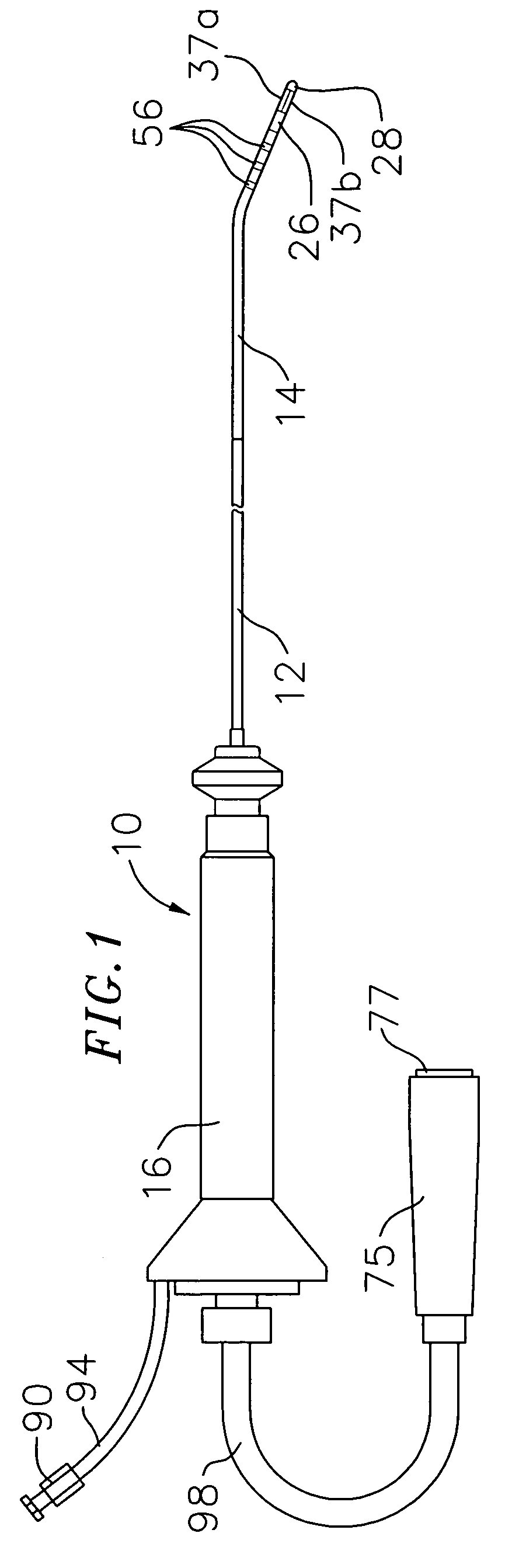
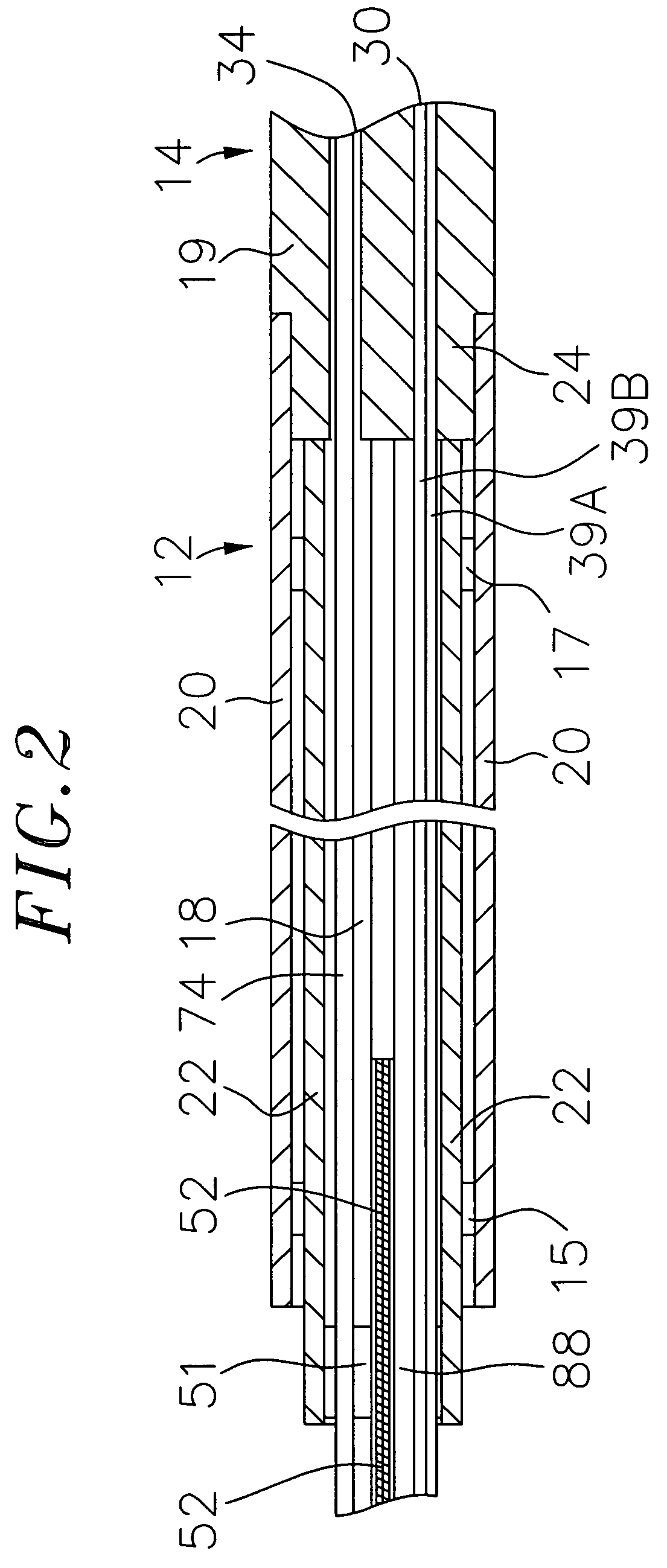
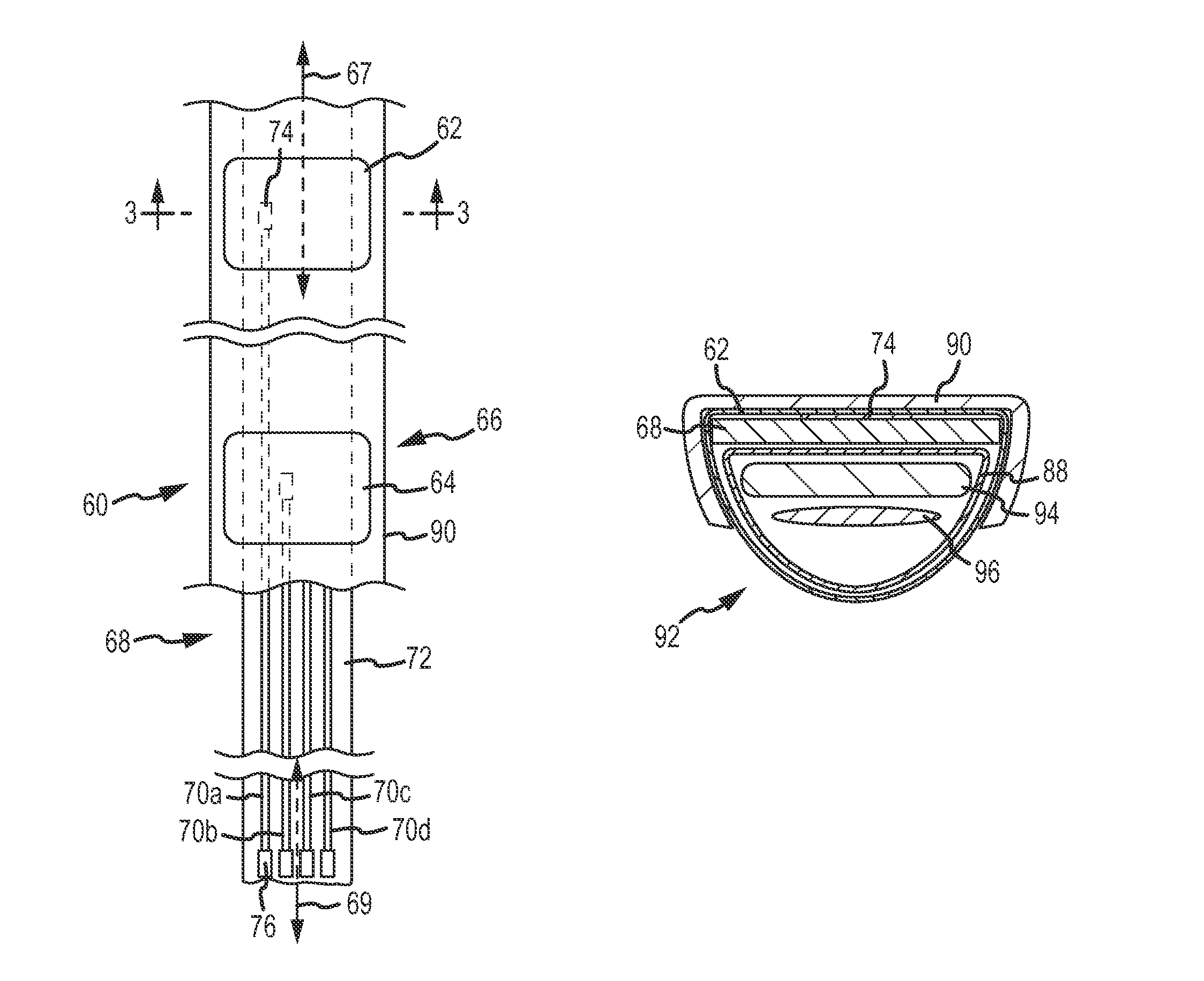
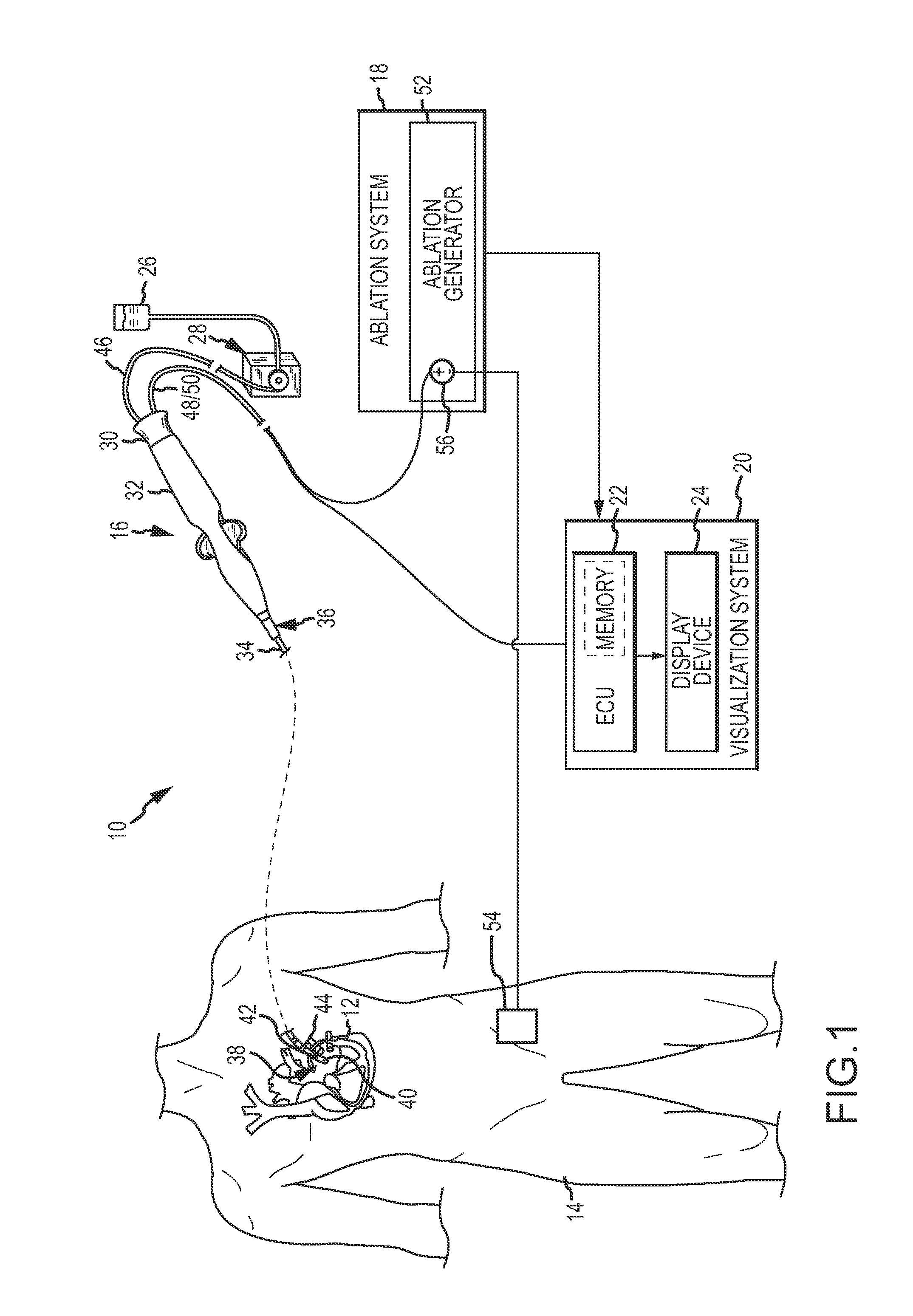
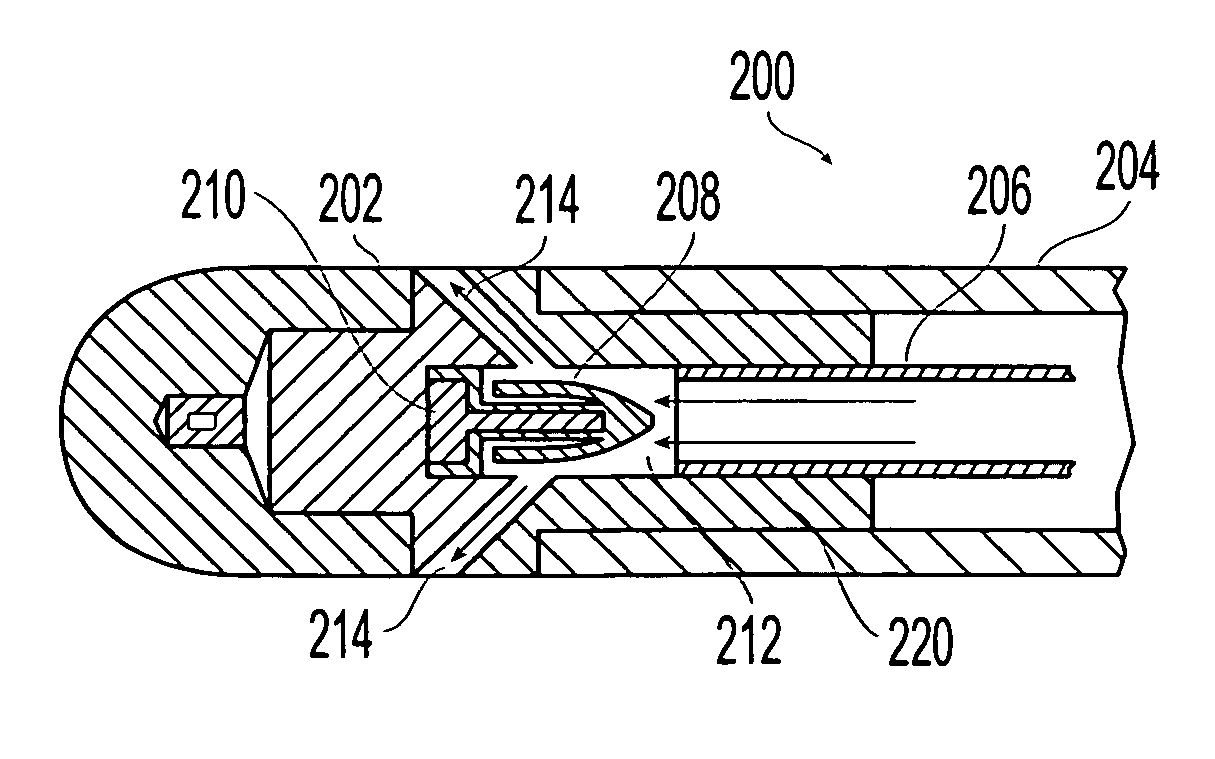
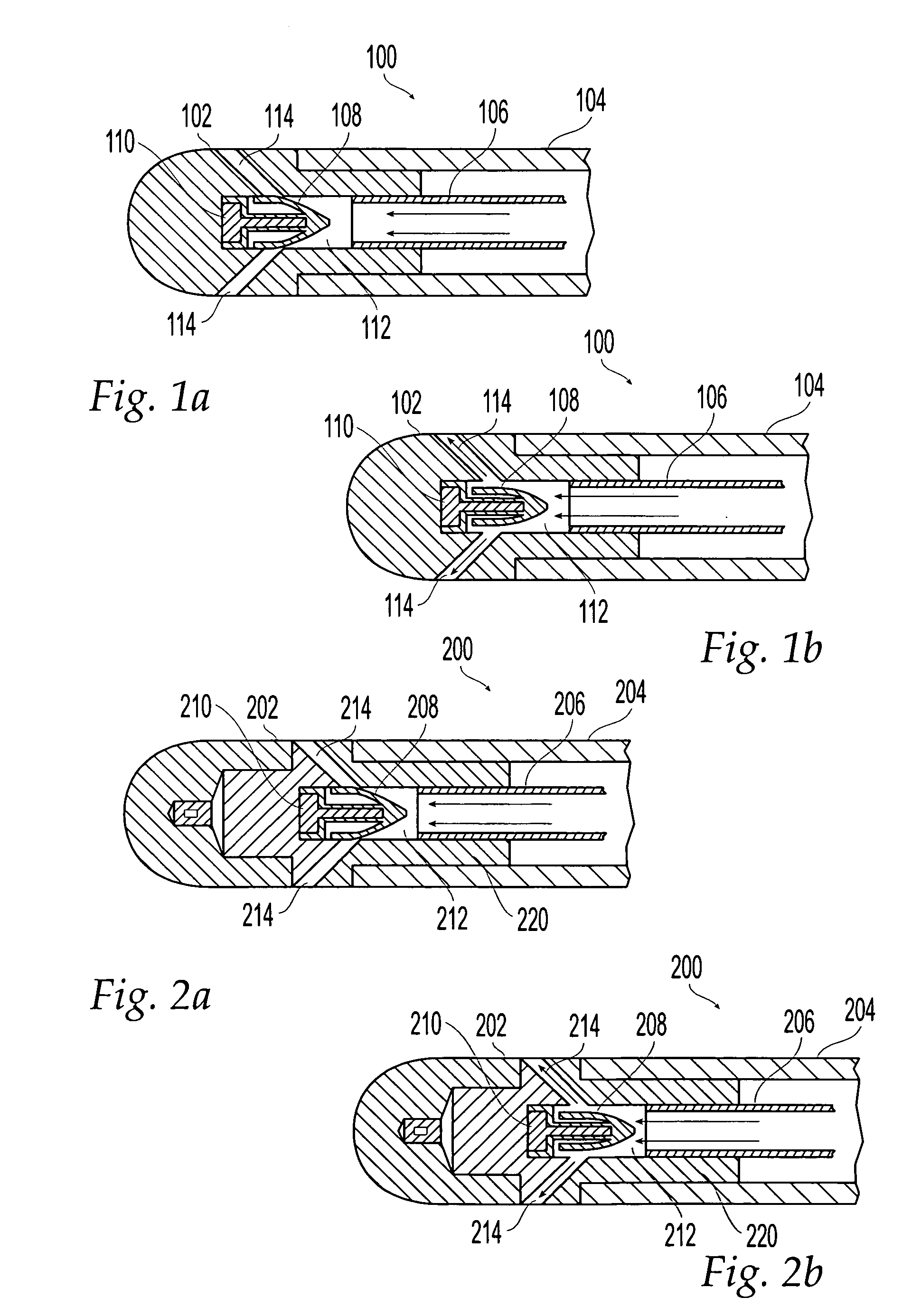
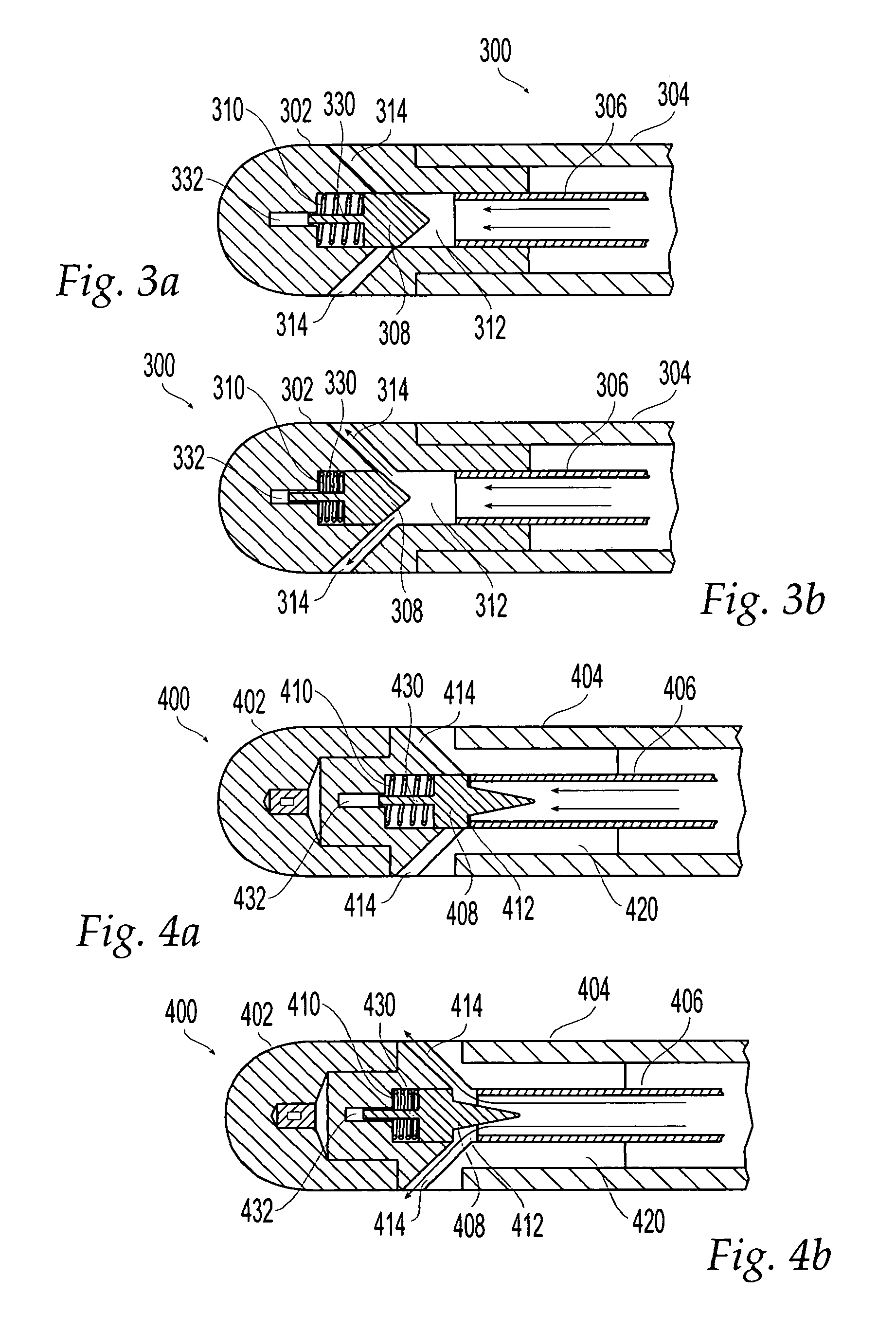
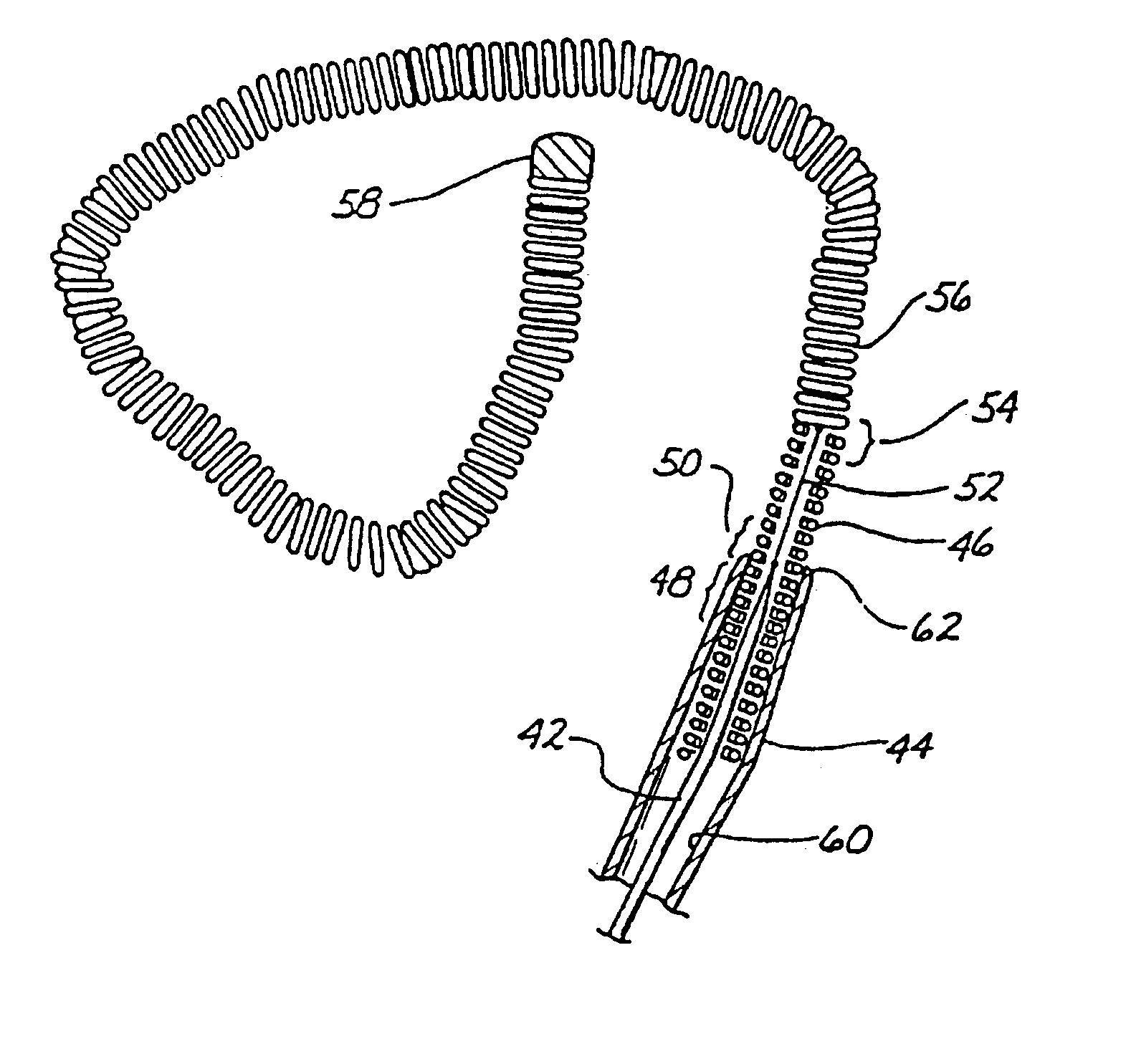
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Catheter electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
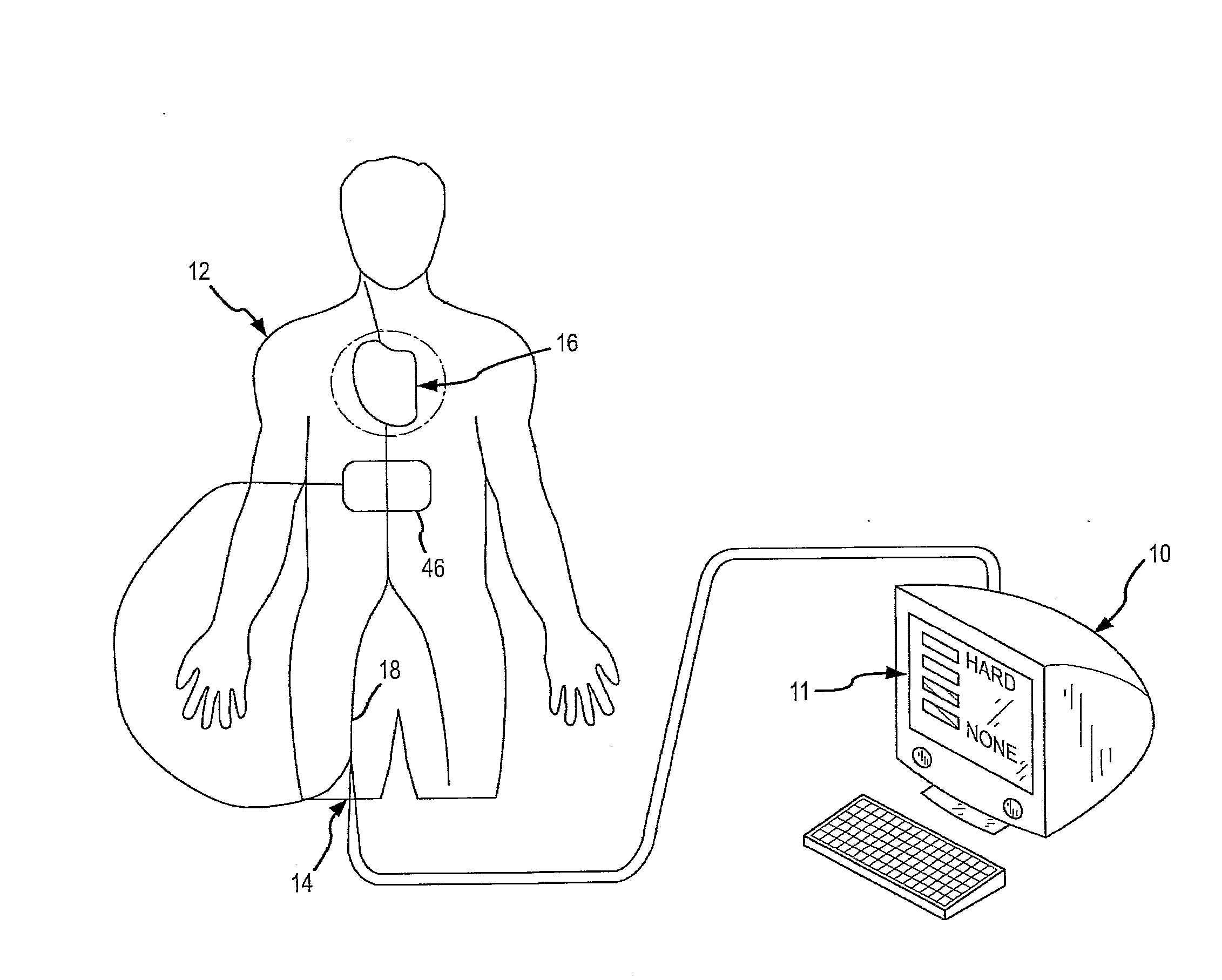
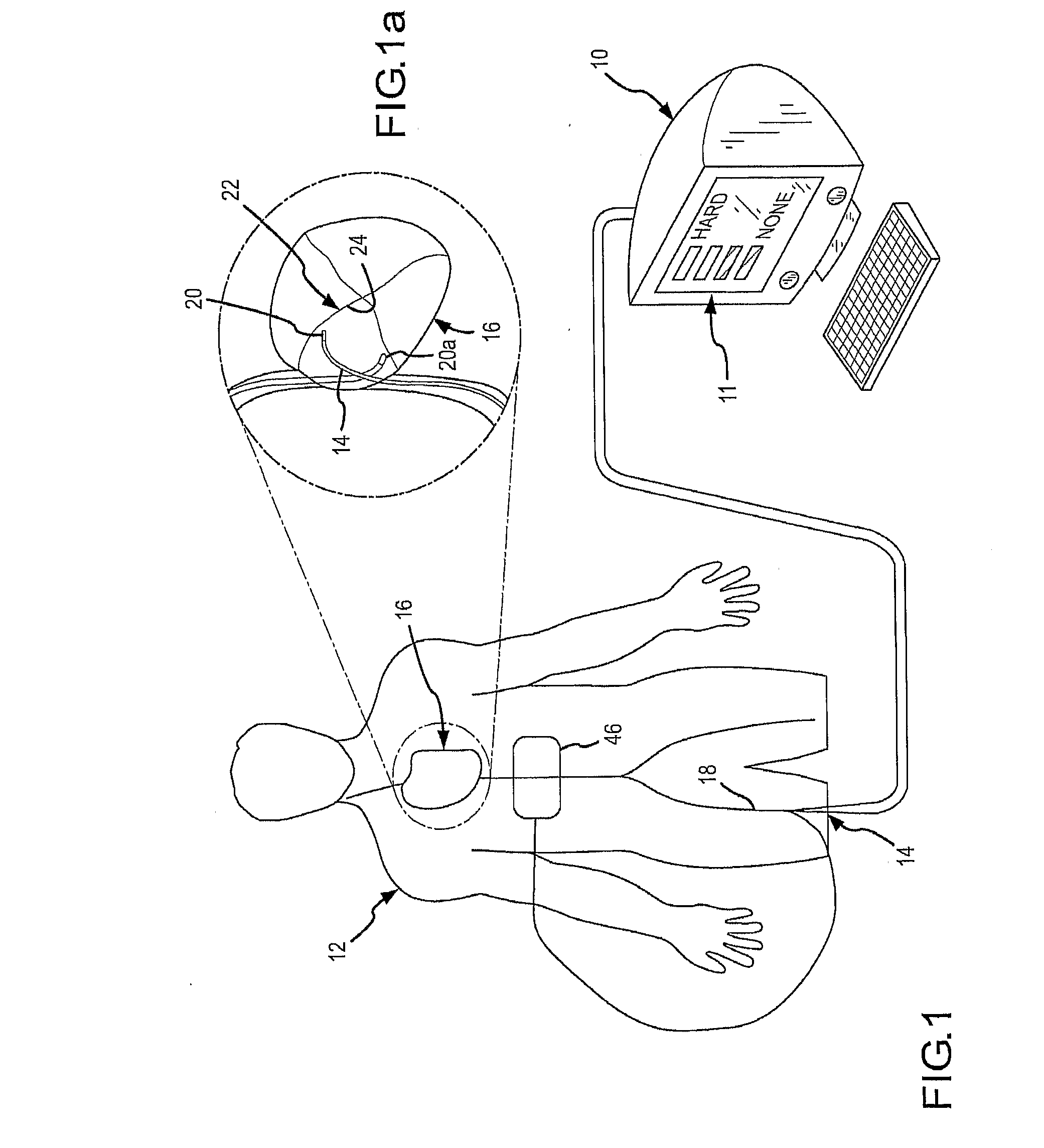
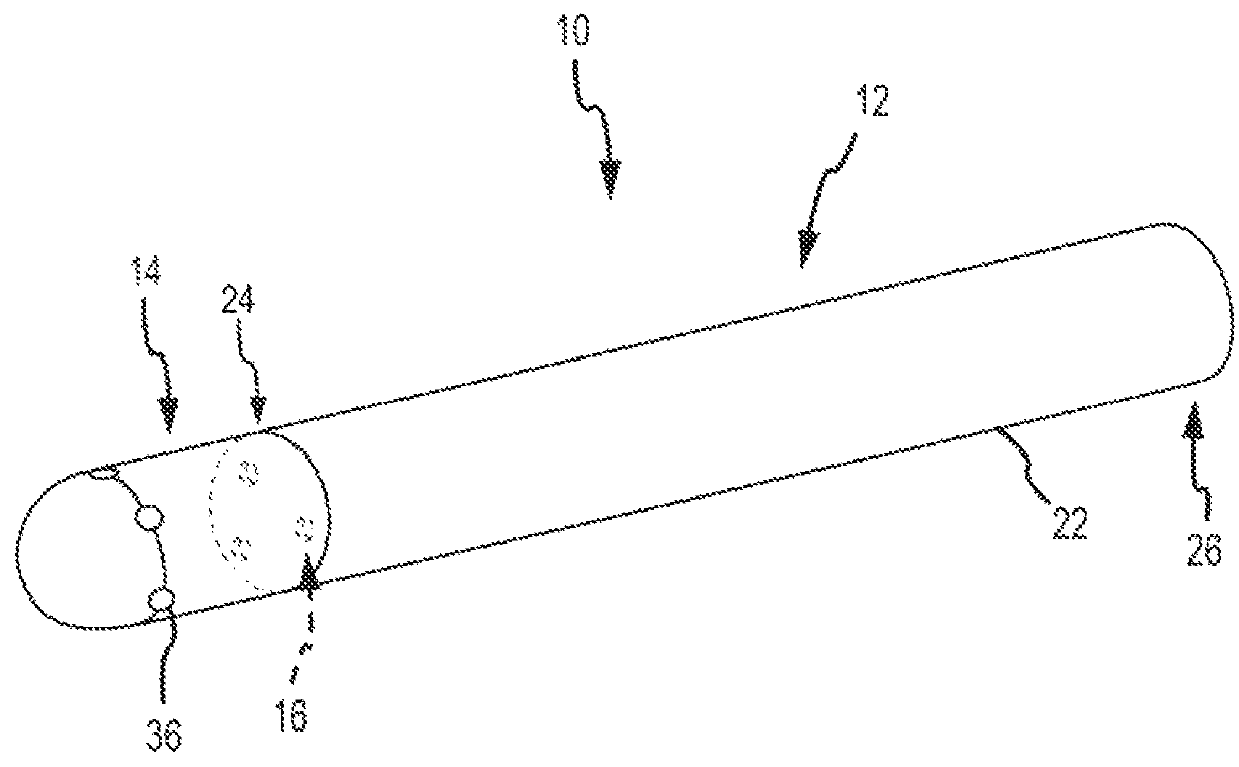
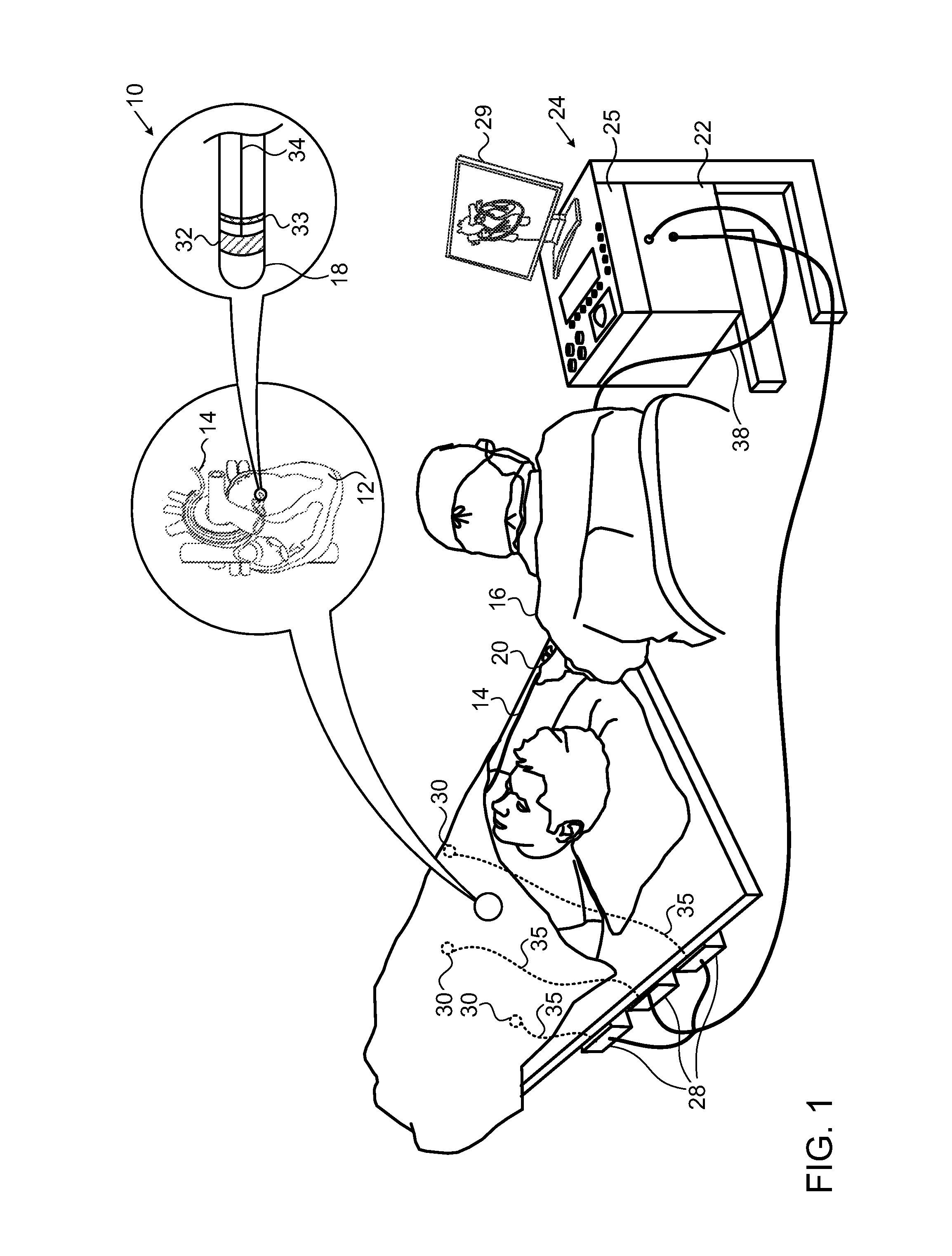
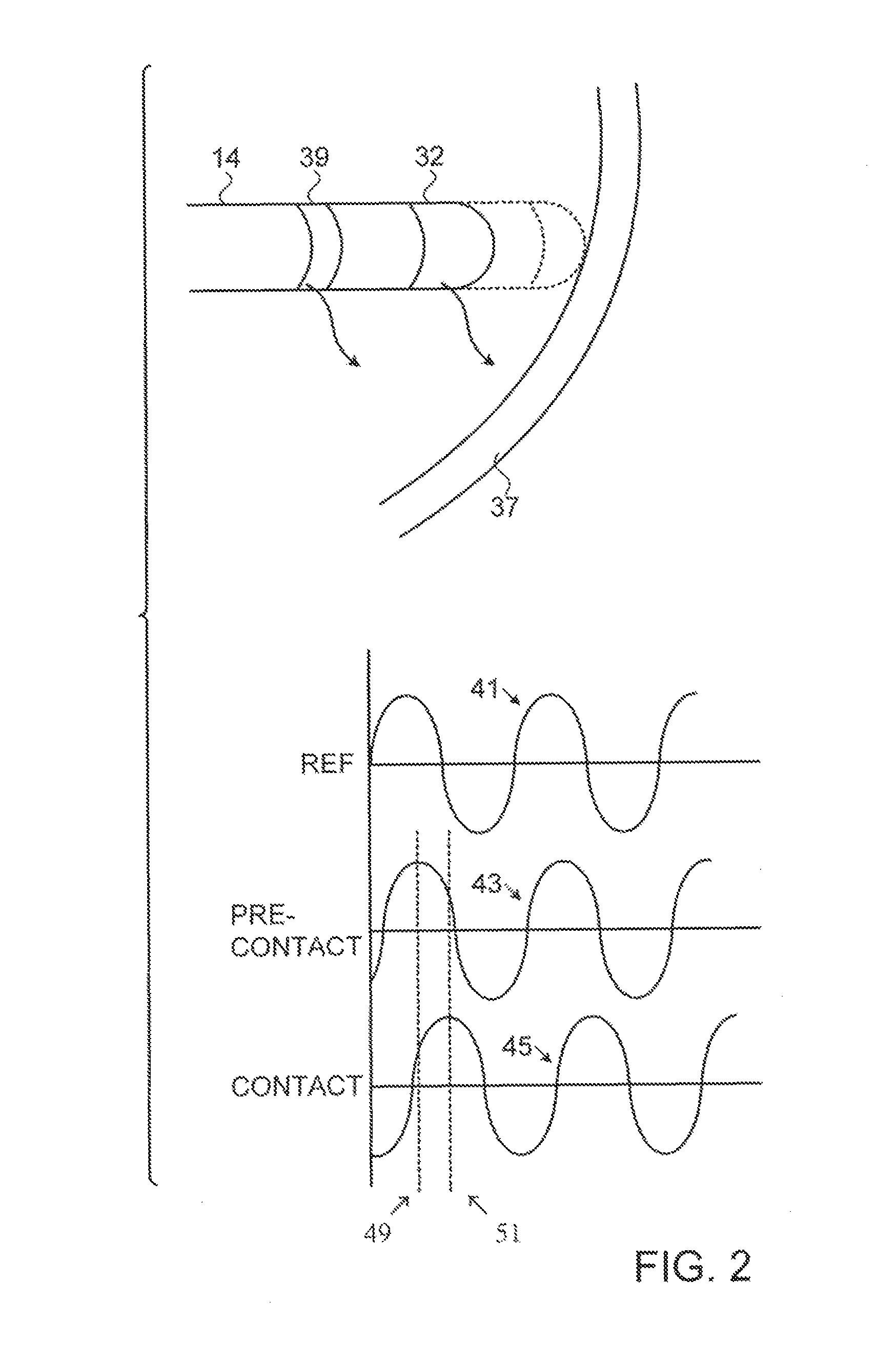
Method for Displaying Catheter Electrode-Tissue Contact in Electro-Anatomic Mapping and Navigation System
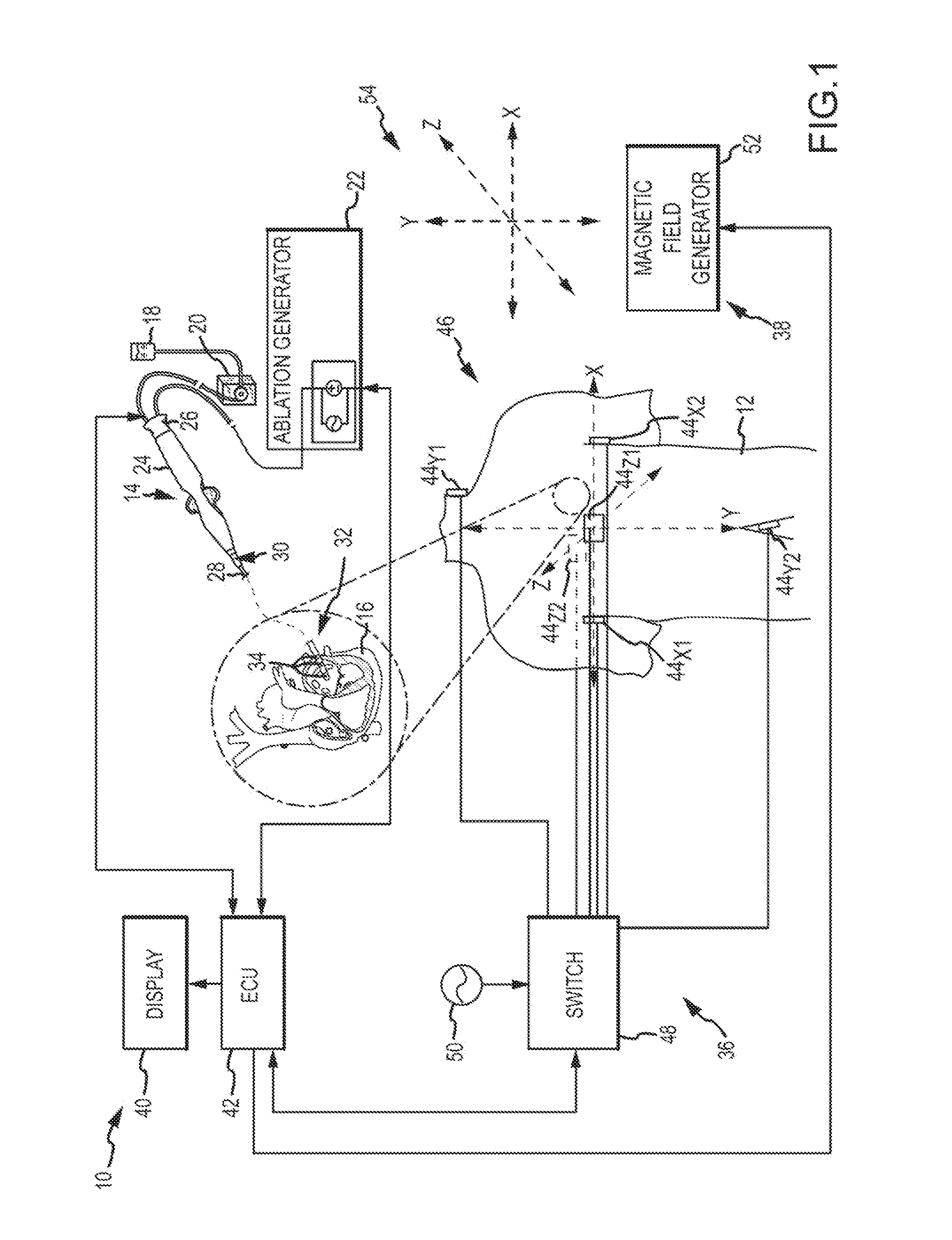
ActiveUS20080288038A1Minimal distractionSurgical navigation systemsInternal electrodesDistractionElectricity
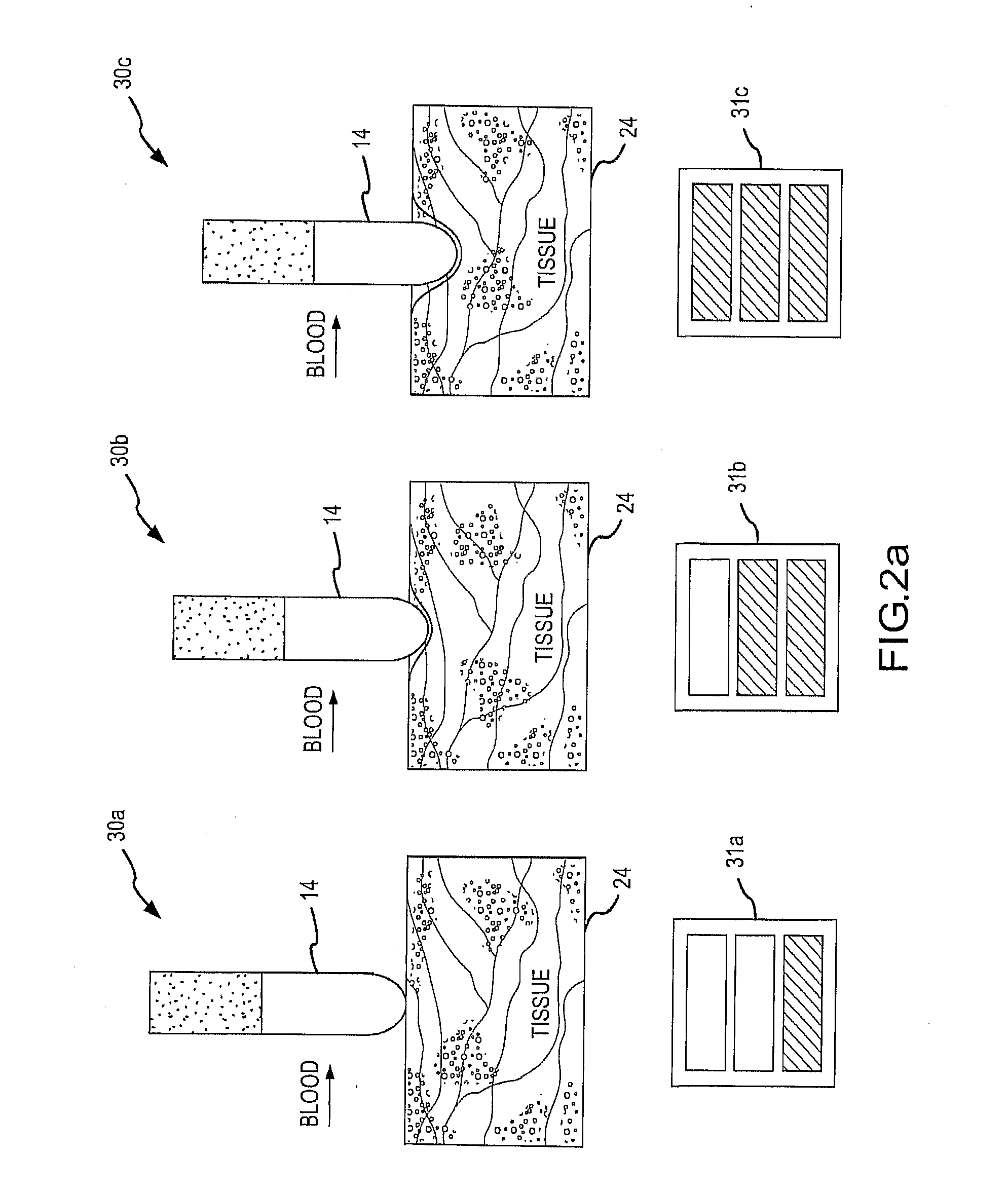
An electrode coupling output system associated with an electrode catheter that provides indication to the physician via the navigation system, concerning the electrical coupling of an electrode, such as an ablative or mapping electrode, with a patient. The indication may be provided by changing the color or other display characteristics of the electrode on the navigation system display or by way of providing a waveform indicating the electrode coupling. In this manner, electrode coupling information is provided to a physician in a manner that minimizes physician distraction.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for measuring force and torque applied to a catheter electrode tip
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
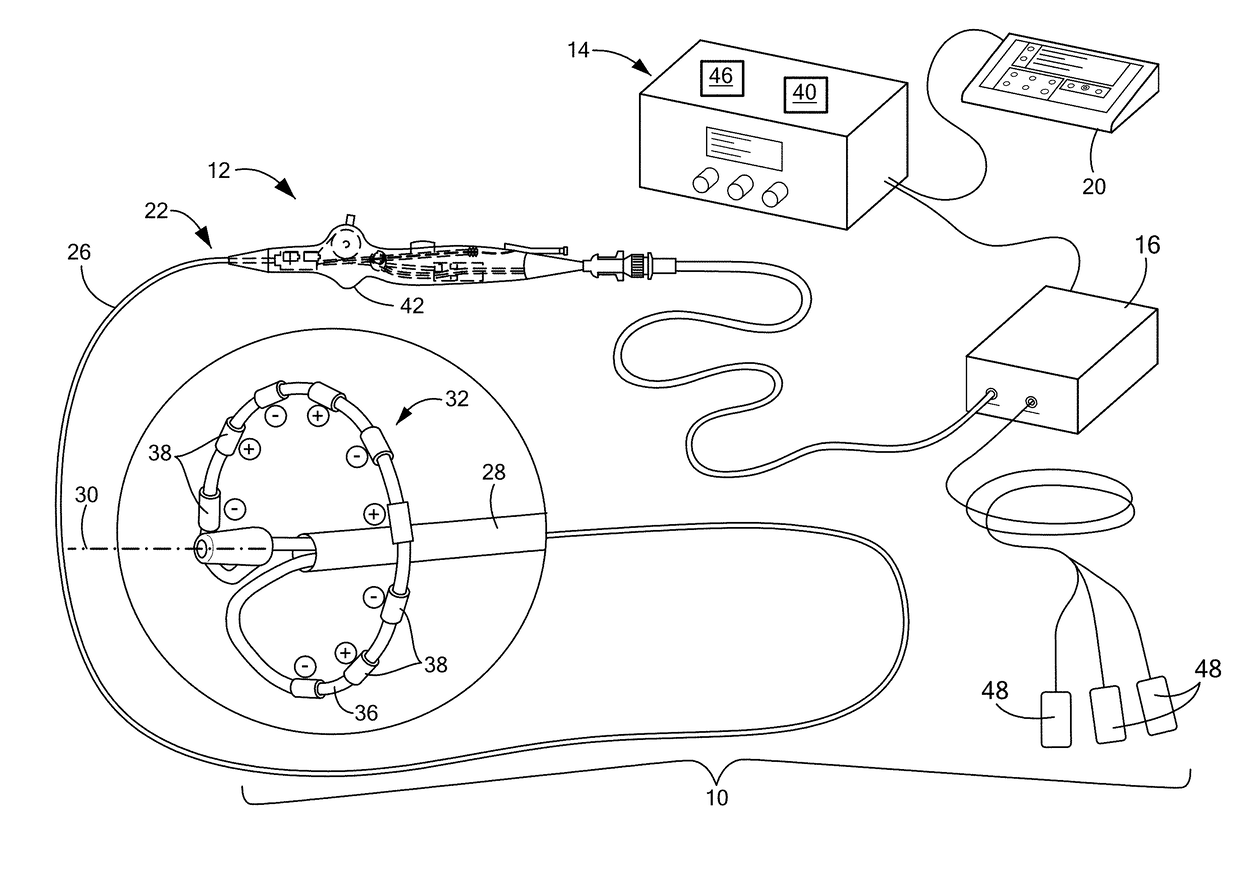
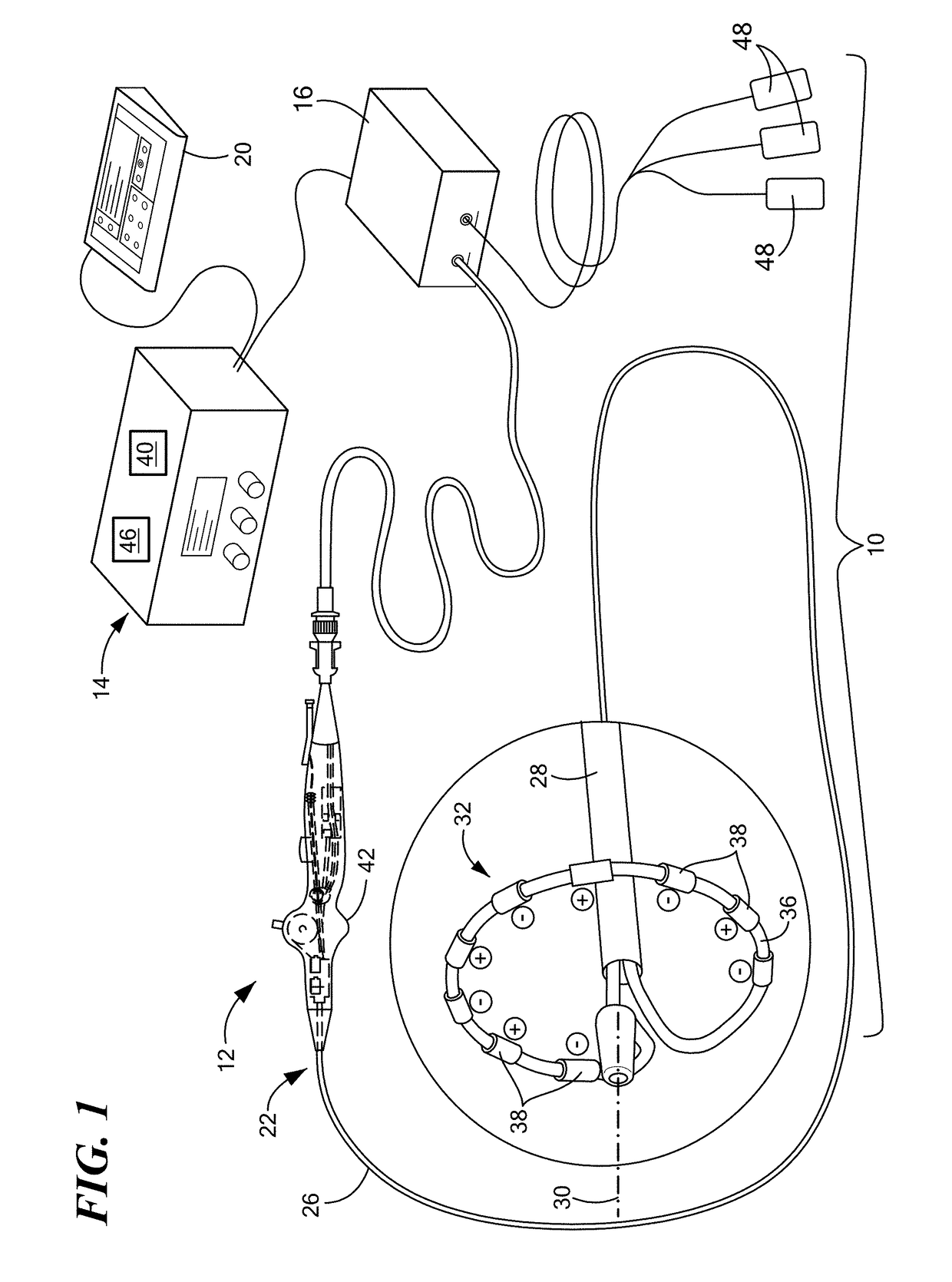
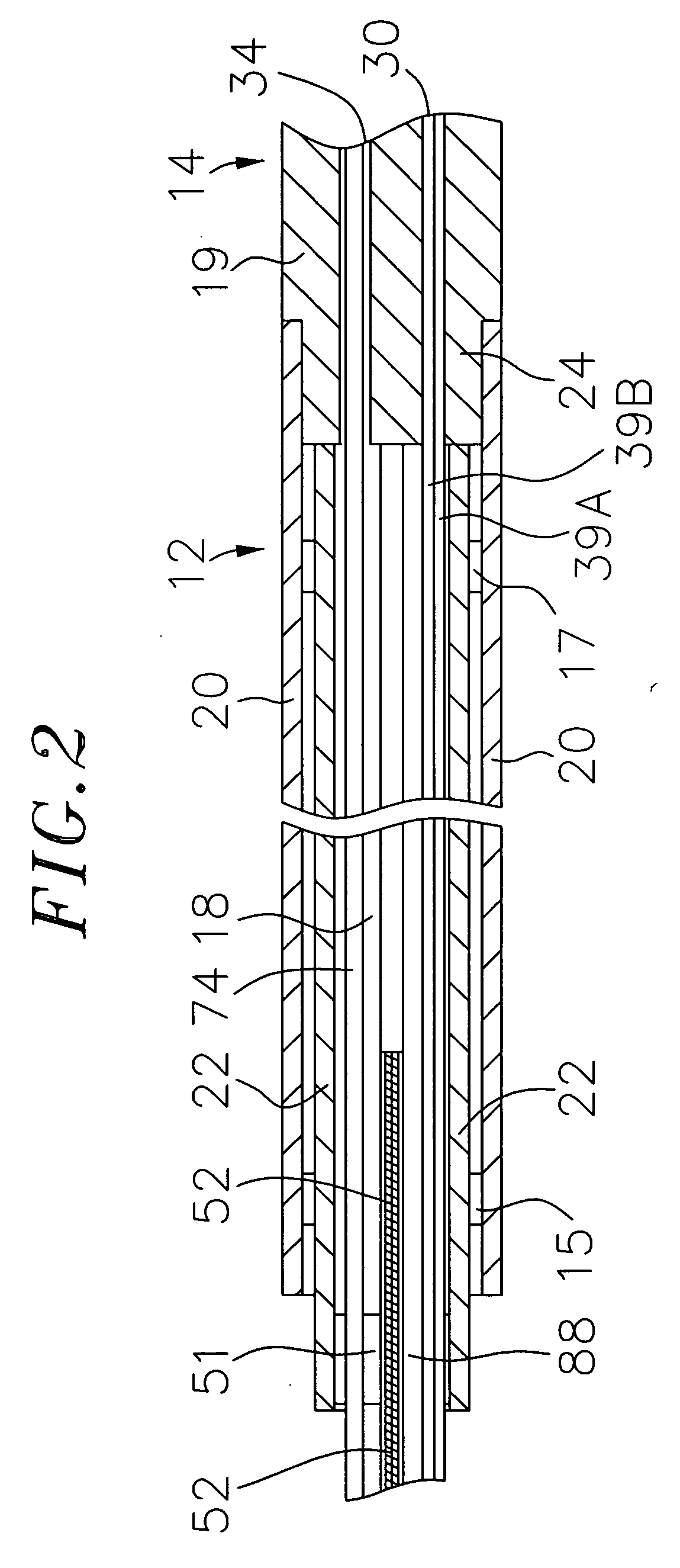
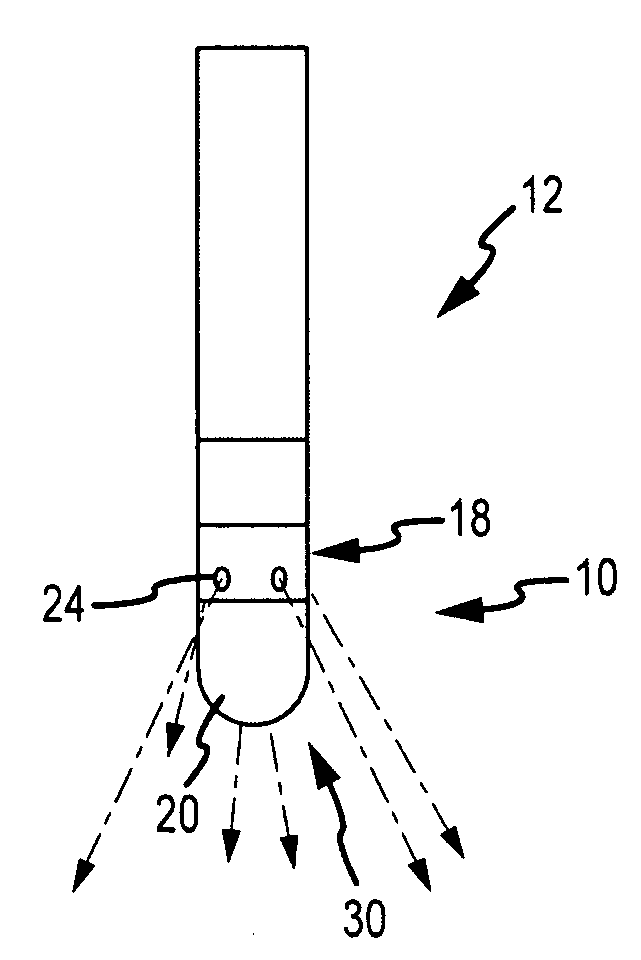
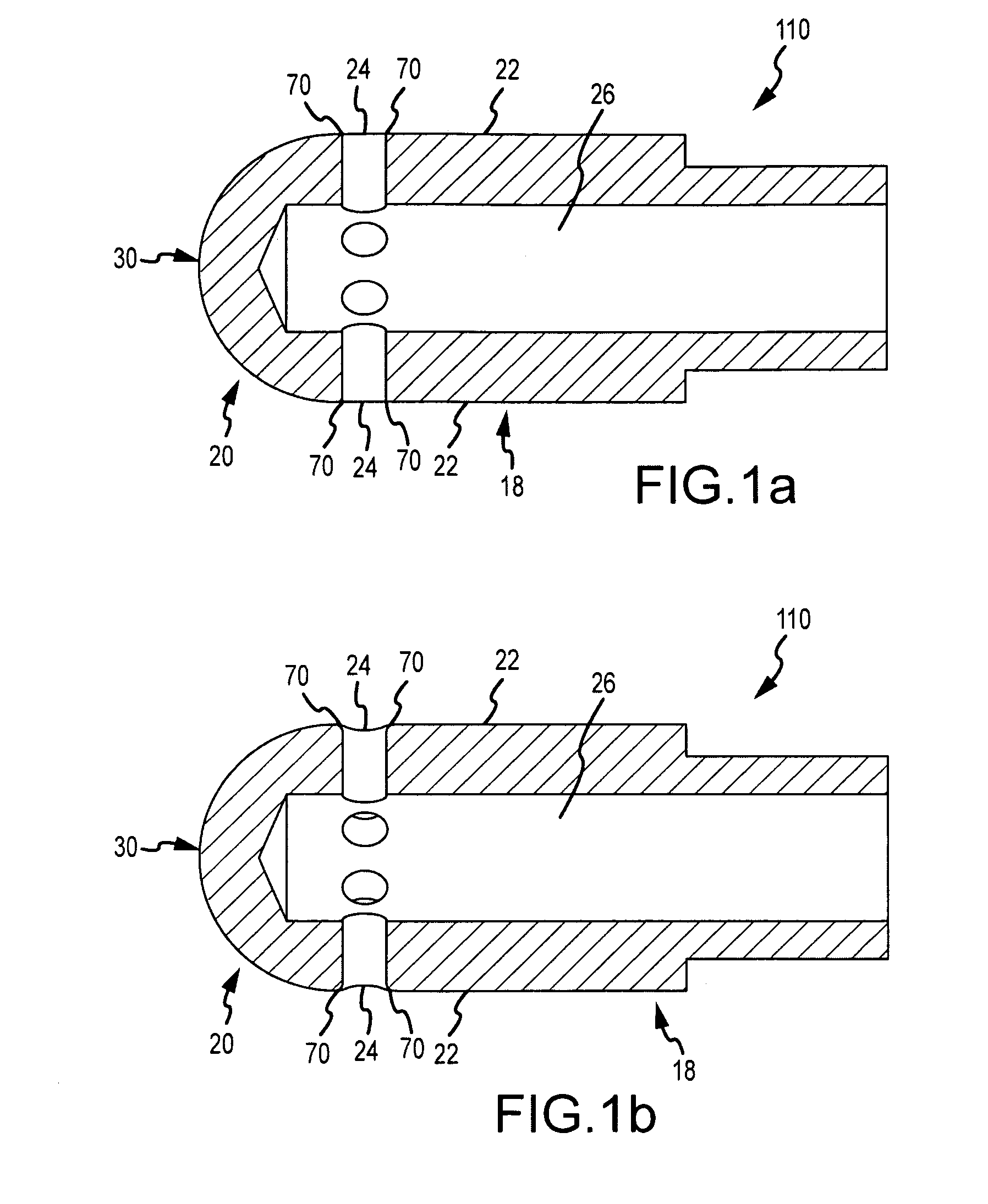
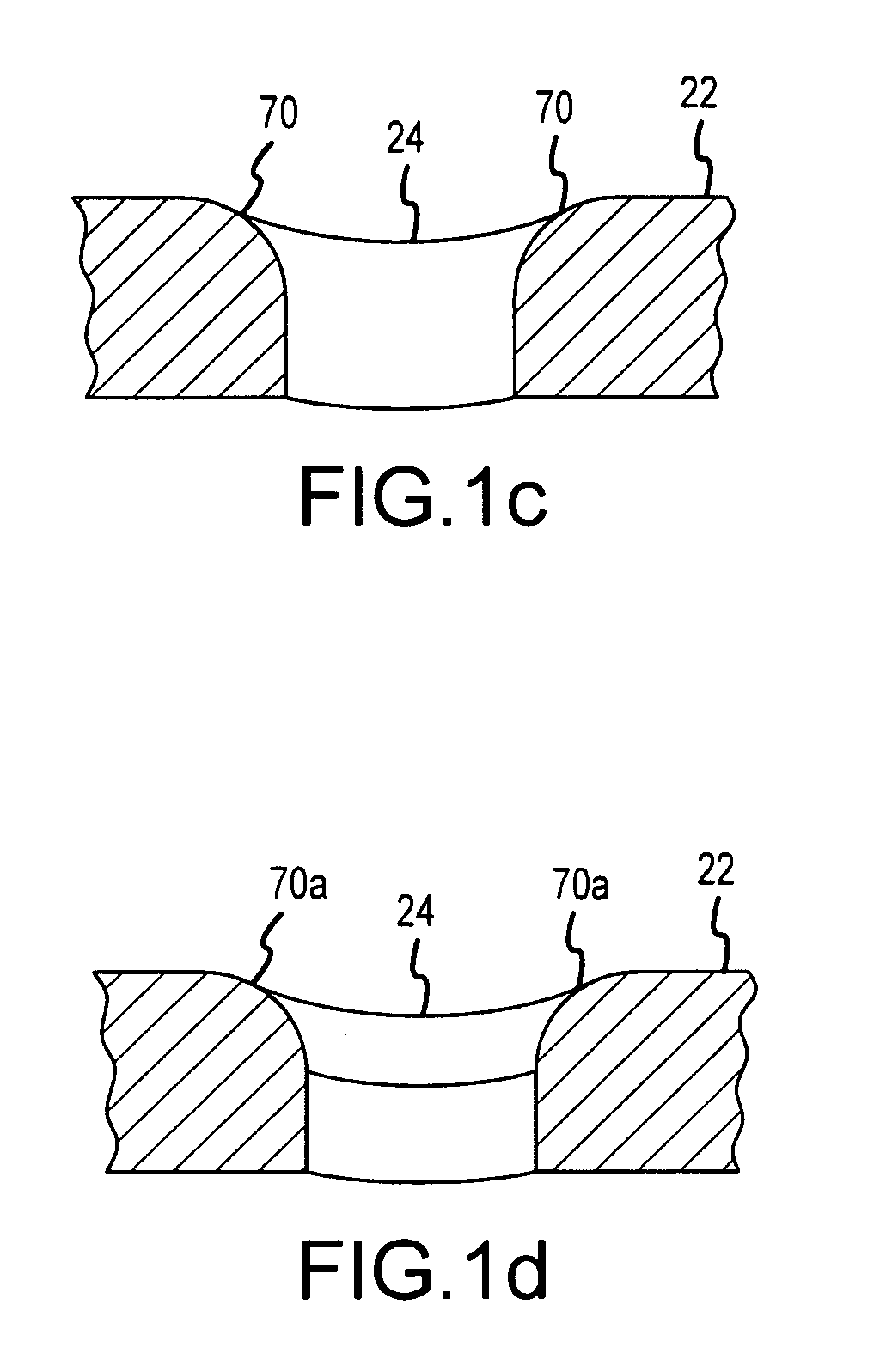
Catheter electrode assemblies and methods of construction therefor
