quality due to a reduction in the brightness of a single color as a result of the conversion from RGB pixels to RGBW pixels is prevented and a reduction in the power is achieved.A processing portion for conversion from RGB to RGBW 106 is formed of a W generating circuit 201, which is the same as in the prior art, a sub-pixel rendering circuit 202, a W intensity calculating portion 203 which transmits a W intensity setting value 205 to a W generating circuit 201, and a low power backlight control circuit 204 which expands data on the basis of the RGBW pixels generated by the sub-pixel rendering portion 202 and lowers the backlight in accordance with the amount by which the data is expanded. The inputted RGB data is used as the RGBW data with the W intensity calculated by the W intensity calculating portion 203. A backlight control signal is generated in accordance with the amount of data expansion in the sub-pixel rendering portion 202.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA +1
Display apparatus
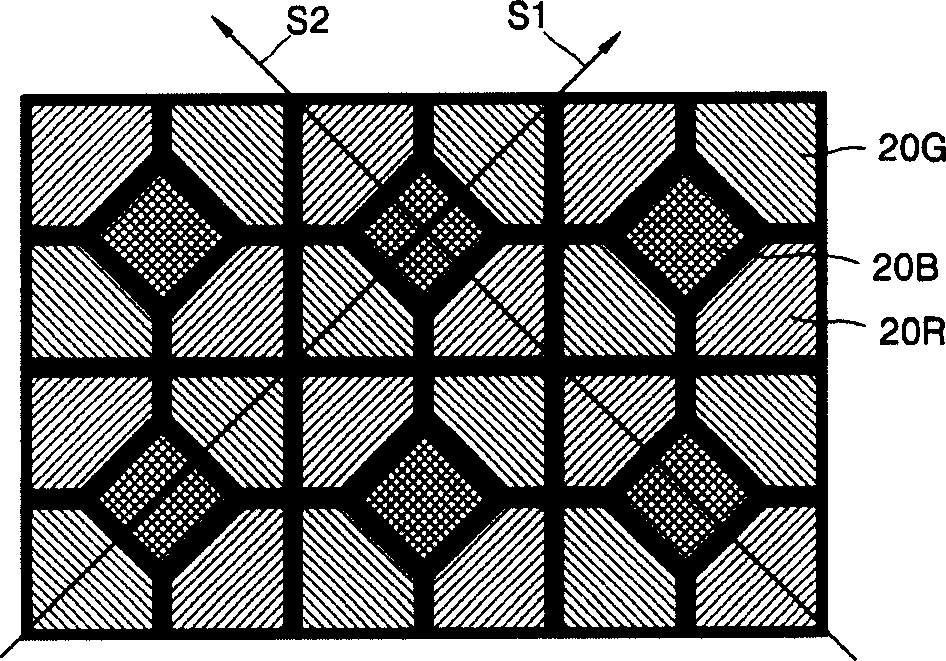
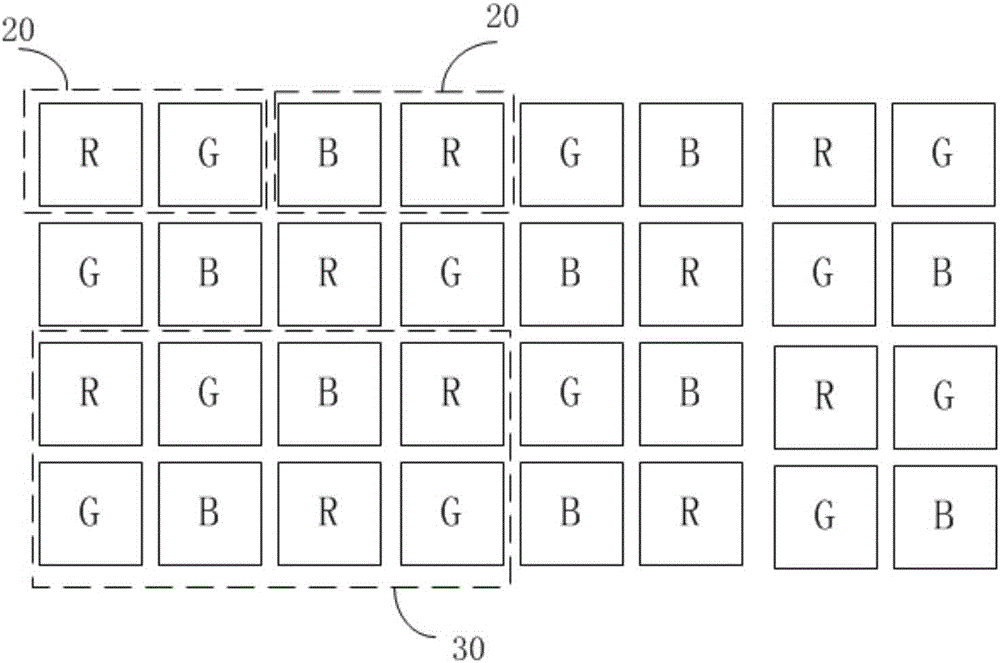
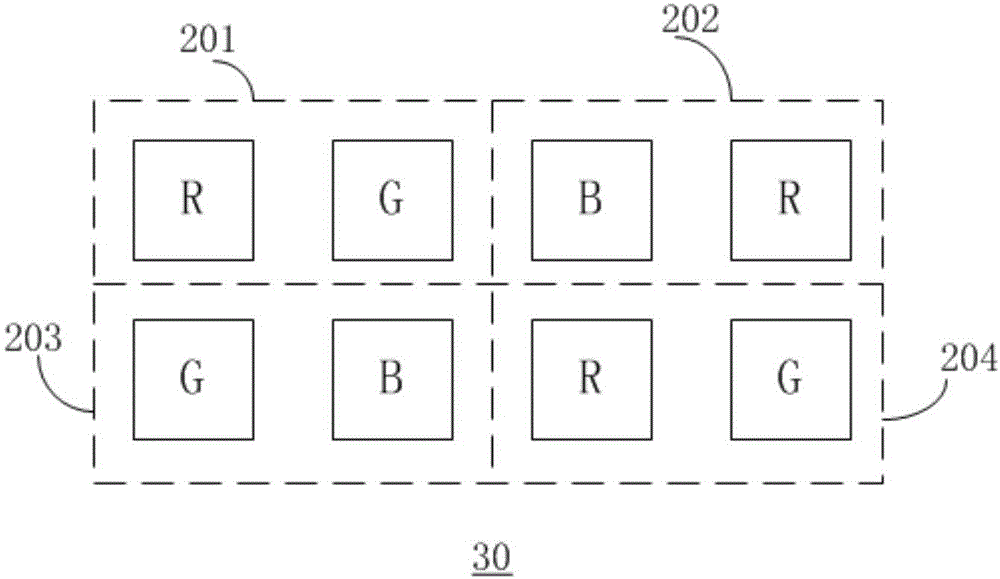
A pixel array structure for populating the display area of a display device (100, 200, 300, 400) includes a repeated first pixel group (110) that consists of one or more first colored subpixels (10), three or more second colored subpixels (20) and two or more third colored subpixels (30). The respective numbers of the first colored subpixels, the second colored subpixels, and the third colored subpixels