Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
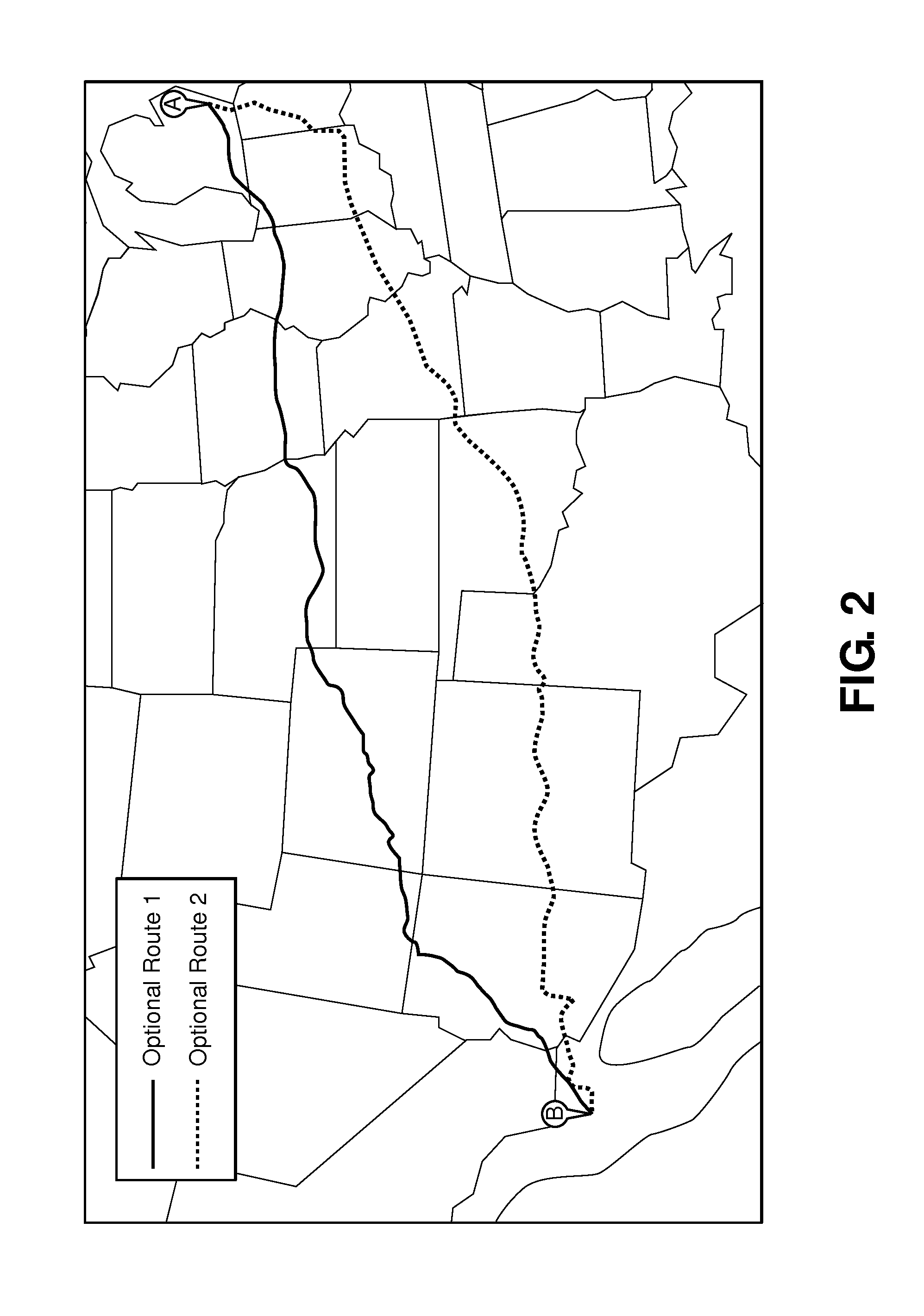
620 results about "Digital mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital mapping (also called digital cartography) is the process by which a collection of data is compiled and formatted into a virtual image. The primary function of this technology is to produce maps that give accurate representations of a particular area, detailing major road arteries and other points of interest. The technology also allows the calculation of distances from one place to another.
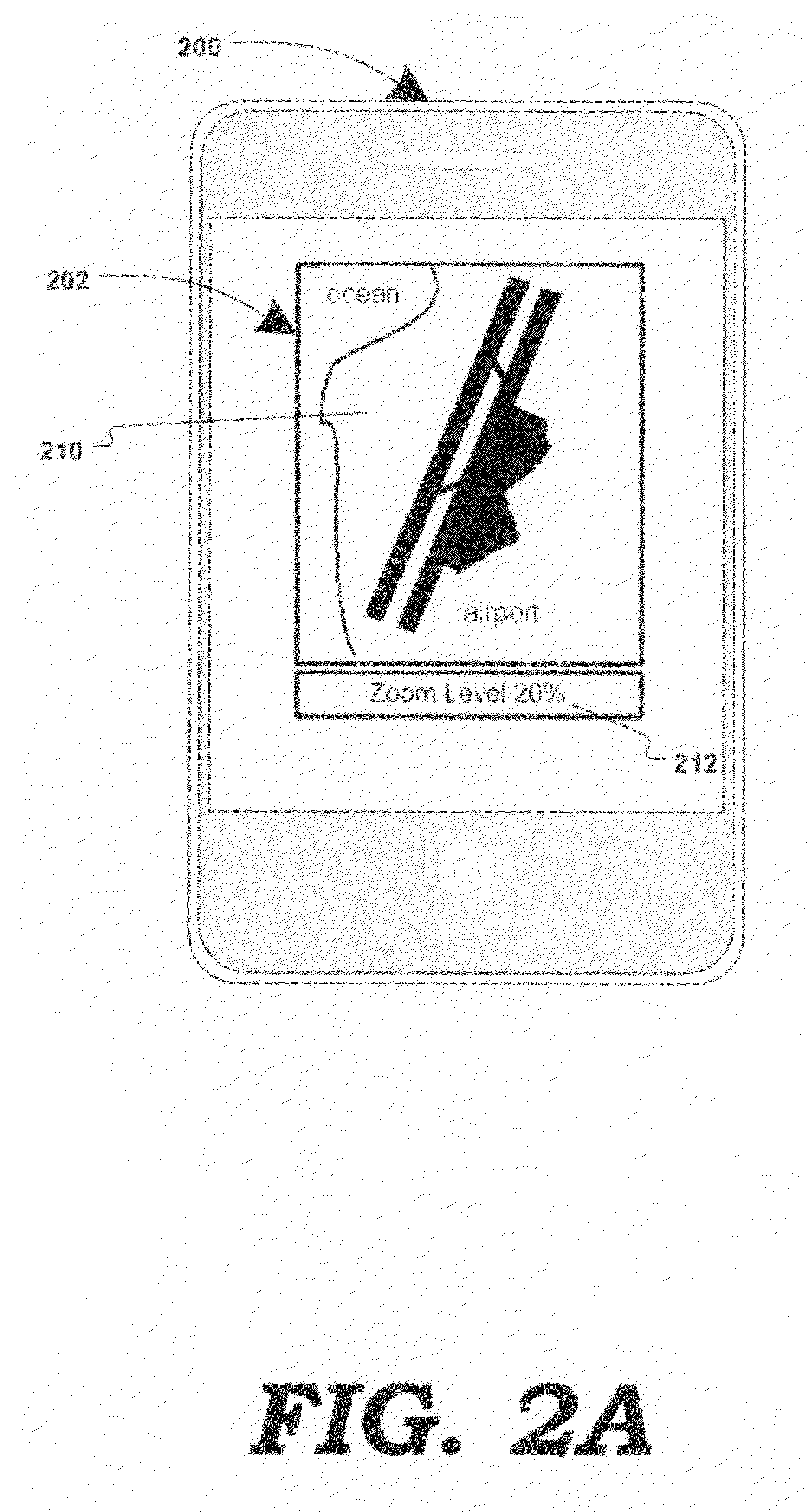
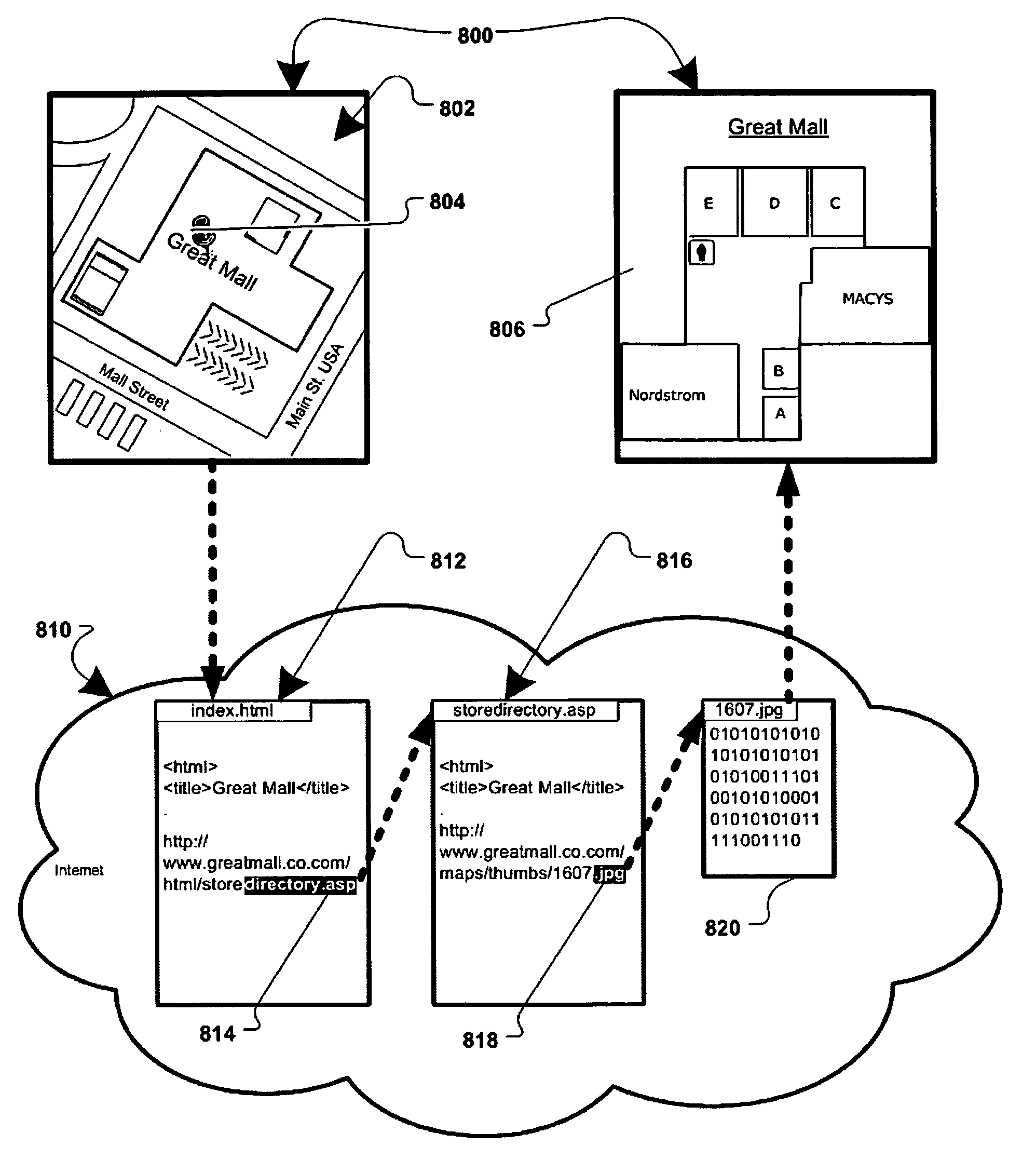
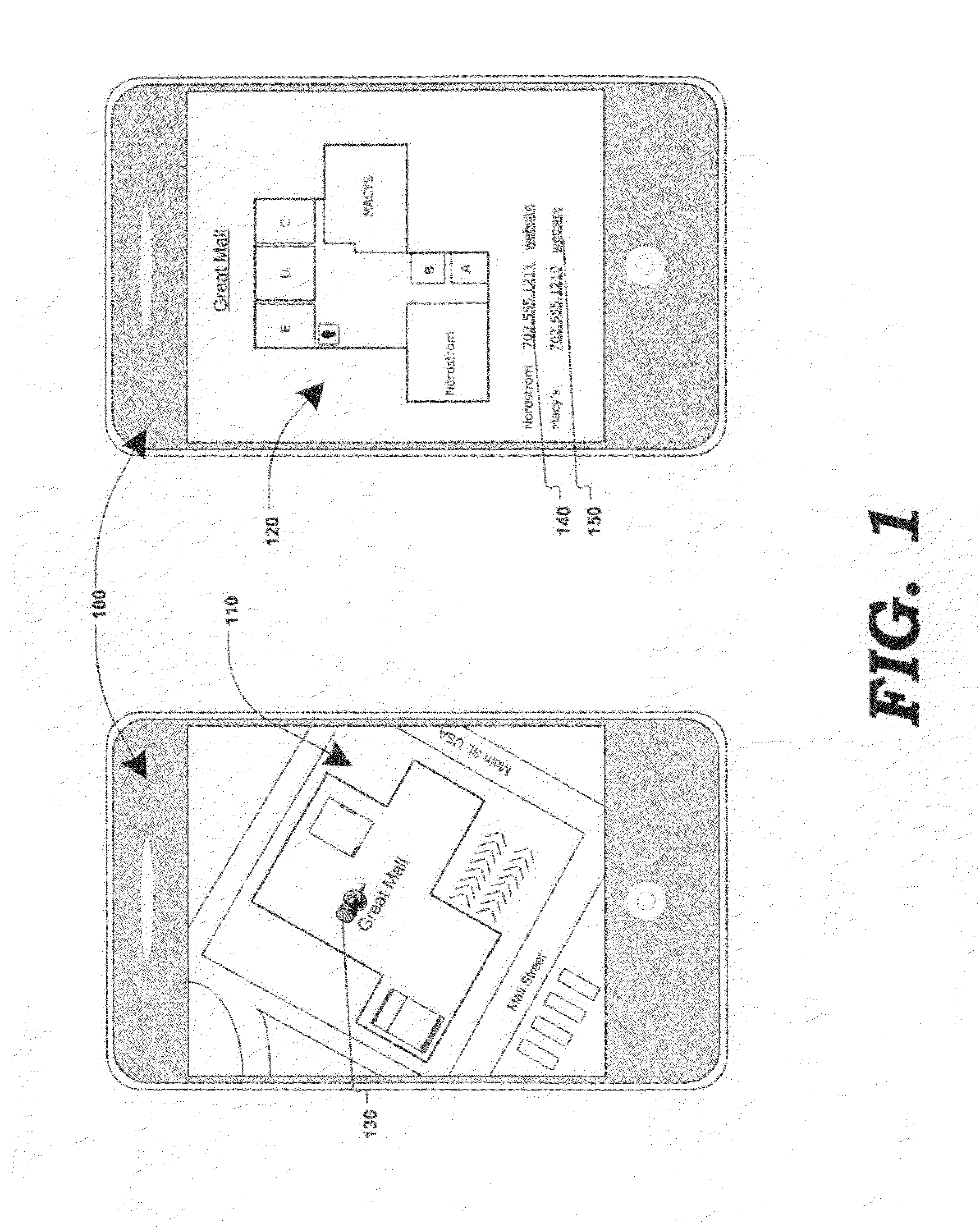
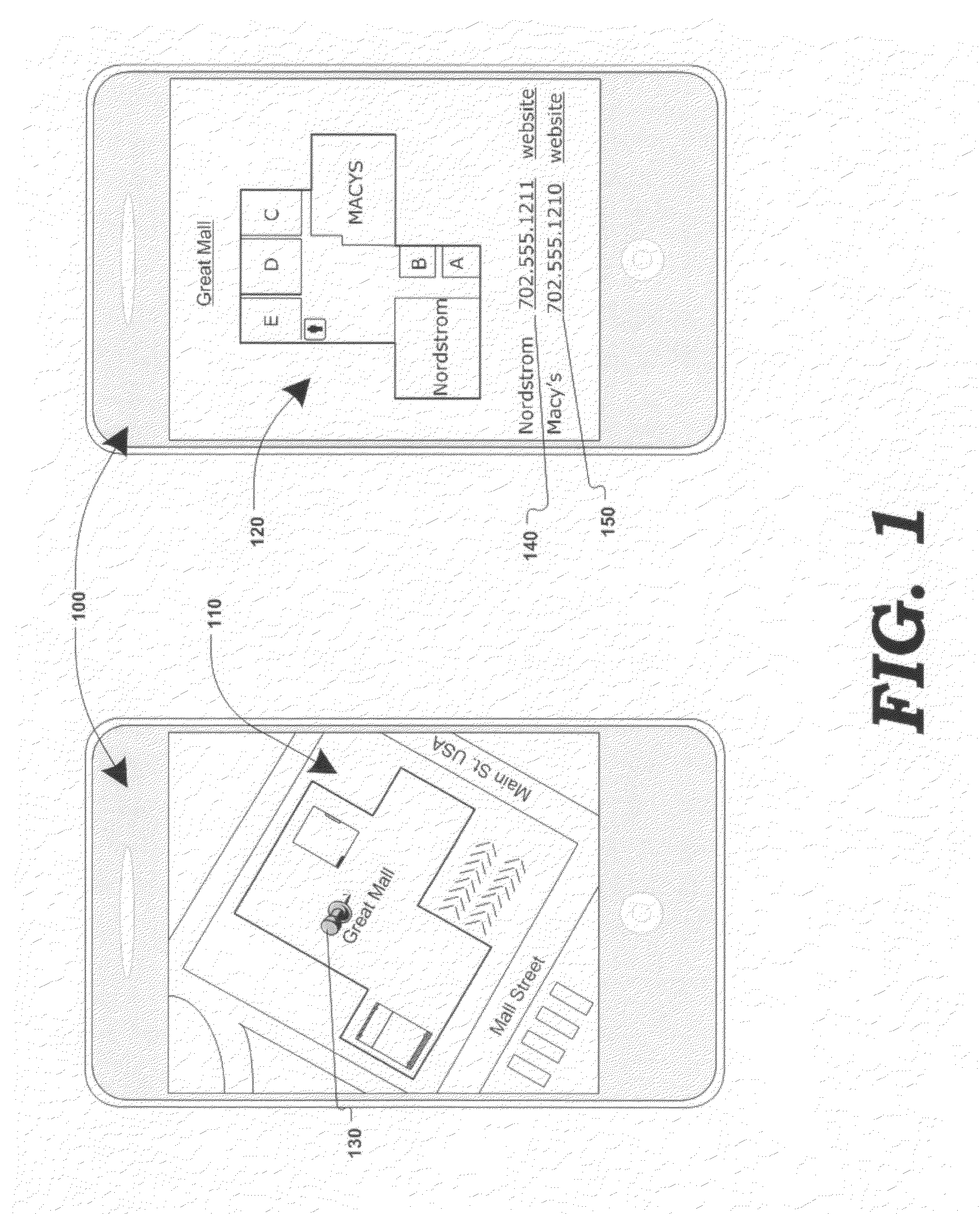
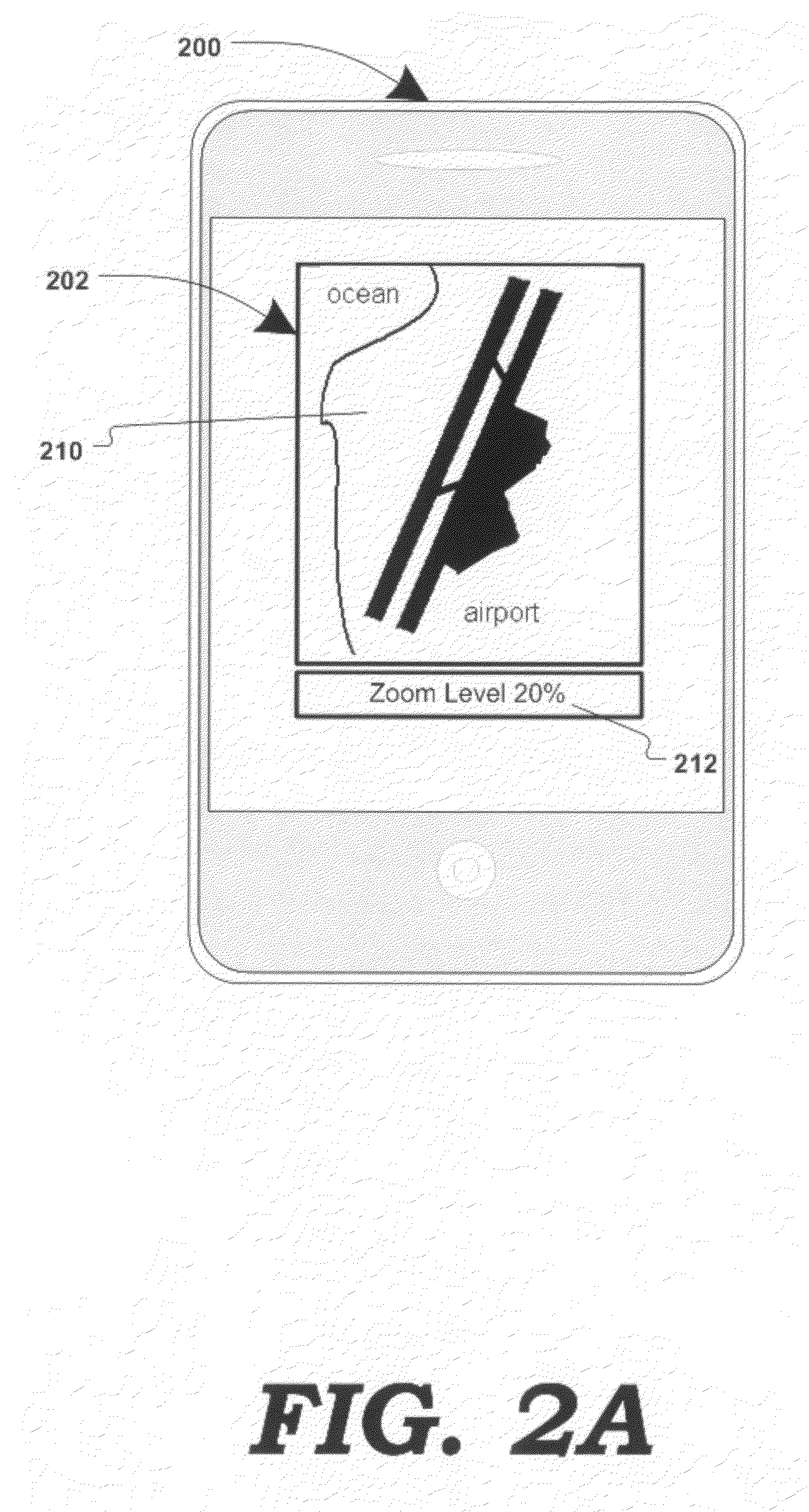
Method and system for associating content with map zoom function
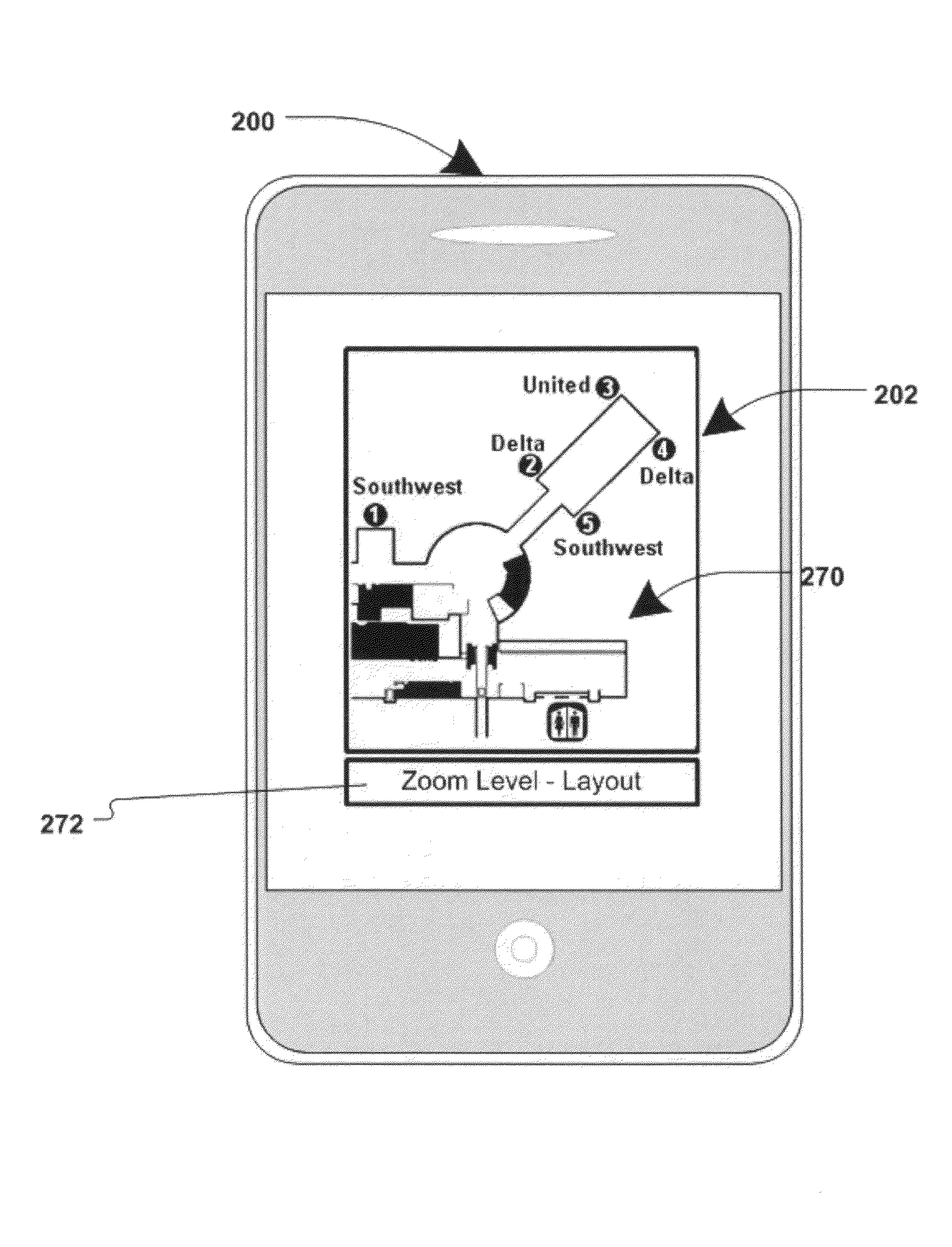
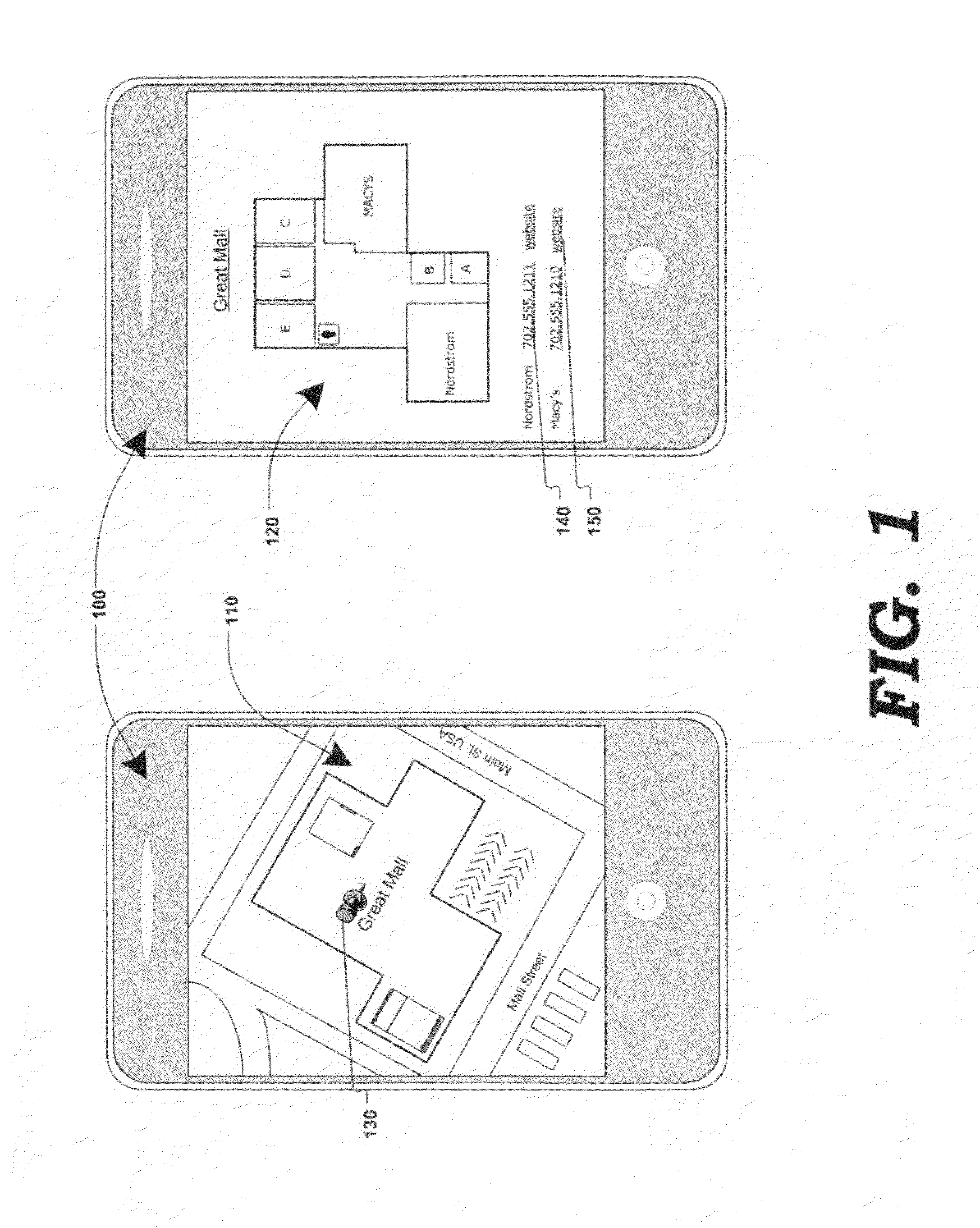
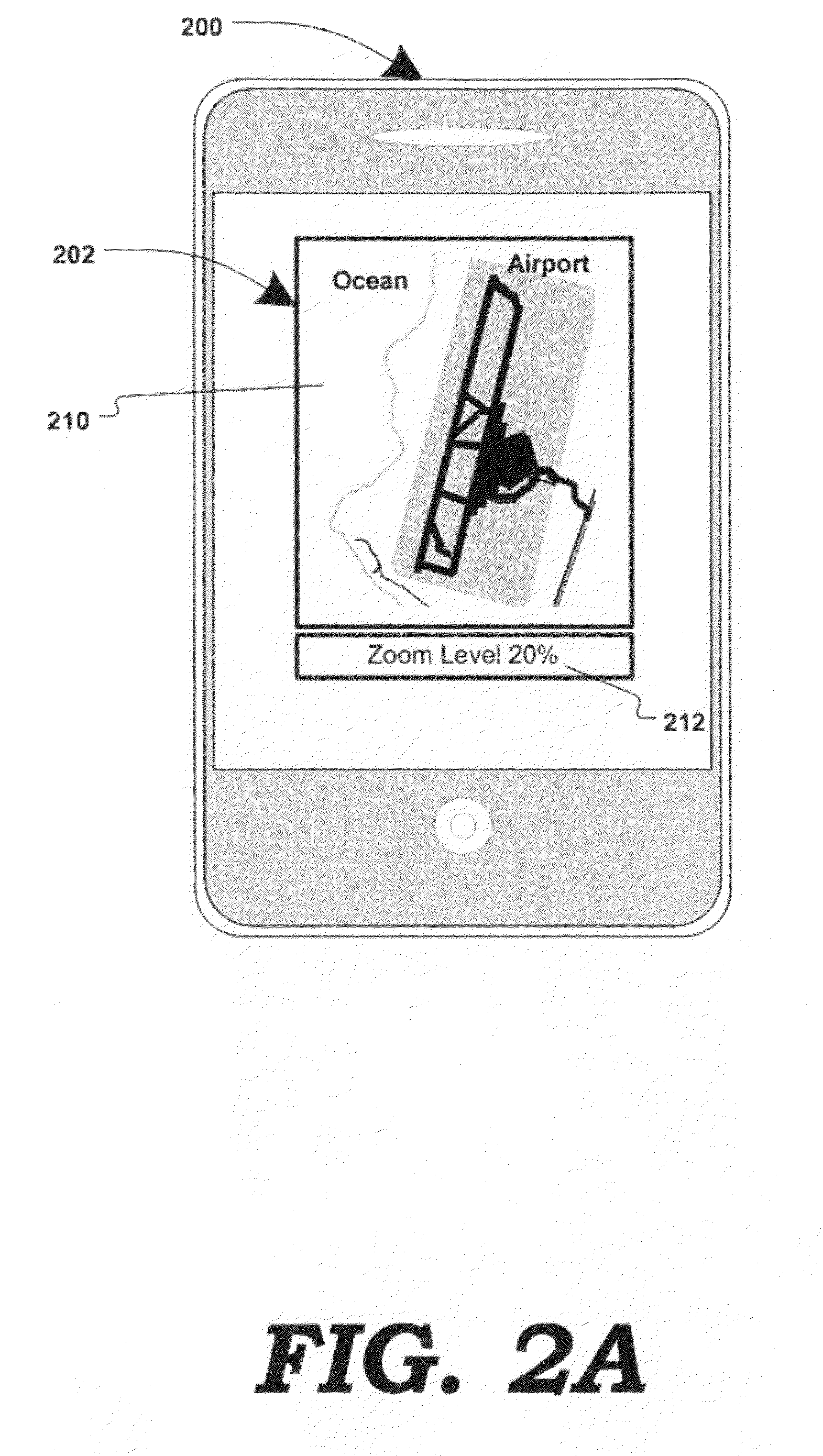
Various methods, systems and apparatus for displaying content associated with a point-of-interest (“POI”) in a digital mapping system, or a region within the digital map, are disclosed. One such method may include detecting a change in the zoom level of an electronic map displayed on a computing device, determining if the new zoom-level is at a pre-determined zoom level (e.g. at maximum zoom), identifying a POI on the map, retrieving content associated with the POI (“POI content”) and displaying the POI content. The method may further include detecting a change in the zoom, or pan, of the digital map while POI content is displayed, and removing the POI content in response.