A family of catheter electrode assemblies includes a flexible circuit having a plurality of electrical traces and a substrate; a ring electrode surrounding the flexible circuit and electrically coupled with at least one of the plurality of electrical traces; and an outer covering extending over at least a portion of the electrode. A non-contact electrode mapping catheter includes an outer tubing having a longitudinal axis, a deployment member, and a plurality of splines, at least one of the plurality of splines comprising a flexible circuit including a plurality of electrical traces and a substrate, a ring electrode surrounding the flexible circuit and electrically coupled with at least one of the plurality of electrical traces; and an outer covering extending over at least a portion of the ring electrode. A method of constructing the family of catheter electrode assemblies is also provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for selectively energizing catheter electrodes
ActiveUS7879029B2Improve abilitiesImprove energy efficiencyControlling energy of instrumentSurgical navigation systemsElectricityCatheter electrode
The present invention is directed to a system, a method and a catheter that provide improved ablation capabilities and improved energy efficiency by selectively energizing catheter electrodes on the basis of impedance measurements. In particular, the invention is directed to the selective energization of catheter radial electrodes that together with a tip electrode form a generally continuous tissue contact surface, wherein the selection is made on the basis of impedance measurement as an indication of the amount of tissue contact of each radial electrode.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Catheter electrode assemblies and methods of construction therefor
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Contact sensor and sheath exit sensor
ActiveUS20080255470A1Improved contact sensingIncrease contactSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationElectrical impedanceCatheter electrode
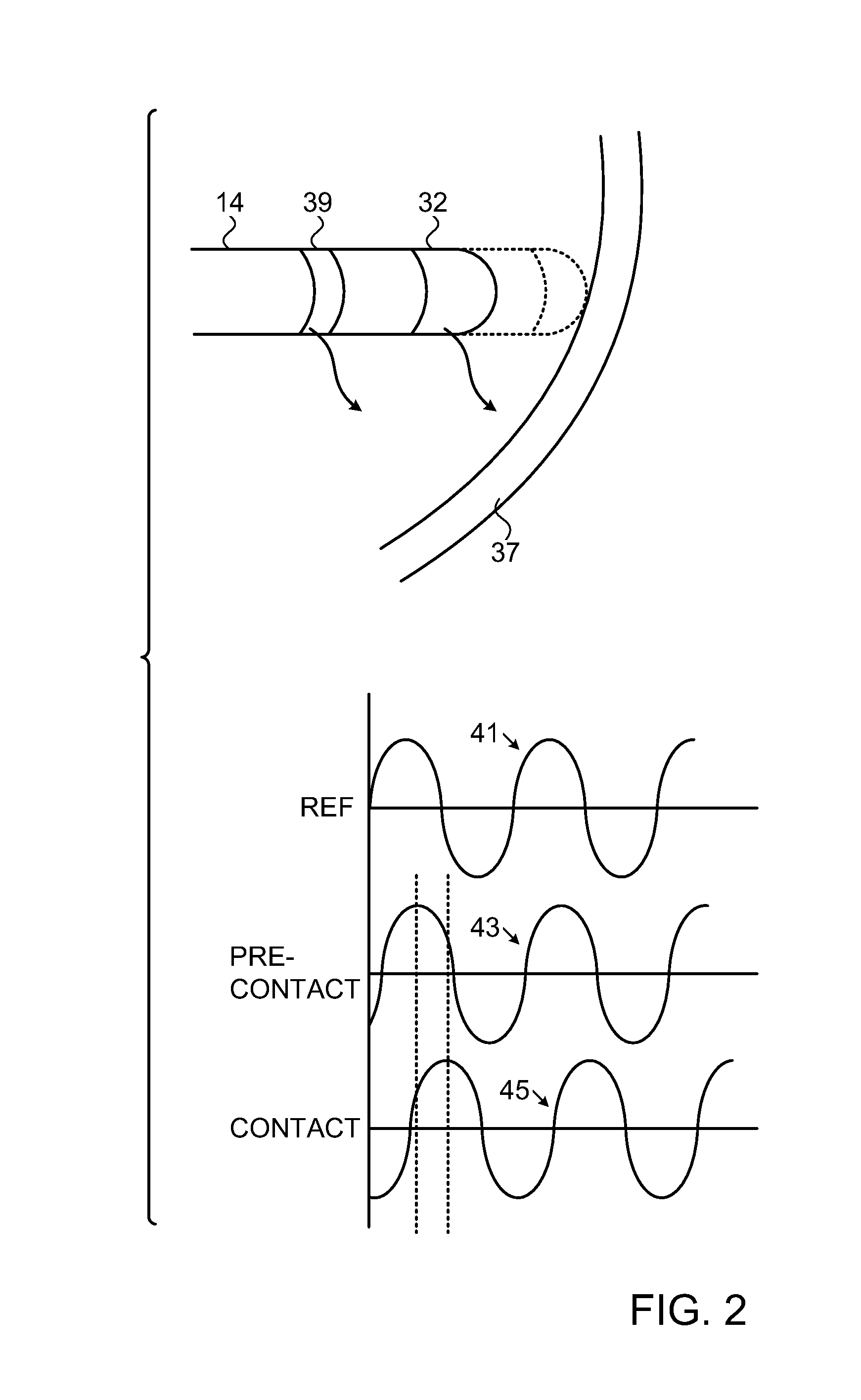