that are provided within the first pixel group are preferably in a respective ratio of 1:3:2. In one embodiment, an input RGB image is remapped to have luminance values corresponding to Cyan-Magenta-Yellow coordinates and the latter are used in combination with subpixel rendering (SPR) to drive the colored subpixels of the pixel array structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Dropout control in subpixel rendering
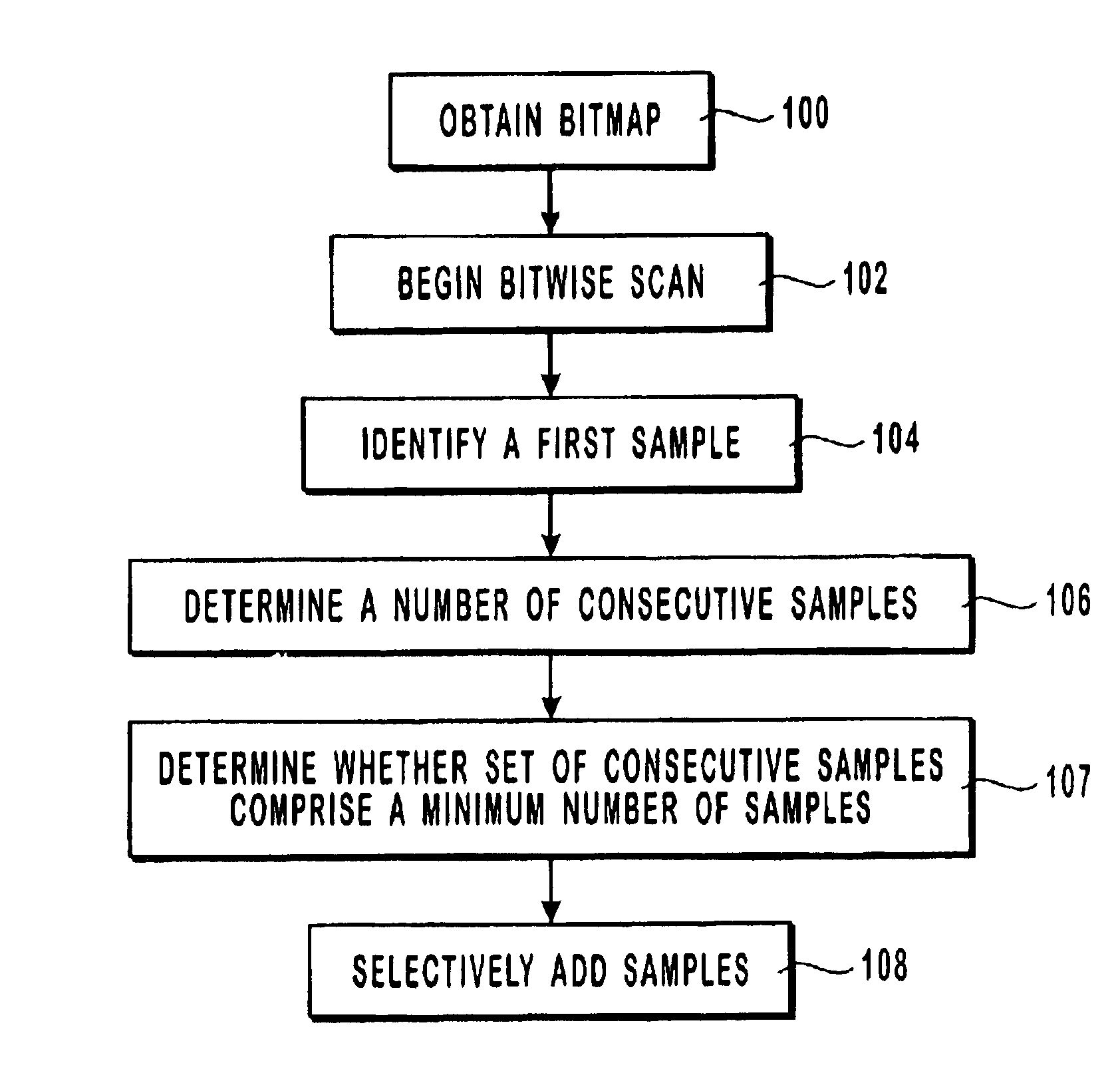
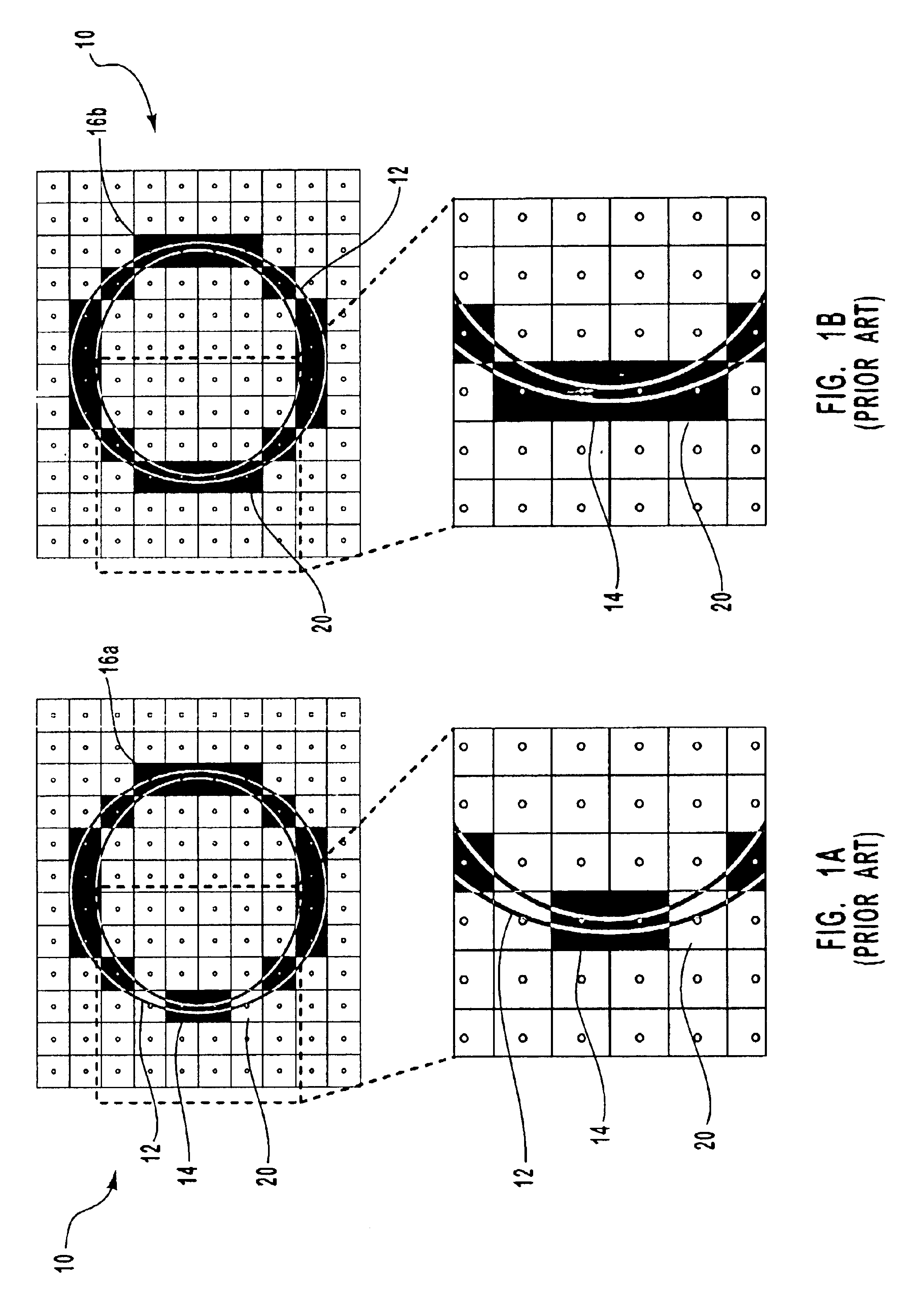
InactiveUS6894702B2Facilitate dropout control operationFacilitate vertical dropout control operation2D-image generationCharacter and pattern recognitionAnti-aliasingDropout voltage
The present invention relates to dropout control in which one or more samples are added to adjacent samples that fall within an image outline. The samples are used in sub-pixel rendering to compensate for unnaturally thin or faint object stems. Horizontal dropout control operations are provided to add samples to sets of horizontally adjacent samples such that each set of samples comprises a minimum number of samples. Vertical dropout control operations are provided to position samples such that the weighted anti-aliasing filtering will take sufficient account of the samples. In one embodiment, an associative table is utilized to calculate alternative patterns of samples. In another embodiment, the baseline of an object is used in the dropout control operations to reduce artifacts that can be created by the addition of samples in the vertical direction.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Device and method for displaying stereoscopic picture