Owner:JAKOBSON GABRIEL +1
Displaying content associated with electronic mapping systems
Various methods, systems and apparatus for displaying alternate content in a digital mapping system, are disclosed. One such method may include detecting a change in a zoom level of an electronic map displaying geographic content (e.g. tile-based digital map, satellite image, etc.) on a computing device (e,g. desktop / laptop, smart phone, etc, running Windows®, Linux®, Mac OS®, iOS®. Android®, etc.); determining a predetermined (eg. maximum) zoom level has been reached; retrieving alternate content, and displaying the alternate content in addition to, or in place of, some-or-all of the geographic content. The method may further include detecting a zoom-out command while the alternate content is being displayed, and in response, restoring the display of the geographic content (e.g. at the maximum zoom level and / or last state of the geographic content display prior to displaying the alternate content.) Alternate content may be associated with any portion of geographic content displayed (e.g. the portion of the geographic content visible at the maximum zoom level) and may be selected via various algorithms and be manipulate-able via map display application controls.
Owner:JAKOBSON GABRIEL +1
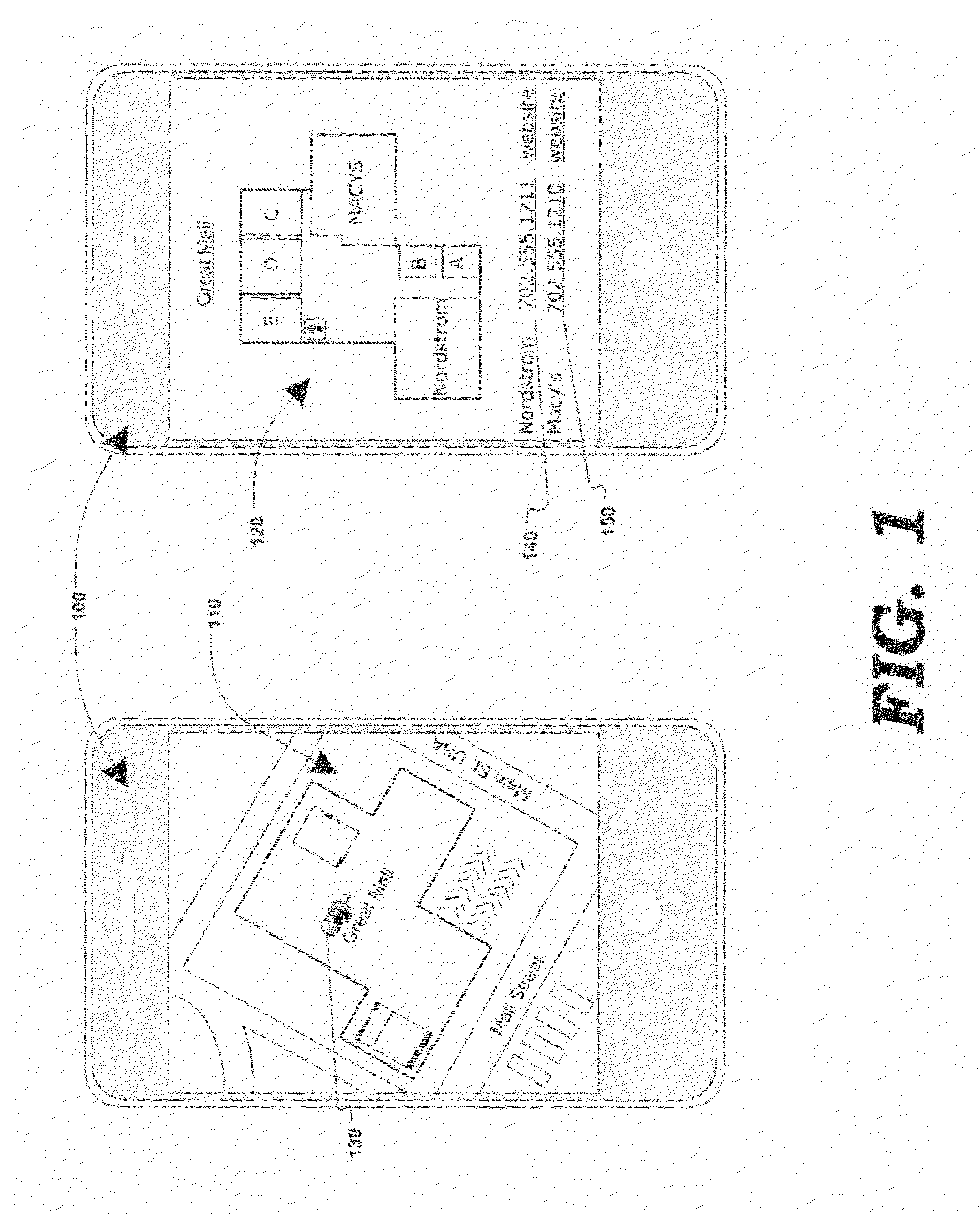
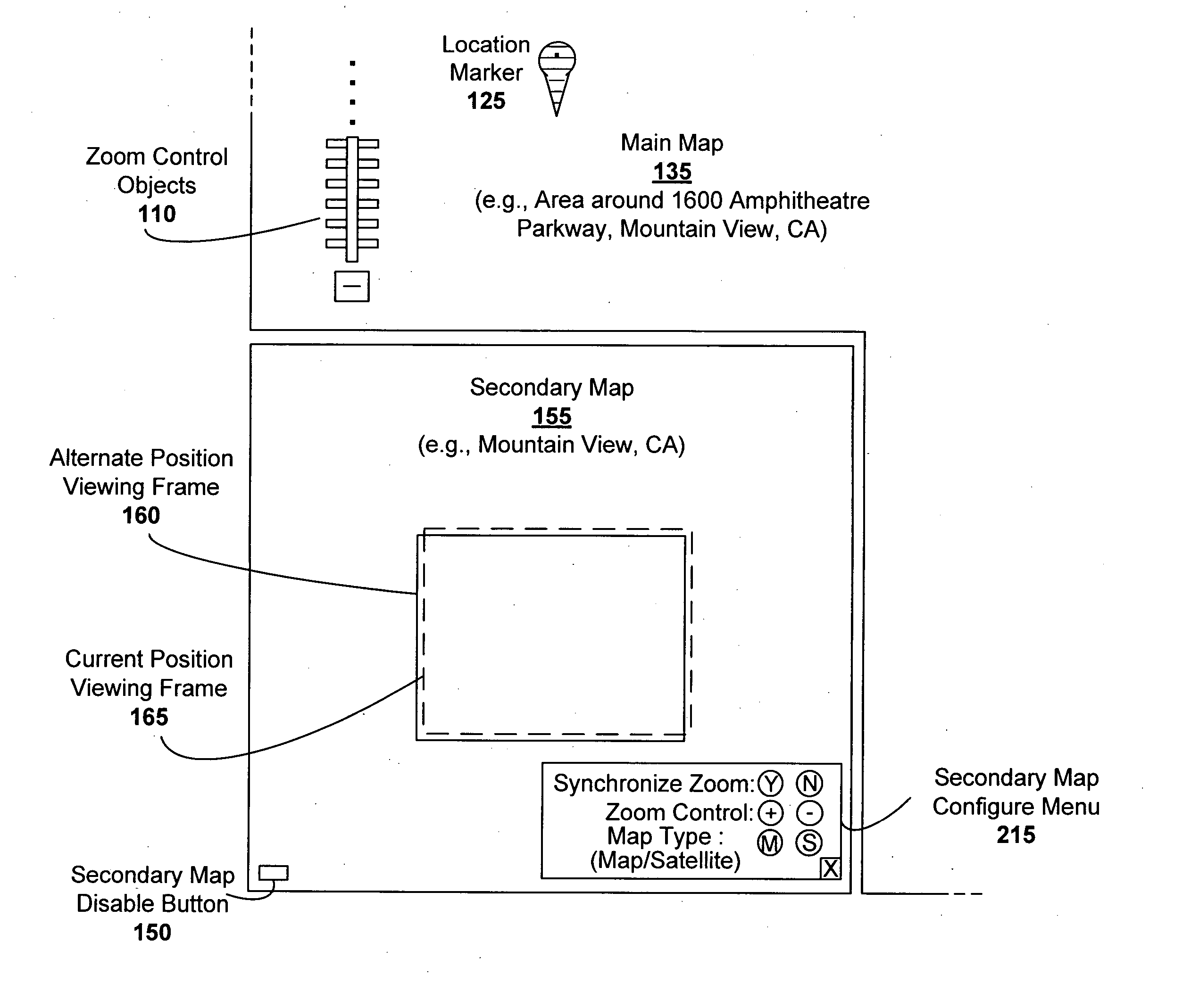
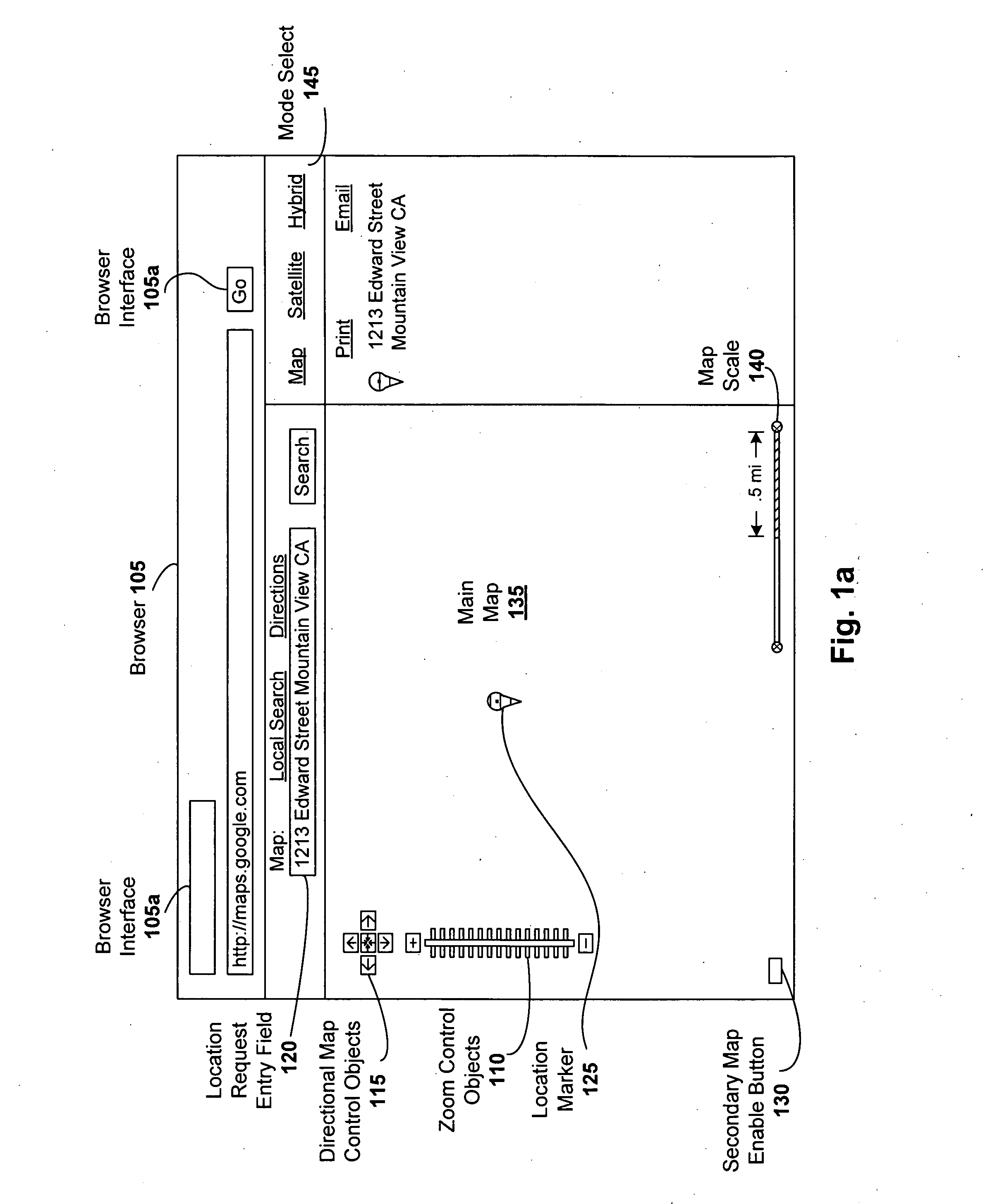
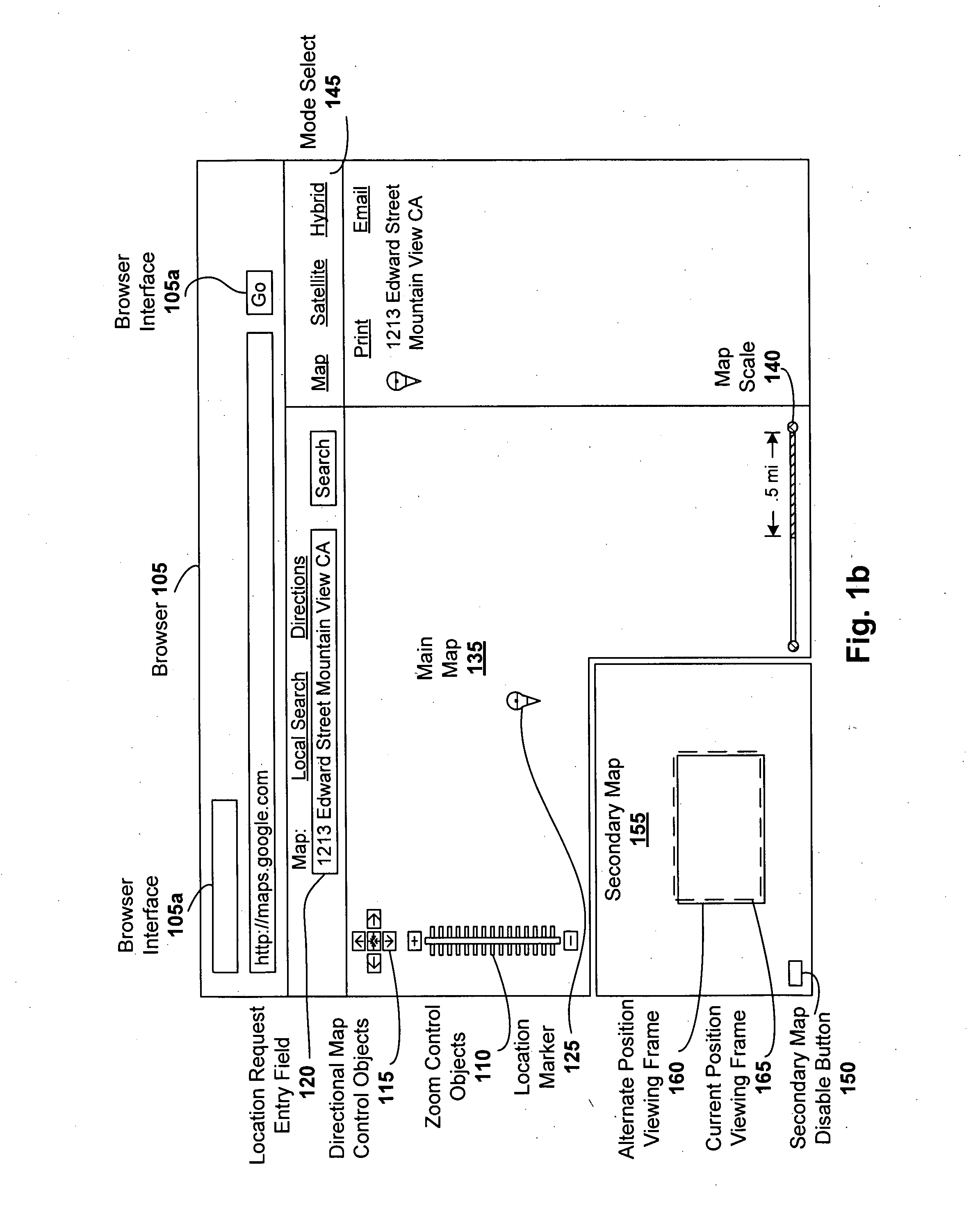
Secondary map in digital mapping system
ActiveUS20060139375A1Instruments for road network navigationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSatellite imageComputer science
Digital mapping techniques are disclosed that provide more flexibility to the user through the use of multiple views of map information, including a secondary map and a main map. The secondary map can provide the user with either a zoomed out or in relative to the main map, or a different type of map view (e.g., satellite images). The secondary map can be turned on and off by the user. The secondary map may include one or more viewing frames that indicate views (e.g., current and alternate views) of the main map. The user can move the main map, viewing frame, or secondary map to achieve desired map views. During such movement, the relationship between the main and secondary maps can be synchronous, partially synchronous, or serial.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
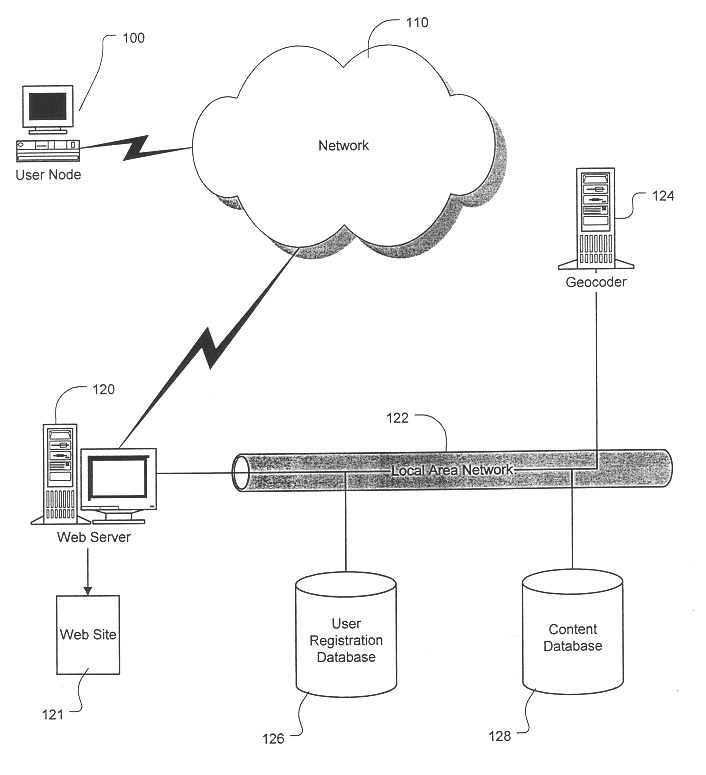
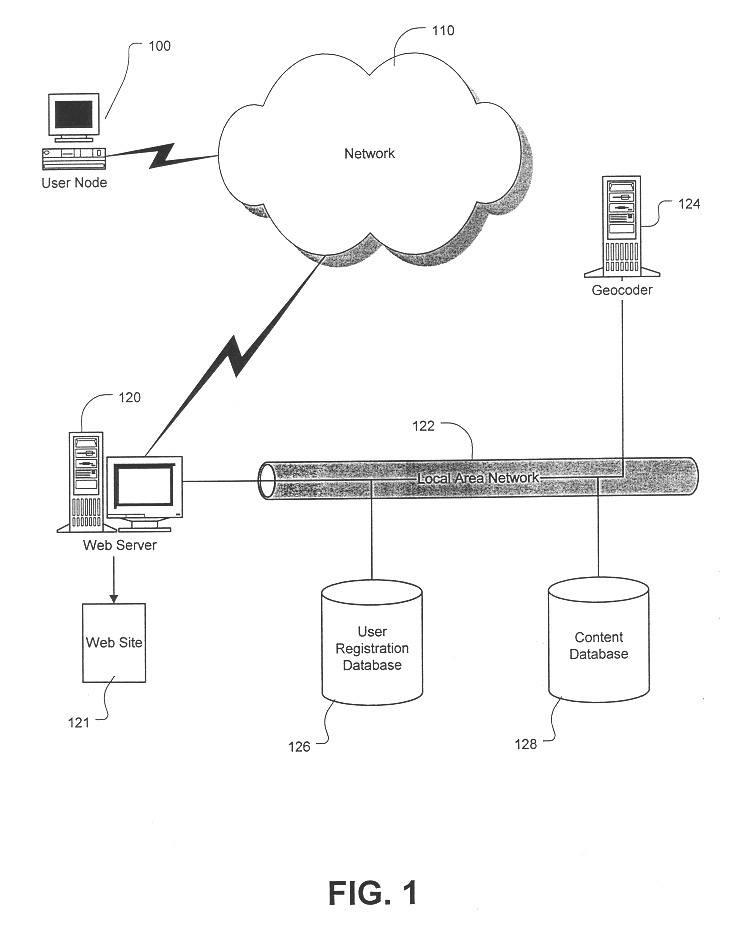
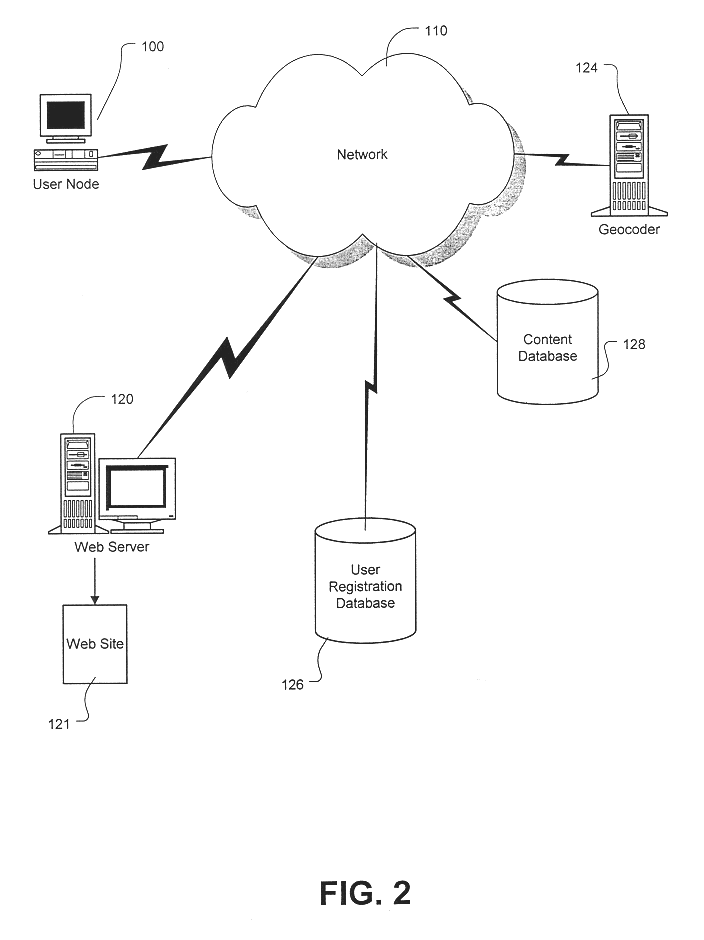
System and method for providing geographically-related content over a network
InactiveUS6629136B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsGeolocationData mining
The present invention is designed to seamlessly deliver localized content to users on a network corresponding to each users' geographic area. In particular, the present invention considers a user's geographic location information (such as an address) in the determination of which geographic areas, if any, correspond to the user, and automatically delivers content associated with those geographic areas. By associating a unique spatial identity with a user, the present invention may use various known digital mapping spatial techniques to provide the user with information relevant to the user's location.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Method and system for associating content with map zoom function
InactiveUS20090198767A1Web data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication softwareWorkstation
Various methods, systems and apparatus for displaying content associated with a point-of-interest (“POI”) in a digital mapping system, are disclosed. One such method may include detecting a change in the zoom level of an electronic map displayed on a computing device, determining if the new zoom-level is at a pre-determined zoom level (e.g. at maximum zoom), identifying a POI on the map, retrieving content associated with the POI (“POI content”) and displaying the POI content. The method may further include detecting a change in the zoom, or pan, of the digital map while POI content is displayed, and removing the POI content in response. One apparatus, according to aspects of the present invention, may include means of detecting a change in the zoom level in a digital map displayed through an application (e.g. a web browser, an application on web-enabled cellular phones, etc., displaying a map generated by a service such as Google Maps®, Yahoo! Maps®, Windows Live Search Maps®, MapQuest®, etc.) on a computing device (e.g. personal computer, workstation, thin client, PDA, cellular phone / smart phone, GPS device, etc.) means of identifying a POI at the pre-determined zoom level, means of obtaining content associated with the POI, and means of displaying the POI content. POI content may be retrieved from a database (e.g. internet-based database); or, in an alternate embodiment, gathered by crawling websites associated with the POI. In one embodiment, POI content may be displayed as an image (e.g. a PNG file, GIF, Flash® component, etc.) superimposed on the digital map (e.g. as an overlay object on the map image.) In alternate embodiments, POI content may replace the digital map and may contain links to other content.