A system and method is provided that allows for determining the local impedance of one or more electrodes of an electrode catheter. Such local impedance may be utilized to identify the relative position of an electrode catheter to a sheath of a guiding introducer. In another arrangement, local impedance of a catheter electrode can be utilized to calibrate a catheter electrode to provide improved contact sensing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System for detecting catheter electrodes entering into and exiting from an introducer
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Catheter electrodes for energy management
ActiveUS20180214202A1Improve efficacyImprove efficiencyElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsEngineeringActive electrode
Methods, systems, and devices for enhancing the efficiency and efficacy of energy delivery and tissue mapping. One system includes a treatment element having a plurality of electrodes and an energy generator that is configured to deliver electric energy pulses to the electrodes in a variety of patterns. For example, electrodes may be arranged in closely spaced pairs. The energy generator may deliver mapping energy to each electrode in each pair individually to map tissue and may deliver ablation energy to the electrodes in each pair together, such that each pair is treated like a single electrode, to deliver ablation energy, such as bipolar ablation energy between adjacent pairs. One system includes at least one concave electrode, the configuration of which concentrates the energy and drives it deeper into the tissue. One system includes neutral electrodes between active electrodes, the energy generator selectively coupling the neutral electrodes to alter the ablation pattern.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for targeting catheter electrodes
InactiveUS20110112396A1Improve accuracyElectrocardiographySurgical instrument detailsGuidance systemCatheter electrode
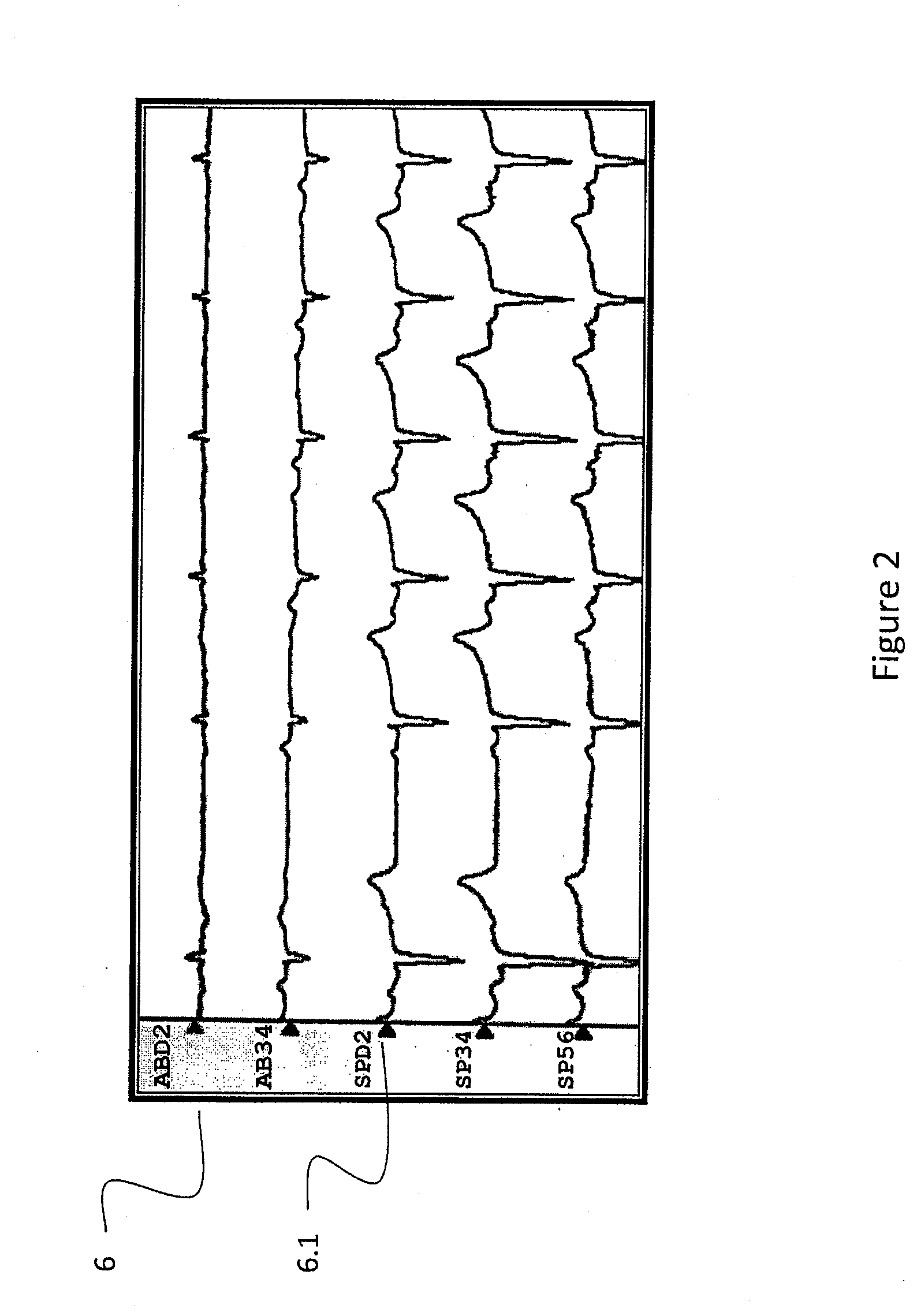
A system and method is described for a catheter guidance system which allows an operator to use a mapping catheter to specify tissue target locations for the automatic guidance of a second therapeutic catheter. The operator places a mapping catheter at a desired location, and commands the catheter guidance system by either selecting a point on that catheter or one of the catheter electrode electrocardiograms. The operator may target the selected dynamic location, or tissue contact beyond that location on a specific side of the mapping catheter.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