InactiveCN101442683AGuaranteed resolutionImprove qualitySteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Display device
The invention provides a stereo image display device and a display method thereof. The display device comprises a pixel matrix, a sub-pixel rendering device, and a shielding mask. The pixel matrix comprises a plurality of sub-pixels. The sub-pixel rendering device provides data for the sub-pixels and makes the sub-pixels combine together to form a plurality of first frames and a plurality of second frames, so as to display a first image and a second image respectively, wherein the first frame can define a plurality of first pixel blocks and a plurality of second pixel blocks, the second frame can also define a plurality of first pixel blocks and a plurality of second pixel blocks, the first frame and the second frame are not overlapped, and the second pixel blocks and the adjacent first pixel block cover partial repeated sub-pixels. The shielding mask projects the plurality of first frames and the plurality of second frames to form a plurality of first and second images.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Sub-pixel rendering method and rendering device
A sub-pixel rendering method includes the steps of acquiring a second pixel array corresponding to an original image, wherein each sub-pixel of the second pixel array corresponds to a gray-scale value; mapping the second pixel array of the original image into a first pixel array; respectively finding out central positions of the sub-pixels of the first pixel array and the second pixel array, determining the sub-pixel, as same color as each sub-pixel in the first pixel array and positioned in a preset region of each sub-pixel in the first pixel array, of the second pixel array, and measuring a distance between the central positions of the sub-pixel of the second pixel array and each sub-pixel in the first pixel array; calculating proportionality coefficients that the sub-pixels of the second pixel array account for the sub-pixel of the first pixel array according to the distances, and calculating gray-scale values corresponding to the sub-pixels in the first pixel array according to the gray-scale values of the sub-pixels in the second pixel array and the proportionality coefficients. The sub-pixel rendering method is simple and easy to implement, fewer hardware resources are required and the software running speed is high.
Owner:TRULY HUIZHOU SMART DISPLAY
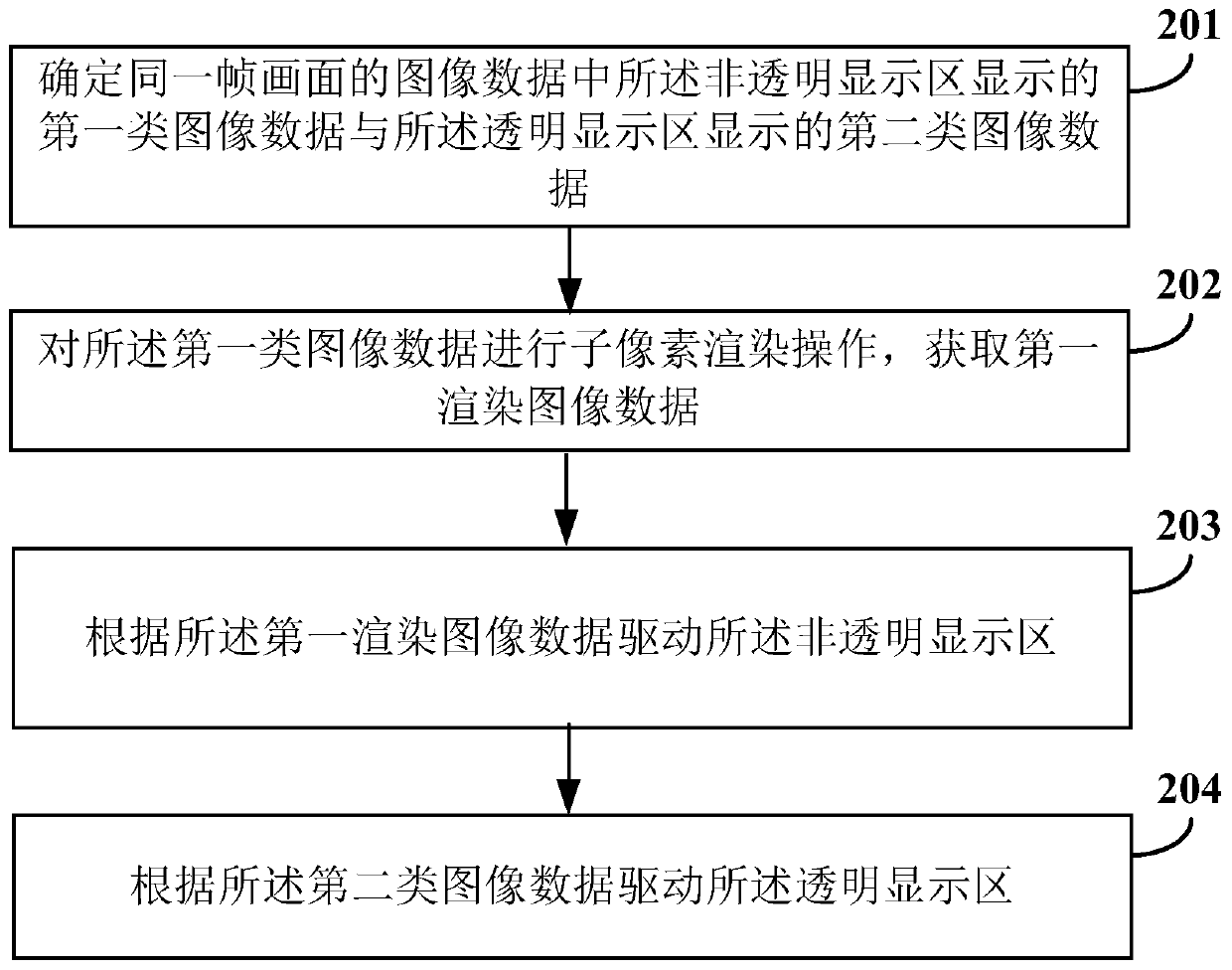
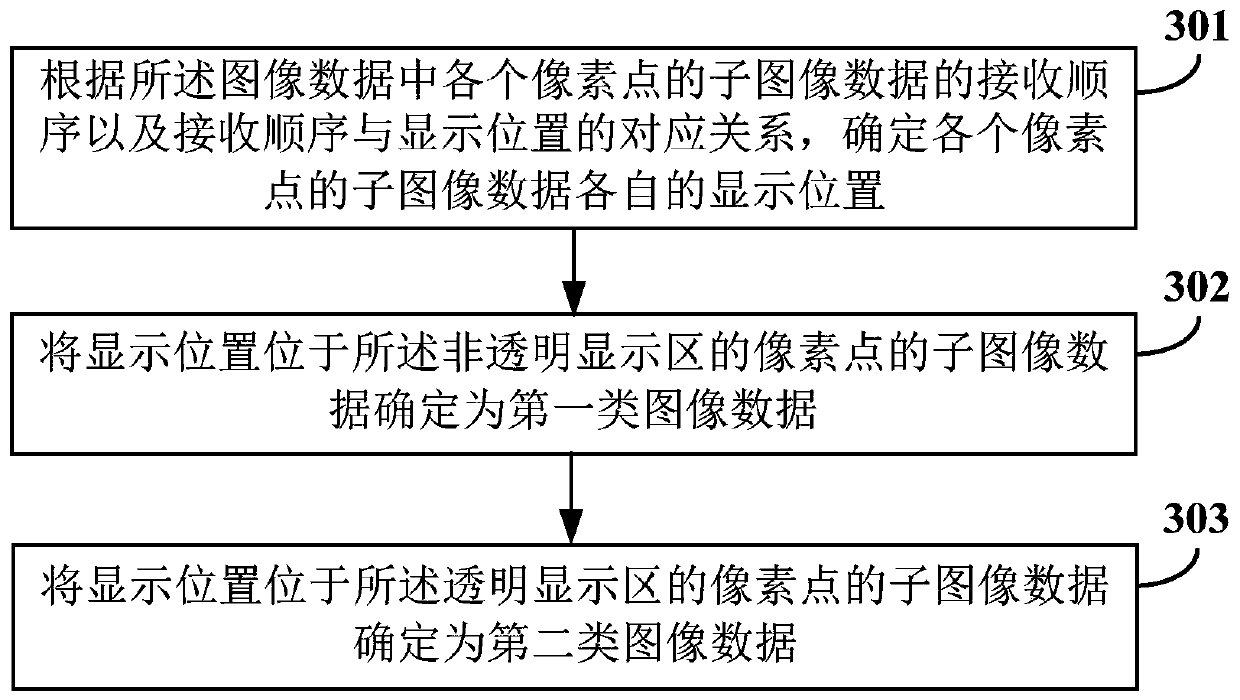
Driving method and device of display panel and display equipment
PendingCN110767159AImprove qualityIncrease display resolutionStatic indicating devicesSubpixel renderingImage resolution