Owner:JAKOBSON GABRIEL +1
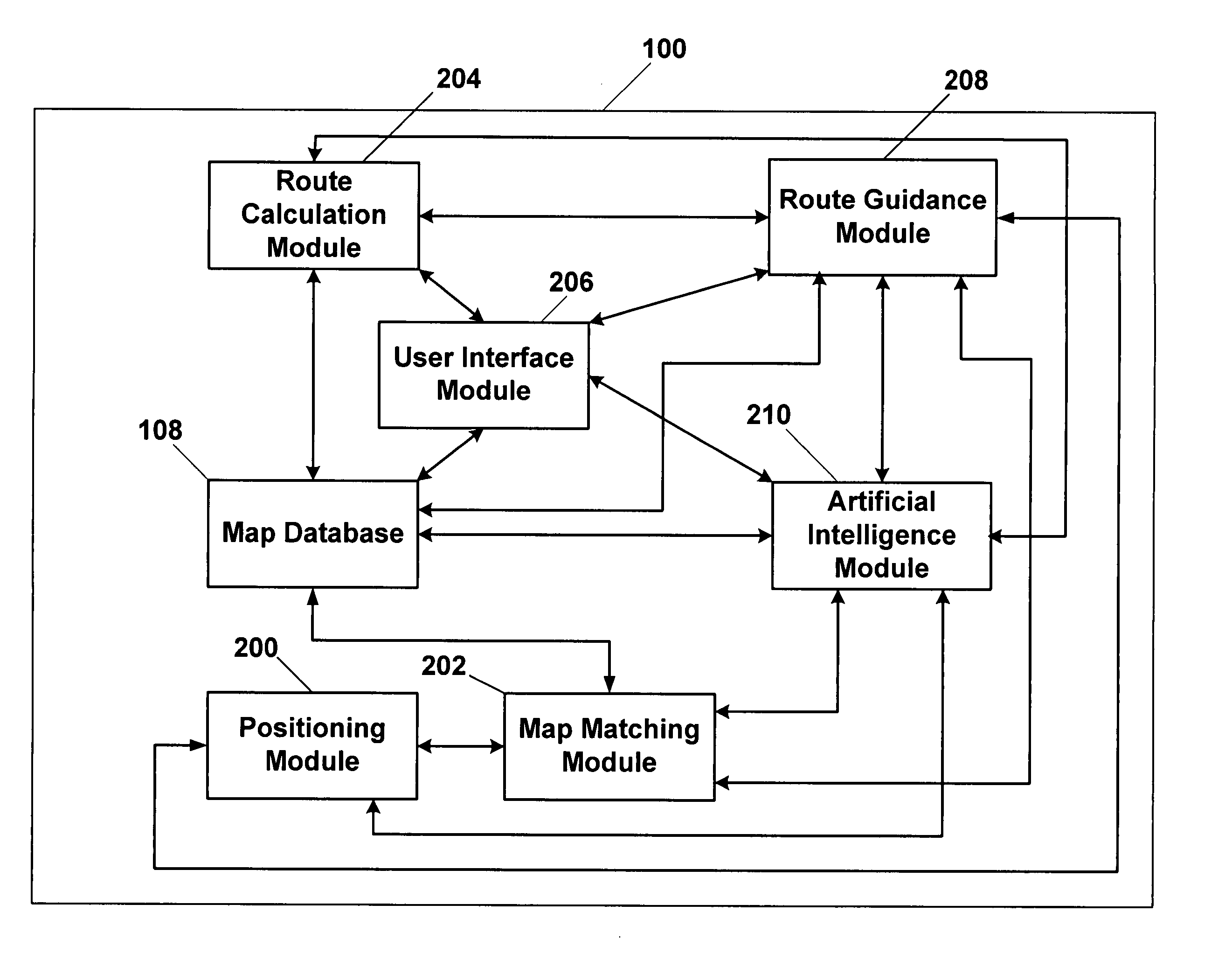
Adaptive navigation system with artificial intelligence
InactiveUS20050102098A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorRoad networks
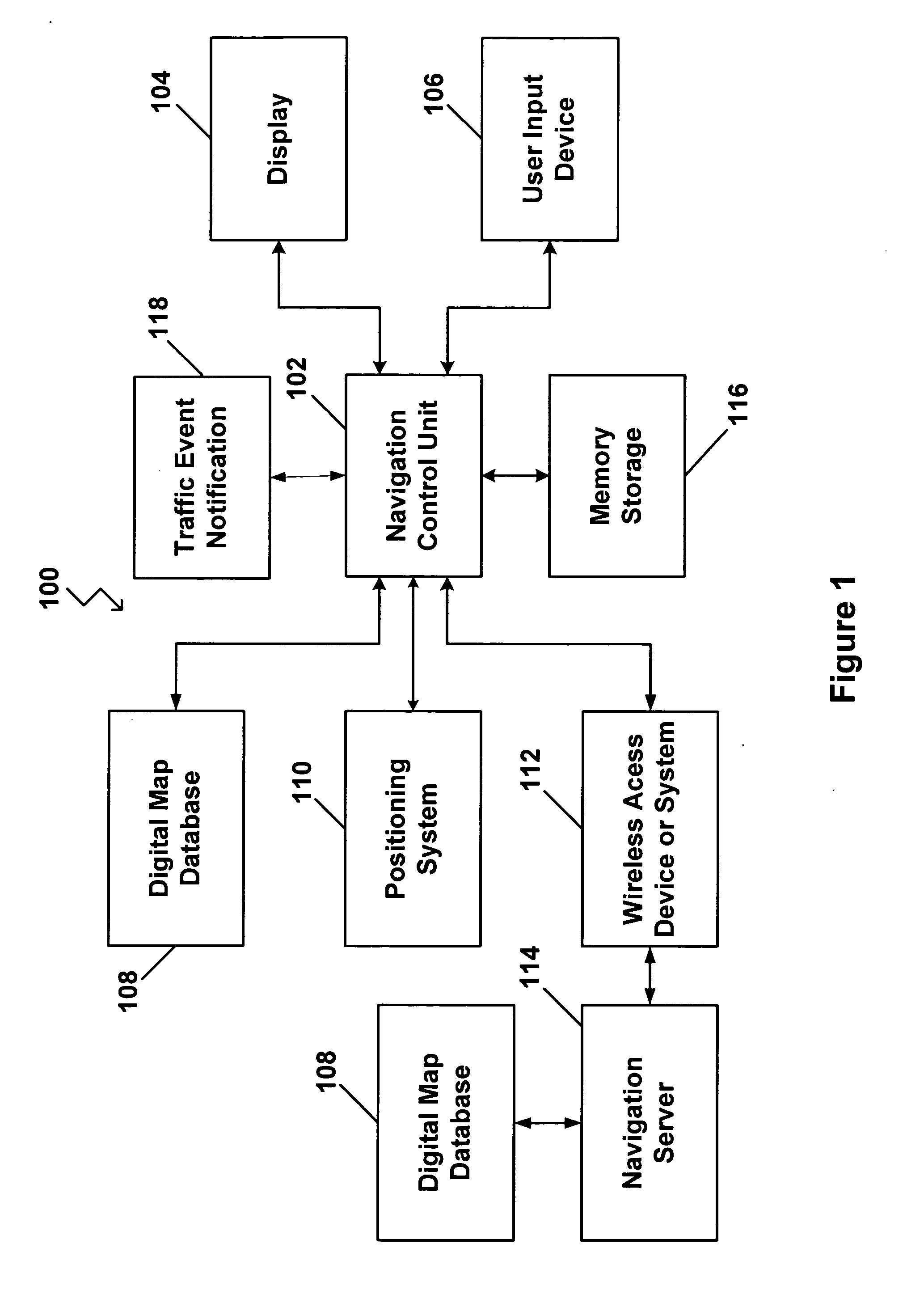
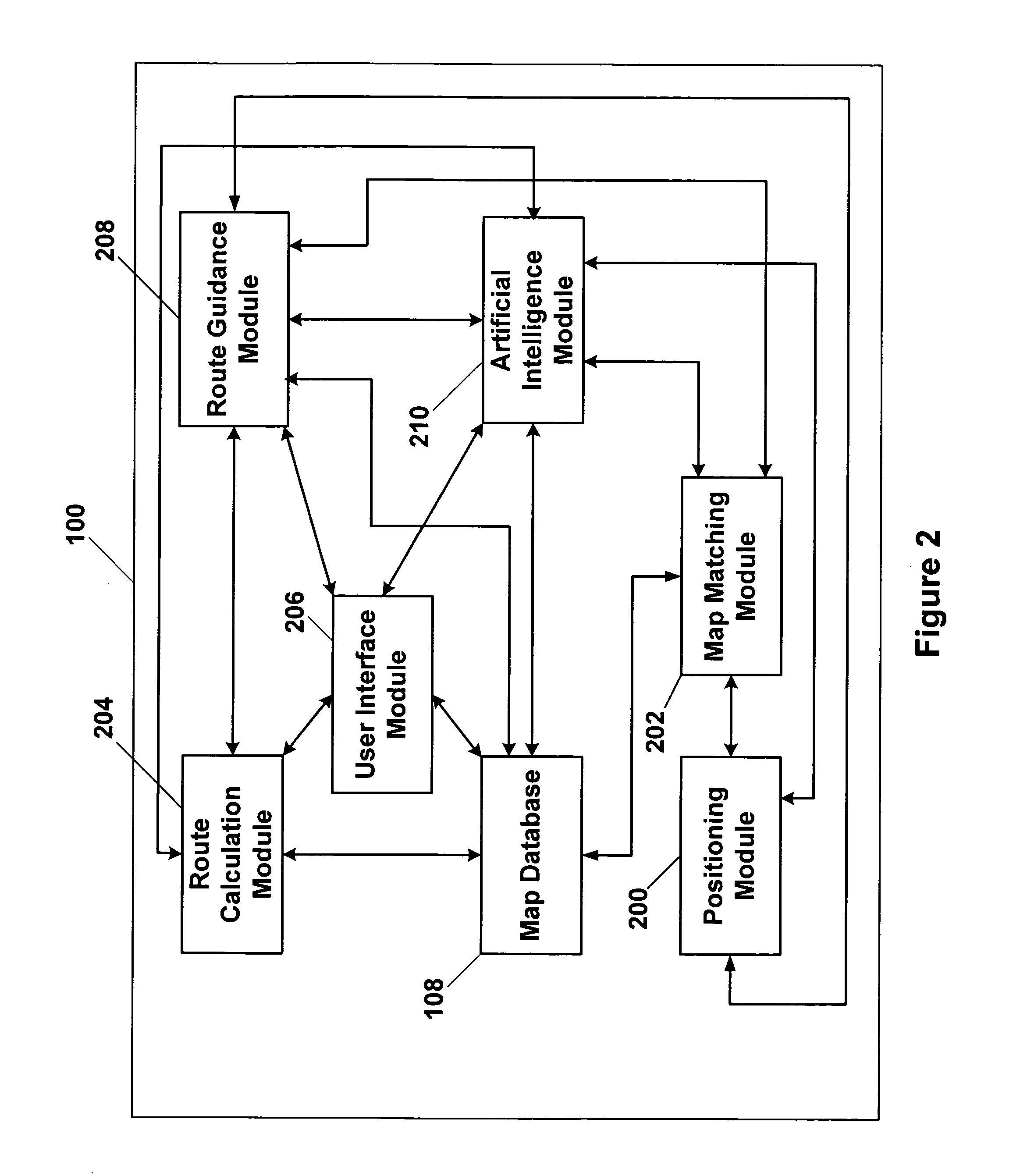
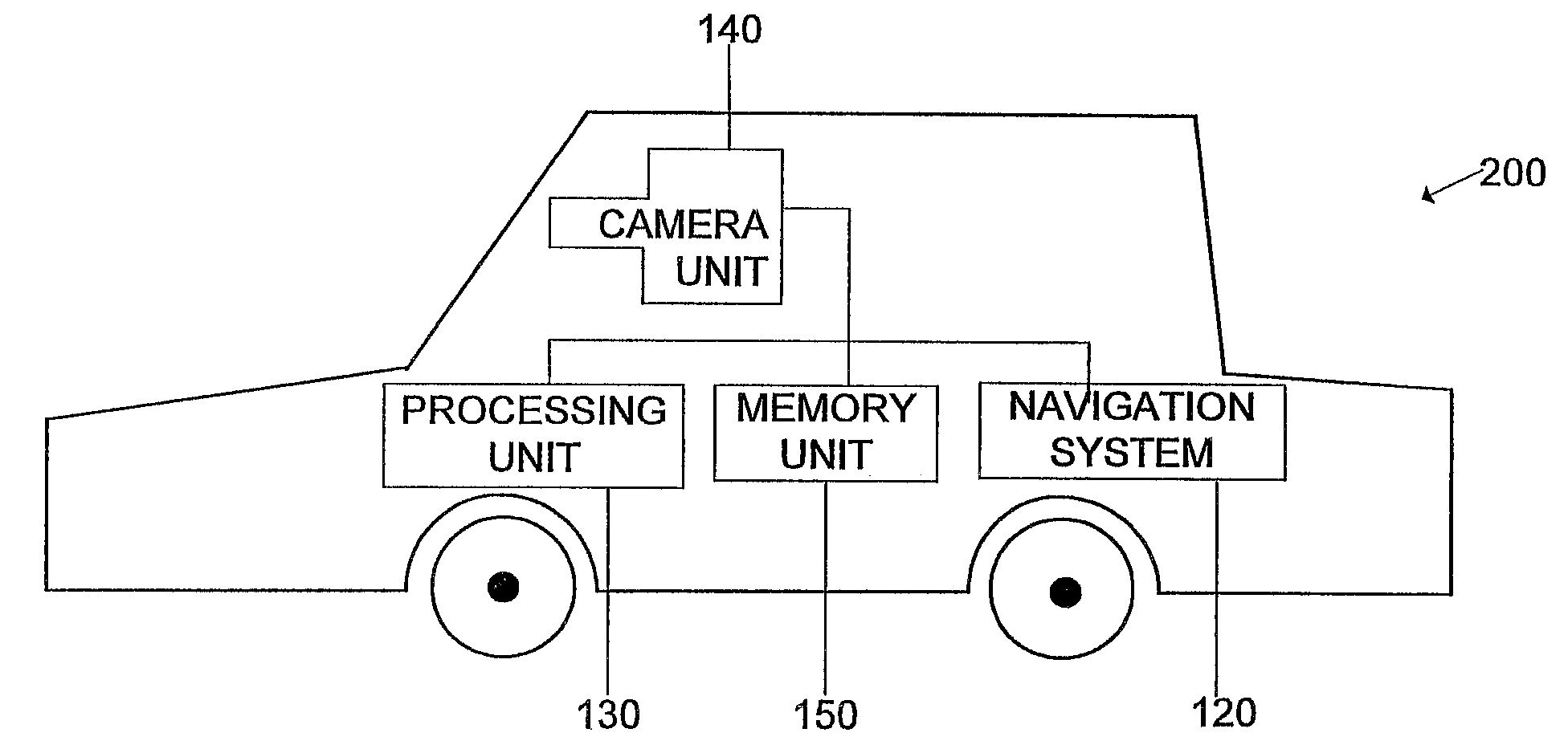
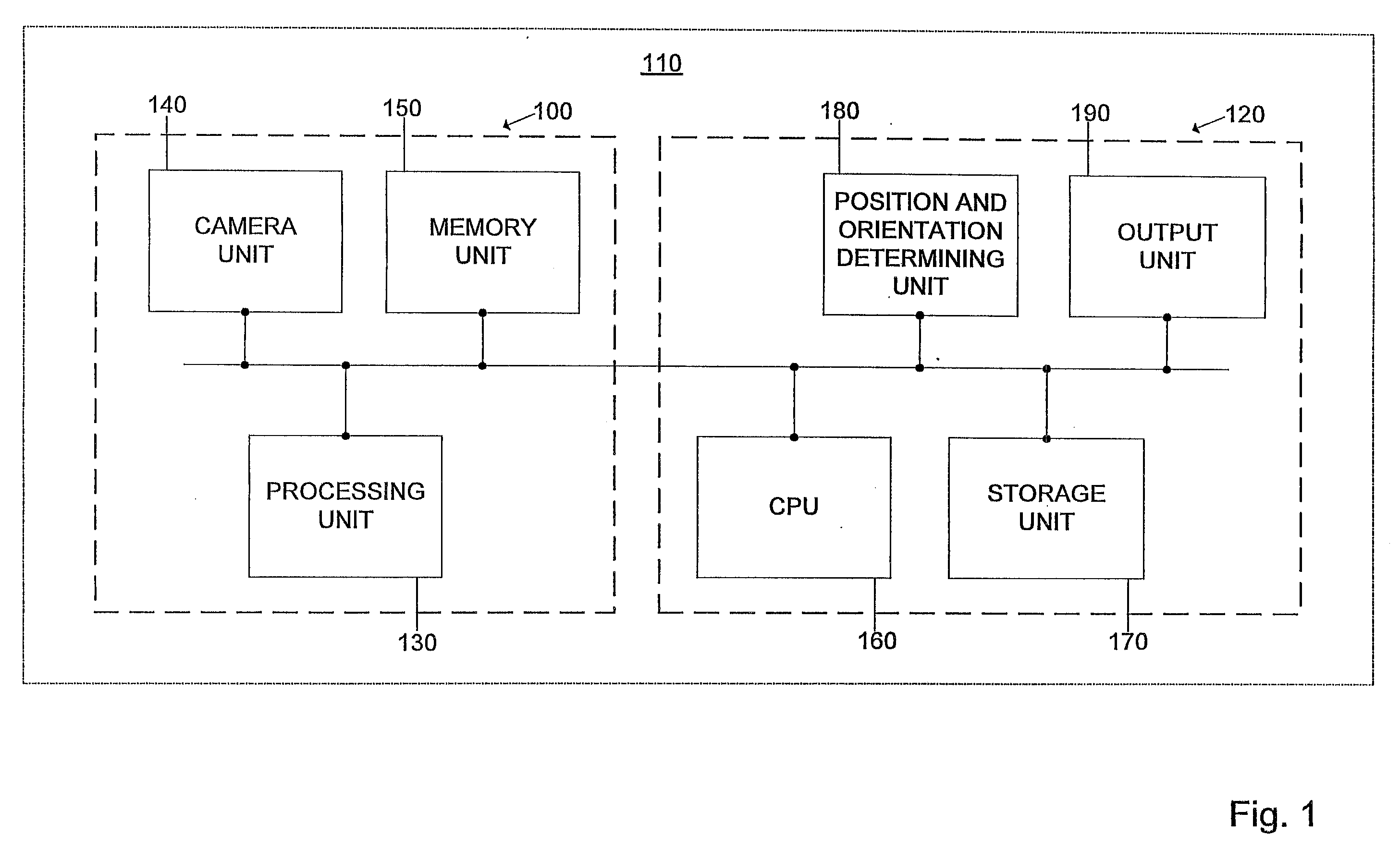
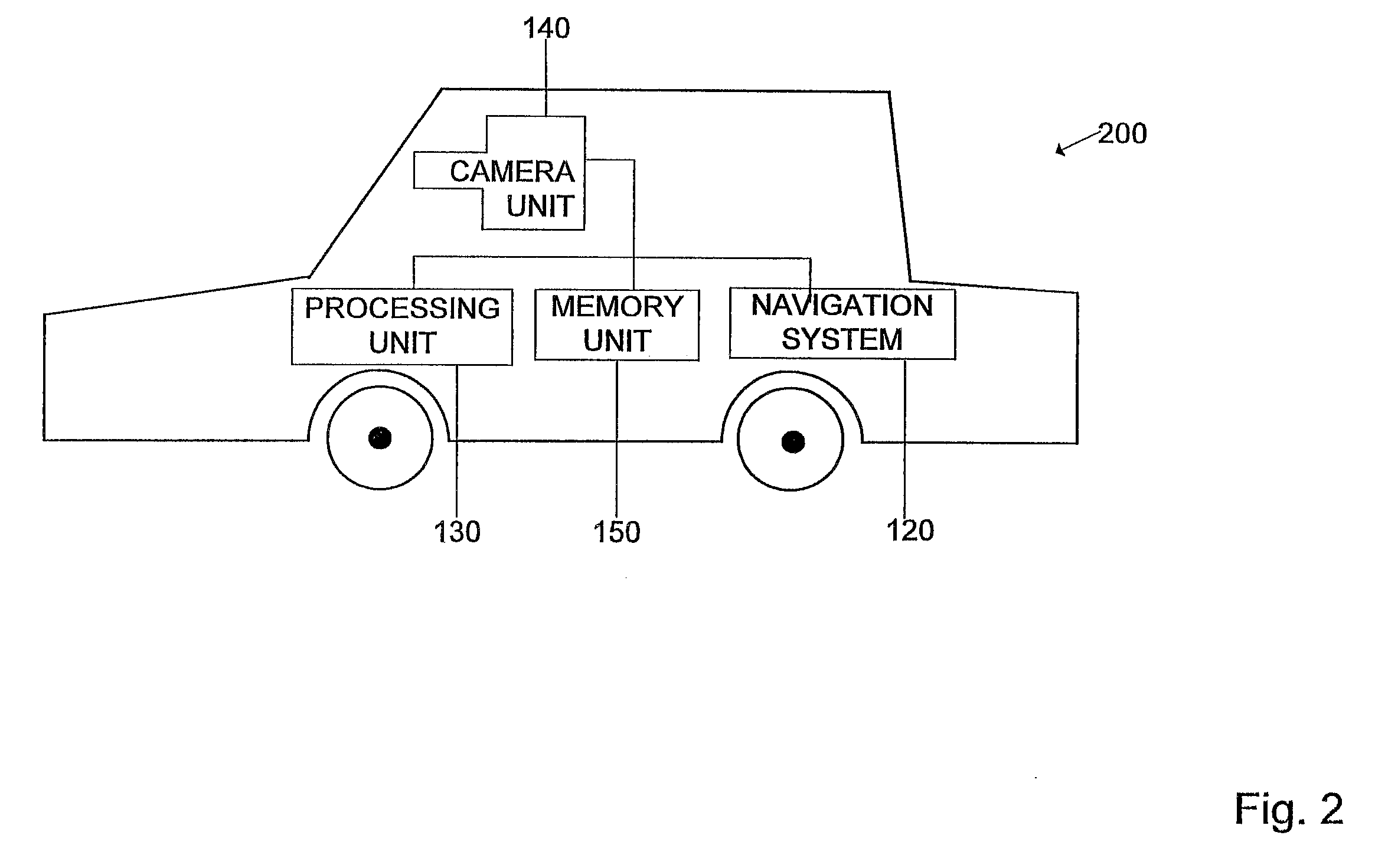
A vehicle navigation system that is capable of learning user habits / preferences, mistakes in a digital map database, and new roads that may have been added or constructed after release of the digital map database is disclosed. The vehicle navigation system monitors a driver's habits and updates a database to thereby cause the vehicle navigation system to have a preference for the driver's habits. The vehicle navigation system may also monitor the geographic position of the vehicle and allow the driver to update or change data contained in the digital map database if an error exists. The vehicle navigation system is also capable of learning new roads that exist that are not included in the road network map of the digital map database and is also capable of adding these new roads to the digital map database.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Accident Avoidance Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070152804A1Avoid accidentsAvoid and minimize effectVehicle seatsAnti-collision systemsCommunications systemDisplay device
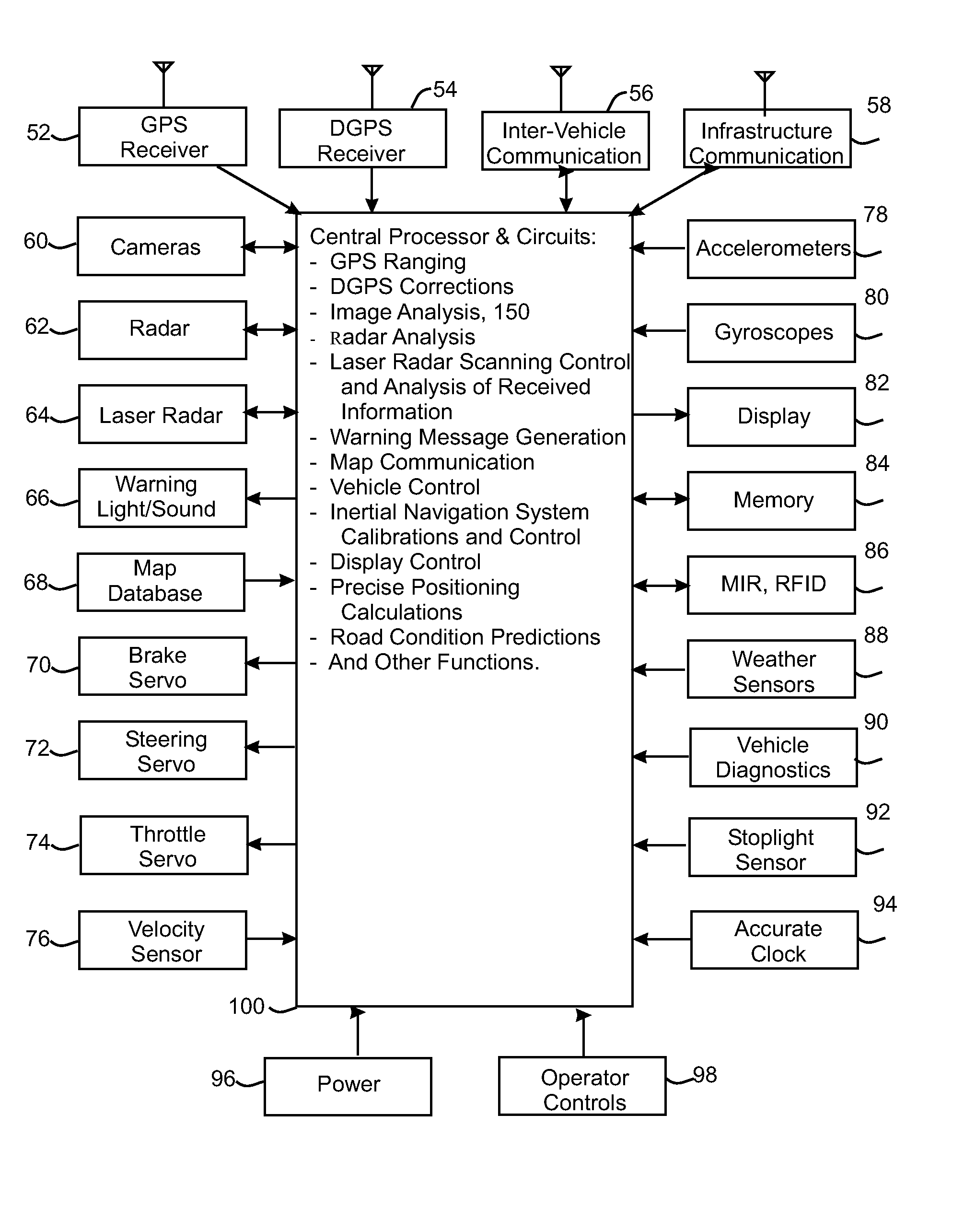
Accident avoidance system for a host vehicle includes a global positioning system residing on the host vehicle for determining the host vehicle's location as the host vehicle travels based on signals received from one or more satellites, a map database having digital maps corresponding to an area including the location of the host vehicle as determined by the global positioning system, a vehicle-to-vehicle communication system residing on the host vehicle operative for receiving signals including location information acquired by global positioning systems residing on other vehicles directly from the other vehicles indicating the locations of the other vehicles, and a navigation system including a display residing on the host vehicle for displaying images to an occupant of the host vehicle showing the digital maps and indications of the locations of the host vehicle and the other vehicles on the digital maps. The navigation system also updates the images shown on the navigation system display to reflect changes in the locations of the host vehicle and the other vehicles.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
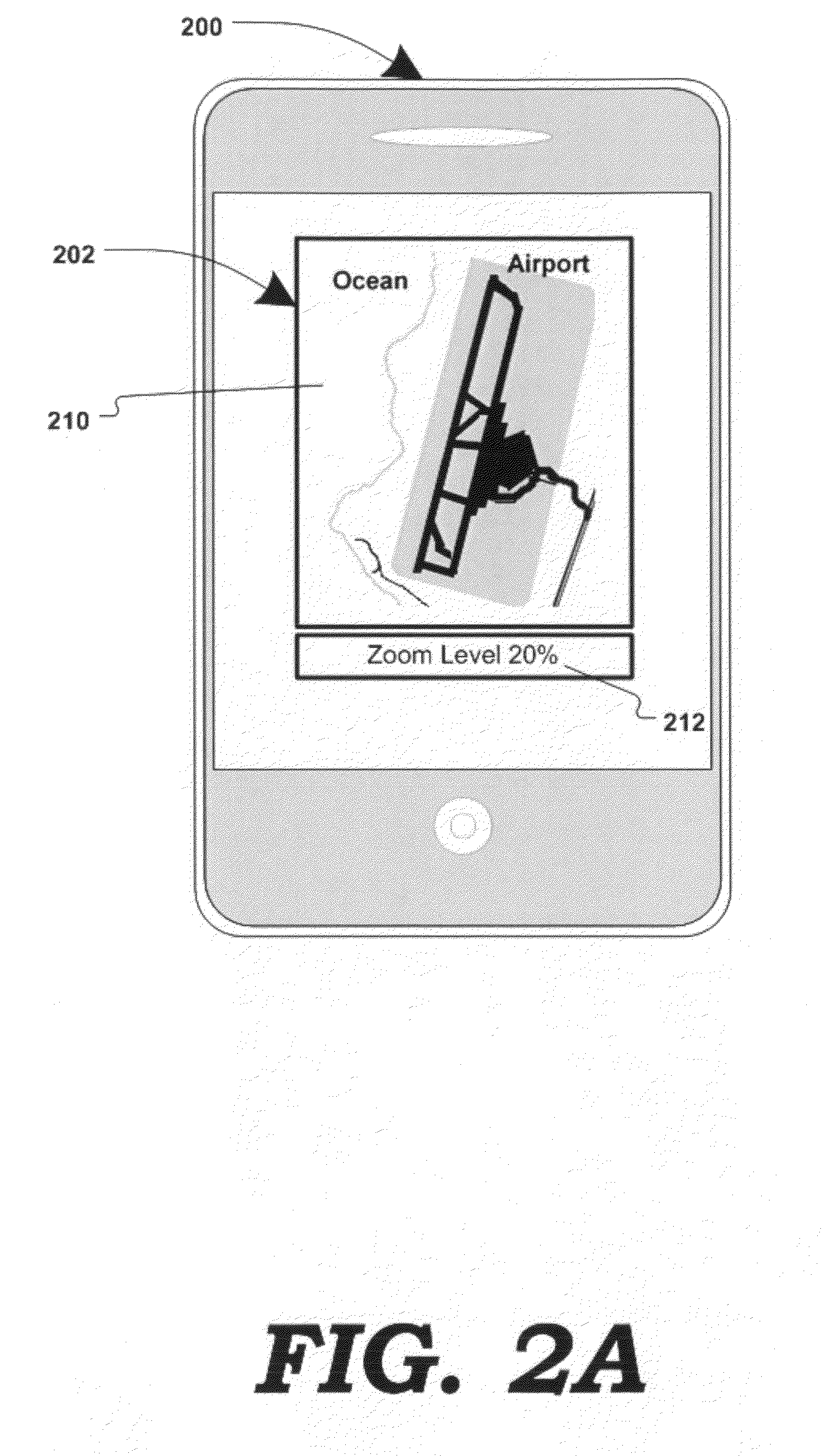
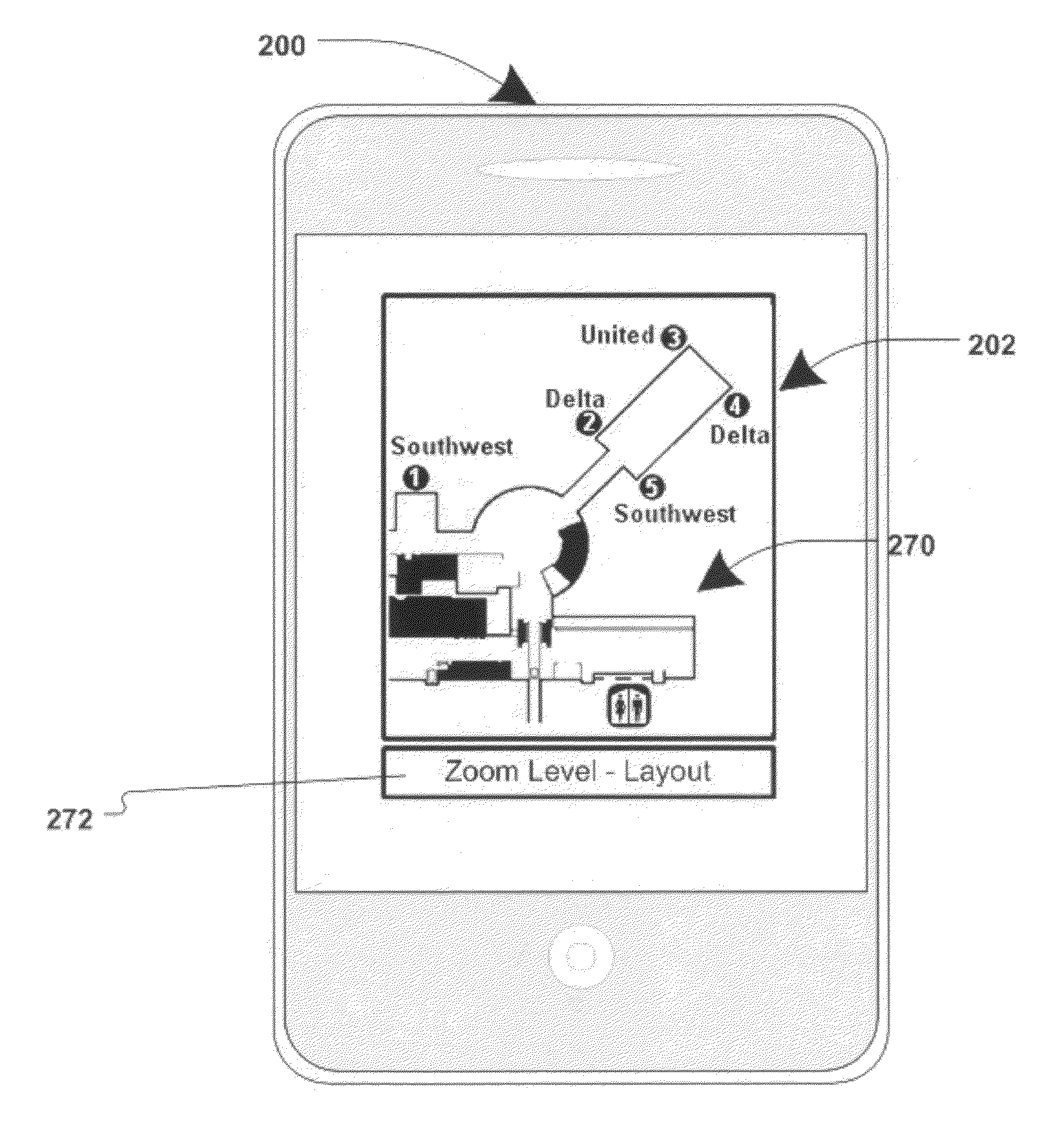
Visually-oriented driving directions in digital mapping system
ActiveUS20050288859A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlSatellite imageHeuristic
Digital mapping techniques are disclosed that provide visually-oriented information to the user, such as driving directions that include visual data points along the way of the driving route, thereby improving the user experience. The user may preview the route associated with the driving directions, where the preview is based on, for example, at least one of satellite images, storefront images, and heuristics and / or business listings.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Displaying content associated with electronic mapping systems
Various methods, systems and apparatus for displaying content associated with a point-of-interest (“POI”) in a digital mapping system, are disclosed. One such method may include detecting a change in the zoom level of an electronic map displayed on a computing device, determining if the new zoom-level is at a pre-determined zoom level (e.g. at maximum zoom), identifying a POI on the map, retrieving content associated with the POI (“POI content”) and displaying the POI content. A POI may be a specific point of interest; or, an entire geographic region of a map displayed at a high zoom level. The method may further include detecting a change in the zoom, or pan, of the digital map while POI content is displayed, and removing or repositioning the POI content in response. One apparatus, according to aspects of the present invention, may include means of detecting a change in the zoom level in a digital map displayed through an application (e.g. a web browser, an application on web-enabled cellular phones, etc., displaying a map generated by a service such as Google Maps®, Yahoo! Maps®, Windows Live Search Maps®, MapQuest®, etc.) on a computing device (e.g. personal computer, workstation, thin client, PDA, cellular phone / smart phone, GPS device, etc.) means of identifying a POI at the pre-determined zoom level, means of obtaining content associated with the POI, and means of displaying the POI content. POI content may be retrieved from a database (e.g. internet-based database); or, in an alternate embodiment, gathered by crawling websites associated with the POI. In one embodiment, POI content may be displayed as an image (e.g a PNG file, GIF, Flash® component, etc.) superimposed on the digital map (e.g. as an overlay object on the map image.) In alternate embodiments, POI content may replace the digital map and may contain links to other content.