System and method for selectively energizing catheter electrodes
ActiveUS20070156128A1Improve abilitiesImprove energy efficiencyControlling energy of instrumentSurgical navigation systemsElectricityCatheter electrode
The present invention is directed to a system, a method and a catheter that provide improved ablation capabilities and improved energy efficiency by selectively energizing catheter electrodes on the basis of impedance measurements. In particular, the invention is directed to the selective energization of catheter radial electrodes that together with a tip electrode form a generally continuous tissue contact surface, wherein the selection is made on the basis of impedance measurement as an indication of the amount of tissue contact of each radial electrode.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
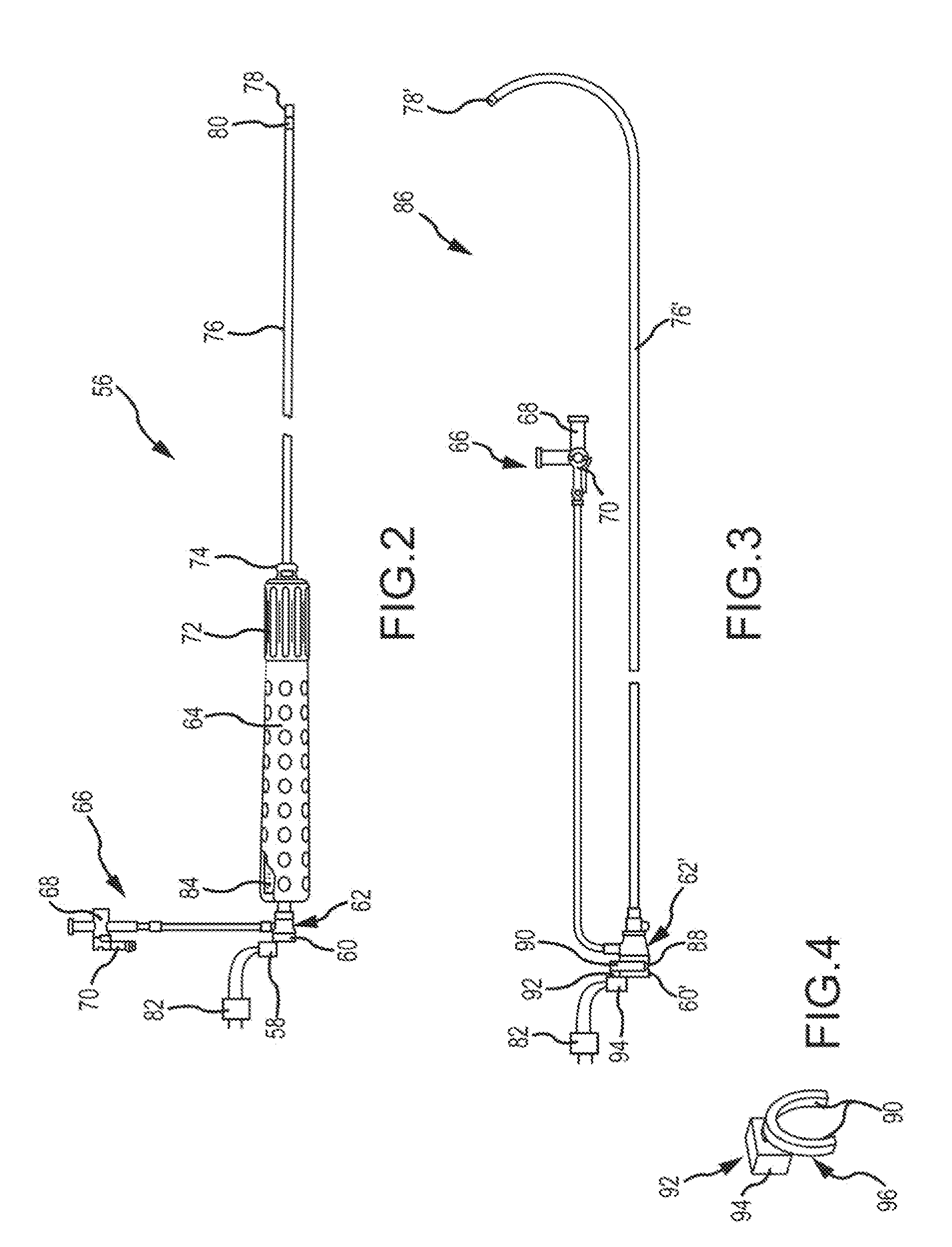
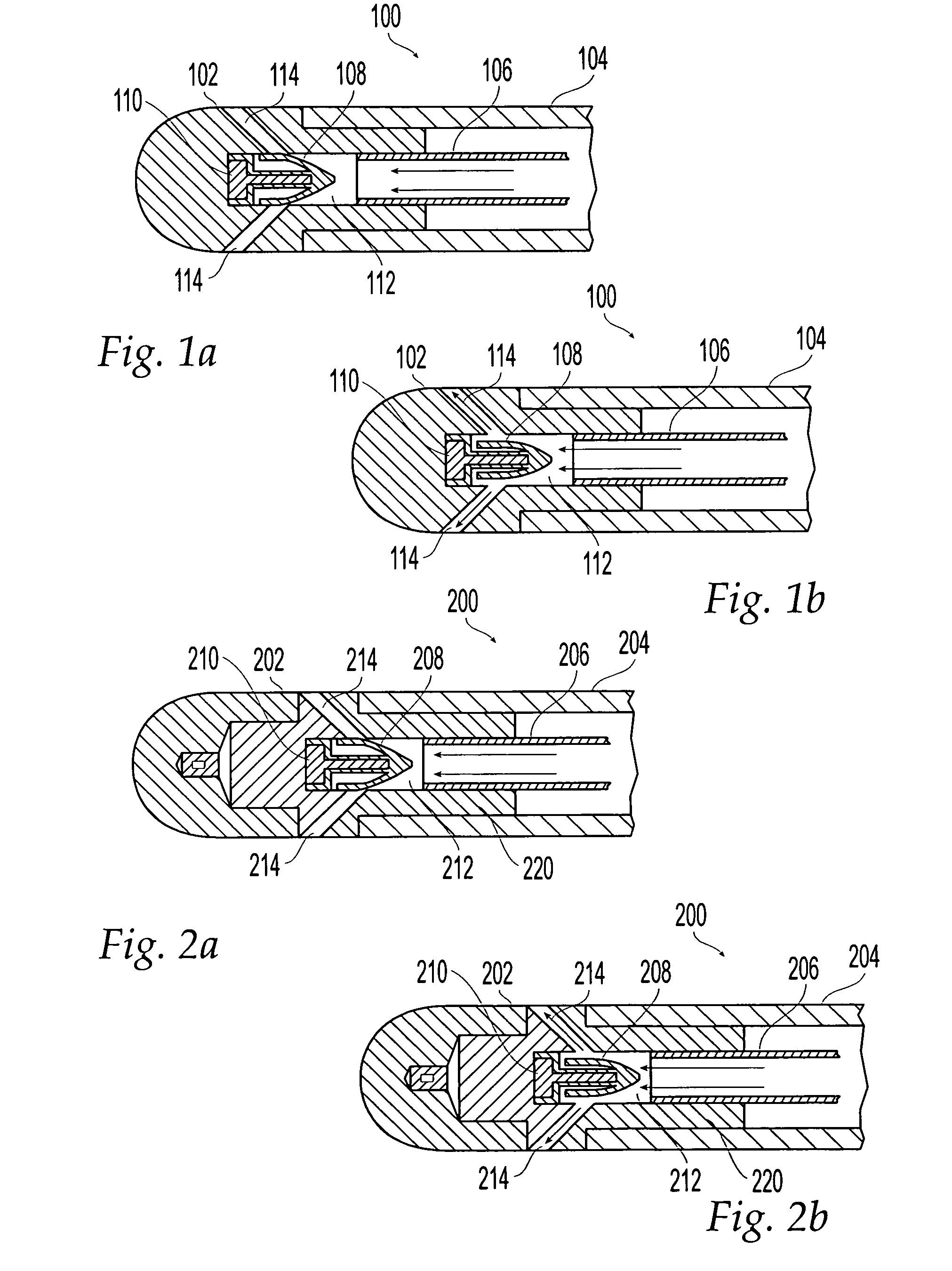
Irrigated ablation electrode having smooth edges to minimize tissue char
ActiveUS20090177193A1Tissue char is minimizedMinimize coagulationSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationCatheter electrode
The invention relates to ablation catheter electrodes that solve in part the problem of tissue charring during radiofrequency ablation. The electrode assemblies of the invention include passageways that lead from the inner lumen of the assemblies to the surface of the assemblies, wherein the passageways have a smooth conjunction with the outer surface. These smooth conjunctions comprise rounded edges or are camfered. In the case of rounded edges, the rounded edges can have fixed radii of about 0.002″ to about 0.008″.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for targeting catheter electrodes
InactiveUS20120296200A1Improve accuracyElectrocardiographySurgical instrument detailsGuidance systemCatheter electrode