The invention relates to a driving method and device of a display panel and display equipment. The display panel comprises a transparent display area and a non-transparent display area which are adjacent to each other. The driving method comprises the following steps: determining a first type of image data displayed in the non-transparent display area and a second type of image data displayed in the transparent display area in the image data of the same frame; performing sub-pixel rendering operation on the first type of image data to obtain first rendered image data; driving a non-transparentdisplay area according to the first rendering image data; and driving the transparent display area according to the second type of image data. According to the embodiment of the invention, the display resolution when the image is displayed in the non-transparent display area can be improved, and the quality of the image displayed in the non-transparent display area is improved.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
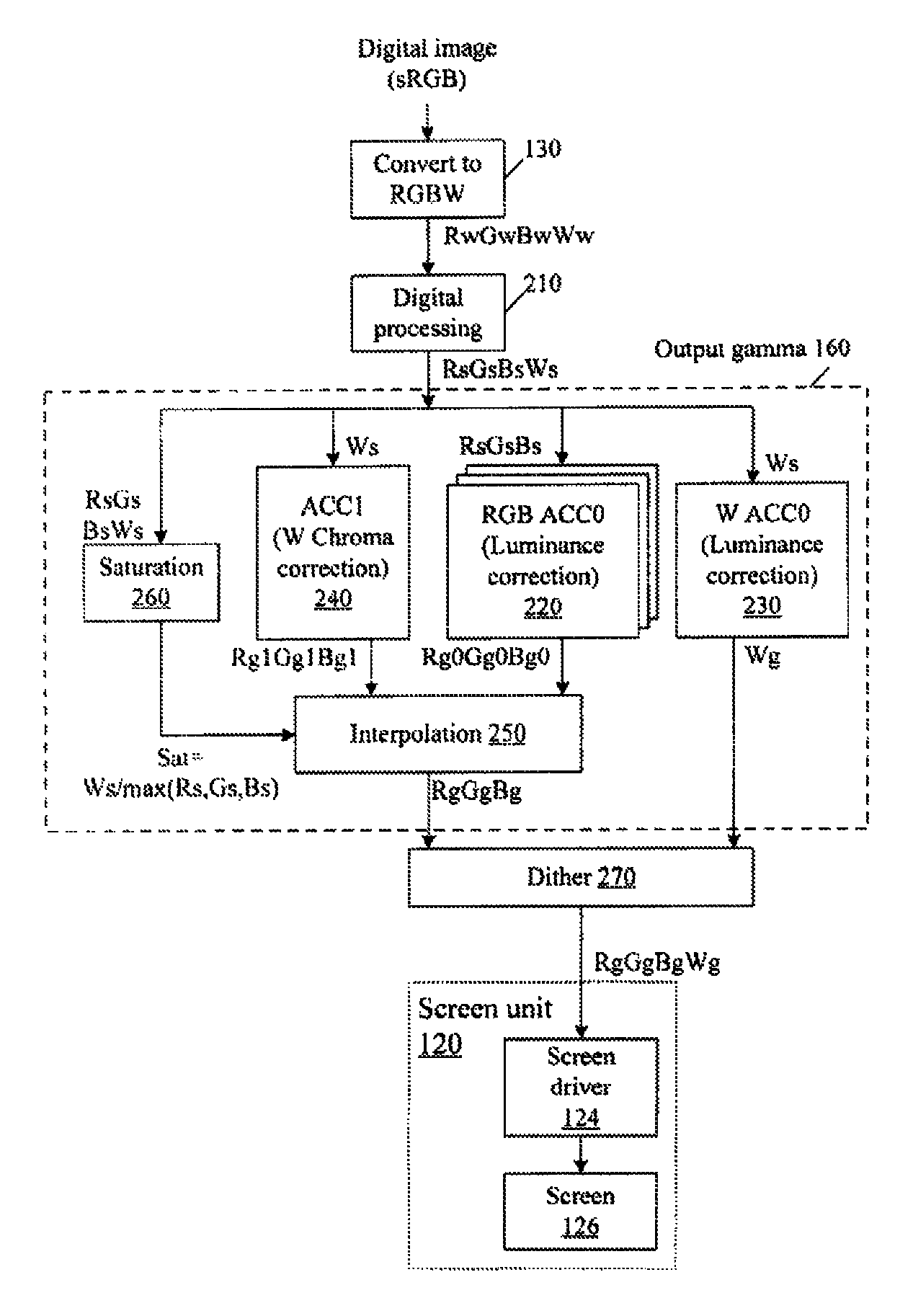
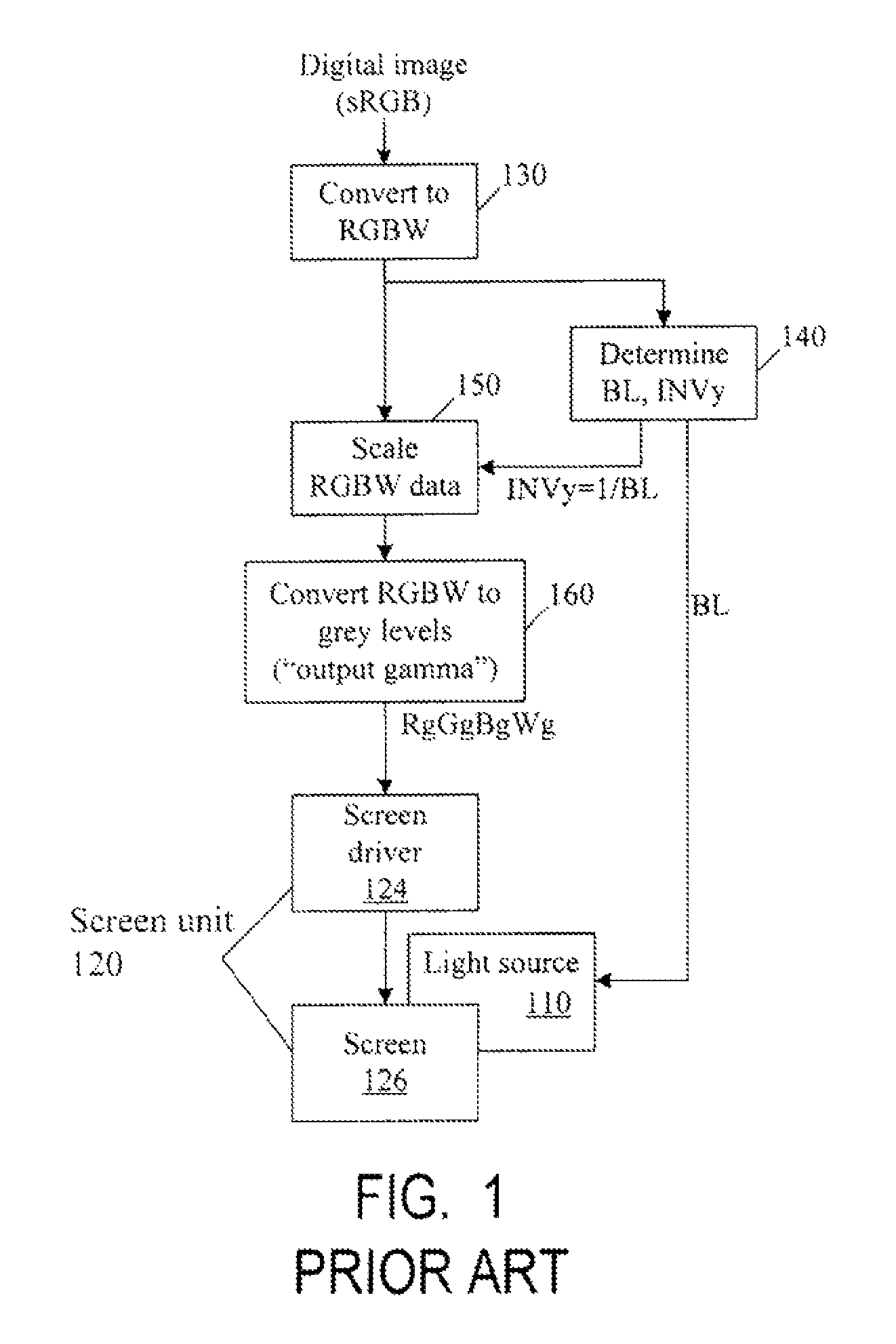
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
ActiveUS9049410B2Image degradation can be highIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
High-resolution micro-lens 3D display with shared sub-pixel color signals
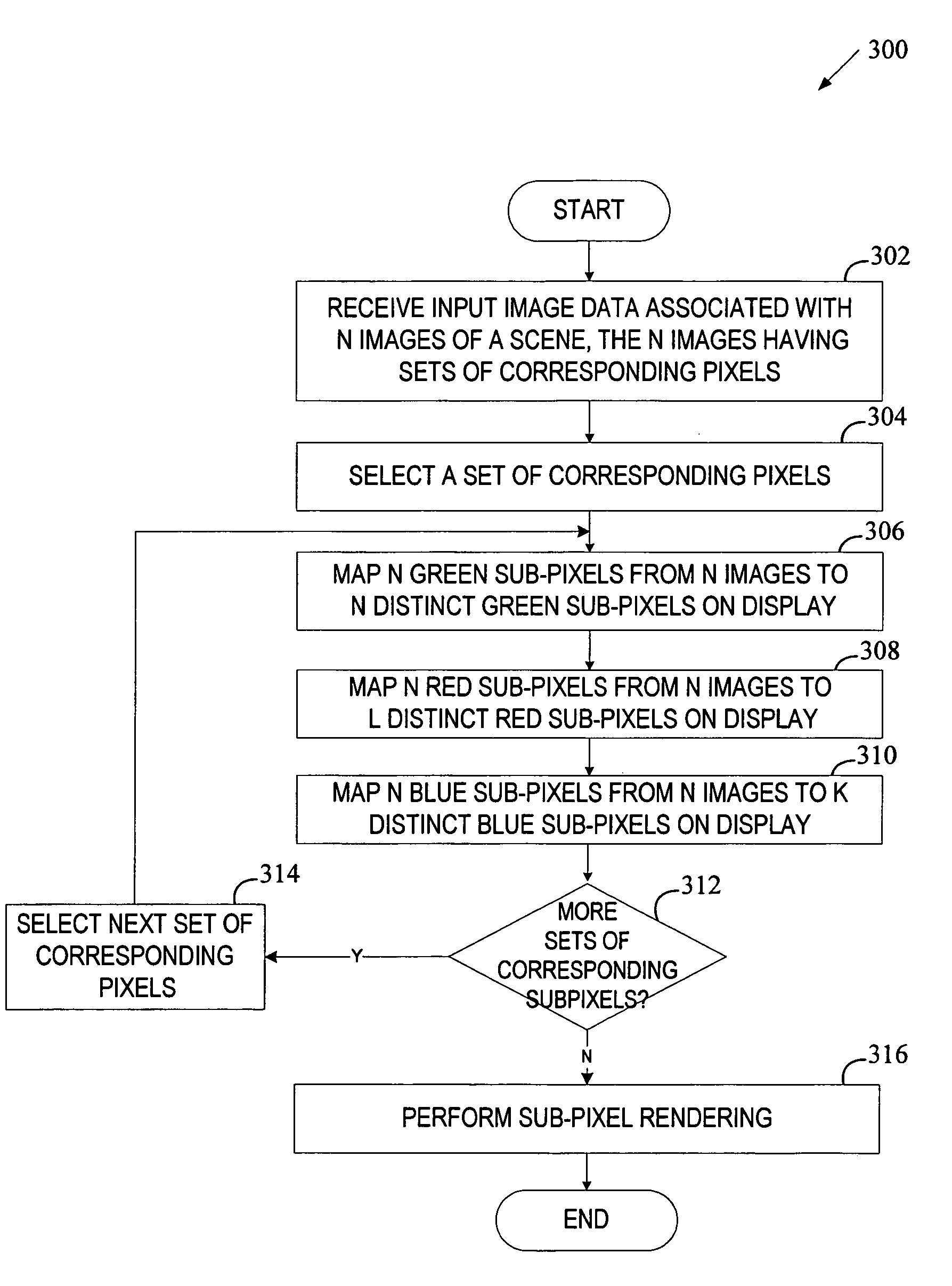
In one embodiment, a sub-pixel rendering method includes receiving 3D image data associated with pixel intensity values of N two-dimensional images having multiple sets of corresponding pixels. Each set of corresponding pixels includes N pixels (one pixel from each of N images) and each pixel has a green sub-pixel, a red sub-pixel and a blue sub-pixel. The method further includes mapping, for