Owner:JAKOBSON GABRIEL +1
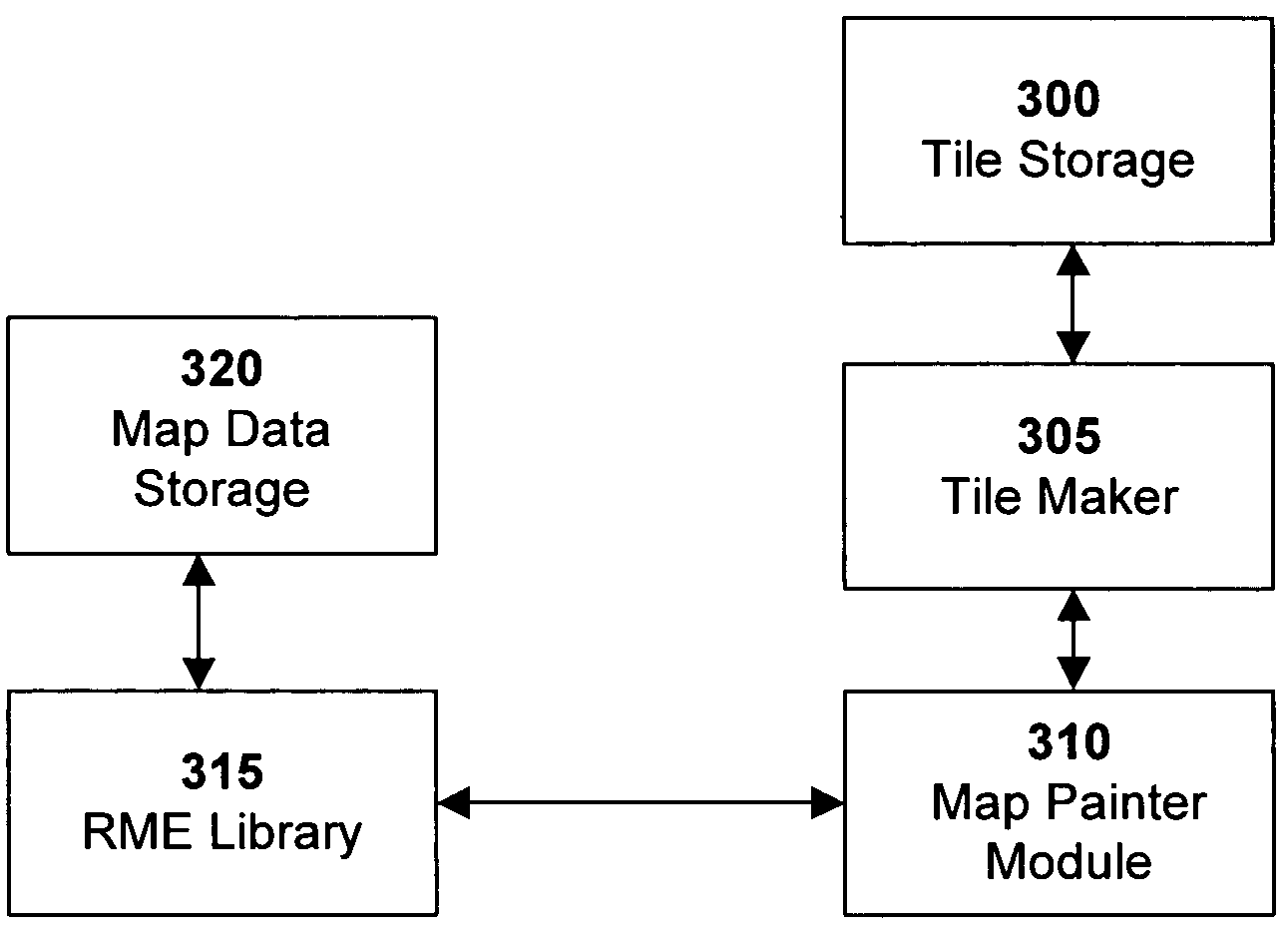
Generating and serving tiles in a digital mapping system
ActiveUS7599790B2Reduce needEasy to deployInstruments for road network navigationDigital data information retrievalMapping techniquesComputer science
Digital tile-based mapping techniques are disclosed that enable efficient online serving of aesthetically pleasing maps. In one particular embodiment, an image tile-based digital mapping system is configured for generating map tiles during an offline session, and serving selected sets of those tiles to a client when requested. Also provided are solutions for handling map labels and other such features in a tile-based mapping system, such as when a map label crosses map tile boundaries. Various processing environments (e.g., servers or other computing devices) can be employed in the system.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
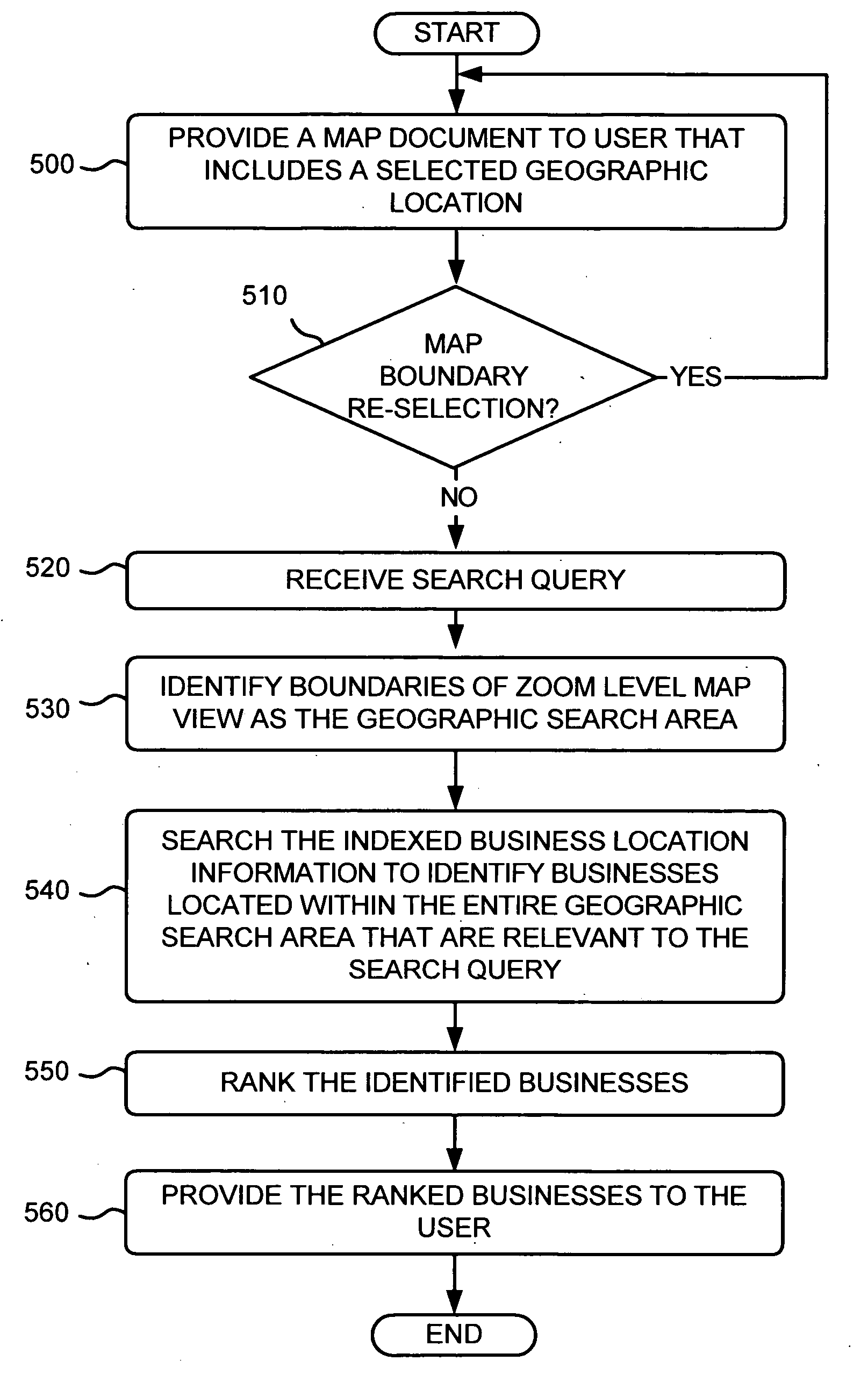
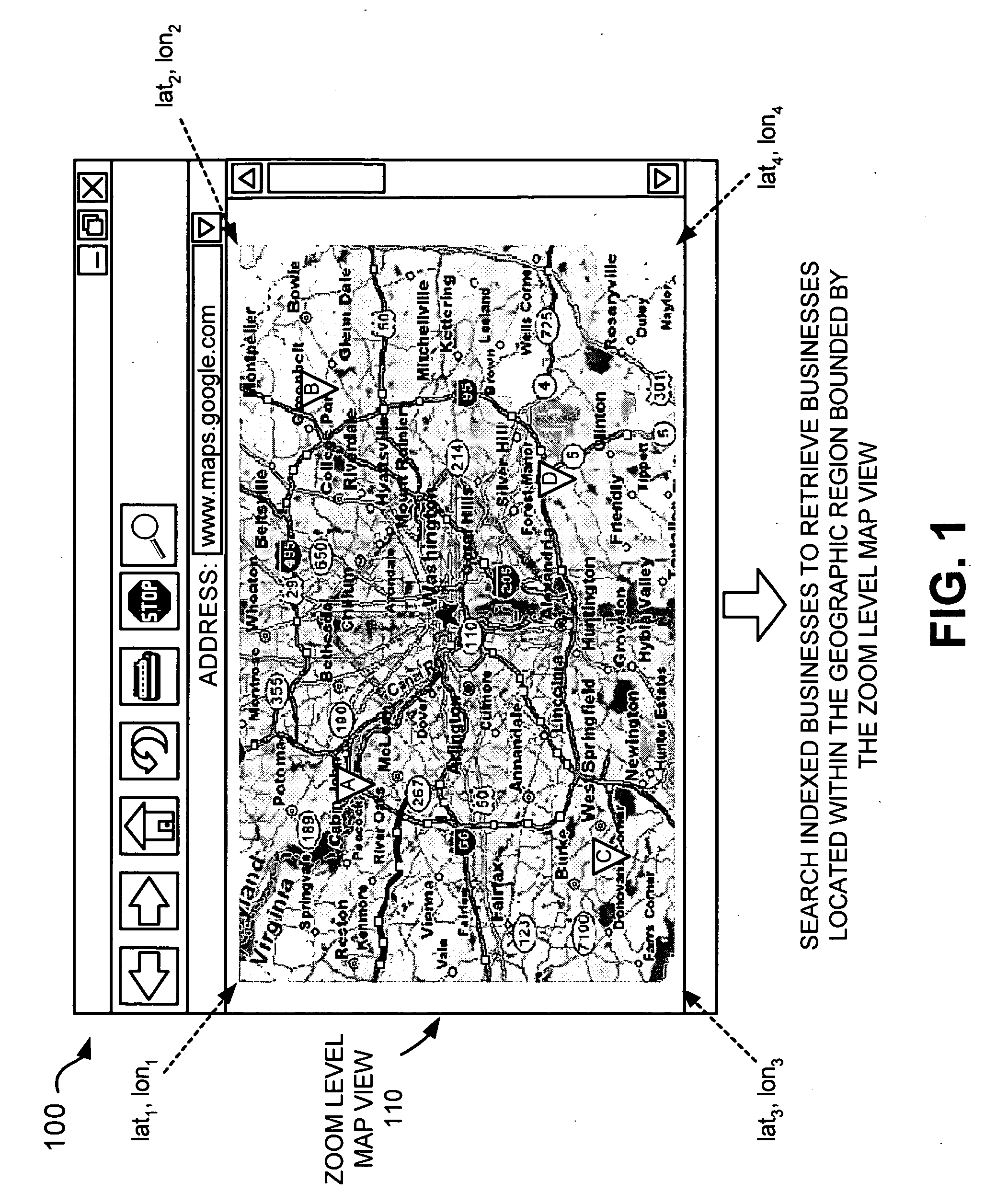
Using boundaries associated with a map view for business location searching
ActiveUS20060271280A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data information retrievalGeographic regionsPaper document
A system aggregates entity location information from multiple documents distributed among multiple locations in a network. The system searches the entity location information to identify a first set of entities located within the entirety of a first geographic region selected by a user. The system provides a first digital map to the user via a network, the first digital map including the first geographic region and further including visual representations of the first set of identified entities and their associated geographic locations.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
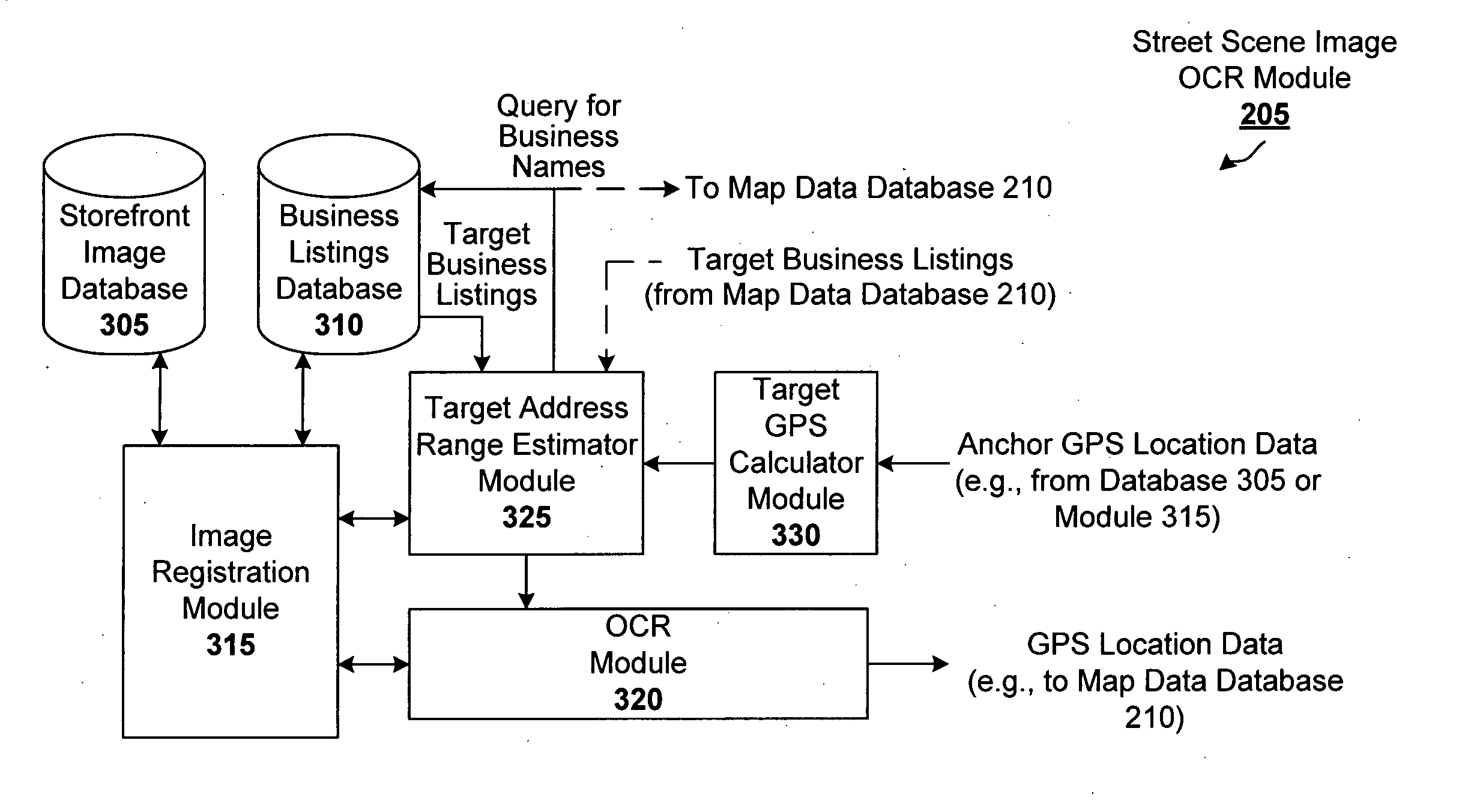
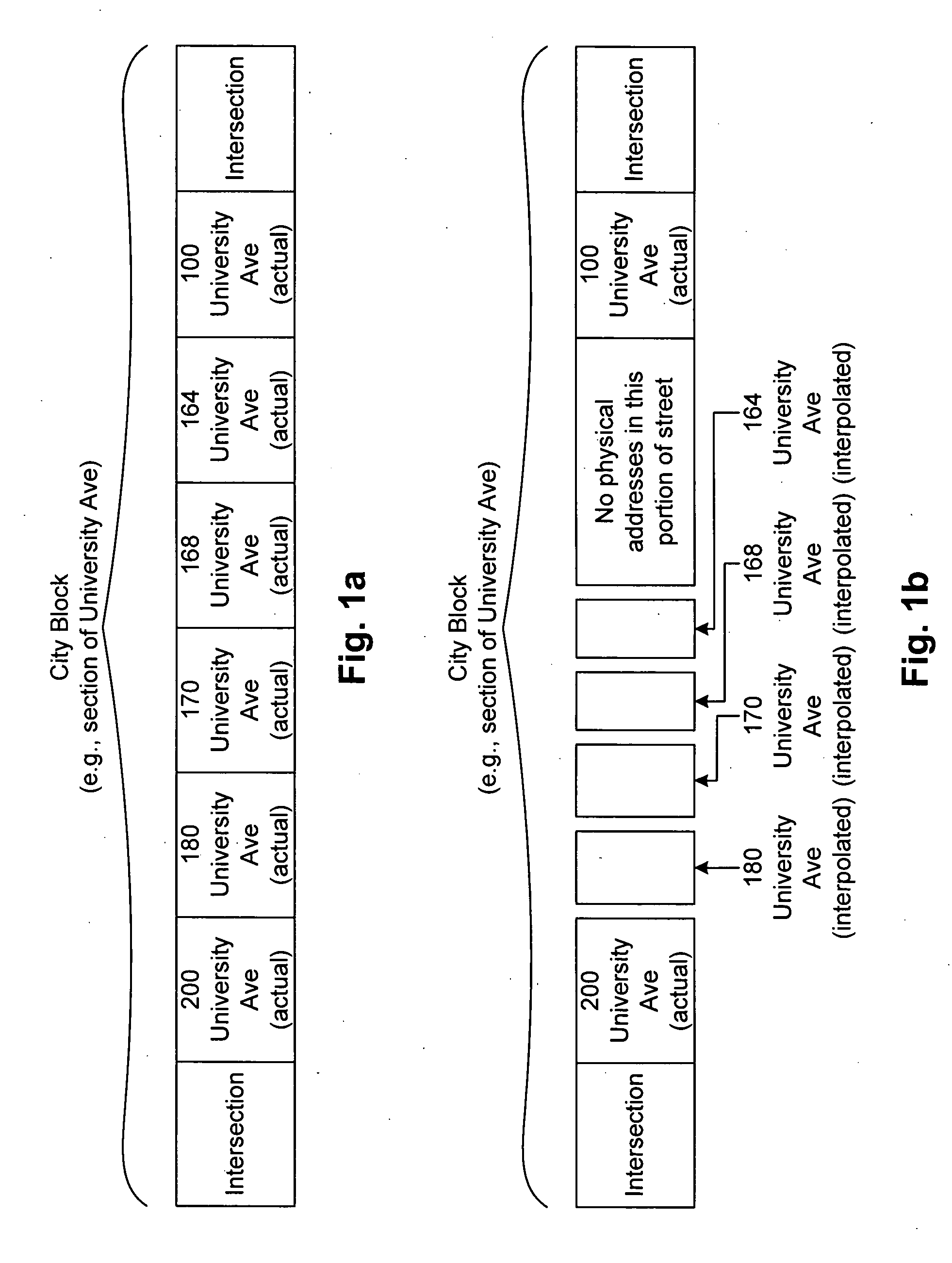
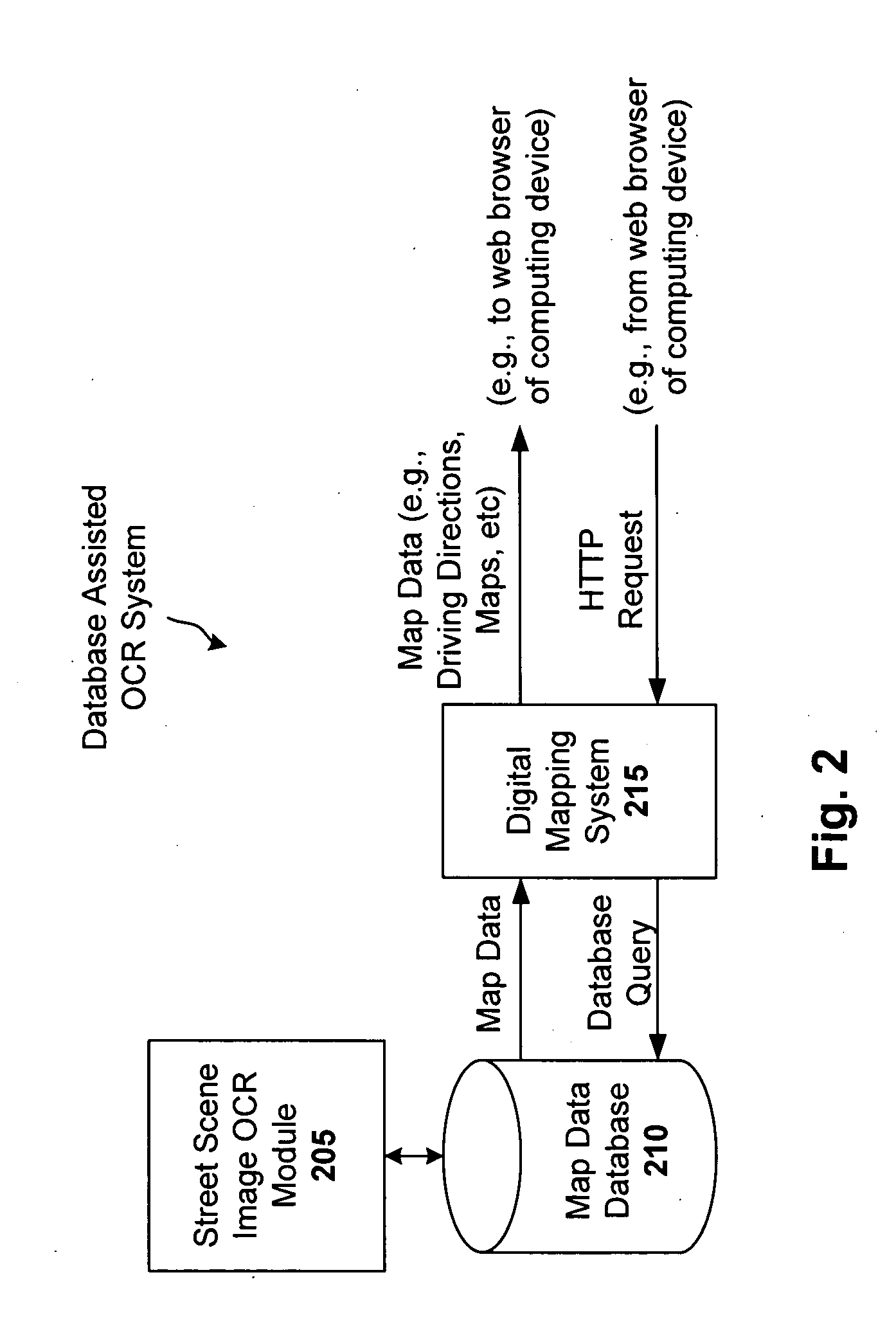
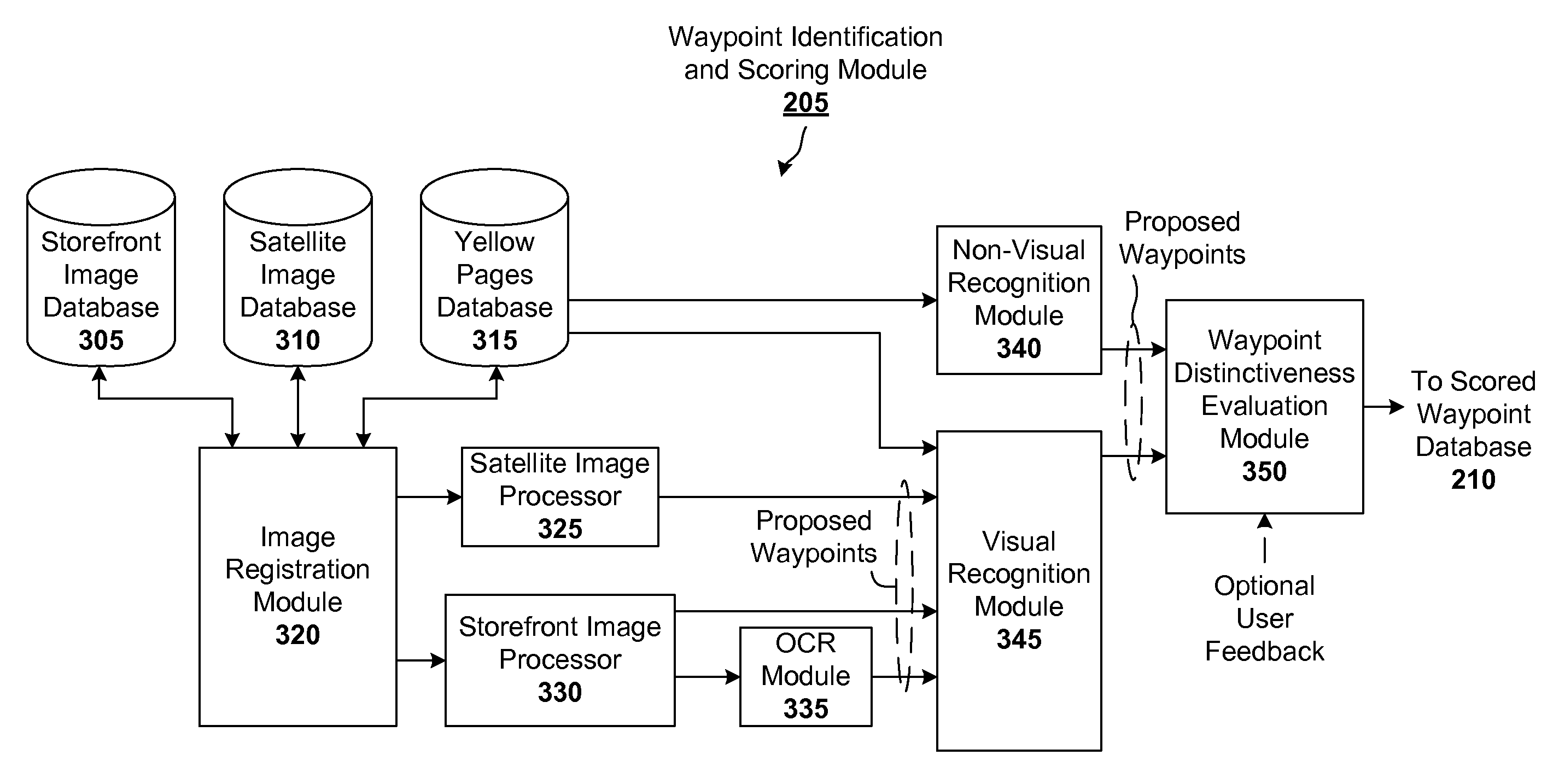
Database assisted OCR for street scenes and other images
Optical character recognition (OCR) for images such as a street scene image is generally a difficult problem because of the variety of fonts, styles, colors, sizes, orientations, occlusions and partial occlusions that can be observed in the textual content of such scenes. However, a database query can provide useful information that can assist the OCR process. For instance, a query to a digital mapping database can provide information such as one or more businesses in a vicinity, the street name, and a range of possible addresses. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, this mapping information is used as prior information or constraints for an OCR engine that is interpreting the corresponding street scene image, resulting in much greater accuracy of the digital map data provided to the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
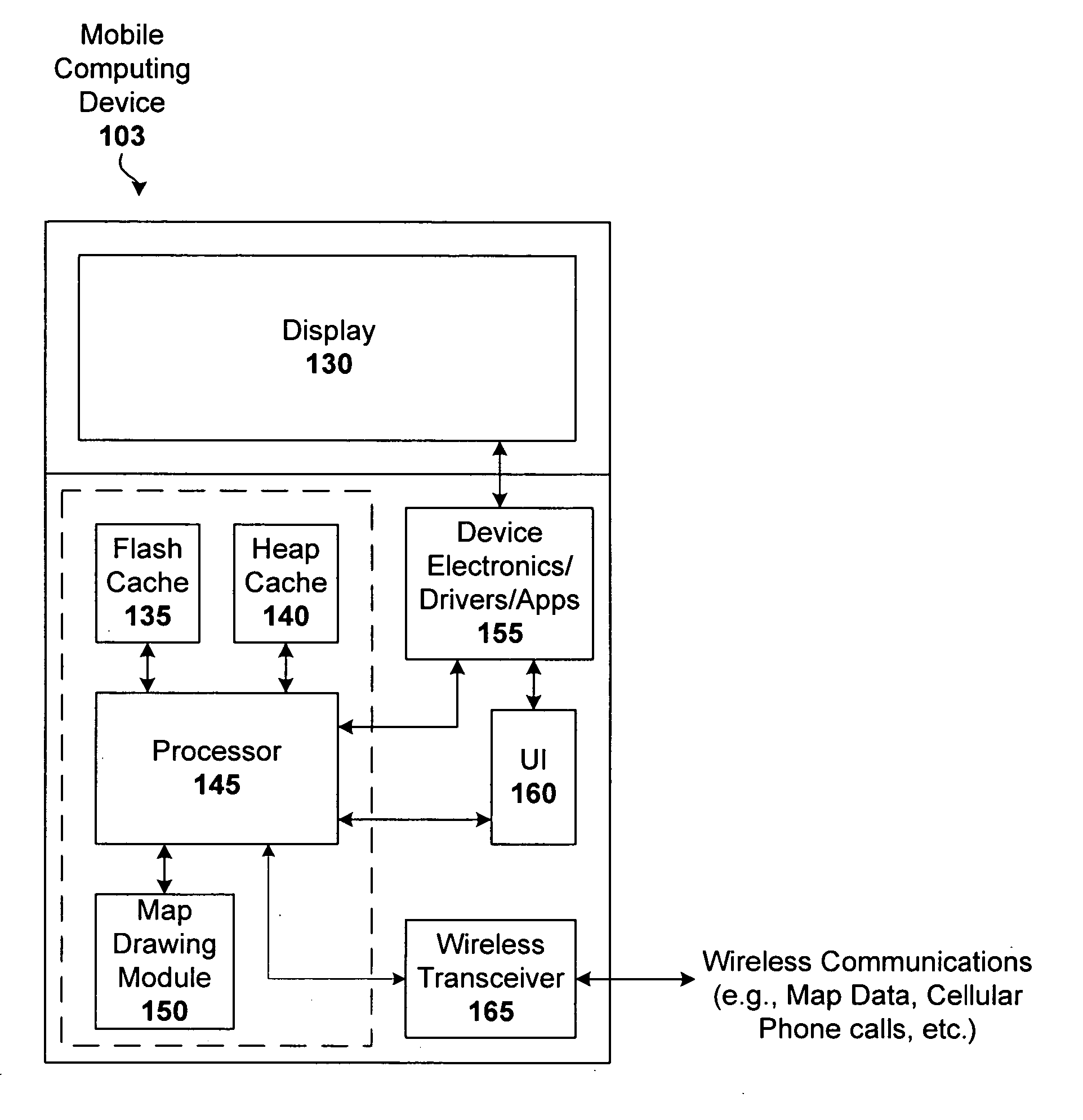
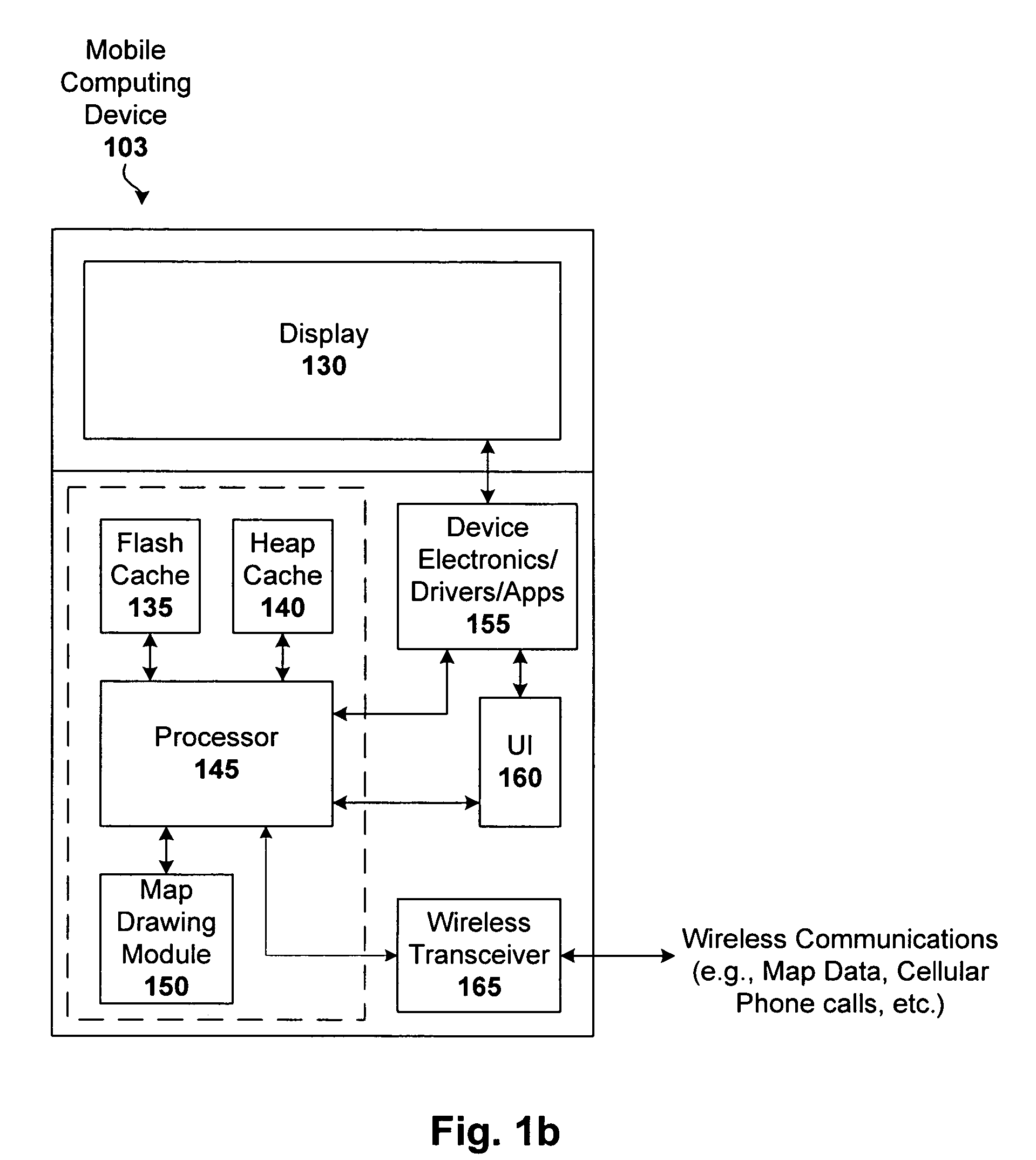
Techniques for displaying and caching tiled map data on constrained-resource services
ActiveUS20070080830A1Reduces required data byteStatic indicating devicesRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile deviceThroughput
Techniques are disclosed that enable users to access and use digital mapping systems with constrained-resource services and / or mobile devices (e.g., cell phones and PDAs). In particular, latency of a mapping application on high-latency and low-throughput networks is minimized. One embodiment utilizes volatile and non-volatile storage of the mobile device to cache pre-computed map images (e.g., map tiles). An asynchronous cache can be used to prevent delays caused by potentially slow non-volatile storage. Meta-data about each map image and usage patterns can be stored and used by the cache to optimize hit rates.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