A system and method is described for a catheter guidance system which allows an operator to use a mapping catheter to specify tissue target locations for the automatic guidance of a second therapeutic catheter. The operator places a mapping catheter at a desired location, and commands the catheter guidance system by either selecting a point on that catheter or one of the catheter electrode electrocardiograms. The operator may target the selected dynamic location, or tissue contact beyond that location on a specific side of the mapping catheter.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
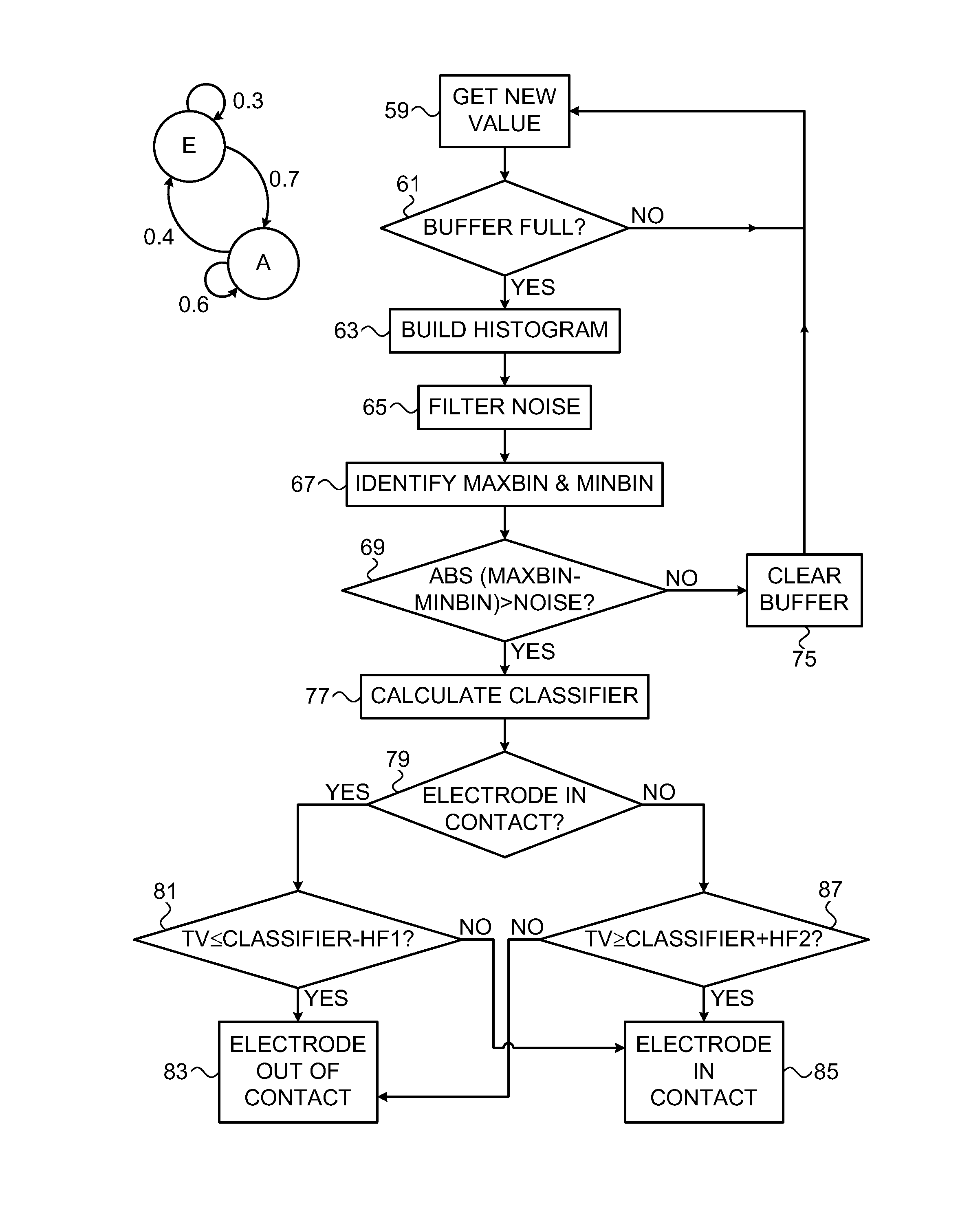
Machine learning in determining catheter electrode contact
Cardiac catheterization is carried out by memorizing a designation of a contact state between an electrode of the probe and the heart wall as one of an in-contact state and an out-of-contact state, and making a series of determinations of an impedance phase angle of an electrical current passing through the electrode and another electrode, identifying maximum and minimum phase angles in the series, and defining a binary classifier adaptively as midway between the extremes. A test value is compared to the classifier as adjusted by a hysteresis factor, and a change in the contact state is reported when the test value exceeds or falls below the adjusted classifier.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
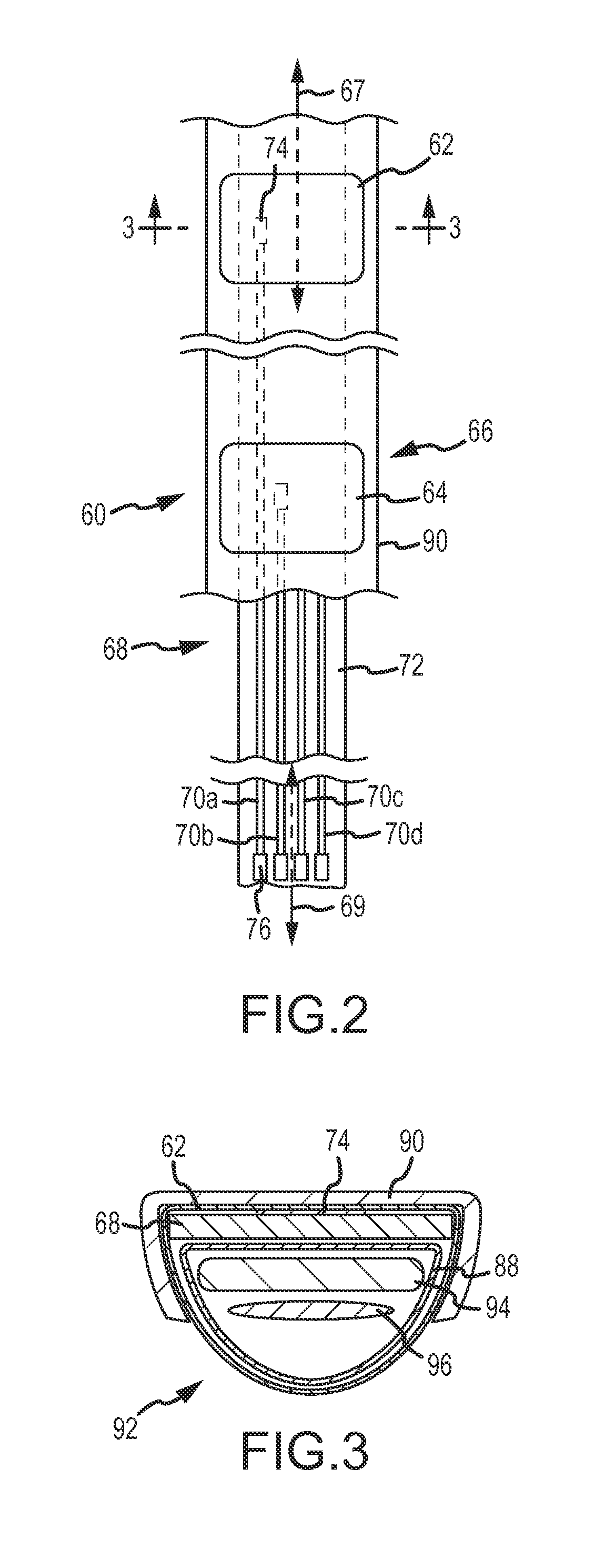
Composite flexible and conductive catheter electrode
InactiveUS20070249923A1Meet functional requirementsAllow flexibilityEnvelopes/bags making machineryEar treatmentContinuous/uninterruptedElectricity
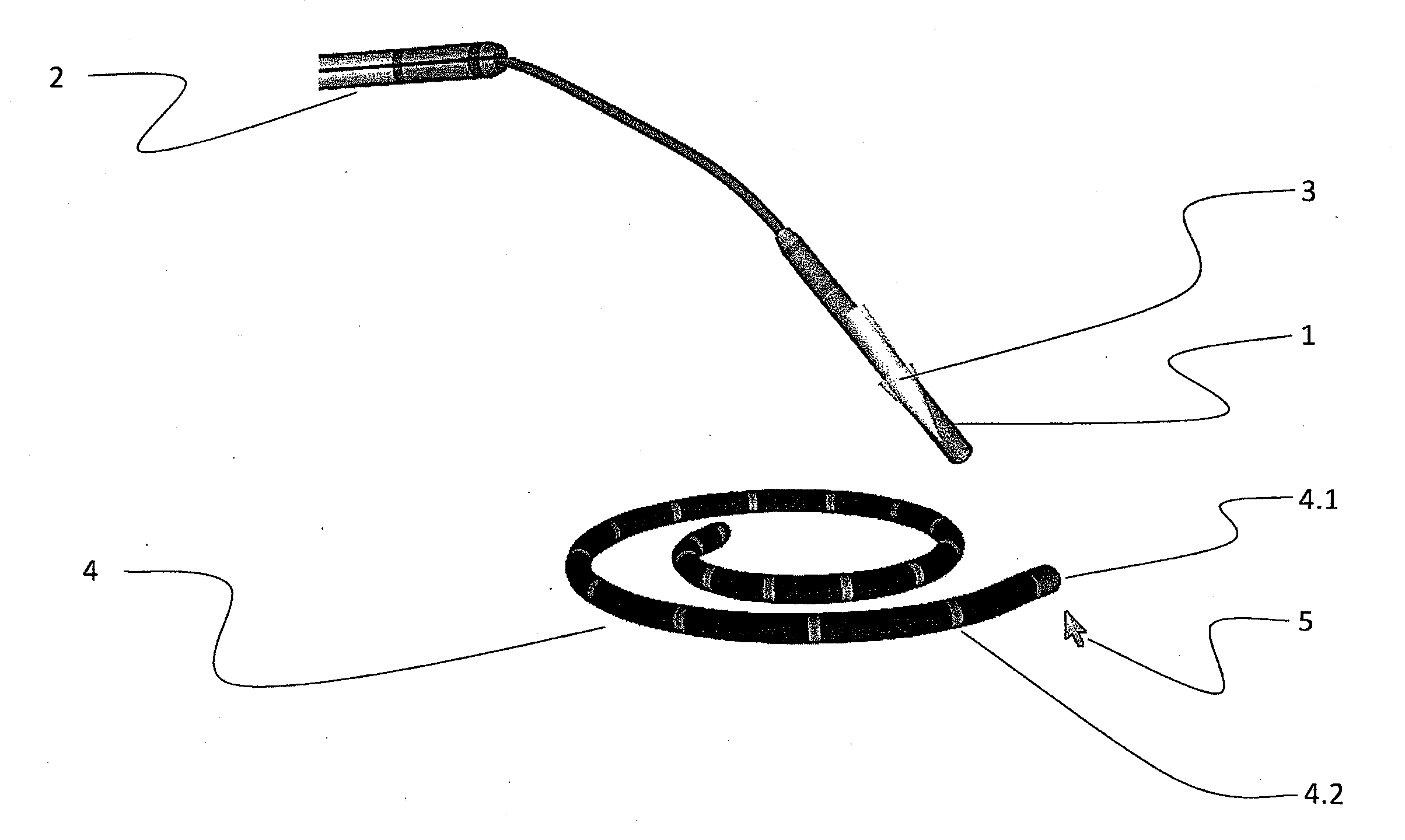
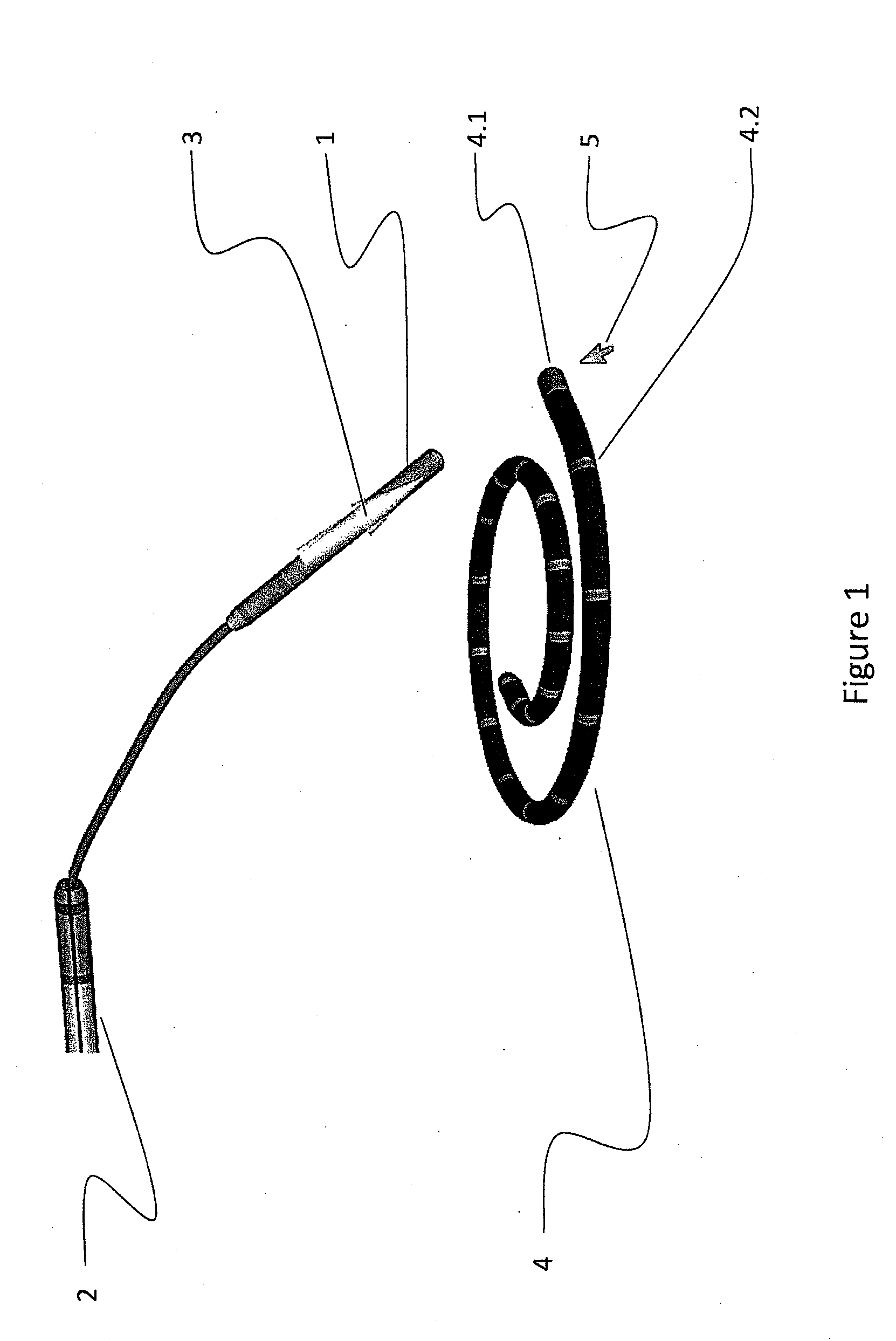
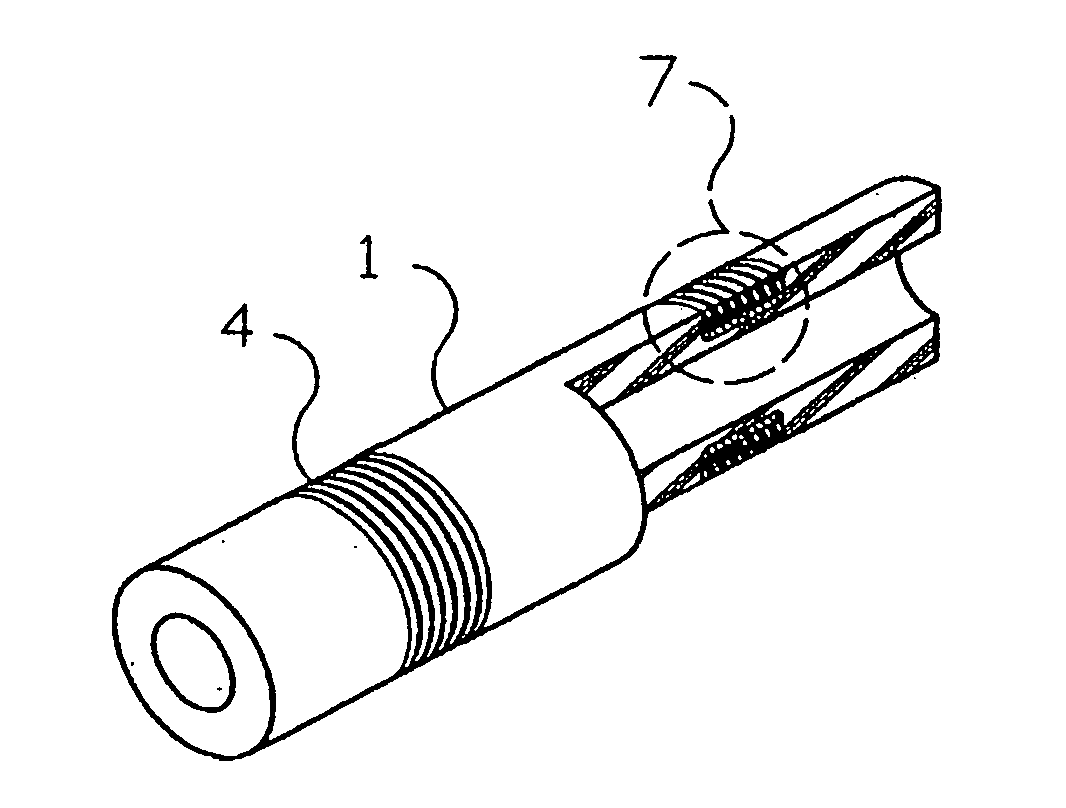
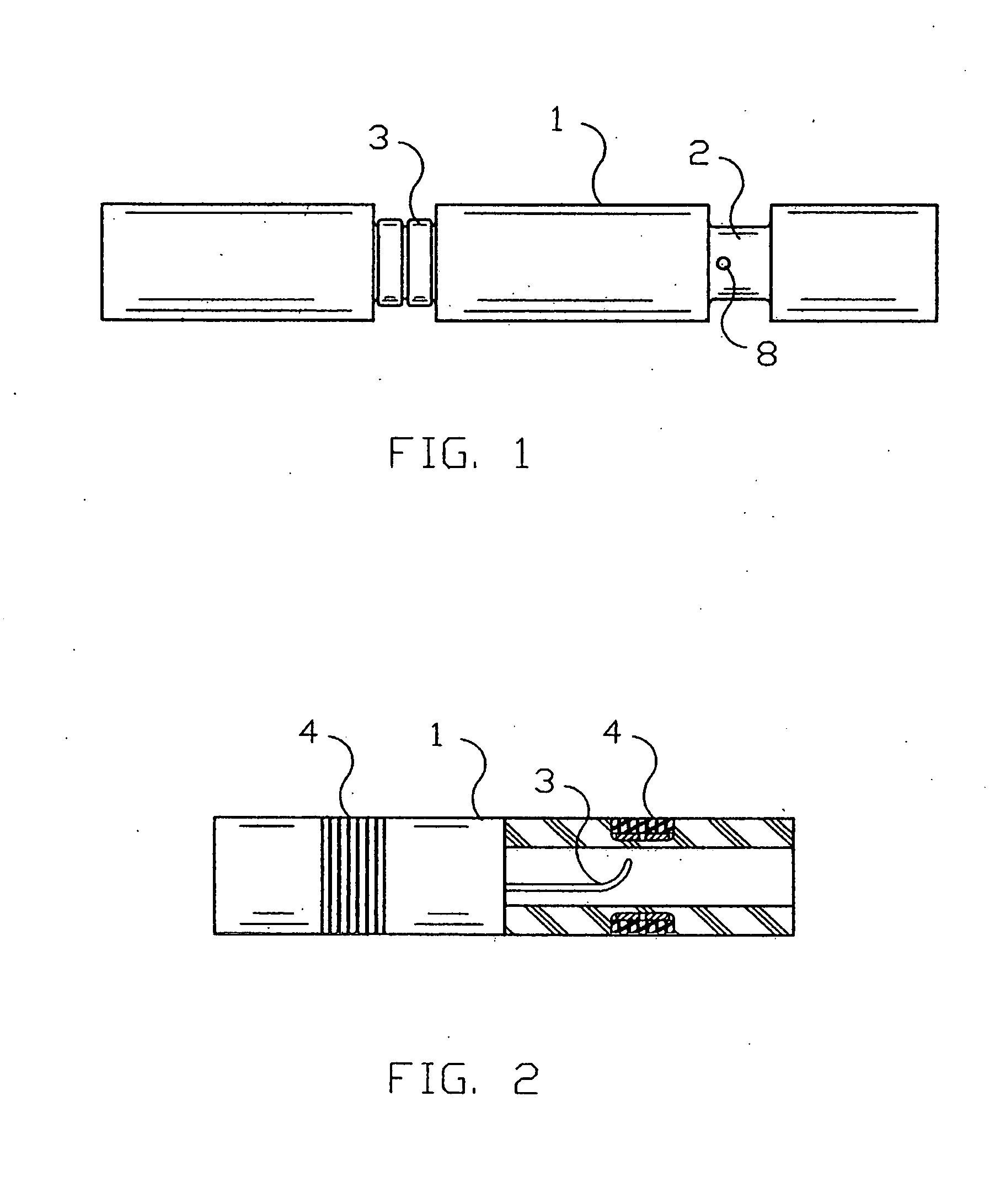
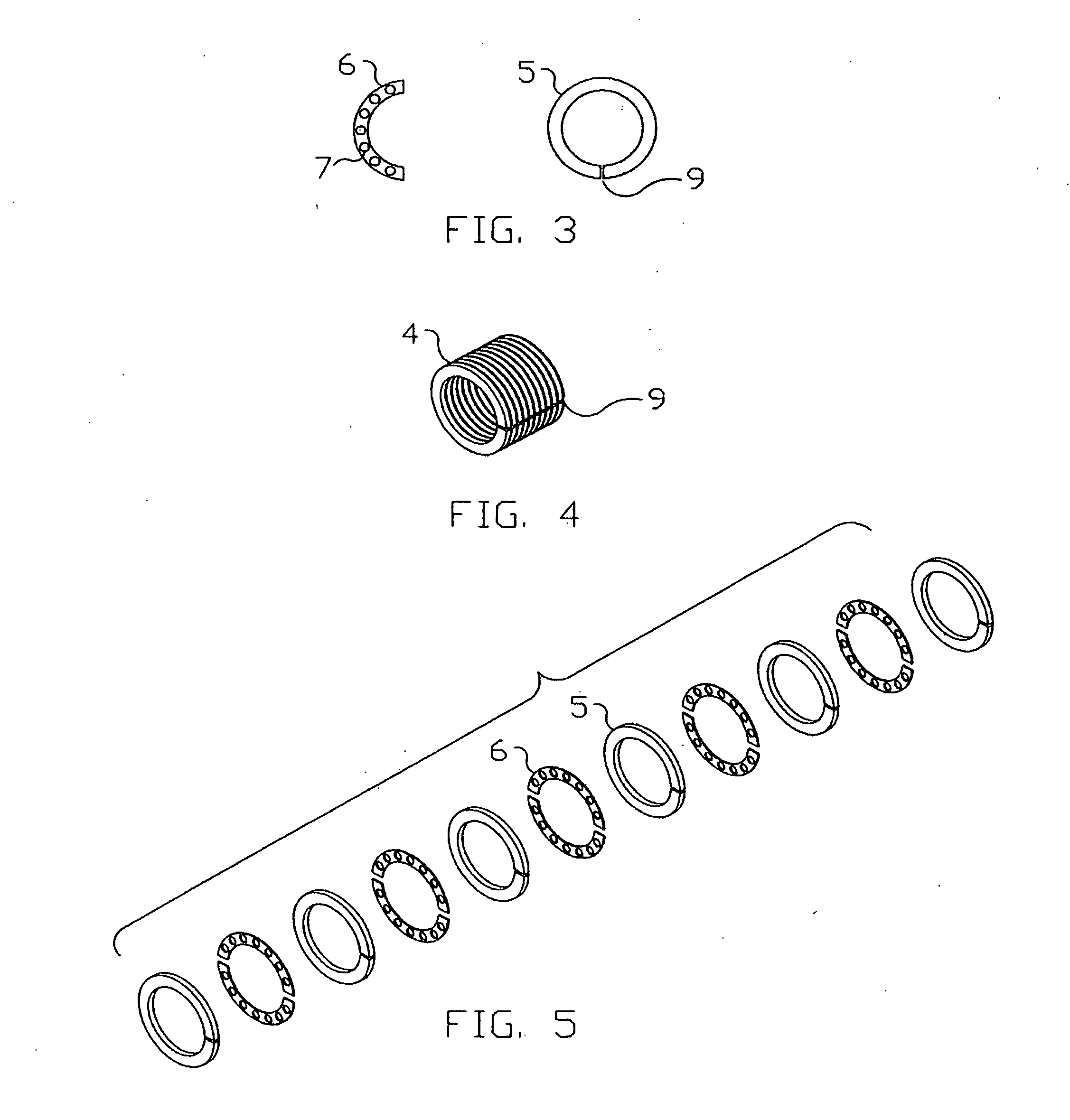
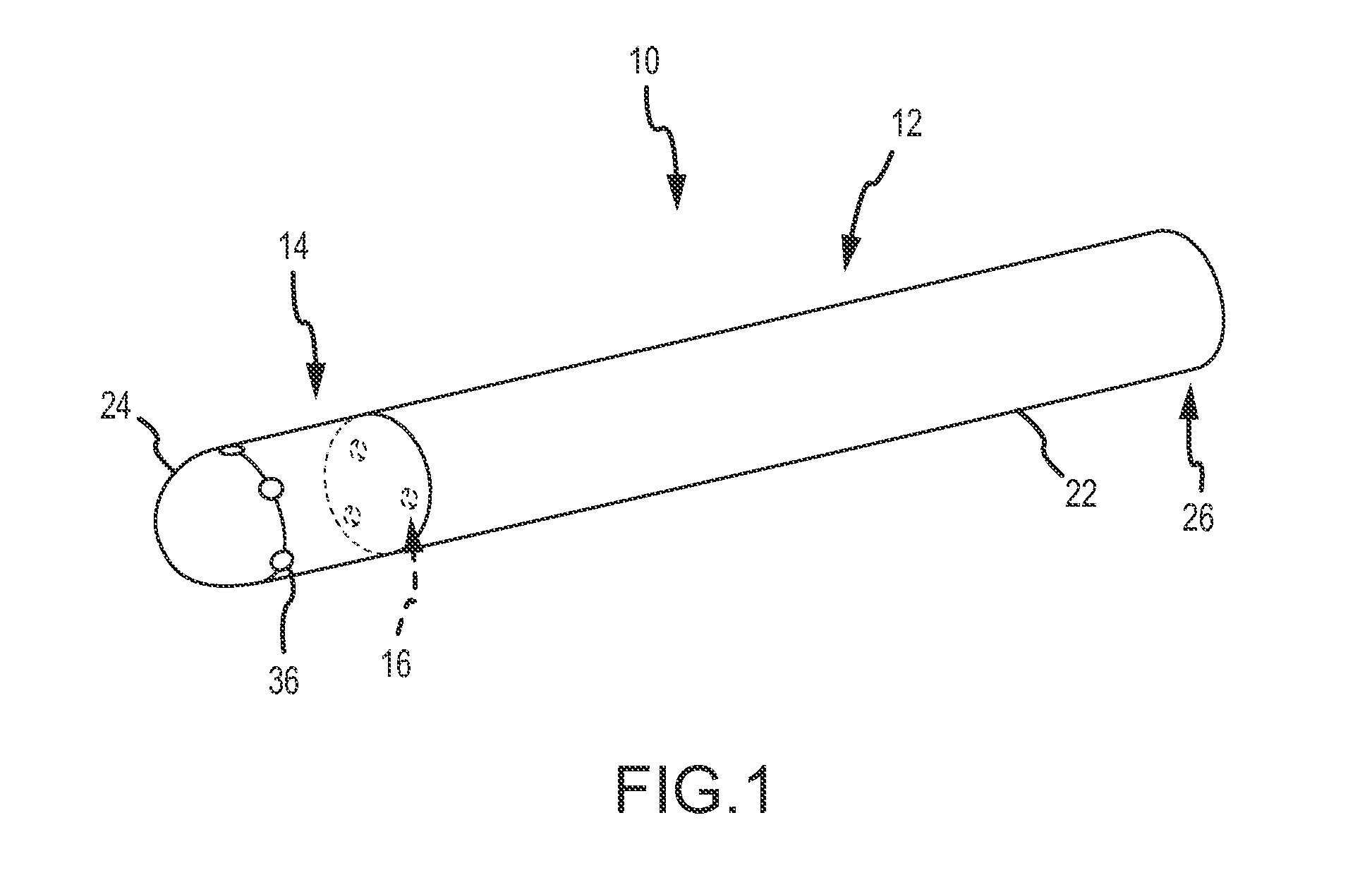
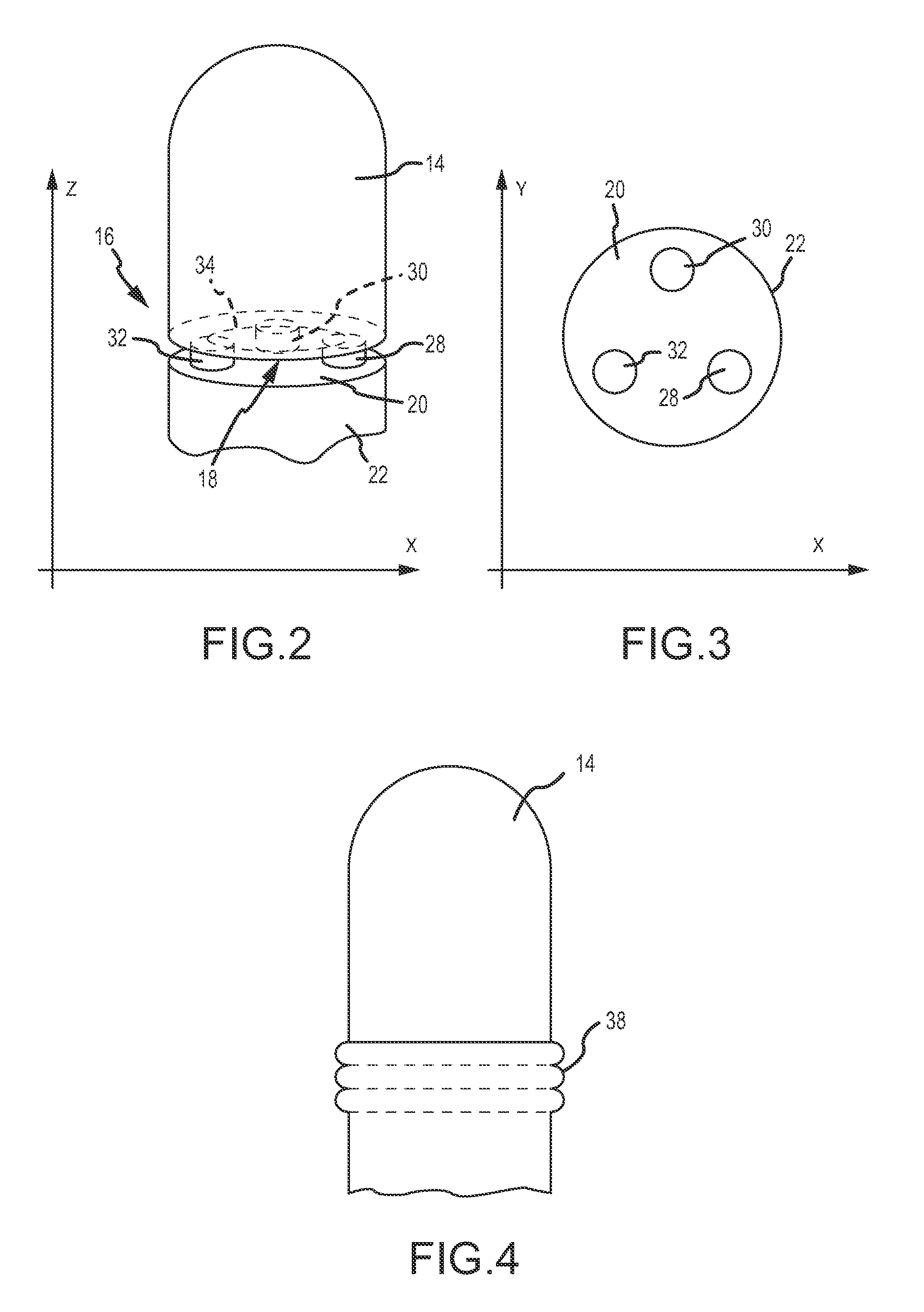
A flexible cardiac catheter for sensing electrical activity within and administering therapy to a patients' heart has a series of flexible, conductive electrode bands positioned in grooves in the catheter's tubular body. The bands consist of alternating flexible and conductive elements, providing flexibility and overall versatility to the catheter. The electrode bands have controllable flexibility due to the elastic properties of the