each selected set, N green sub-pixels, N red sub-pixels and N blue sub-pixels to M sub-pixels on a display to form a stereogram of the scene. The above mapping includes mapping N green sub-pixels from N images to N green sub-pixels on the display, mapping N red sub-pixels from N images to L red sub-pixels on the display, and mapping N blue sub-pixels from N images to K blue sub-pixels on the display, where L does not exceed N and K is lower than N.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Rendering method of display panel, display panel and display device
ActiveCN110648620ANo bright line problemImprove the display effectStatic indicating devicesIdentification meansPixel densityComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a rendering method of a display panel, the display panel and a display device. The display panel includes: a display area including a first display area and a second display area; AND sub-pixels which comprise first sub-pixels and second sub-pixels, wherein the first sub-pixels are located in the first display area, the second sub-pixels are located in the second display area, and the pixel density of the second display area is smaller than that of the first display area. The rendering method comprises the steps that the first display area performs display in a sub-pixelrendering mode, and the first sub-pixels adjacent to the second display area perform white display without the help of the second sub-pixels. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the bright line problem at the junction of the first display area and the second display area can be avoided, and the display effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Subpixel layouts and subpixel rendering methods for directional displays and systems
Display devices and systems are configured with display panels substantially comprising one of several embodiments of three primary color or multi-primary color subpixel repeating groups that are particularly suitable for directional display devices which produce at least two images simultaneously, such as autostereoscopic three- dimensional display devices or multi-view devices. Input image data indicating an image is rendered to a device configured with one of the illustrated subpixel repeating groups using a subpixel rendering operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
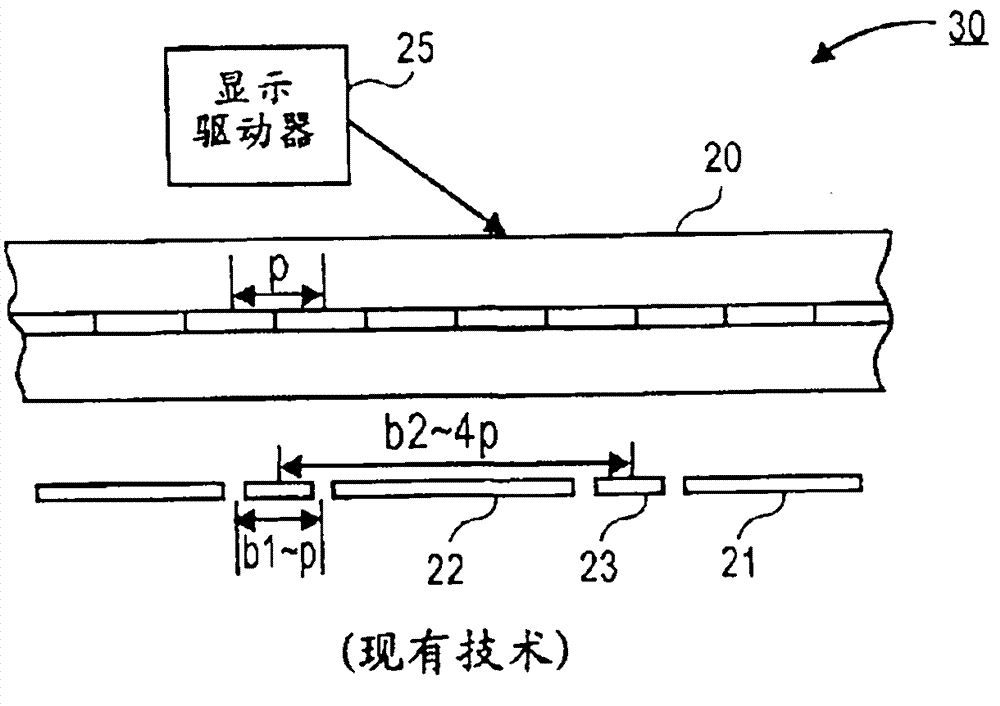
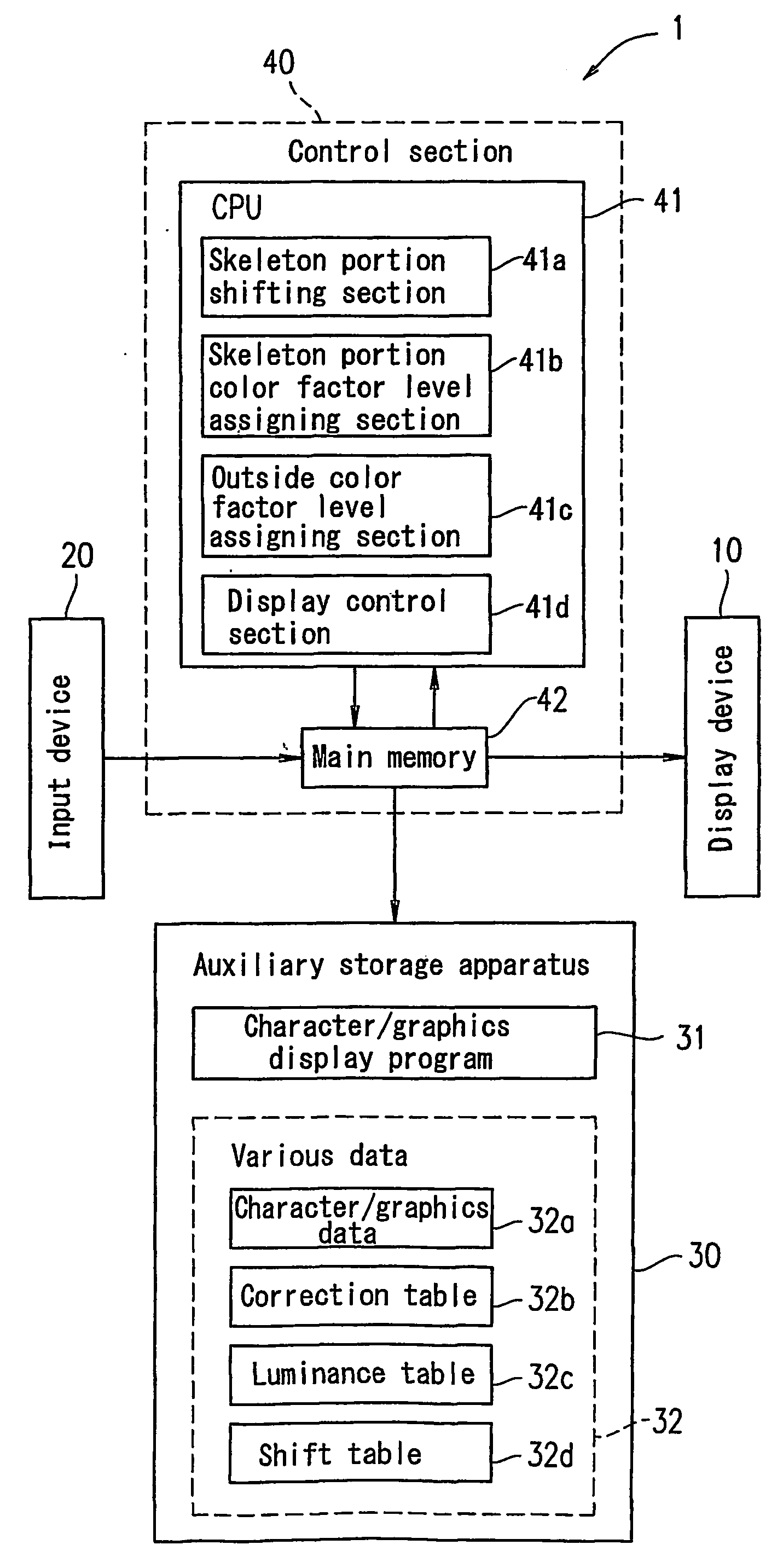
Display apparatus, information display method, information display program, readable recording medium, and information apparatus
InactiveUS20050219261A1Adjustable thicknessCathode-ray tube indicatorsSubpixel renderingComputer graphics (images)
A display apparatus (1) comprises a display device (10) and a control section (40) for displaying characters by using sub-pixel rendering. Each character is displayed in a frame having a predetermined size. The control section (40) has a skeleton portion shifting section (41a) which shifts a center of a skeleton portion of a character toward a center of the frame using sub-pixel precision.