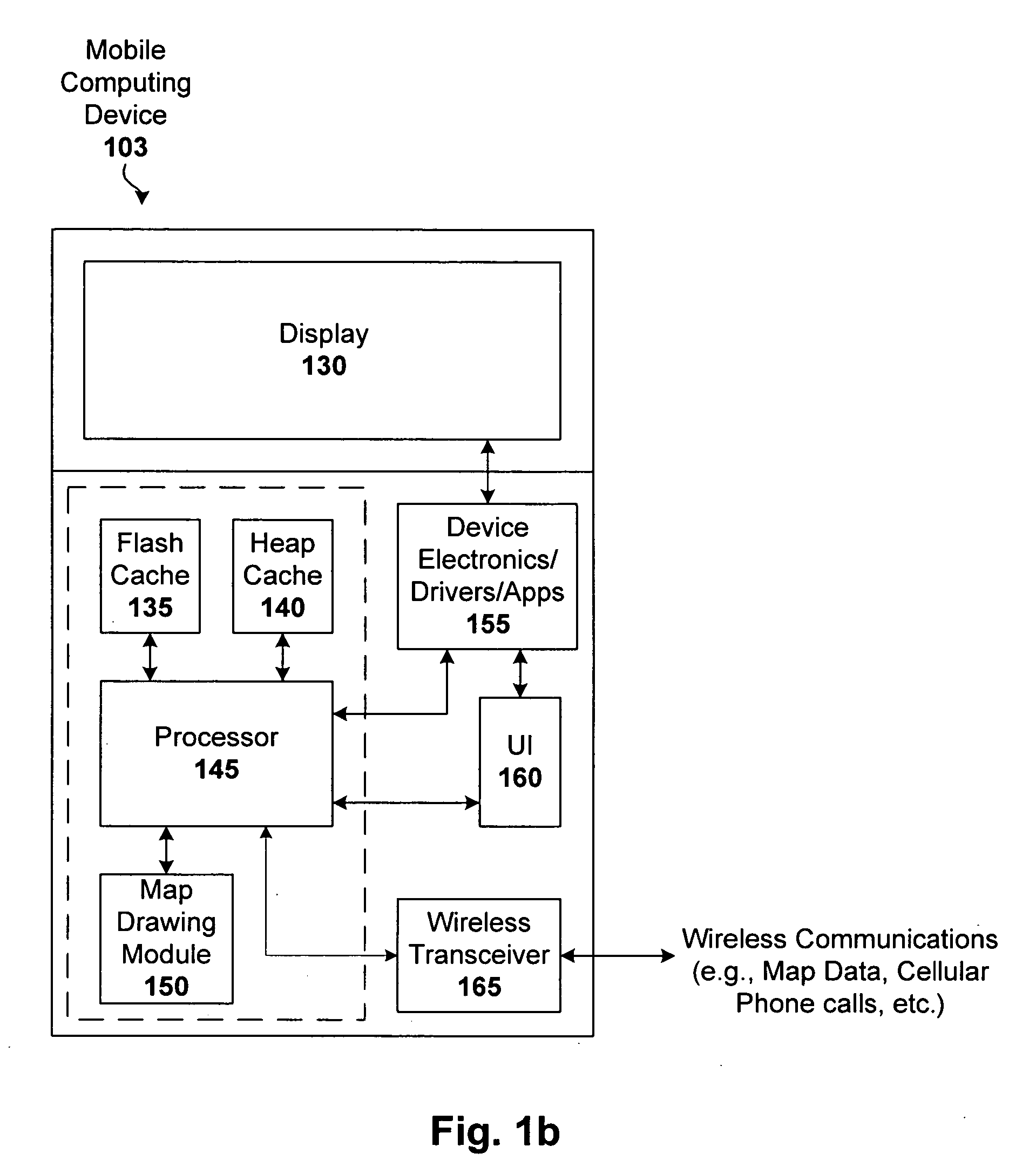
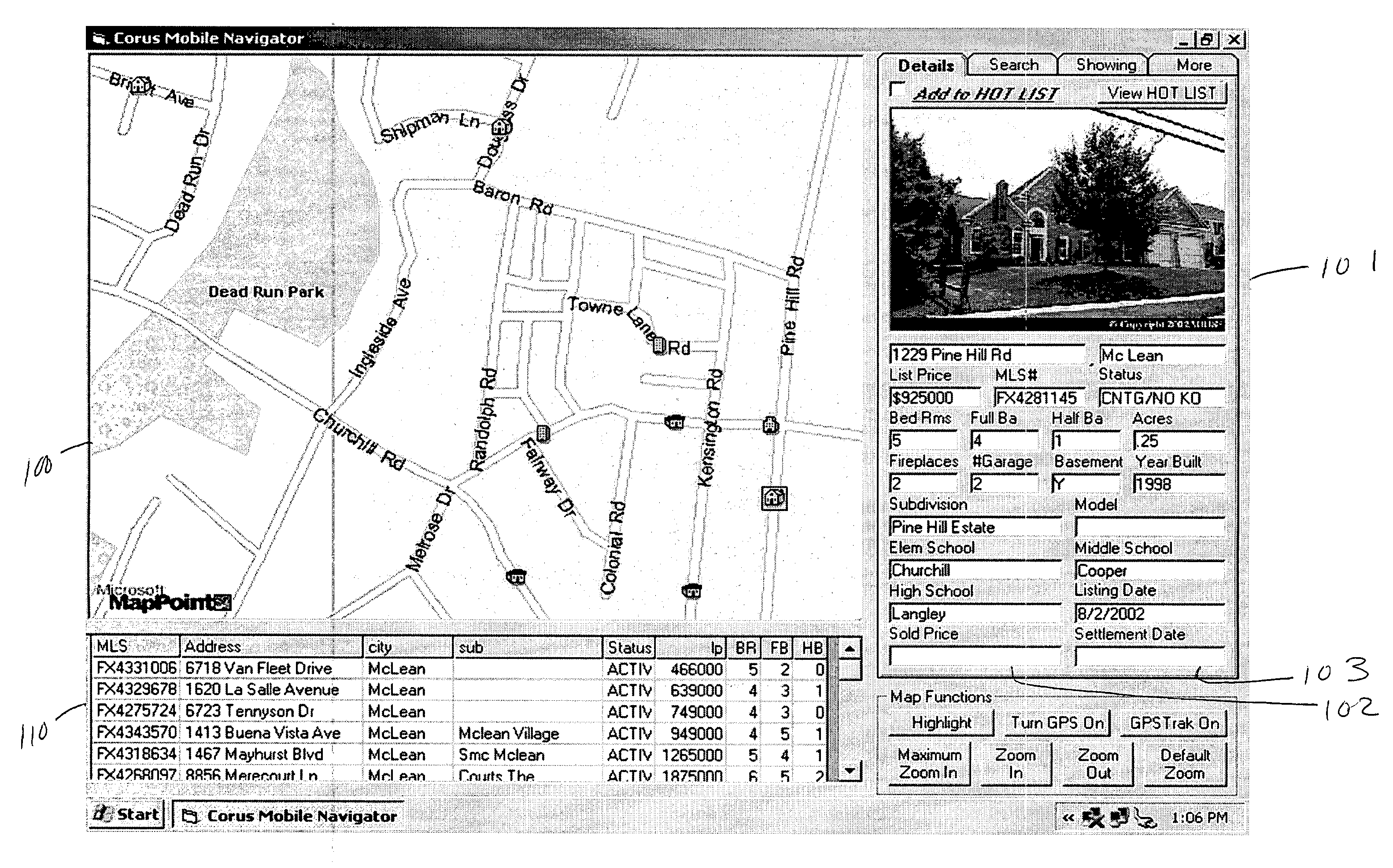
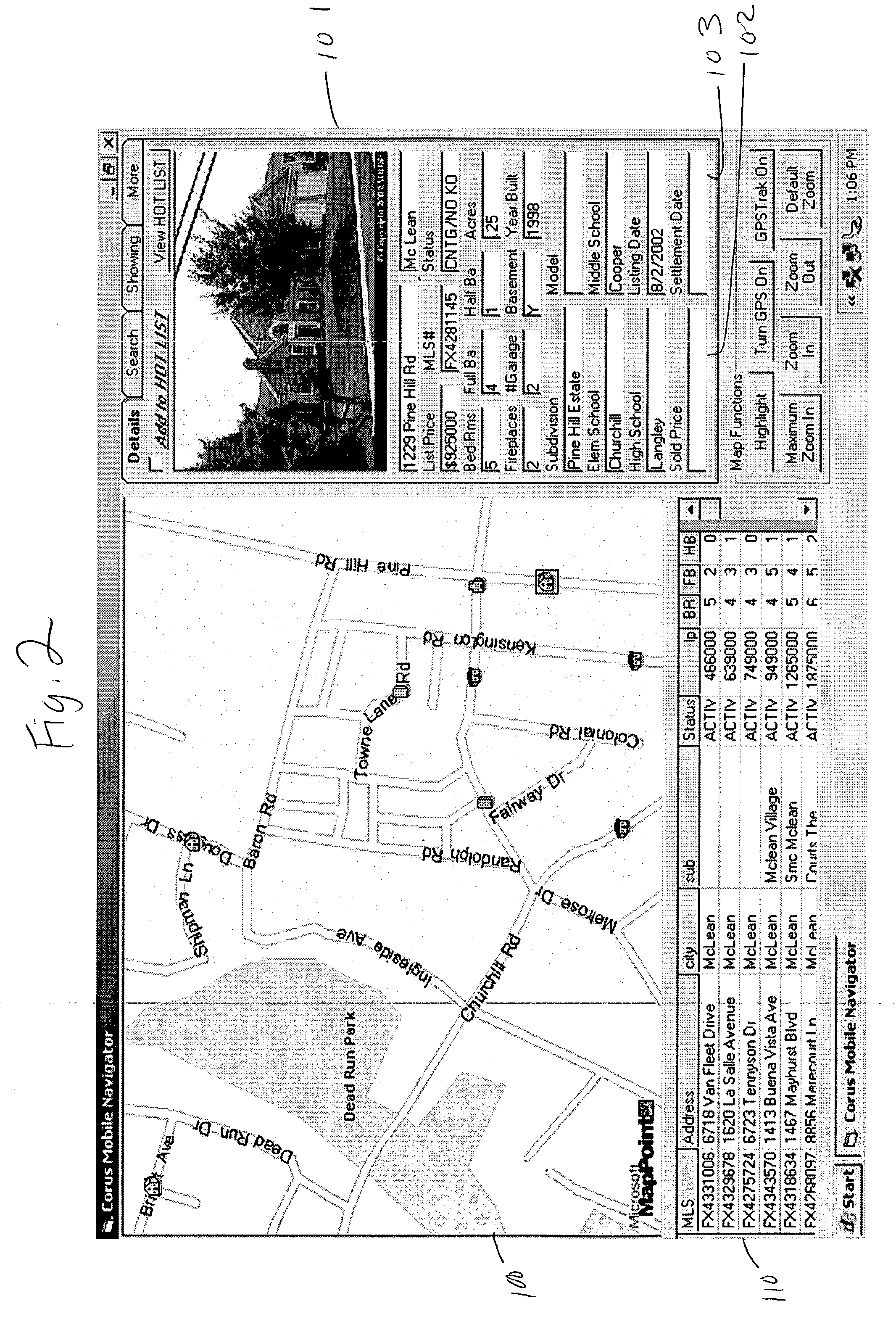
Market status icons in real-estate information search and retrieval system
InactiveUS20040021584A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlInformation searchingMarket information systems
The present invention is directed to icons used to represent properties in a real-estate market information system. The icons of the present invention provide additional information about the property associated with the icon when displayed on a digital map. Icon indicia, such as shape, color or size, in the present invention is determined by combining at least two property attributes of the property associated with the property icon. In a preferred embodiment, the icons used in the present invention are indicative of the type of property and the market status of the property associated with the icon. The icons can be constructed such that further property attributes, such as square-footage range, could be also, or alternatively, be indicated by icon indicia.
Owner:CORUS REALTY +1
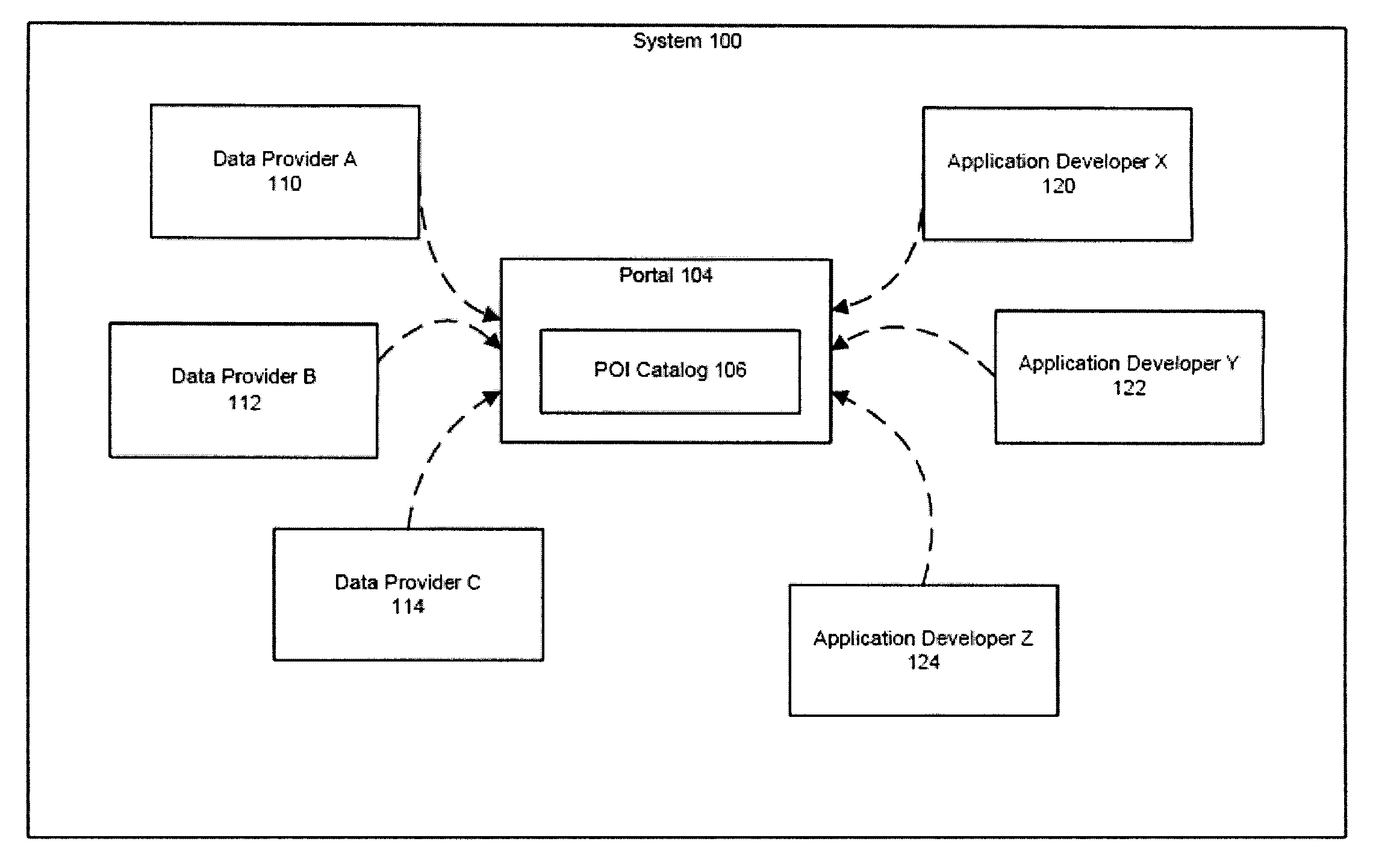
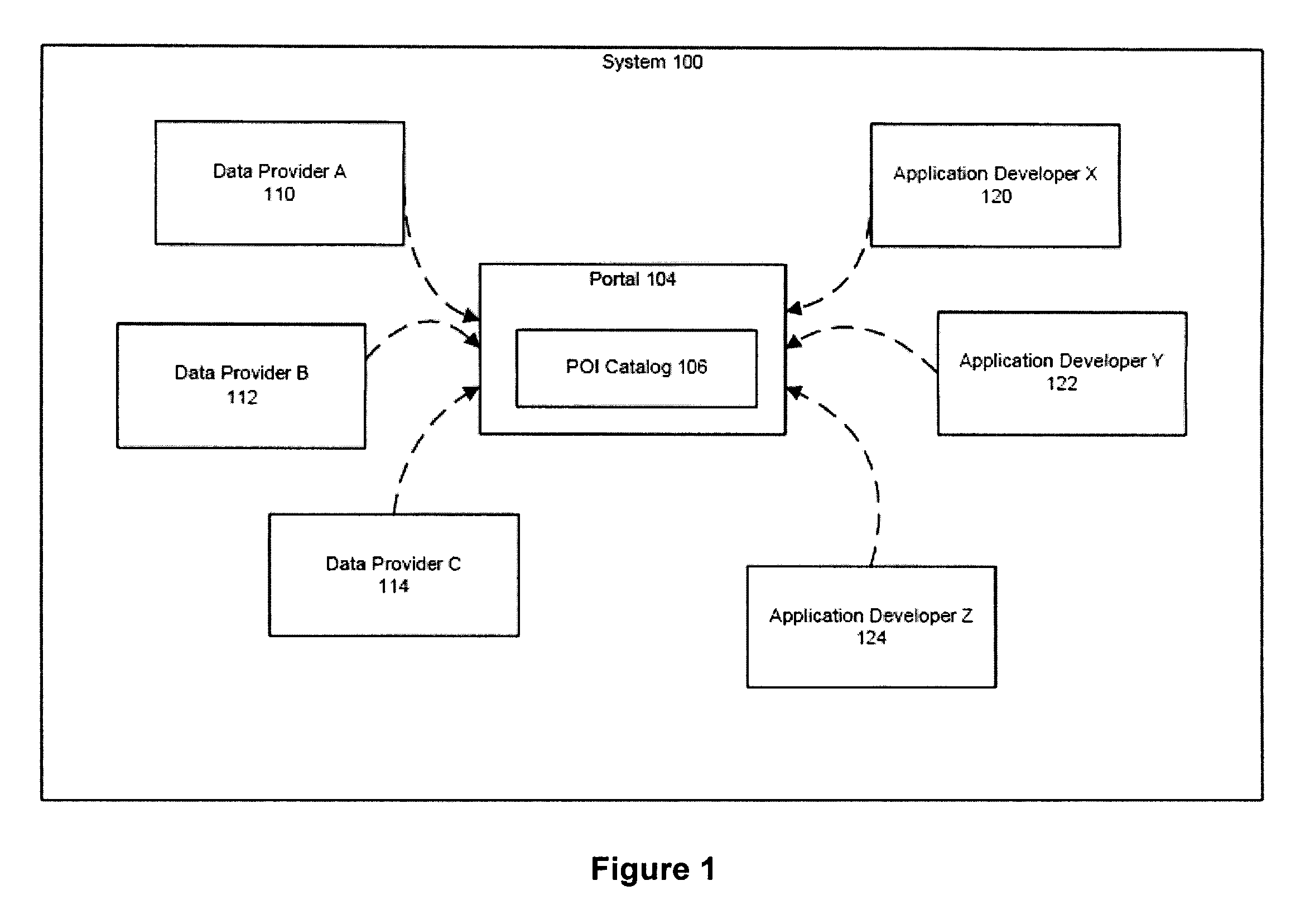
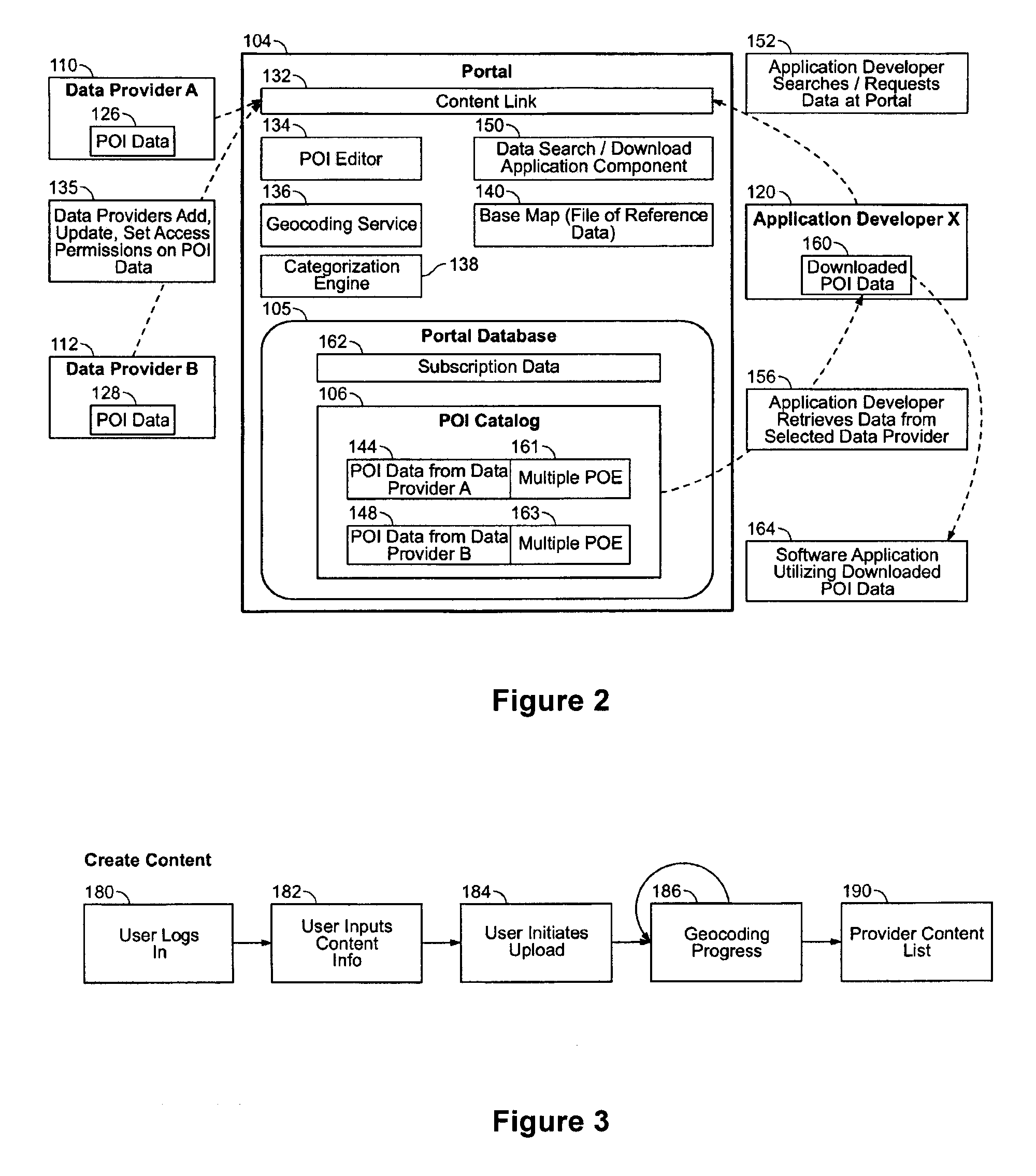
System and method for providing multiple participants with a central access portal to geographic point of interest data
InactiveUS20080163073A1Ensure consistencyMultiple digital computer combinationsCommerceData needsMultiple point
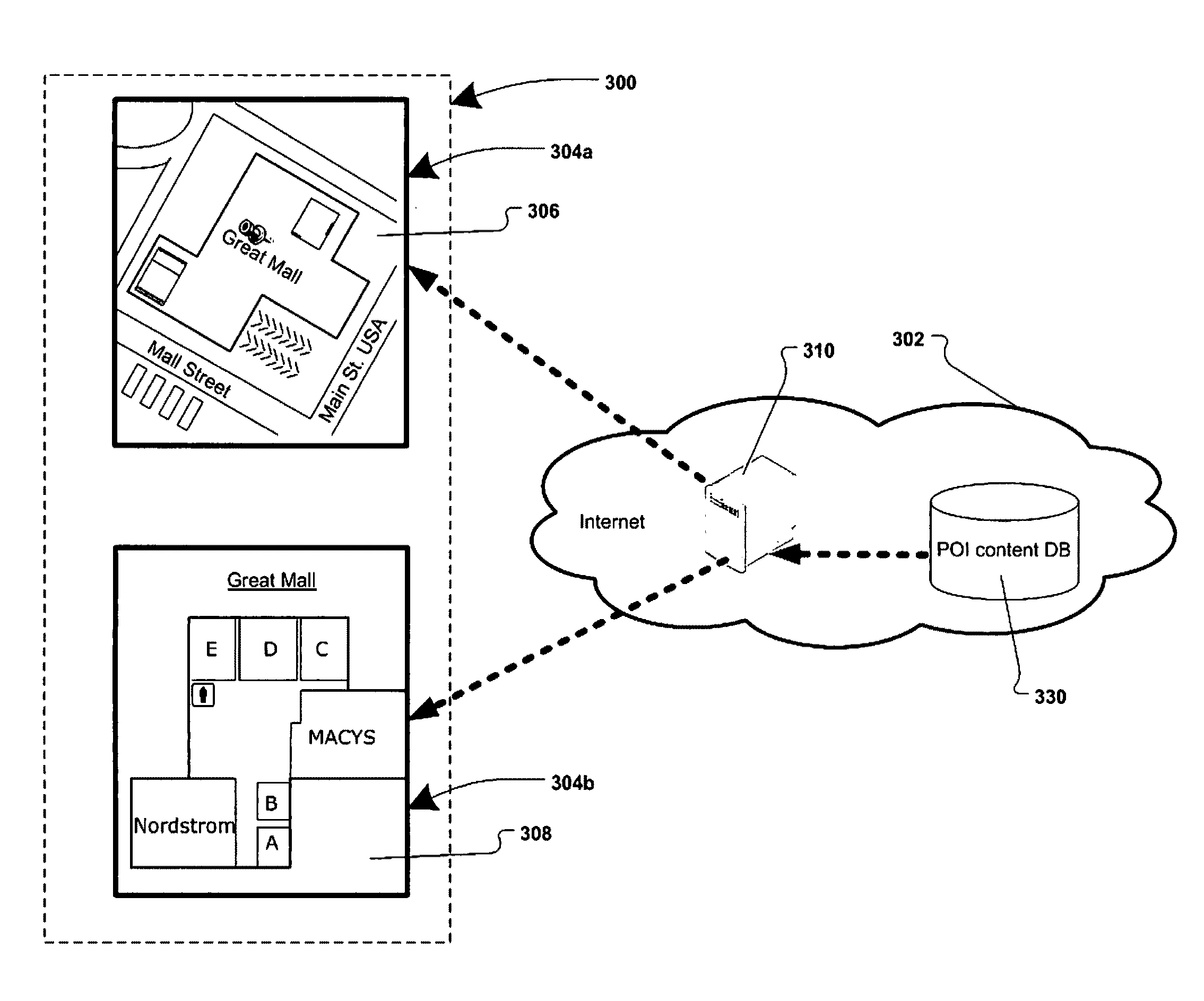
A system and method of providing multiple participants with a centrally accessible content portal for geographic point of interest (POI) data, for subsequent use in creating map-based or spatial applications. Different entities can dynamically upload, update, retrieve, and use digital map and POI data. Additional features include the ability to handle the large amounts of POI data needed by multiple Application Developers, including data that is dynamic, or frequently changing; the ability to update POI attribute information and deliver it to the Application Developers; the ability to associate multiple points of entry (POE) with a POI, and to aggregate data from multiple Content Providers; and the use of a common geocoding engine and common digital map reference across all Content Providers, which ensures the consistency of the geocoding throughout all the POI data.
Owner:TELE ATLAS NORTH AMERICA
Method for computing an energy efficient route
ActiveUS20110307166A1Reduce travel speedReduce pollutionEnergy efficient ICTAnalogue computers for vehiclesEngineeringTraffic conditions
Probe data is analyzed to derive Longitudinal Speed Profiles (LSPs) and an Optimal Longitudinal Speed Profile (18) for each road segment or link in a digital map network. The Longitudinal Speed Profiles (LSPs) profiles are calculated during defined time spans whereas the Optimal Longitudinal Speed Profile (18) is based on the LSP for the time span corresponding only to free flow traffic conditions. All of the LSPs can used to create a respective energy cost for each time span, or only the OLSP (18) can be used (or alternatively the RRDSL 16 or LRRDSL 17) to calculate an energy cost for the free flow conditions only. The energy cost can be used to predict the energy required by a vehicle to traverse the link Navigation software can use the energy cost to plan the most energy efficient route between two locations in the digital map. Sensory signals can be activated if a driver strays from the Optimal Longitudinal Speed Profile (18) to achieve extremely high levels of energy efficiency.