flexible elements and continuous uninterrupted electrical current conductance from the one-piece design of the conductive element. The synergy of the components of the composite flexible and conductive bands will help solve problems current electrode bands have and will allow for a freedom in the design of catheter electrode band configurations in the future.
Owner:KEENAN ERICK
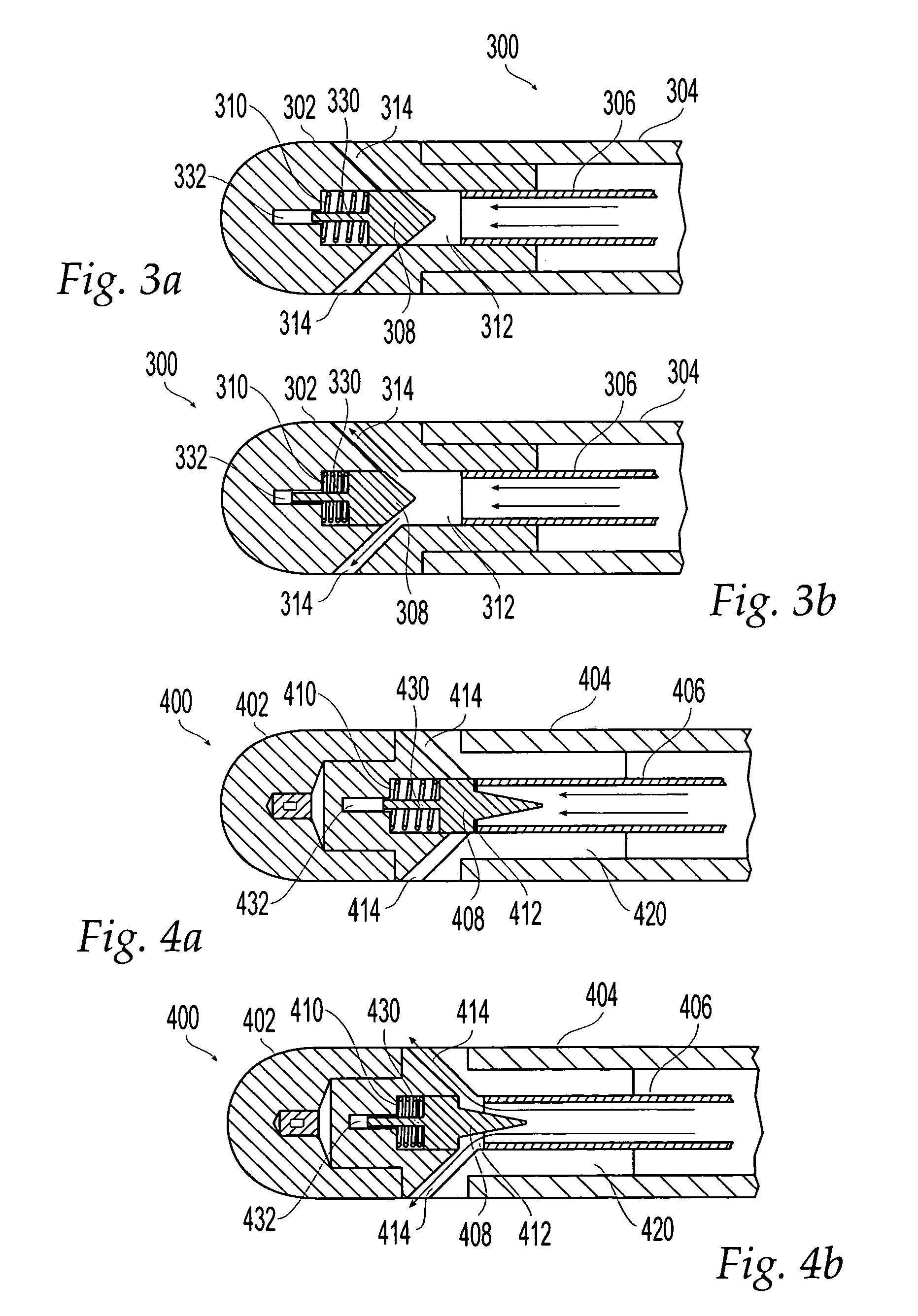
Ablation catheter electrode arrangement
An ablation catheter employing a continuous or nearly continuous flexible electrode arrangement. In one implementation, the flexible electrode include at least one electrode defining a saw tooth pattern. In another implementation, the flexible electrode is arranged in an interlaced pattern. Generally, the flexible electrodes are configured to adapt to the change in shape of the portion of the catheter that the electrode is connected with. Moreover, the flexible electrodes are arranged to provide a continuous or nearly continuous lesion of the target tissue. In some implementations, the flexible electrode may be connected with the catheter in a biased configuration, and as such may assist in changing the shape of a curve in the catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Catheter electrode and rail system for cardiac ablation
The instant invention is directed toward an ablation catheter and sheath incorporating wire rail system. The catheter may have a combination of rigid and flexible components to orient an ablation electrode at the distal tip toward the target tissue. The wire rail acts to guide an ablation tip along the tissue to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions on a trabecular surface, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Irrigated ablation catheter having a valve to prevent backflow
ActiveUS7824406B2Prevent backflowMedical devicesSurgical instruments for heatingCooling effectElectrical impedance