Owner:SHARP KK
Image device with pixel dots with multi-primary colors
Owner:VP ASSETAB
Display device and sub-pixel rendering method
ActiveCN105096754AUniform brightnessIncrease opening ratioIdentification meansDisplay deviceComputer science
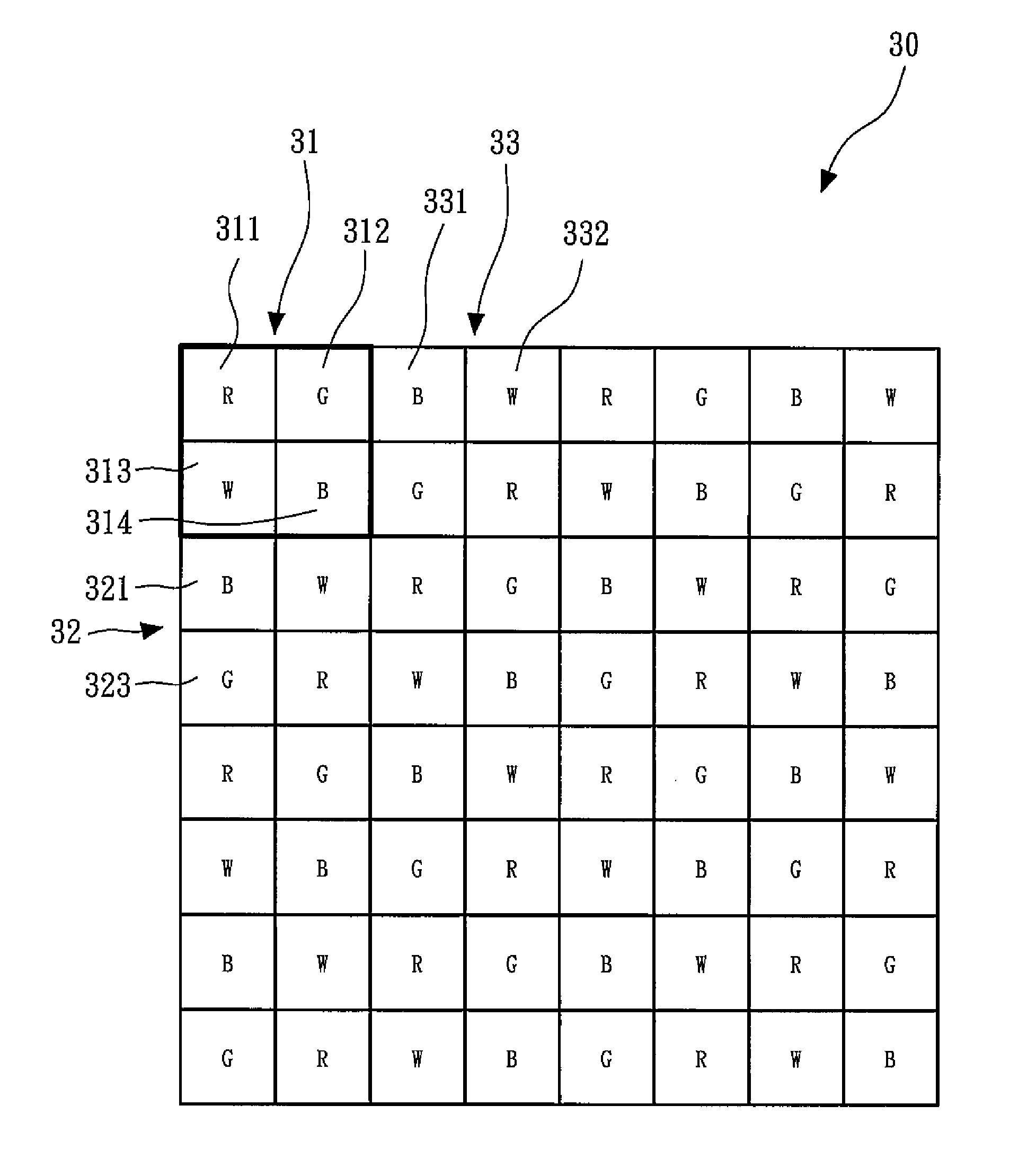
The invention discloses a display device and a sub-pixel rendering method. The display device comprises a pixel array, wherein the pixel array comprises a plurality of first sub-pixels, a plurality of second sub-pixels and a plurality of third sub-pixels; the first sub-pixels and the second sub-pixels are arranged in an alternating spacing manner in the first direction, and the third sub-pixels are continuously arranged along the first direction; the first sub-pixels and the third sub-pixels are arranged in an alternating spacing manner in the second direction, and the second sub-pixels are continuously arranged along the second direction; the first direction is vertical to the second direction; any one first sub-pixel is adjacent to two second sub-pixels in the first direction, and is adjacent to two third sub-pixels in the second direction. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the sub-pixels with the maximum brightness in the pixel array are uniformly distributed, and thus the brightness of the whole pixel array is uniform.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS +1
Array substrate, display device and subpixel rendering method
ActiveCN105185268AImprove distribution uniformityImprove the display effectIdentification meansDisplay deviceComputer science
An embodiment of the invention discloses an array substrate, a display device and a subpixel rendering method. The array substrate comprises a pixel array. The pixel array comprises first pixel sequences and second pixel sequences which are arranged at intervals along a first direction, wherein each first pixel sequence comprises a plurality of first pixel units arranged along a second direction, and each first pixel unit comprises a first subpixel, a second subpixel and a third subpixel which are arranged along the second direction; each second pixel sequence comprises a plurality of second pixel units arranged along the second direction, and each second pixel unit comprises a third subpixel, a first subpixel and a second subpixel arranged along the second direction; the lengths, in the second direction, of each first subpixel, each second subpixel and each third subpixel are identical, and the widths, in the first direction, of each first subpixel, each second subpixel and each third subpixel are identical; each first pixel unit and the two second pixel units adjacent to the first pixel unit are arranged in a staggered manner, and the stagger distances are respectively width and the difference between length and width; the first direction is vertical to the second direction. By setting the stagger distances among the pixel units, the oblique line display effect is optimized.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS +1
Image color balance adjustment for display panels with 2d subpixel layouts
The subpixel rendering component of a display system provides the capability to substitute a second subpixel rendering filter for a first subpixel rendering filter for computing the values of certain subpixels on the display panel when the input image data being rendered indicates an image feature that may give rise to a color balance error at some portion of the displayed output image. An image processing method of correcting for color balance errors detects the location of a subpixel being rendered, and for certain subpixels, detects whether the input image data indicates the presence of a particular image feature. When the image feature is detected for particular subpixels being processed, a second subpixel rendering image filter is substituted for a first subpixel rendering image filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Sub-pixel rendering method
The embodiment of the invention provides a sub-pixel rendering method applied to rendering of a Delta type sub-pixel arrangement structure. The method comprises the steps of dividing multiple sub-pixels into multiple pixel regions, wherein each pixel region comprises 2*2 logical pixels, each logical pixel comprises two sub-pixels, and each logical pixel corresponds to one pixel; calculating the average color difference delta EH between two adjacent rows of pixels in each pixel region and the average color difference delta EV between two adjacent lines of pixels in each pixel region, and comparing delta EH with delta EV; when delta EH is larger than delta EV, making two pixels in the same row in the pixel region share two sub-pixels; and when delta EH is smaller than delta EV, making two pixels in the same line in the pixel region share two sub-pixels. Different sub-pixel rendering methods are adopted according to the values of delta EH and delta EV, and the technical effect of solving the problem of distortion during displaying of an image border region can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com