Owner:TOMTOM INT BV
Image recongition system
ActiveUS20080056535A1Facilitate recognition of objectAccurate identificationInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisImaging dataImage identification
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Integrated laser mapping tablet and method of use
InactiveUS6895356B2Road vehicles traffic controlActive open surveying meansTablet computerMeasurement device
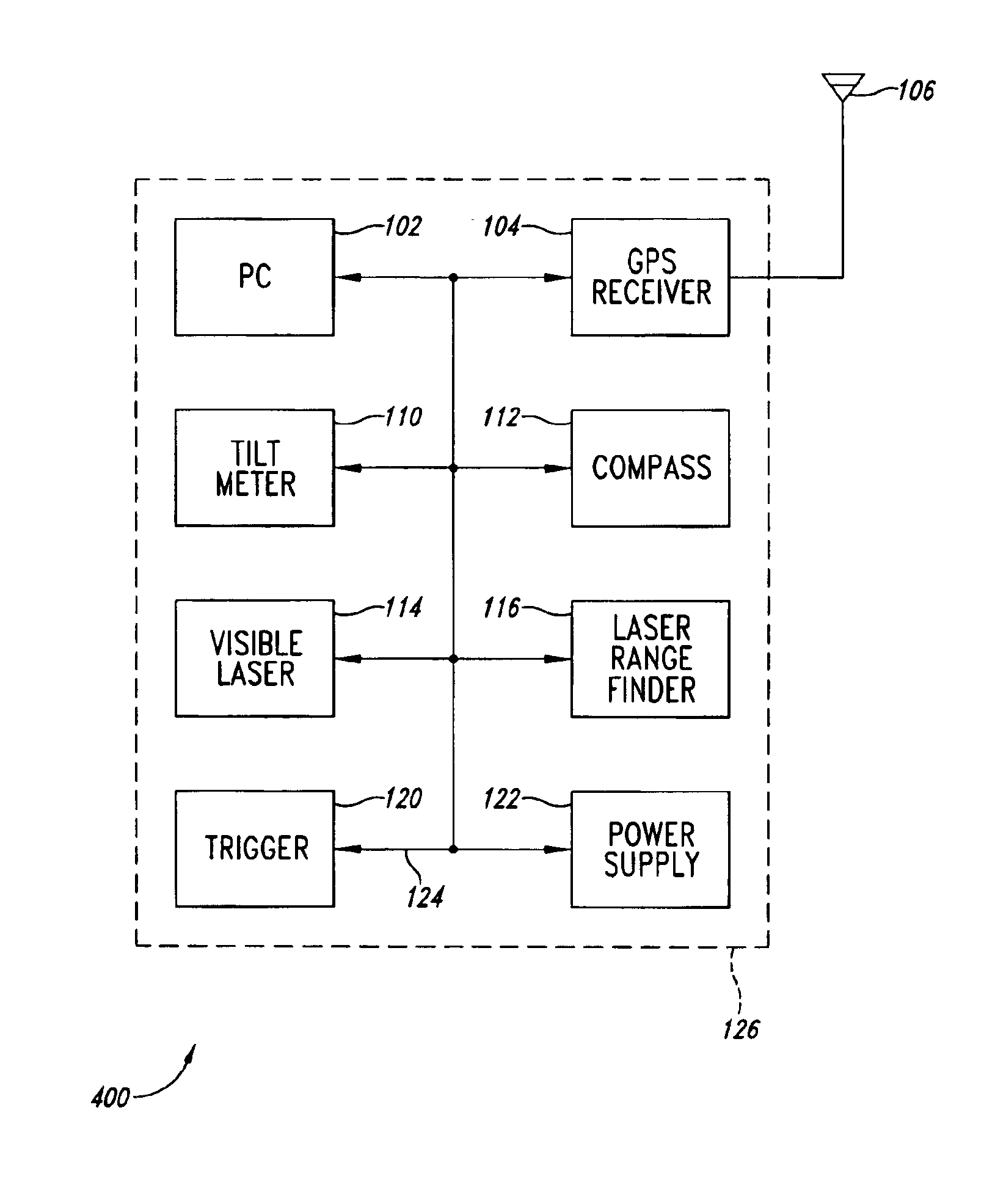
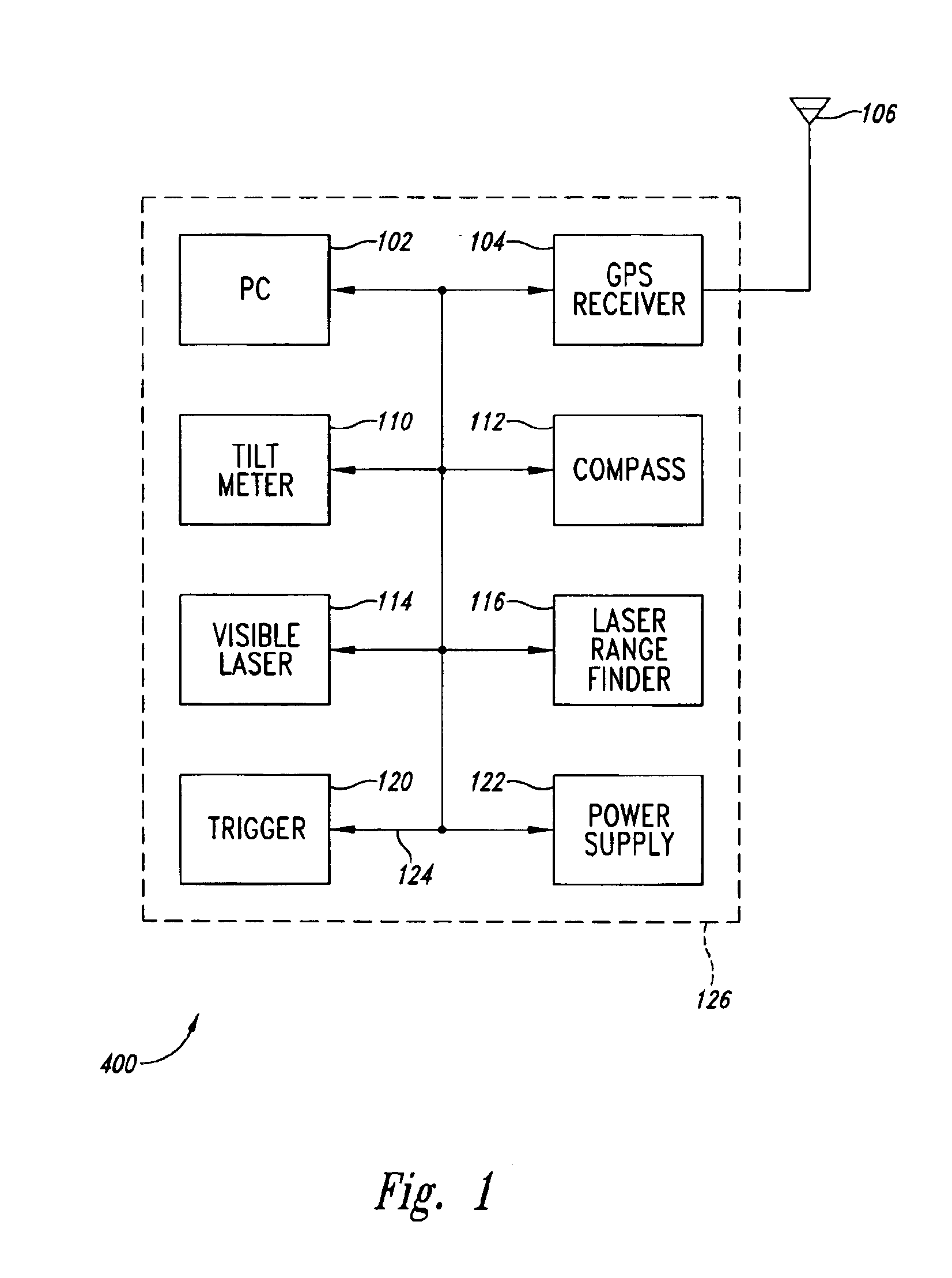
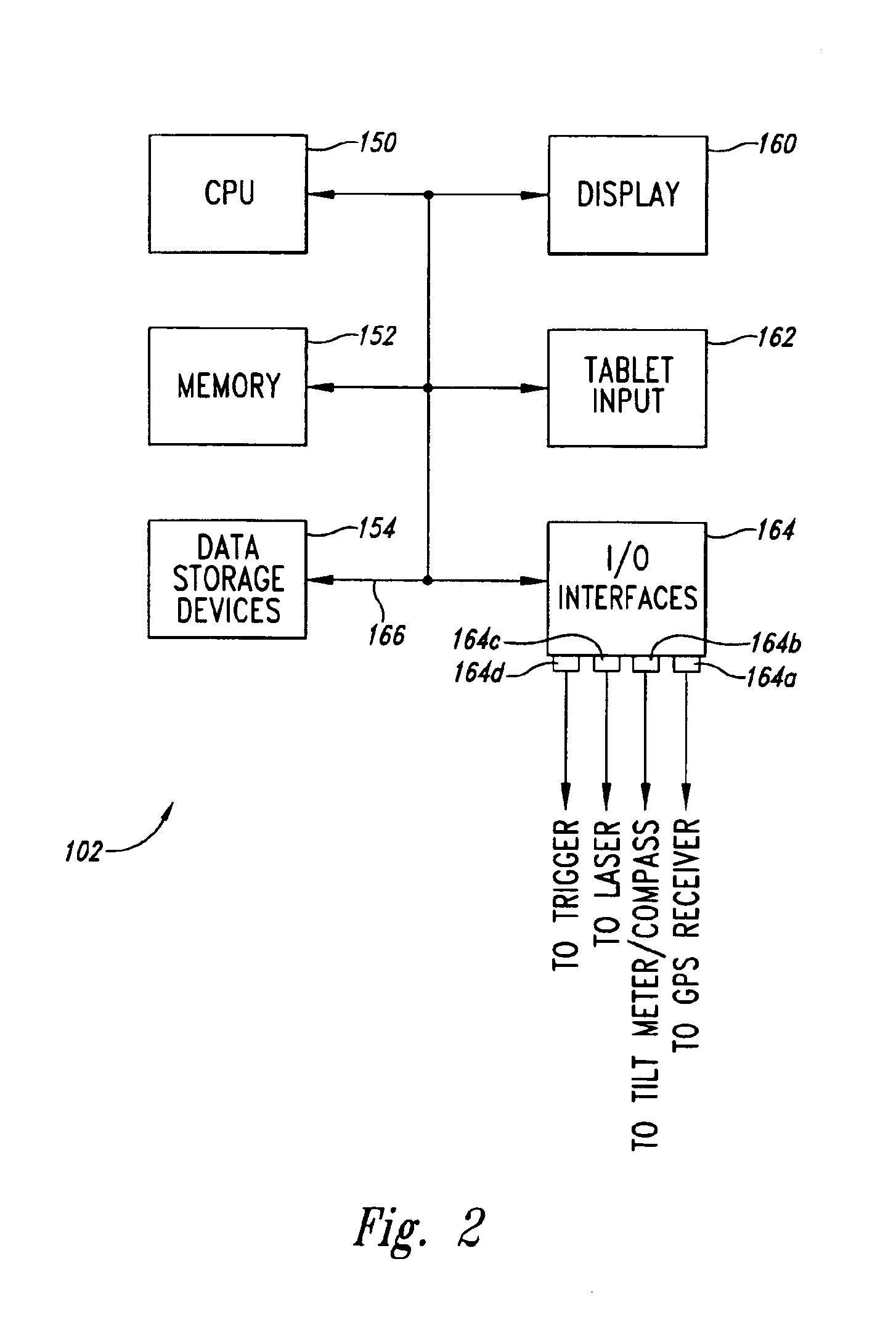
An integrated digital mapping device contains a personal pen tablet computer (PC), GPS receiver, tilt meter (liquid filled or accelerometer-based), compass and laser range finder integrated into a single housing. The laser range finder is combined with a visible laser to provide convenient aiming. The device also includes a trigger to initiate a measurement cycle. In response to activation of a measurement cycle, the GPS receiver determines the precise location of the measurement device while the other components provide a measurement of tilt angle (up or down inclination pitch), azimuth, and distance an object or area of interest. The roll (left or right sideways tilt) of the tilt meter also provides information when the tablet is aligned with planar objects. The data from a measurement cycle is converted into a predetermined data format for use with the conventional digital mapping software application program operating within the PC.
Owner:RUBICON DIGITAL MAPPING ASSOCS
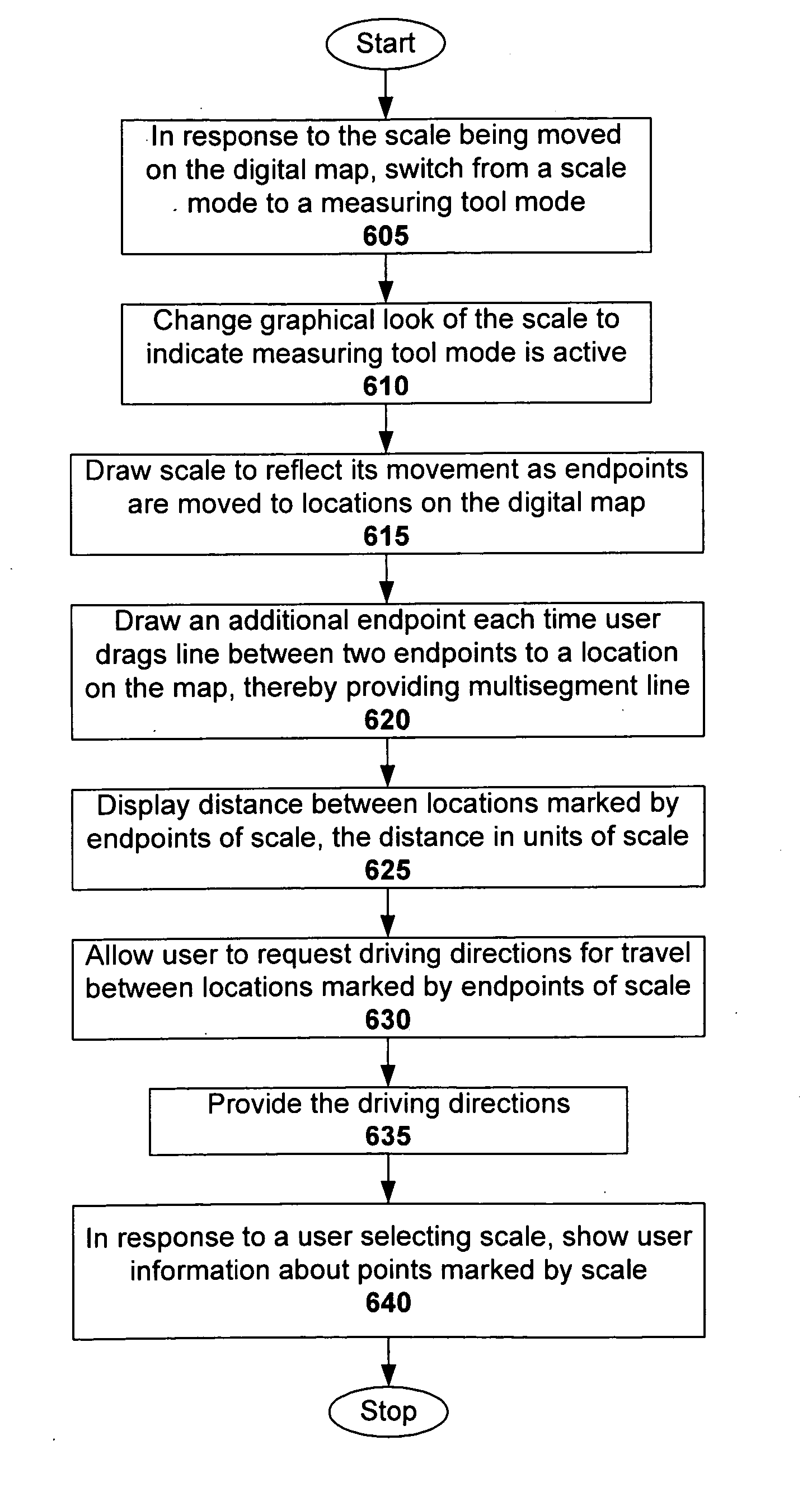
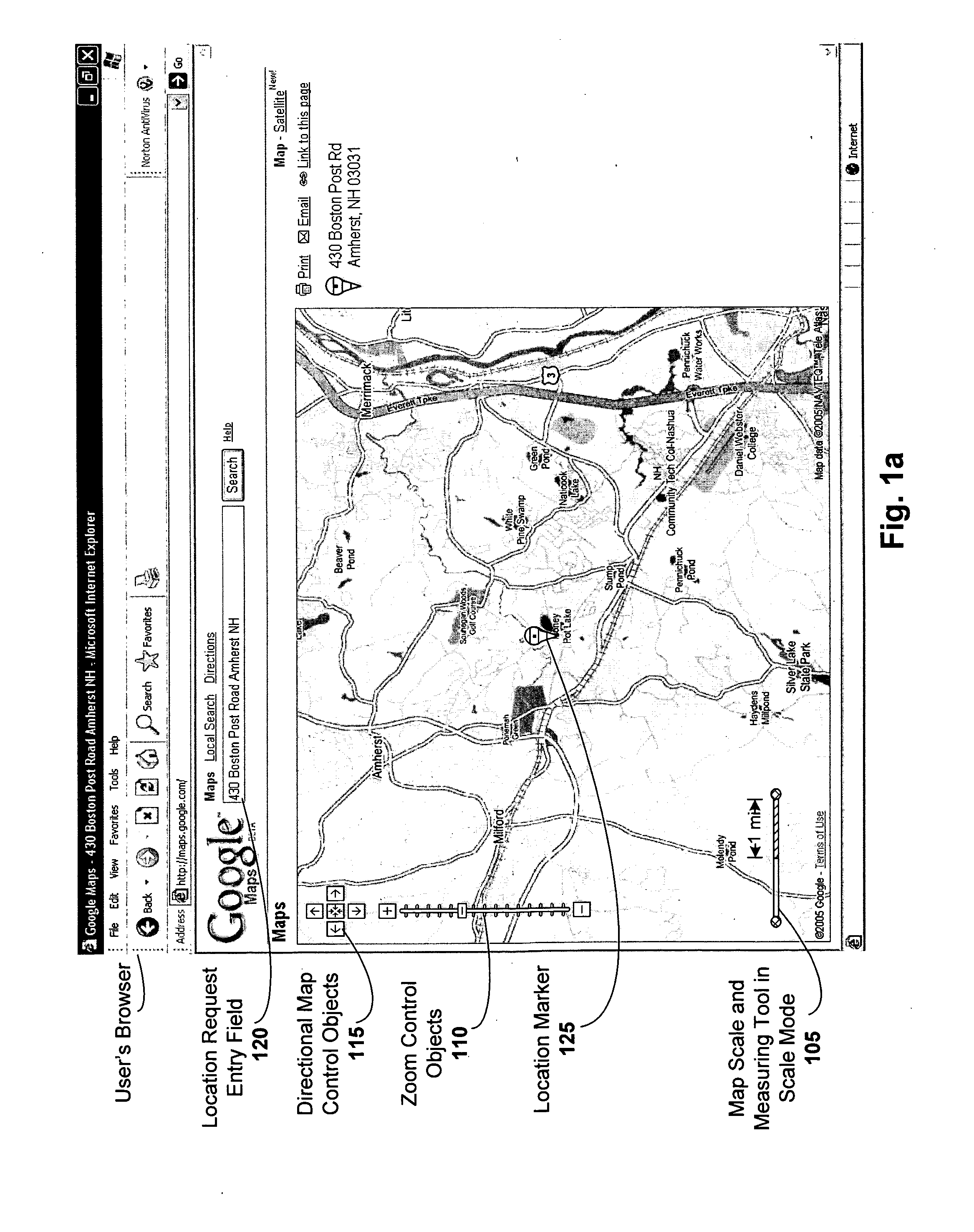
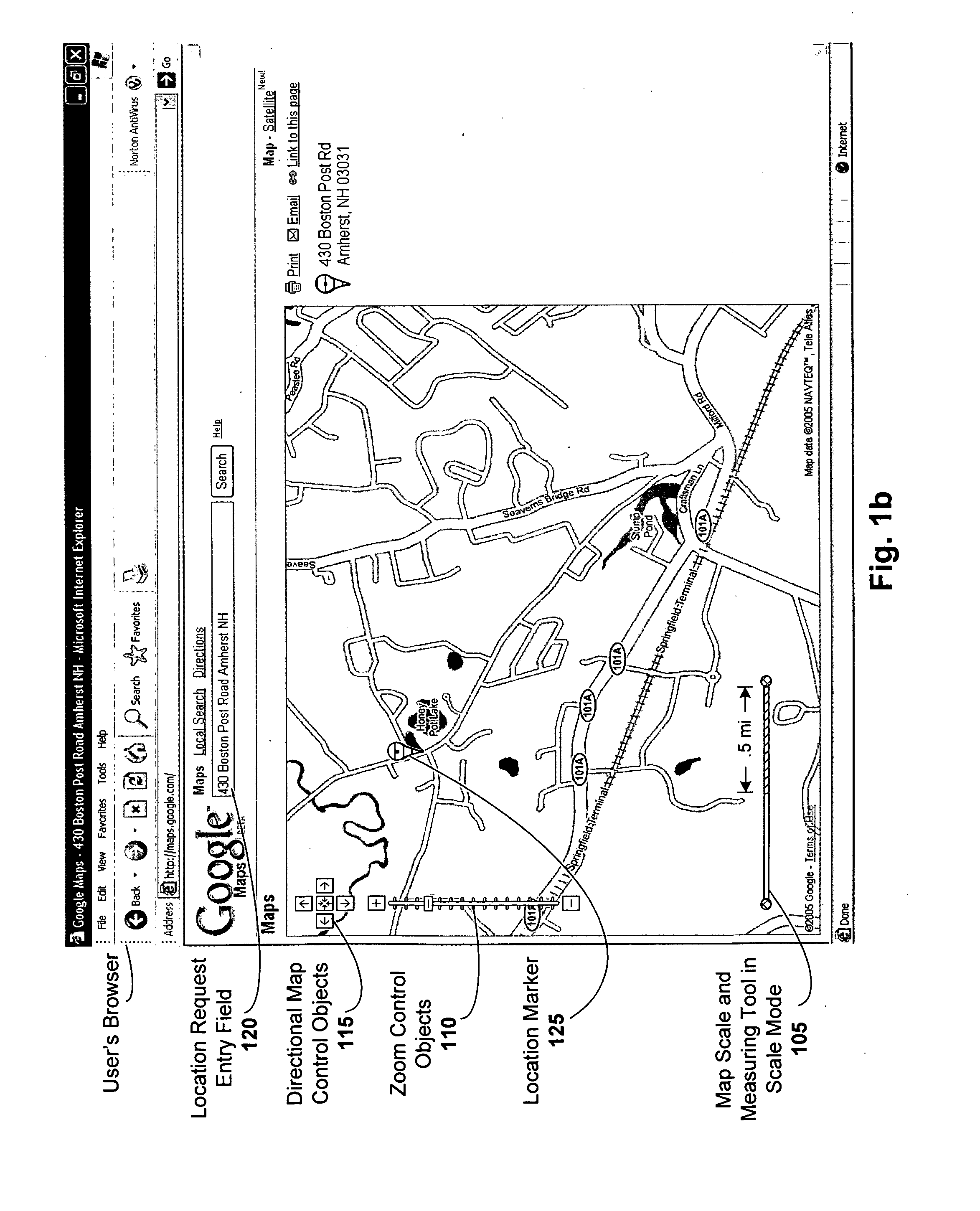
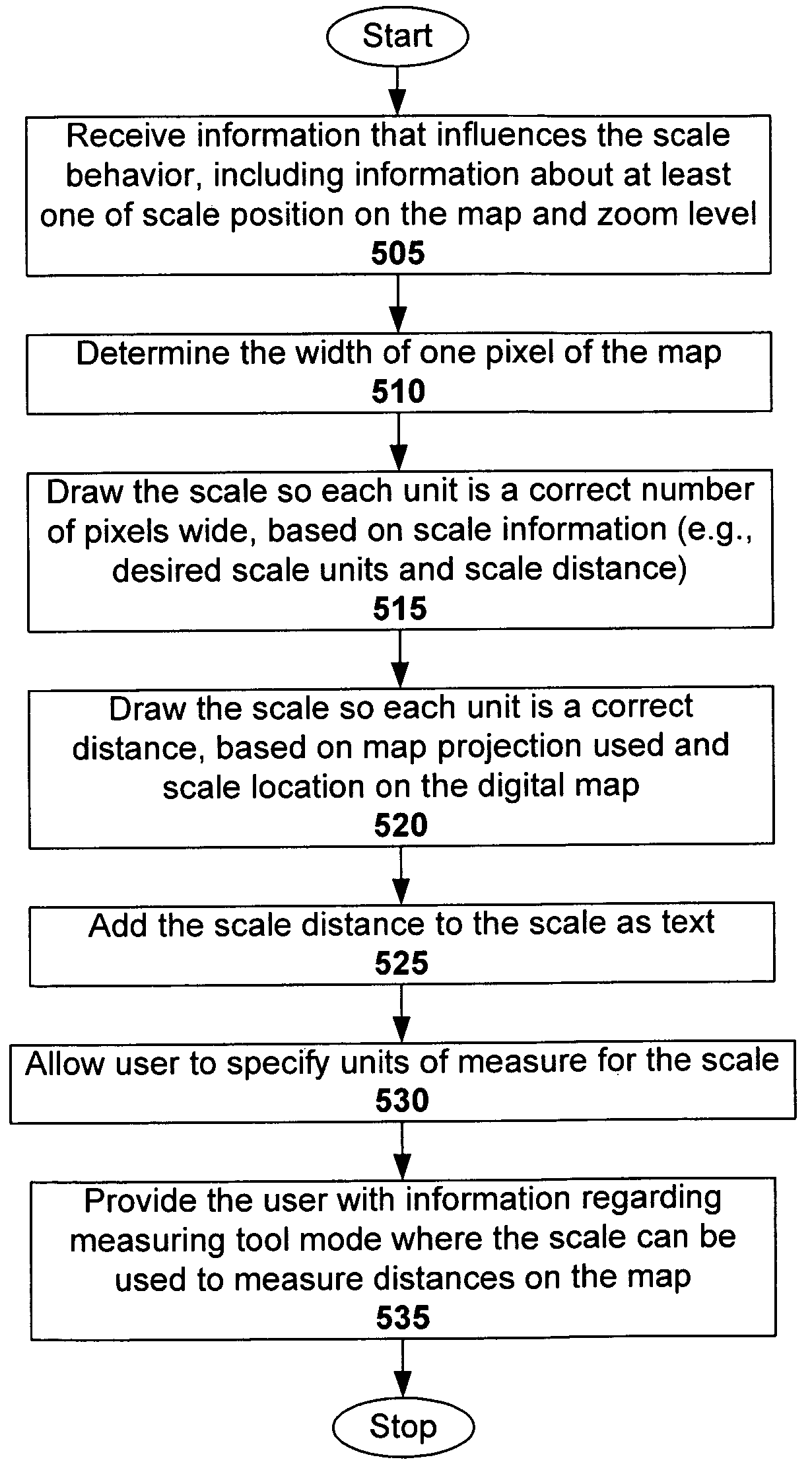
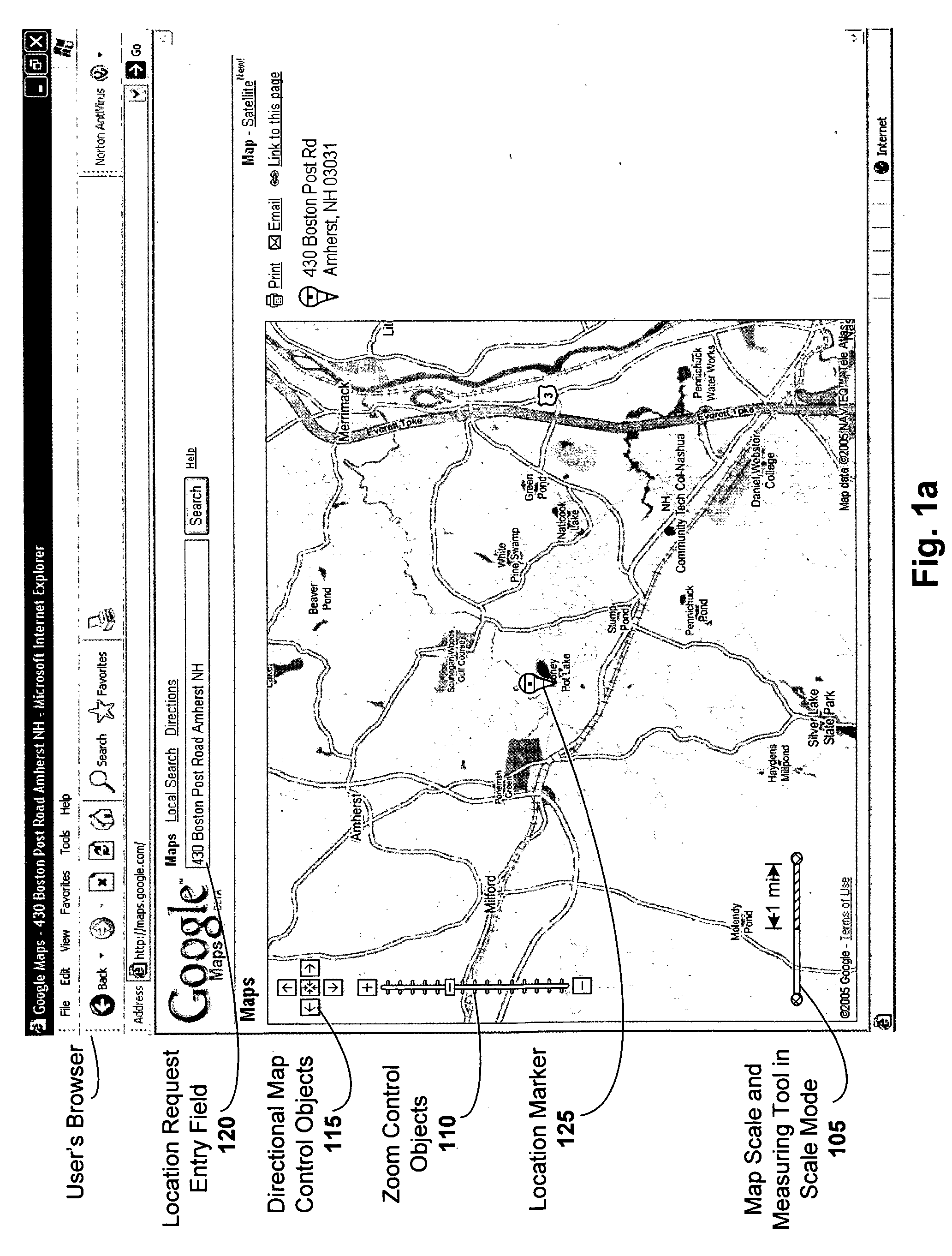
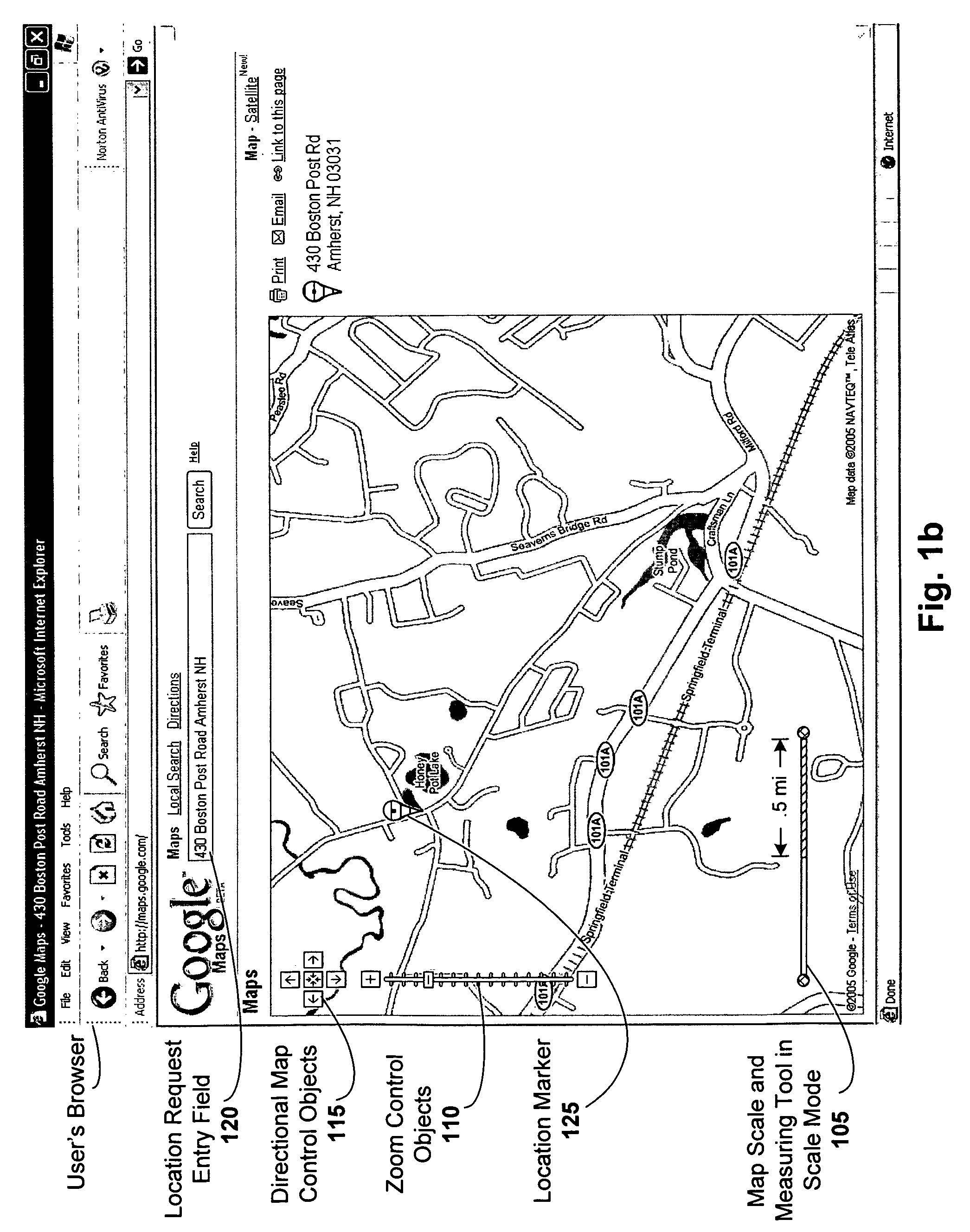
Combined map scale and measuring tool
ActiveUS20060206264A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data information retrievalDrag and dropRelevant information
A combined map scale and measuring tool can be used in digital mapping systems. In the scale mode, the scale indicates the correct scale, for example, at the center of the map. It can be updated with every pan, zoom or resize operation the user performs, and can further update to compensate for map distortion caused by the map projection. The tool mode is entered once the user drags one or both of the scale endpoints onto the map. The distance between two endpoints of the tool can be displayed. A new point can be added each time the user drags a line between existing endpoints of the tool. Info windows can be opened that include relevant information about the endpoints (e.g., latitude / longitude, geo code), and provide option to convert the tool segments to driving directions. A drag and drop location marker is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
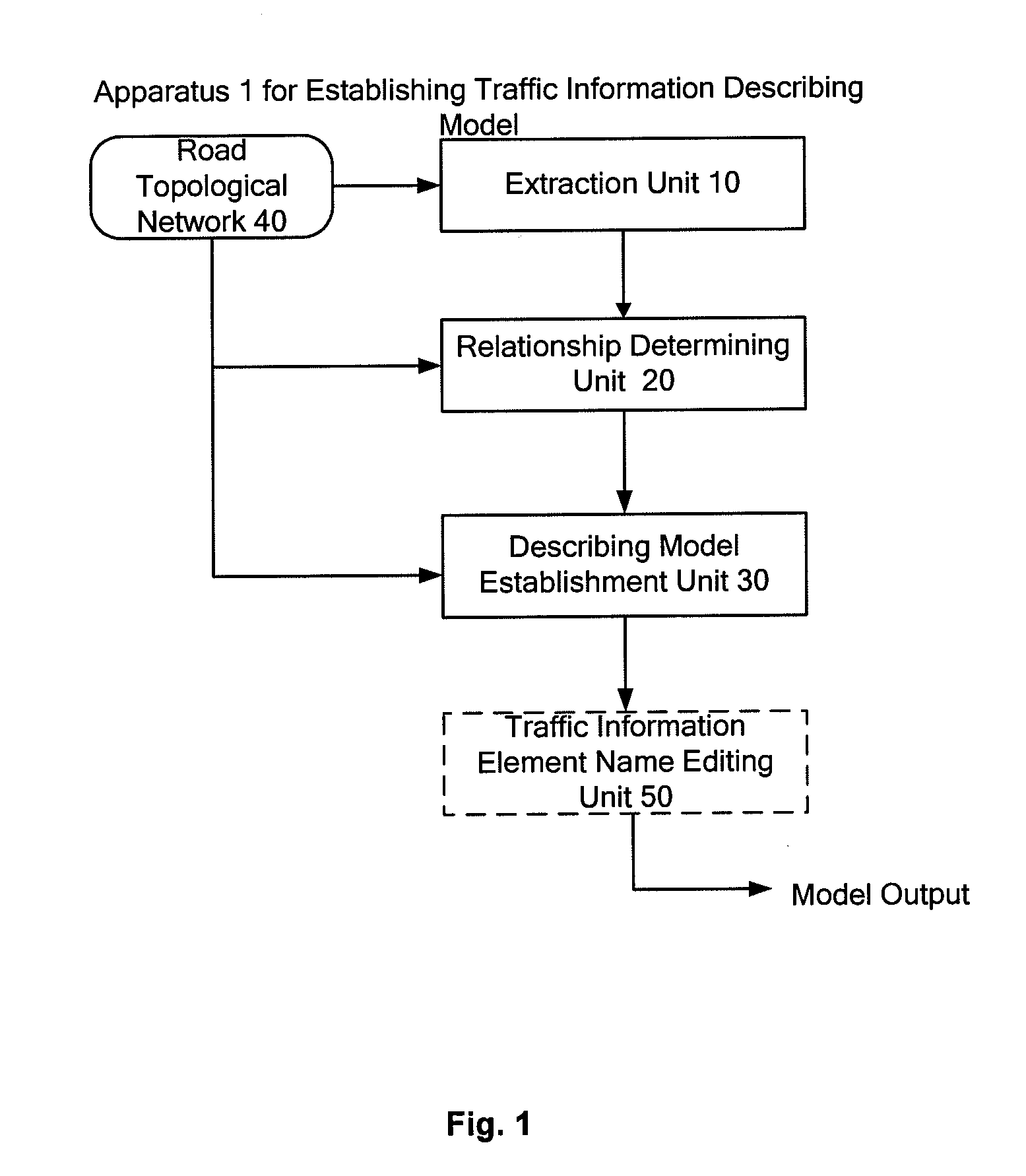
Method and apparatus for traffic information conversion using traffic information element knowledge base
InactiveUS20110160986A1Easy to processExtracting the intersection on the real roads accuratelyAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficRoad networksTrunk road
A method and apparatus for conversion of traffic information based on traffic information element knowledge base are provided. According to the present invention, a road network is described using roads, intersections and sections as traffic information elements and a correspondence between these elements and a road topological network in a digital map is established, so that a universal traffic information describing model, which is compatible with language used in people's daily life, can be established. Further, a traffic information element knowledge base can be generated based on the roads, intersections and sections, their respective attributes and the relationship between them, to support inter-conversion between road topological network traffic information and text-based traffic information. With the universal traffic information describing model and the traffic information element knowledge base according to the present invention, it is possible to support fusion and conversion for traffic data from various sources and to support various forms of presentation and interaction for traffic information, such as presentation of traffic information on digital navigation map, textual description of traffic information, map presentation of traffic information for urban trunk roads, interaction for natural language queries of traffic information, etc.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
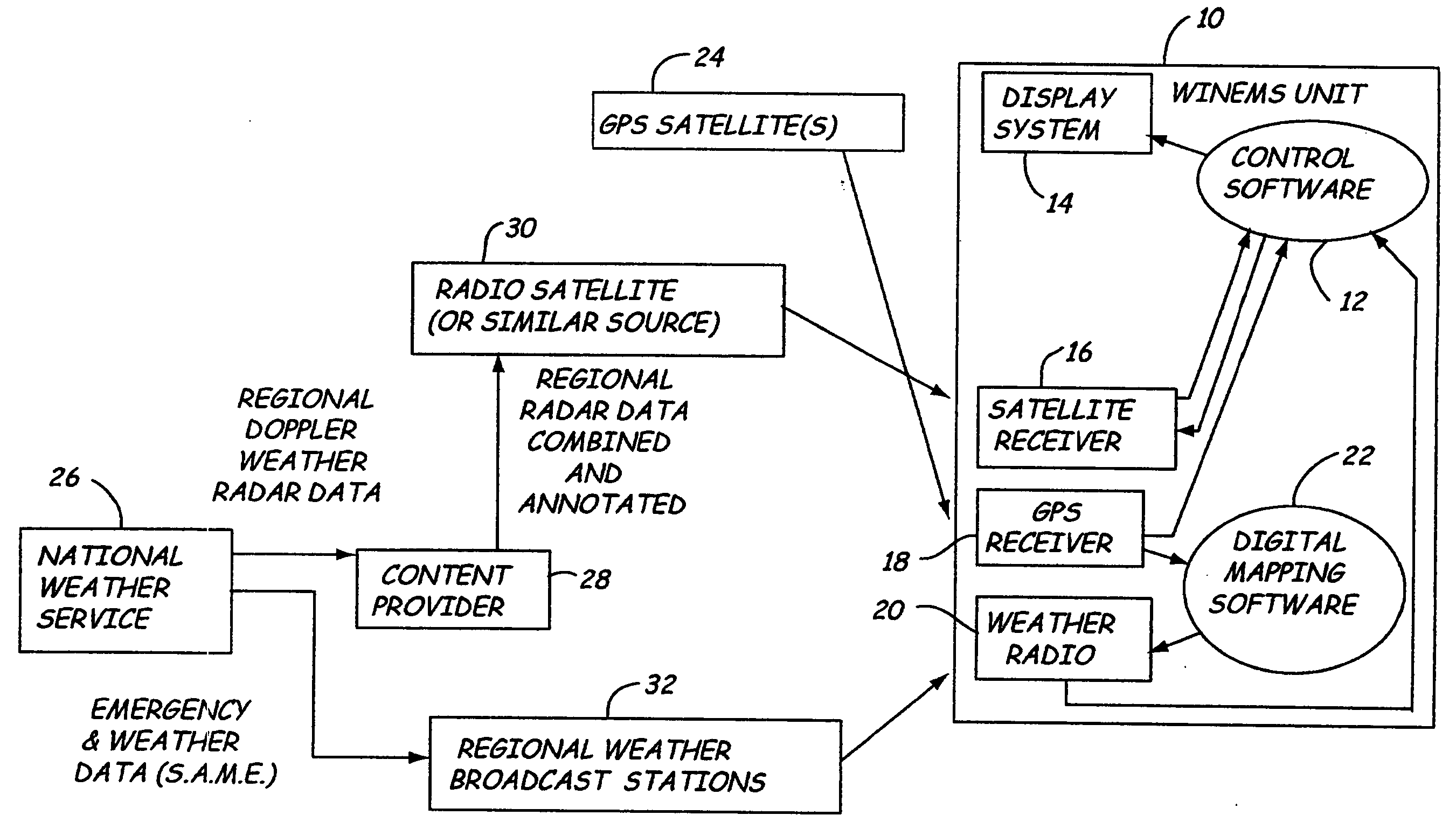
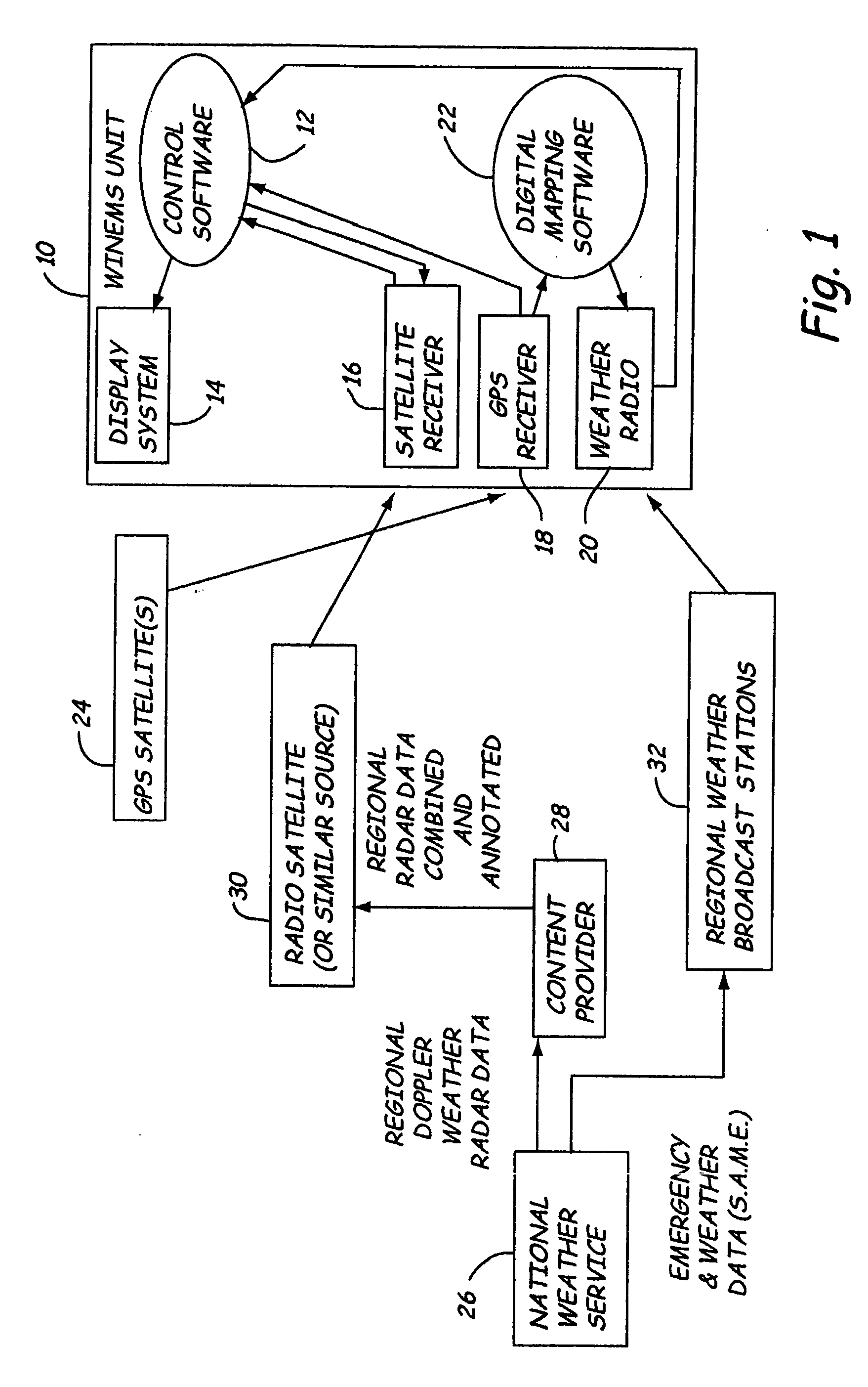
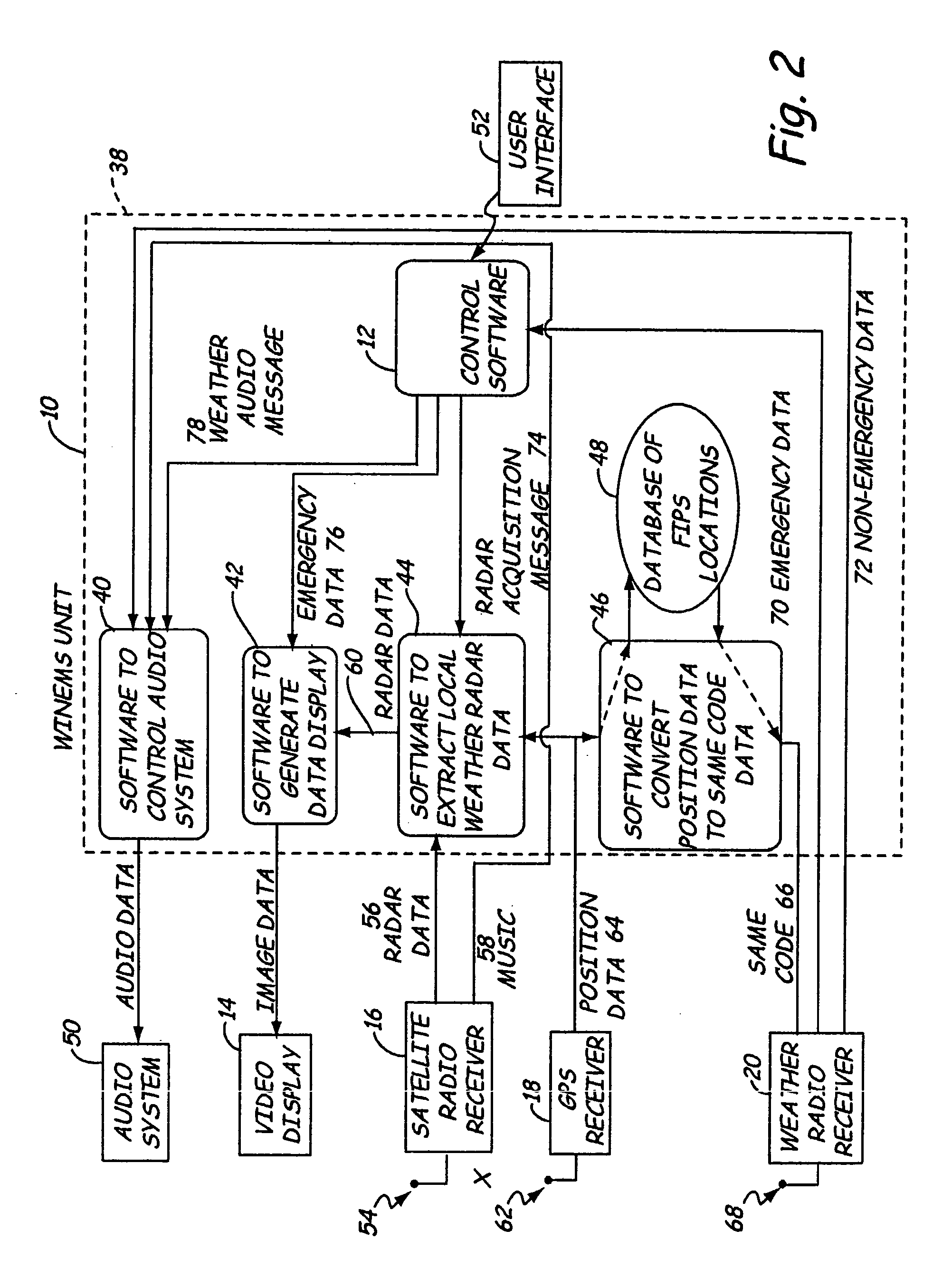
Weather information network enabled mobile system (WINEMS)
InactiveUS20050027449A1Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsWeather condition predictionInformation networksInformation system
A Weather Information Network Enabled Mobile System for providing information to a user regarding an emergency event. The WINEMS system receives location data, such as from a GPS system, and correlates the location data with the emergency alert to display a map showing both a location of the WINEMS system and a location of the emergency event. Preferably, the locations are displayed on a digital map.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA UNIV OF
Techniques for displaying and caching tiled map data on constrained-resource services