The invention relates to an ablation catheter which controls the temperature and reduces the coagulation of biological fluids on an electrode of a catheter, prevents the impedance rise of tissue in contact with the electrode, and maximizes the potential energy transfer to the tissue, thereby allowing an increase in the lesion size produced by the ablation. The electrode includes passages positioned to allow saline flow out of an inner cavity of the electrode. This fluid flow produces the desired cooling effect and is accomplished, for example, by saline irrigation flow with a valve element to block flow of blood into the inner cavity of the electrode.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
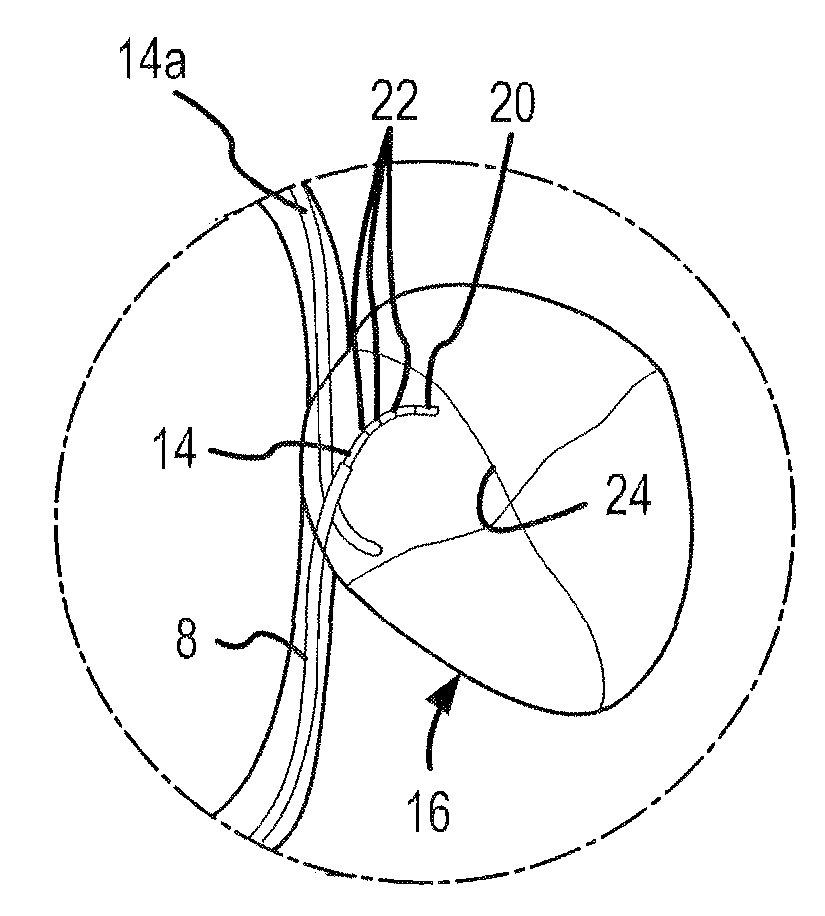
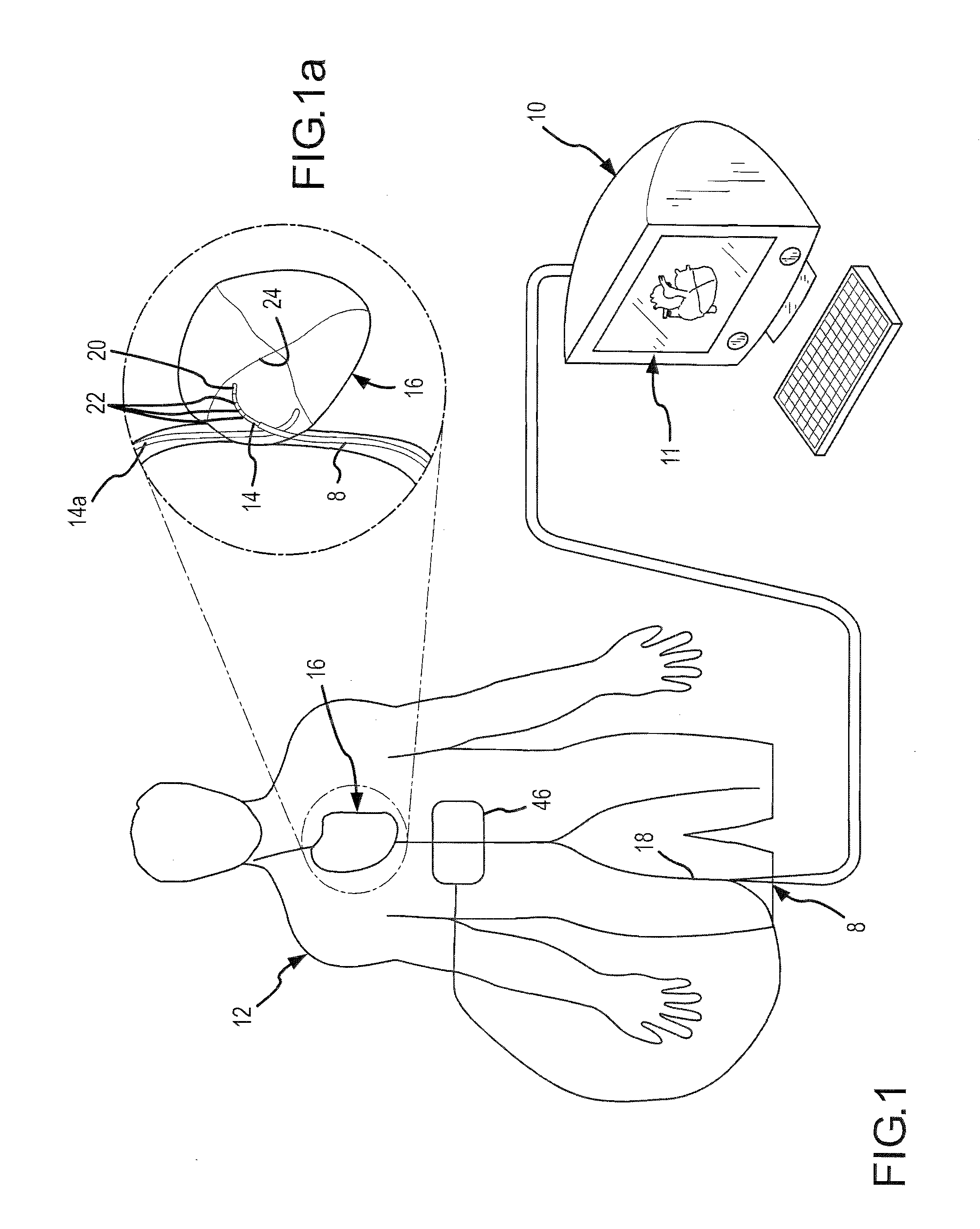
Endovascular electrolytically detachable wire and tip for the formation of thrombus in arteries, veins, aneurysms, vascular malformations and arteriovenous fistulas
An artery, vein, aneurysms vascular malformation or arterial fistula is occluded through endovascular occlusion by the endovascular insertion of a platinum wire and / or tip into the vascular cavity. The vascular cavity is packed with the tip to obstruct blood flow or access of blood in the cavity such that the blood clots in the cavity and an occlusion if formed. The tip may be elongate and flexible so that it packs the cavity by being folded upon itself a multiple number of times, or may pack the cavity by virtue of a filamentary or fuzzy structure of the tip. The tip is then separated from the wire mechanically or by electrolytic separation of the tip from the wire. The wire and the microcatheter are thereafter removed leaving the tip embedded in the thrombus formed within the vascular cavity. Movement of wire in the microcatheter is more easily tracked by providing a radioopaque proximal marker on the microcatheter and a corresponding indicator marker on the wire. Electrothrombosis is facilitate by placing the ground electrode on the distal end of the microcatheter and flowing current between the microcatheter electrode and the tip.REEAXMINATION RESULTS The questions raised in reexamination request 90 / 007,231, filed Oct. 4, 2004 have been considered and the results thereof are reflected in this reissue patent which constitutes the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 307 as provided in 37 CFR 1.570(e), for ex parte reexaminations, or the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 316 as provided in 37 CFR 1.99(e) for inter partes reexaminations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Contact sensor and sheath exit sensor