ActiveUS7315259B2Reduces required data byteStatic indicating devicesRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile deviceCellular telephone
Techniques are disclosed that enable users to access and use digital mapping systems with constrained-resource services and / or mobile devices (e.g., cell phones and PDAs). In particular, latency of a mapping application on high-latency and low-throughput networks is minimized. One embodiment utilizes volatile and non-volatile storage of the mobile device to cache pre-computed map images (e.g., map tiles). An asynchronous cache can be used to prevent delays caused by potentially slow non-volatile storage. Meta-data about each map image and usage patterns can be stored and used by the cache to optimize hit rates.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
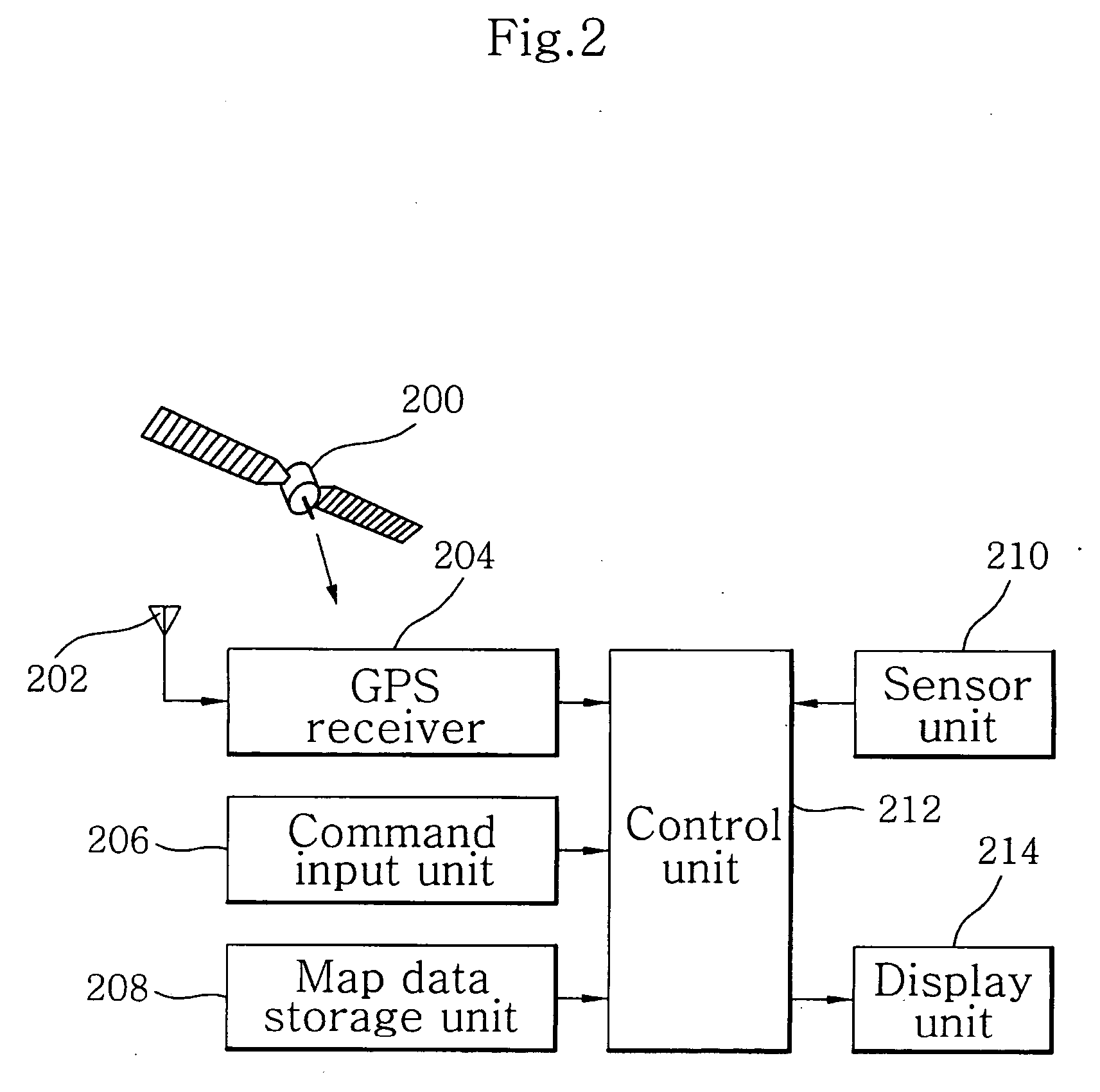
Apparatus and method for detecting vehicle location in navigation system
ActiveUS20050149261A9Accurate detectionAccurate estimateInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGps receiverEngineering
When a vehicle location is estimated using only detection signals from a sensor unit installed on a vehicle since the value of dilution of precision (DOP) of a navigation message received by a GPS receiver is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold in a navigation system, the vehicle location is precisely estimated using a traveled distance, a travel angle difference, and lateral and longitudinal inclinations of the vehicle. The value of DOP of the navigation message received by the GPS receiver is compared with the predetermined threshold. If the value of DOP is less than the predetermined threshold, reference vehicle location information is set using the navigation message. If the value of DOP is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold, the reference vehicle location information is set using vehicle location information just previously map-matched and the detection signals from the sensor unit. The vehicle location is estimated using the set reference vehicle location information and the detection signals from the sensor unit and then map-matched on a digital map stored in a map data storage unit, thereby displaying the map-matched results on a display unit.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
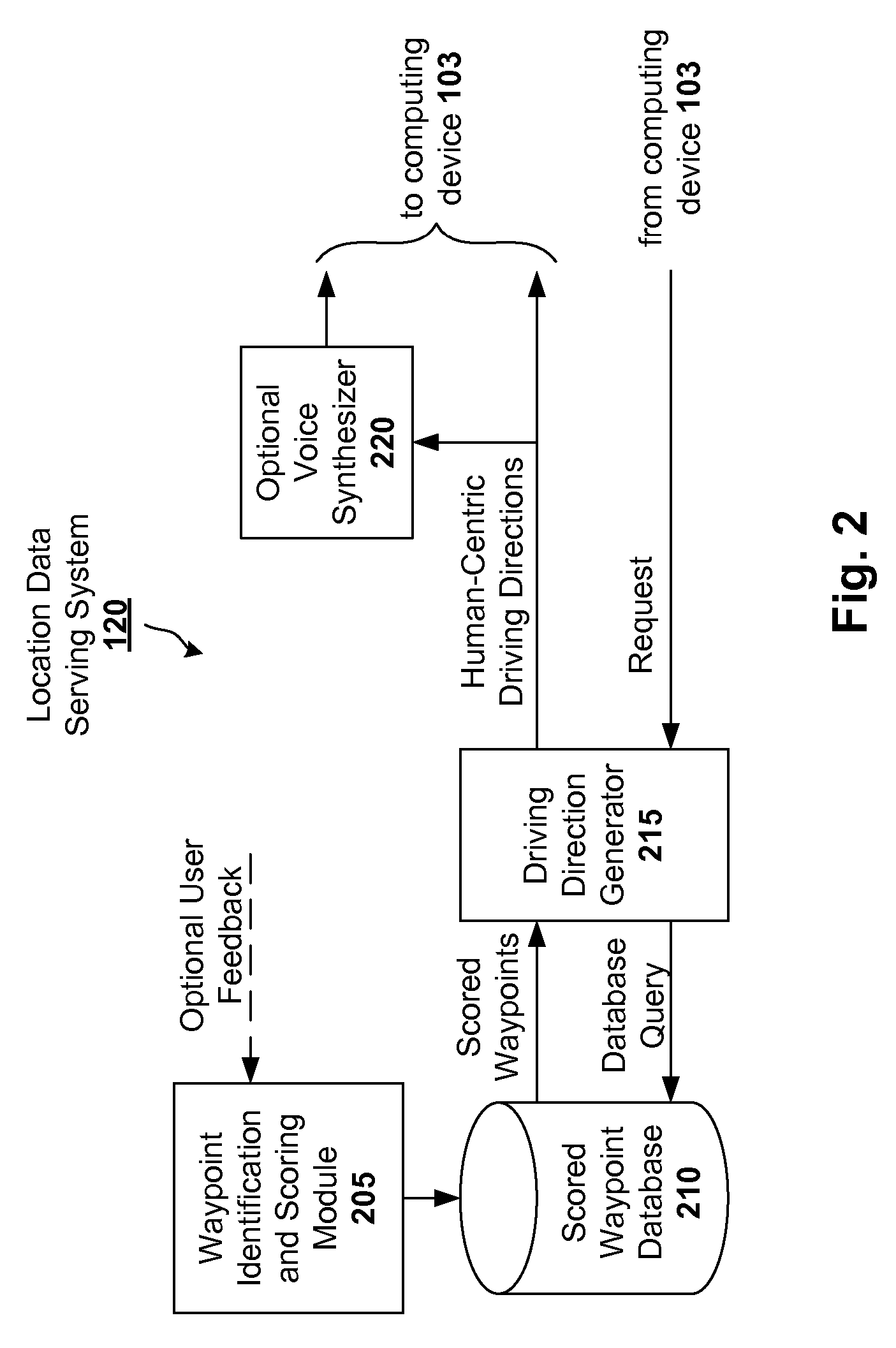
Generating Human-Centric Directions in Mapping Systems
ActiveUS20070016368A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGraphicsHeuristic
Digital mapping techniques are disclosed that provide visually-oriented information to the user, such as driving directions that include visual data points along the way of the driving route, thereby improving the user experience. The user may preview the route associated with the driving directions, where the preview is based on, for example, at least one of satellite images, storefront images, and heuristics and / or business listings. The visually-oriented information can be presented to the user in a textual, graphical, or verbal format, or some combination thereof.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
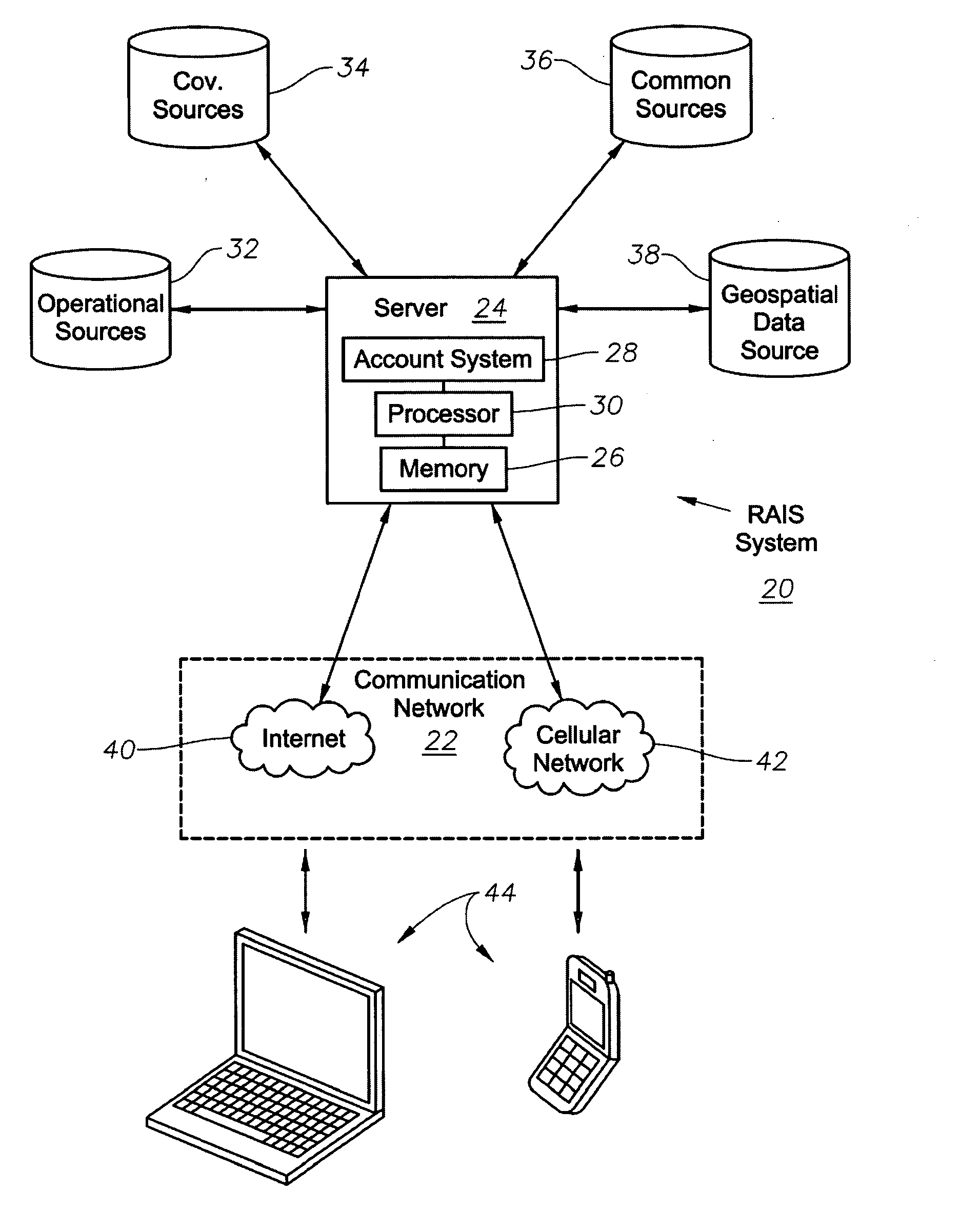
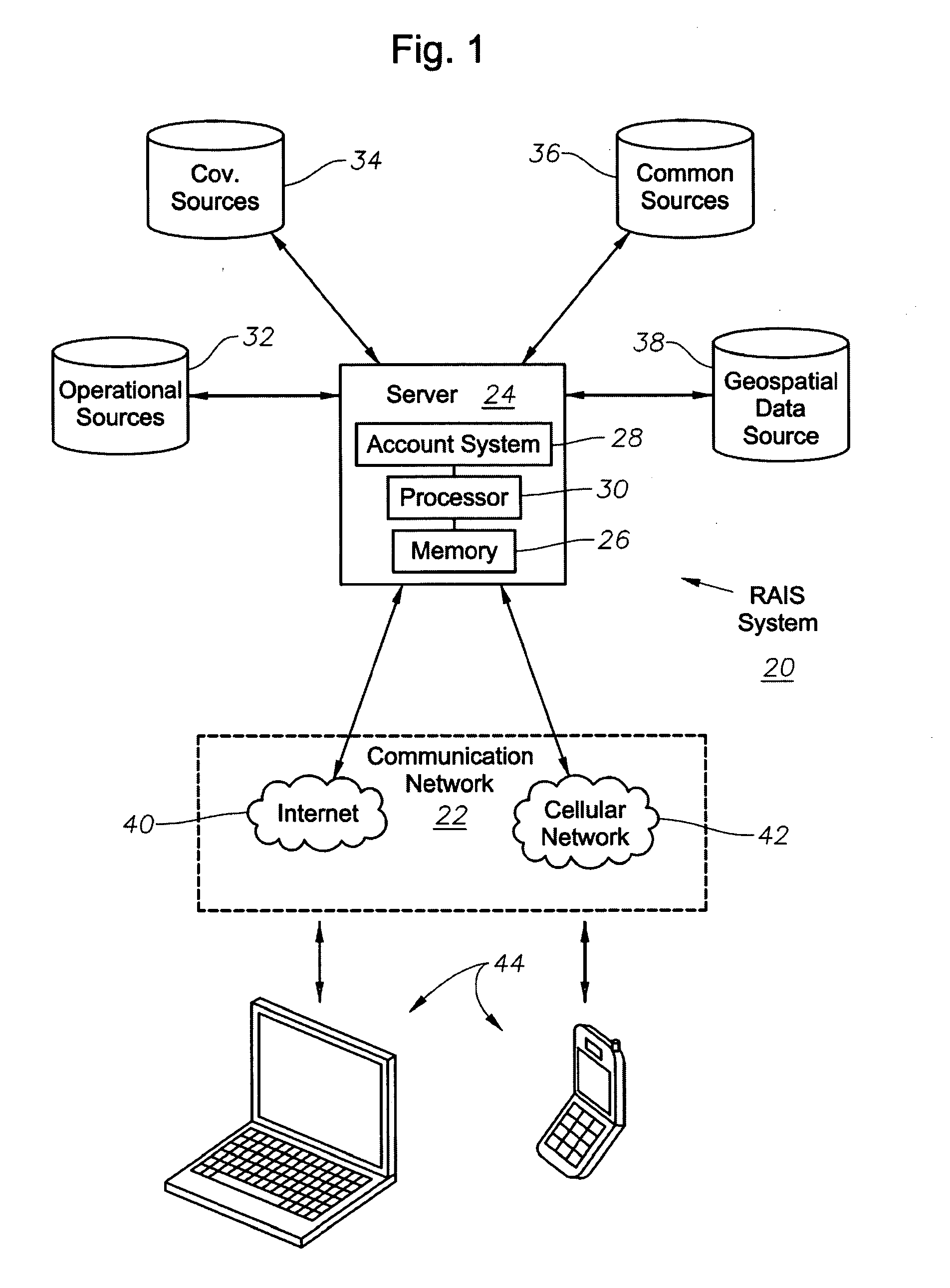
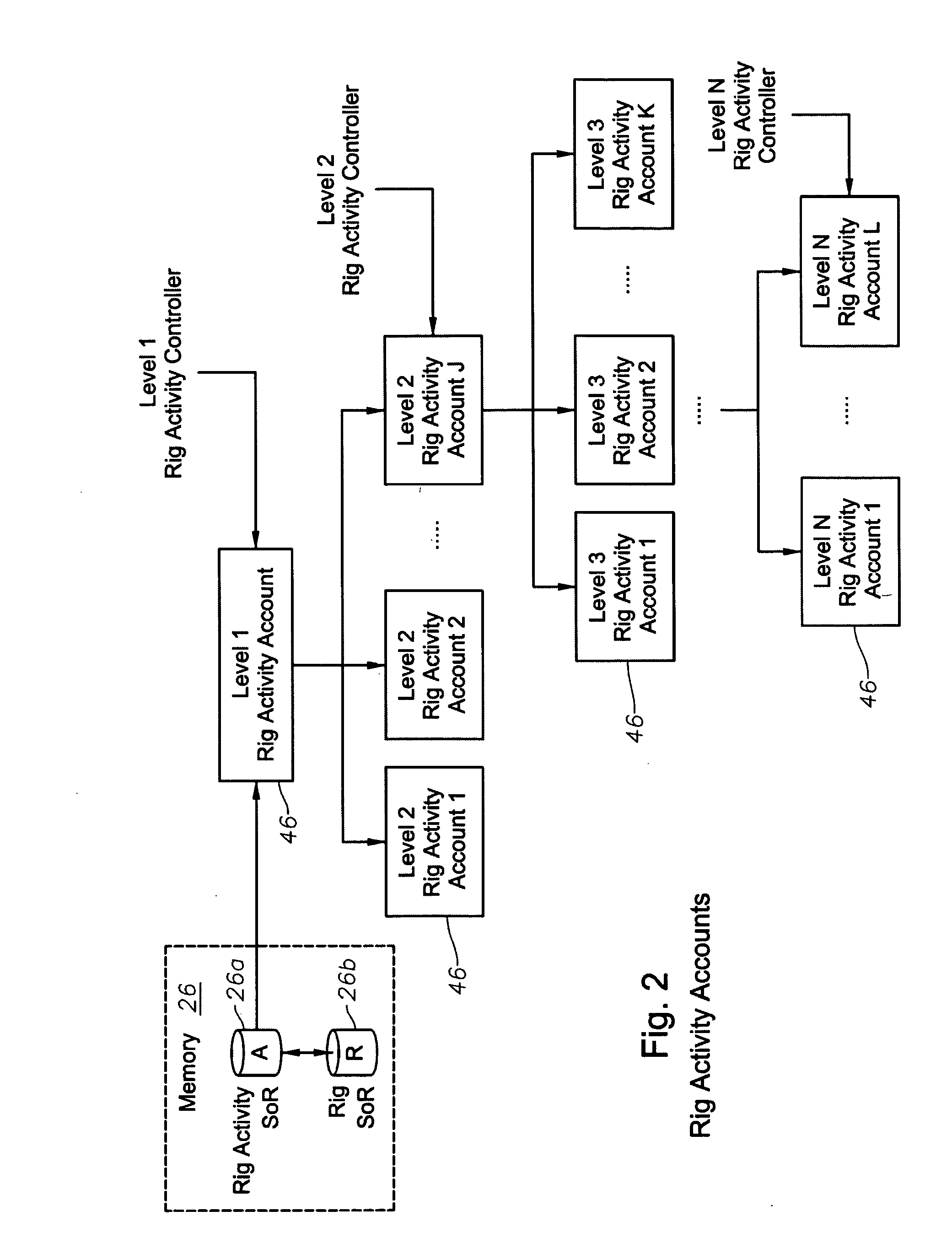
System, Program Product, and Method For Drilling Rig Activity Accounting and Visualization
ActiveUS20100114493A1Improve data qualityEasy to controlElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingError detection/correctionLibrary scienceLocation data
A system to monitor drilling rig activity and to provide and manage drilling rig information, program product, and associated methods are provided. The system can include a communication network, a drilling rig information management server, a database accessible to the processor of the server, and drilling rig information management program product stored in the memory of the drilling rig information management server and including instructions that when executed by the processor of the drilling rig information management server cause the server to perform the operations of retrieving drilling rig location data from the database responsive to user selection of a geospatial location attribute, accessing digital mapping data to display a digital map associated with the user selected geospatial location attribute, and providing data to display indicia of a drilling rig location for at least one drilling rig overlaid upon and spatially oriented to at least portions of the digital map.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Combined map scale and measuring tool
ActiveUS7620496B2Instruments for road network navigationDigital data information retrievalDrag and dropRelevant information
A combined map scale and measuring tool can be used in digital mapping systems. In the scale mode, the scale indicates the correct scale, for example, at the center of the map. It can be updated with every pan, zoom or resize operation the user performs, and can further update to compensate for map distortion caused by the map projection. The tool mode is entered once the user drags one or both of the scale endpoints onto the map. The distance between two endpoints of the tool can be displayed. A new point can be added each time the user drags a line between existing endpoints of the tool. Info windows can be opened that include relevant information about the endpoints (e.g., latitude / longitude, geo code), and provide option to convert the tool segments to driving directions. A drag and drop location marker is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
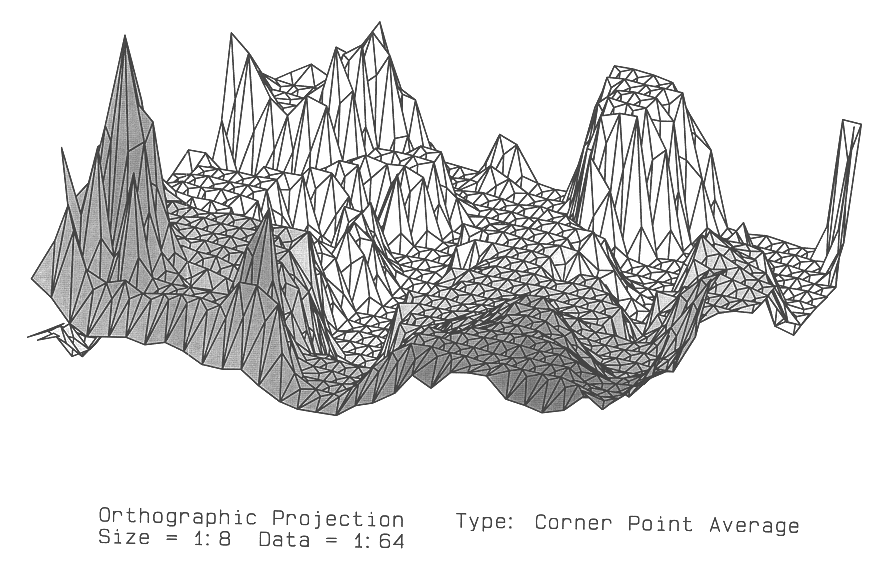
Digital map compression and display method
A digital elevation database is compressed to create a compressed digital map database which is used by a digital computer system for displaying three-dimensional terrain data in the form of polygons. The compressed digital map database is produced from a database of elevation points by selecting every mth row and every nth column, thereby resulting in a reduction of database storage requirements. During program run-time the intersection of rows and columns forms cells with four corners. The elevation value of a center elevation point for each cell is formed by various methods, thereby creating a cell made up of four three-dimensional triangles. One method for creating the elevation of the center elevation point uses the elevations of the four corners of the cell. Another method uses extrapolated elevation values from the cell's extended diagonals. The three-dimensional triangles formed from the center elevation point are then transformed and projected using standard computer graphics methods on a digital computer to produce a three-dimensional projected display.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC +1
Method for creating speed profiles for digital maps
ActiveUS20110307165A1Smooth transitionEnergy efficient ICTAnalogue computers for vehiclesDriver/operatorEngineering
Probe data collected at times of low traffic density is analyzed to derive a Raw Road Design Speed Limit (RRDSL, 16) for each road segment or group of segments in a digital map. The RRDSL (16), comprised of longitudinally distributed Pt speeds, is associated with the road segment and stored in a digital medium to indicate the limits of the road section in free flow traffic. The longitudinally distributed speeds may be limited by local speed limits or other business logic to establish a Legal Raw Road Design Speed Limit (LRRDSL, 17). Either the RRDSL (16) or the LRRDSL (17) can be further modified to smooth acceleration and deceleration rates between changes in the longitudinally distributed speeds to create an Optimal Longitudinal Speed Profile (OLSP, 18), which represents optimized energy consumption. A signal can be produced if a driver's current speed rises unacceptably above a longitudinally distributed speed in real time. The signal can be audible, visible and / or haptic. Real-time traffic density information can be inferred by comparing current speed data to the longitudinally distributed speed for that position. If the current speed is consistently lower than the longitudinally distributed speed for that position, an inference is drawn that the road section is inefficient. Road efficiency assessments can be transmitted to a service center and / or other vehicles, and used by navigation software.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
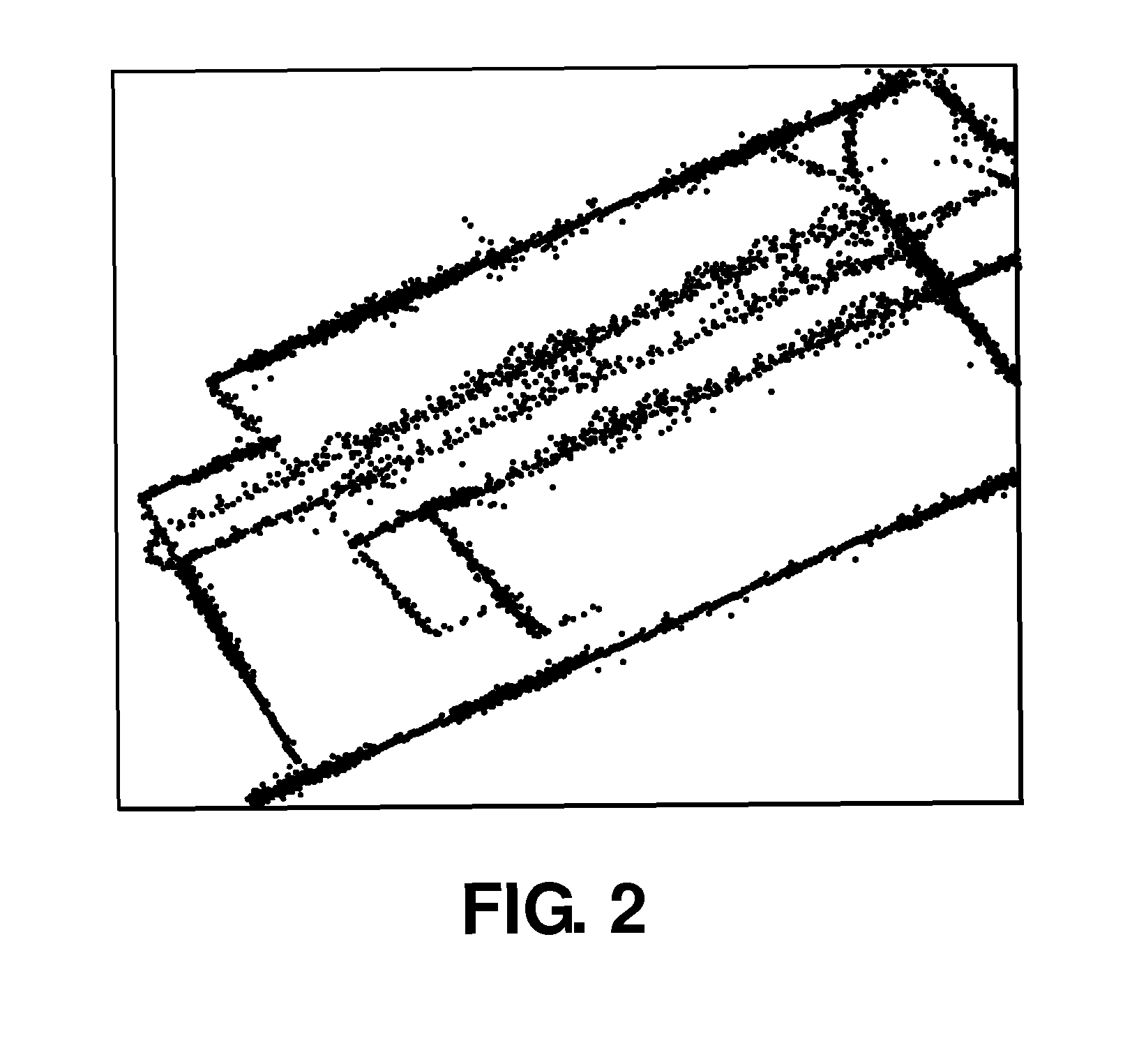
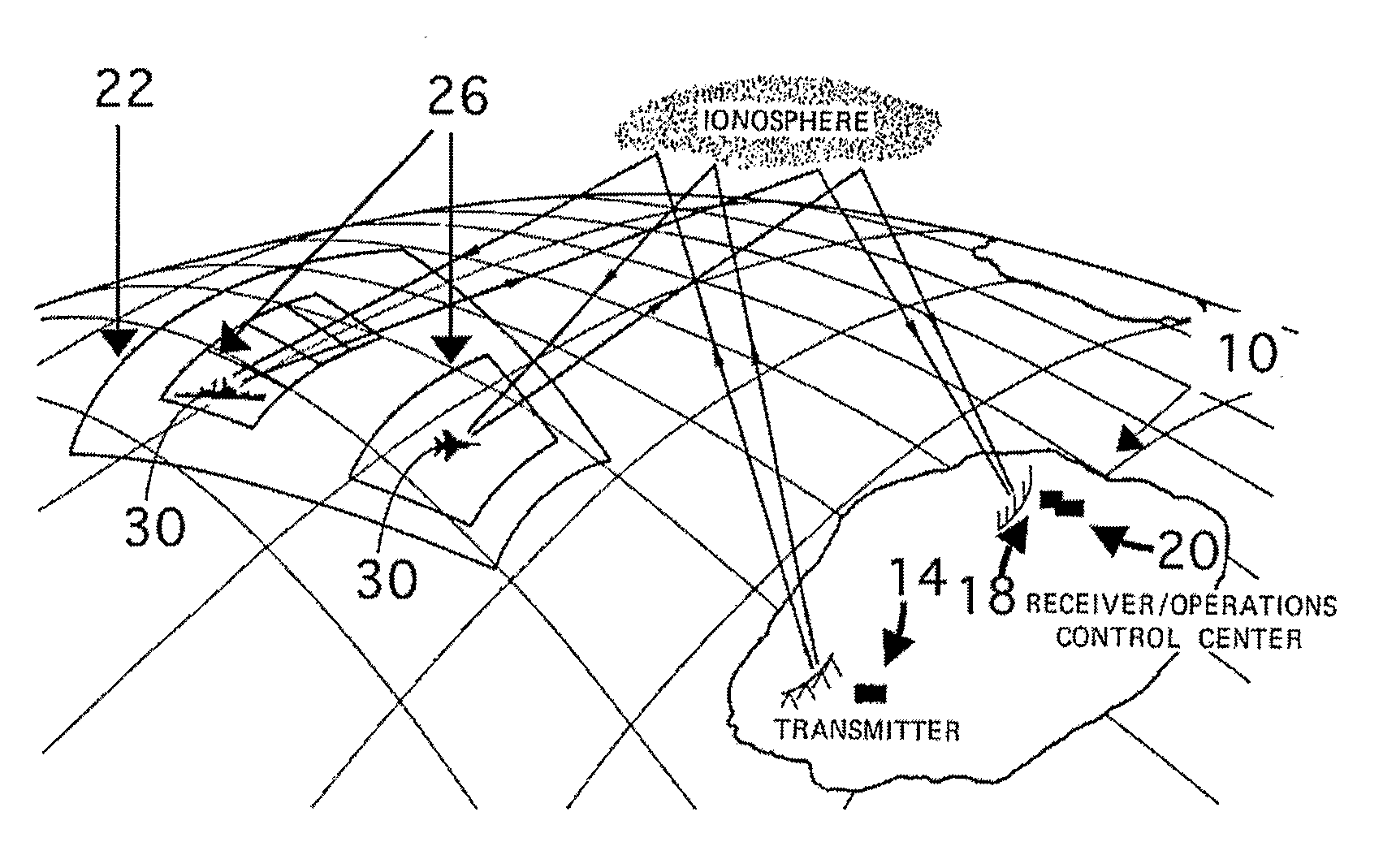
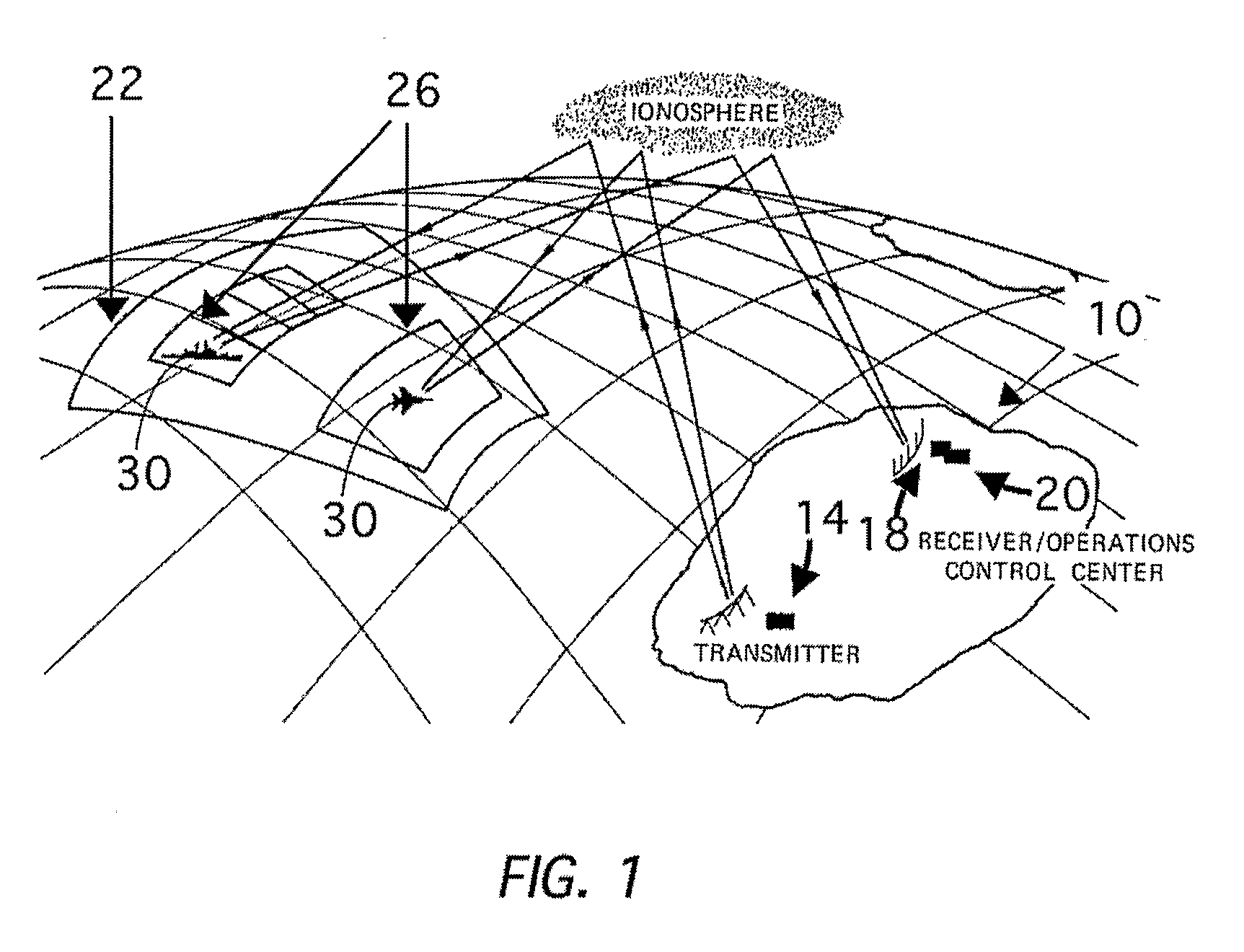
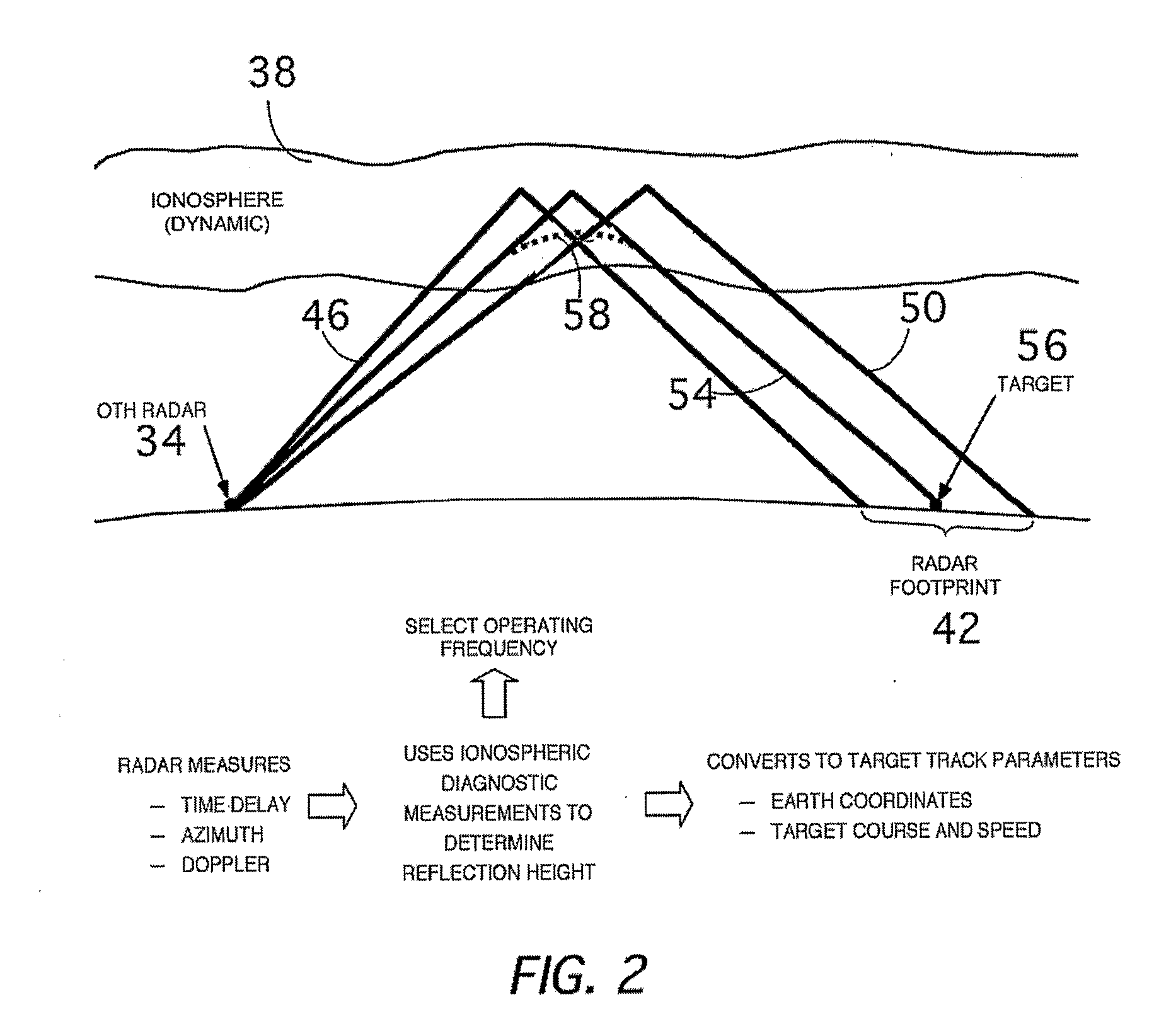
Method and system for multiple target class data recording, processing and display for over-the-horizon radar
A method and apparatus are disclosed that enable an over-the-horizon-radar (OTHR) system to detect and track multiple target classes simultaneously, where target classes are defined by the speed and acceleration of the tracked objects. The OTHR is tasked in a staring mode, with a bandwidth and waveform repetition frequency that enable detection of Doppler shifts from all target types, with sufficient clutter reduction and range resolution. The backscattered echoes are buffered for each target class and processed independently. The output of an automatic tracking algorithm then preferentially plots target progress on a single digital map for all target classes.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
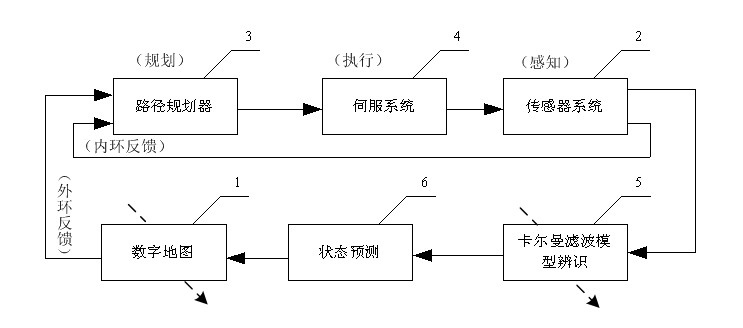
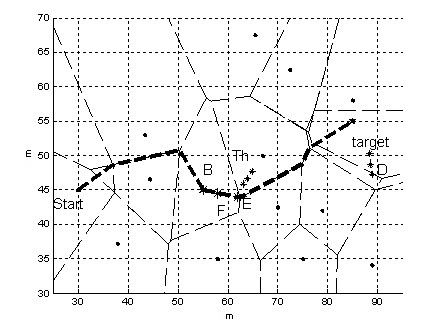
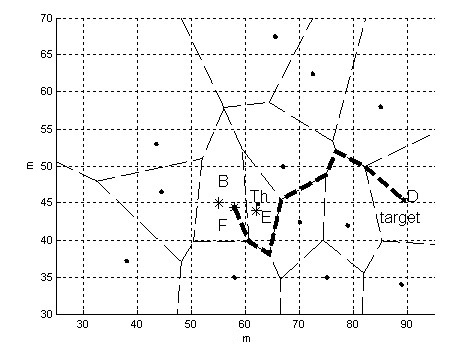
Kalman filter prediction-based robot obstacle avoidance method
InactiveCN101943916AEasy to implementImprove real-time performanceControl using feedbackKaiman filterObservation data
The invention relates to a Kalman filter prediction-based robot obstacle avoidance method. In a complex environment, the robot travelling environment changes dynamically; and when an environment of a preplanned mission is determined to have a significant change, the target objective is modified, the target is planned in real time, and the path is modified. In the obstacle avoidance method, a path scheduler sorts a target set according to a digital map, the target set and the state of the robot acquired by a sensor system so as to generate a robot travelling point sequence; the robot travelling point sequence is executed by a servo system; when the sensor system detects a new obstacle, a Kalman filter model is established according to observation data; and parameters are identified and modified by using the observation data and an expectation maximization model identification algorithm of a classical linear dynamic system; and the digital map is updated for the next turn of local re-planning of the path scheduler. The method can realize obstacle avoidance path planning of the robot generated locally and dynamically in an undetermined environment, and has the advantages of simple implementation and good real-time performance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com