ActiveUS8265745B2Increase contactSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationElectrical impedanceCatheter electrode
A system and method is provided that allows for determining the local impedance of one or more electrodes of an electrode catheter. Such local impedance may be utilized to identify the relative position of an electrode catheter to a sheath of a guiding introducer. In another arrangement, local impedance of a catheter electrode can be utilized to calibrate a catheter electrode to provide improved contact sensing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
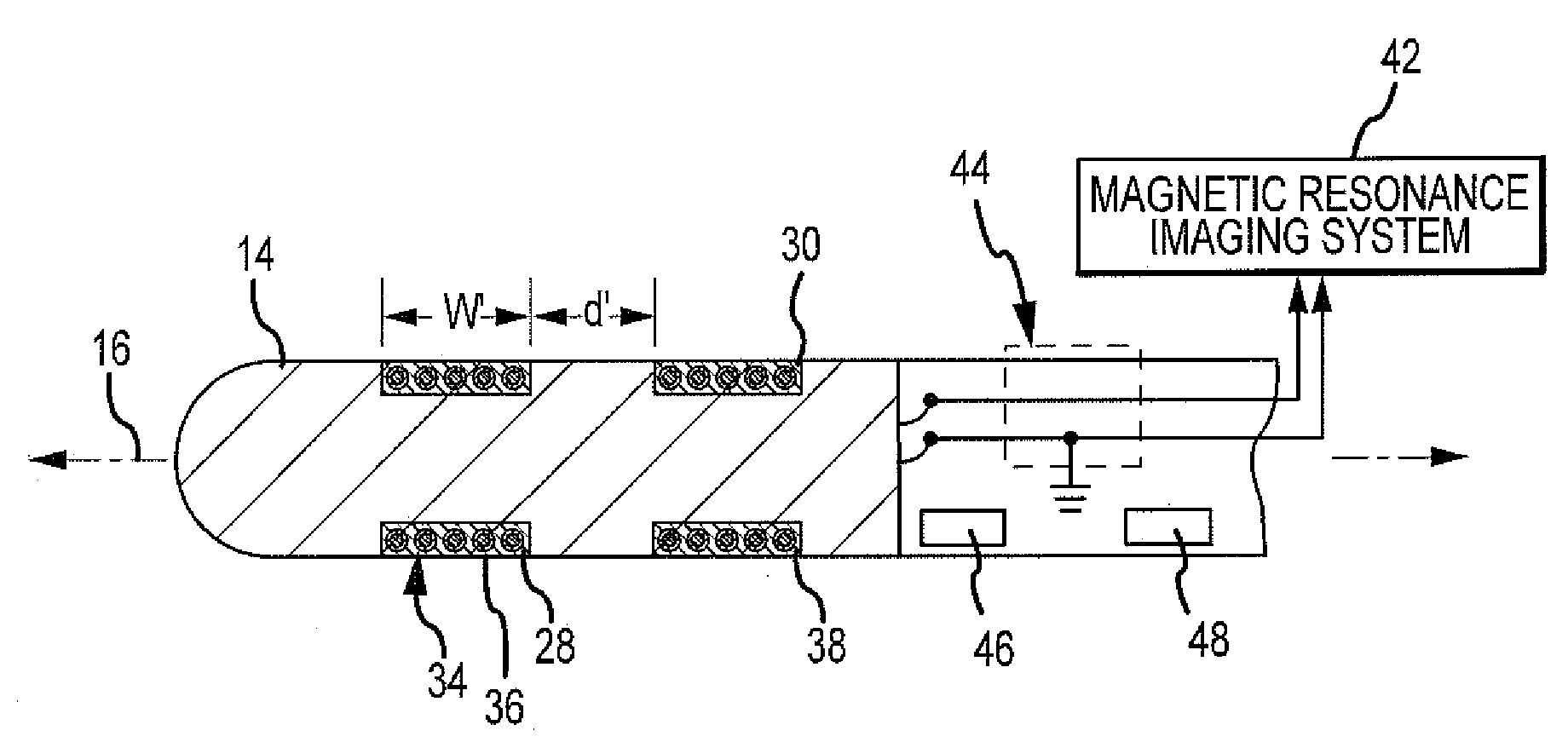
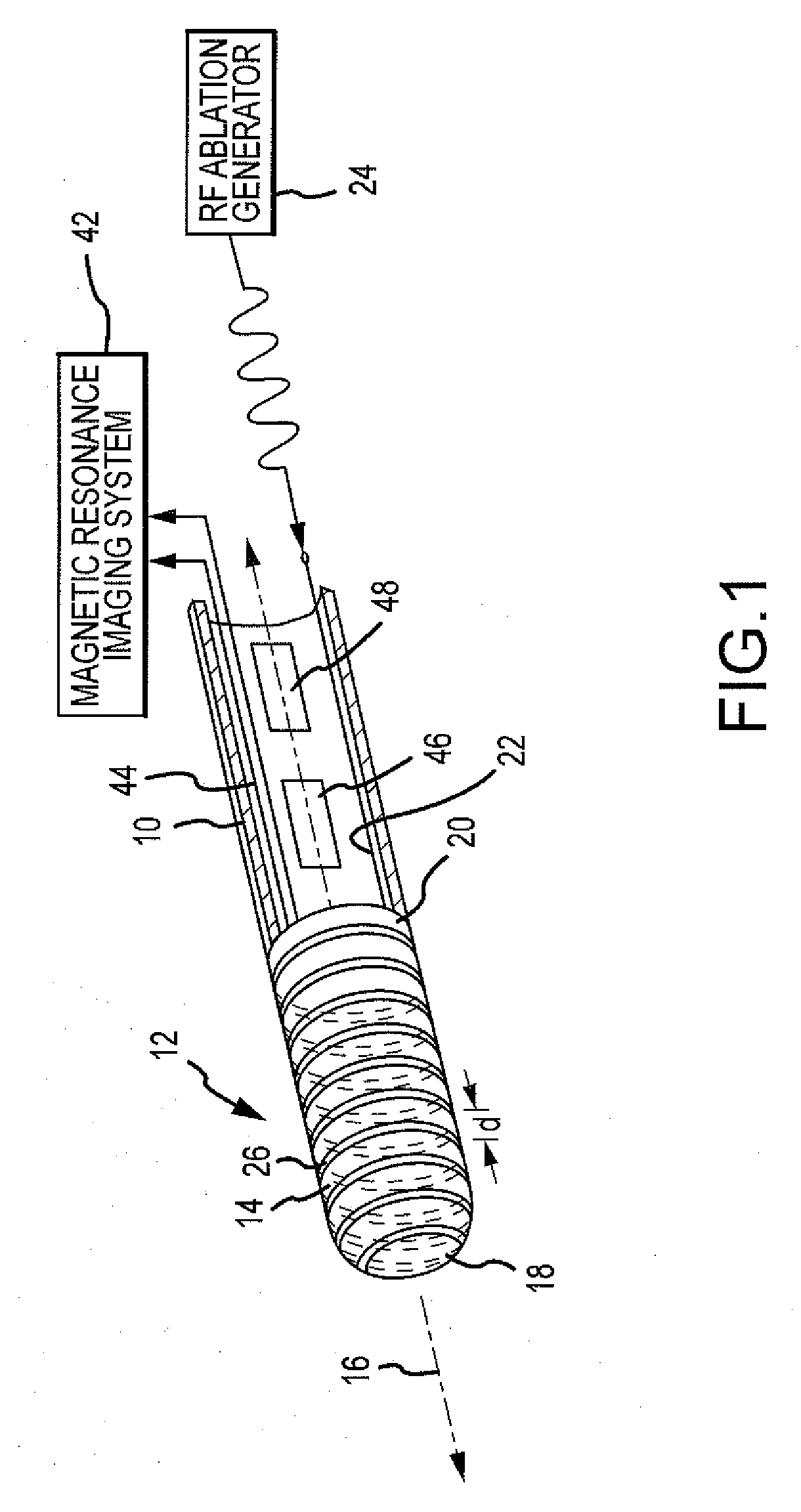
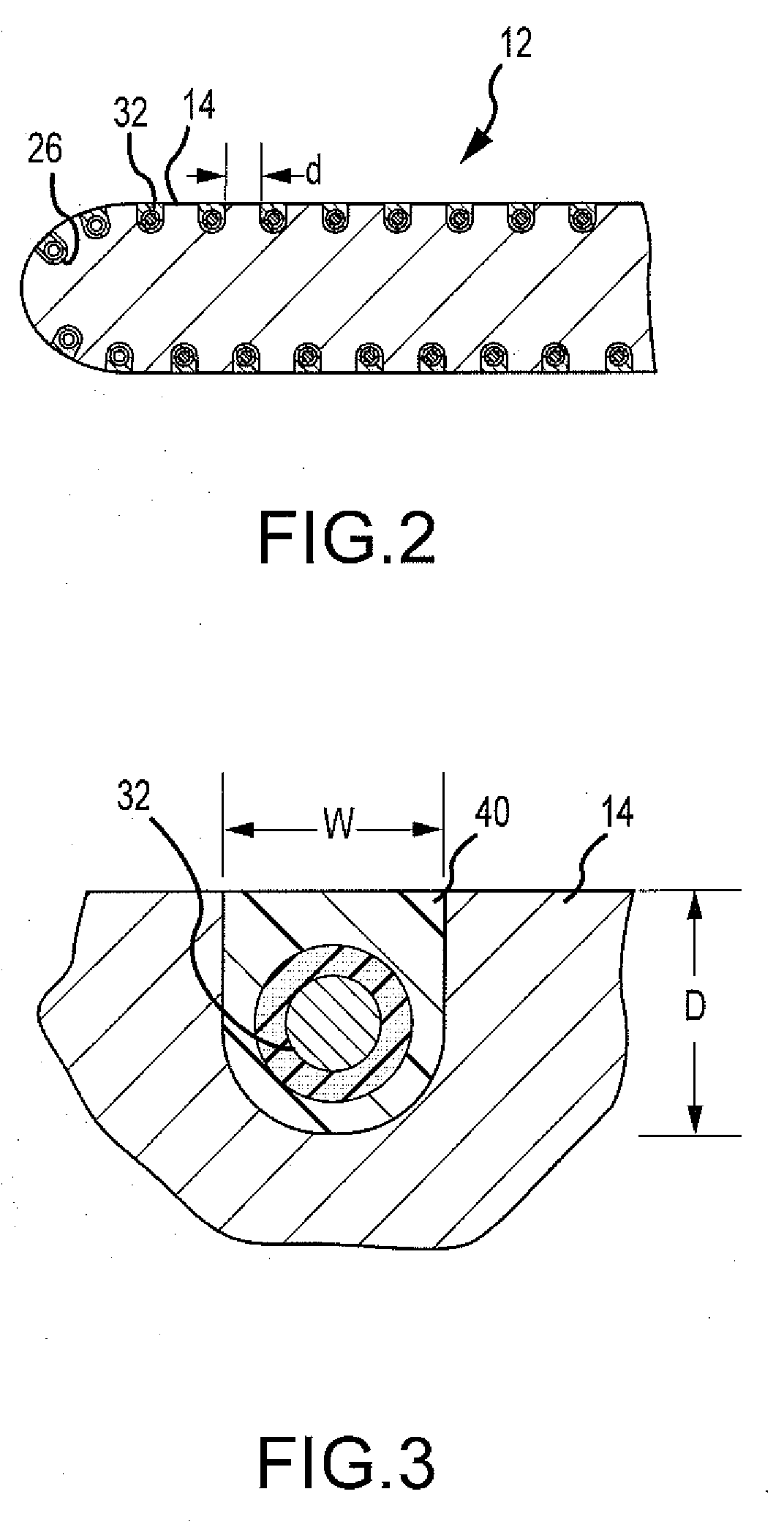
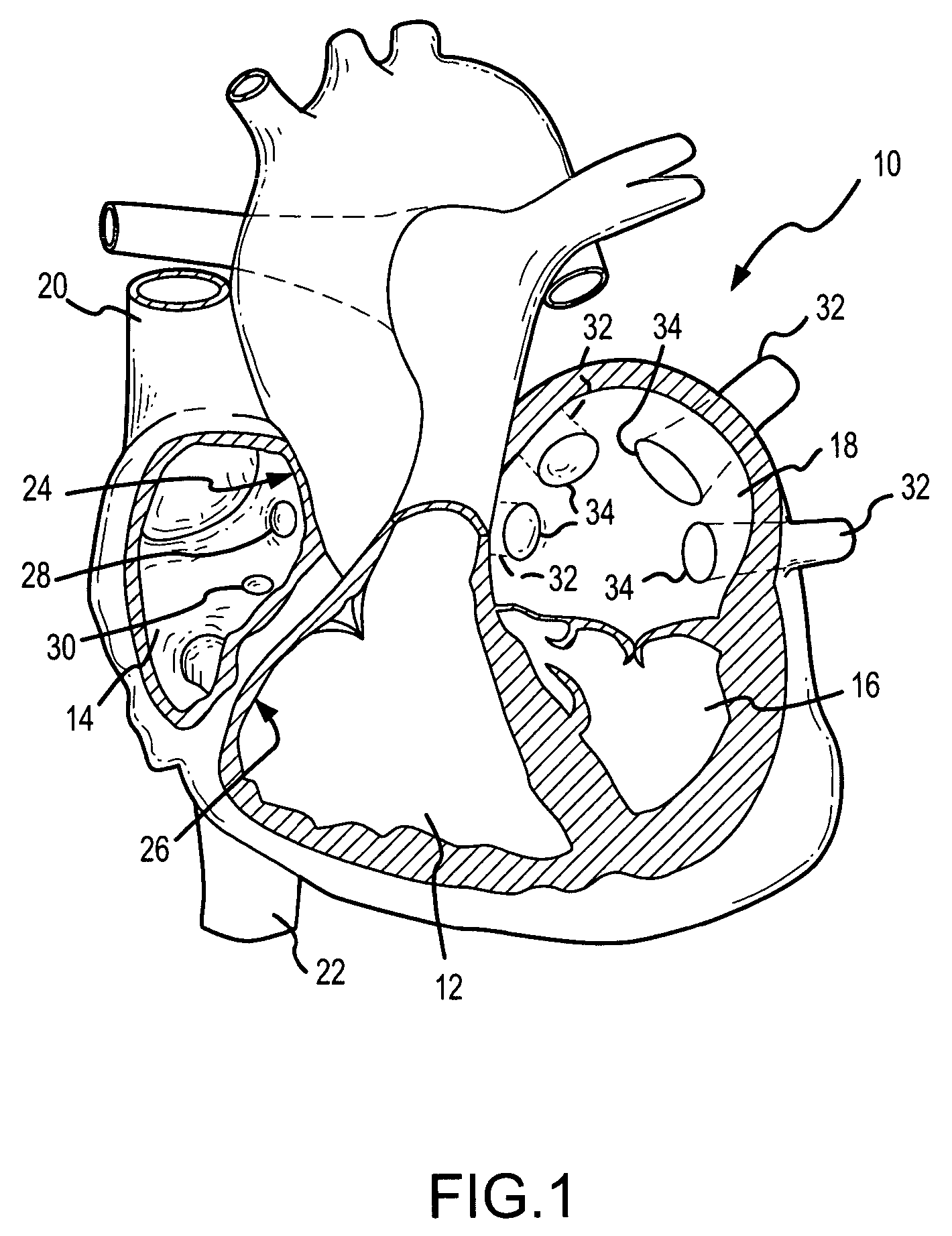
Catheter electrode that can simultaneously emit electrical energy and facilitate visualization by magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20090171187A1Reduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEngineeringConductive materials
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Ablation catheter electrode arrangement
InactiveUS20050004440A1Internal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringCatheter electrodeTarget tissue
An ablation catheter employing a continuous or nearly continuous flexible electrode arrangement. In one implementation, the flexible electrode include at least one electrode defining a saw tooth pattern. In another implementation, the flexible electrode is arranged in an interlaced pattern. Generally, the flexible electrodes are configured to adapt to the change in shape of the portion of the catheter that the electrode is connected with. Moreover, the flexible electrodes are arranged to provide a continuous or nearly continuous lesion of the target tissue. In some implementations, the flexible electrode may be connected with the catheter in a biased configuration, and as such may assist in changing the shape of a curve in the catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
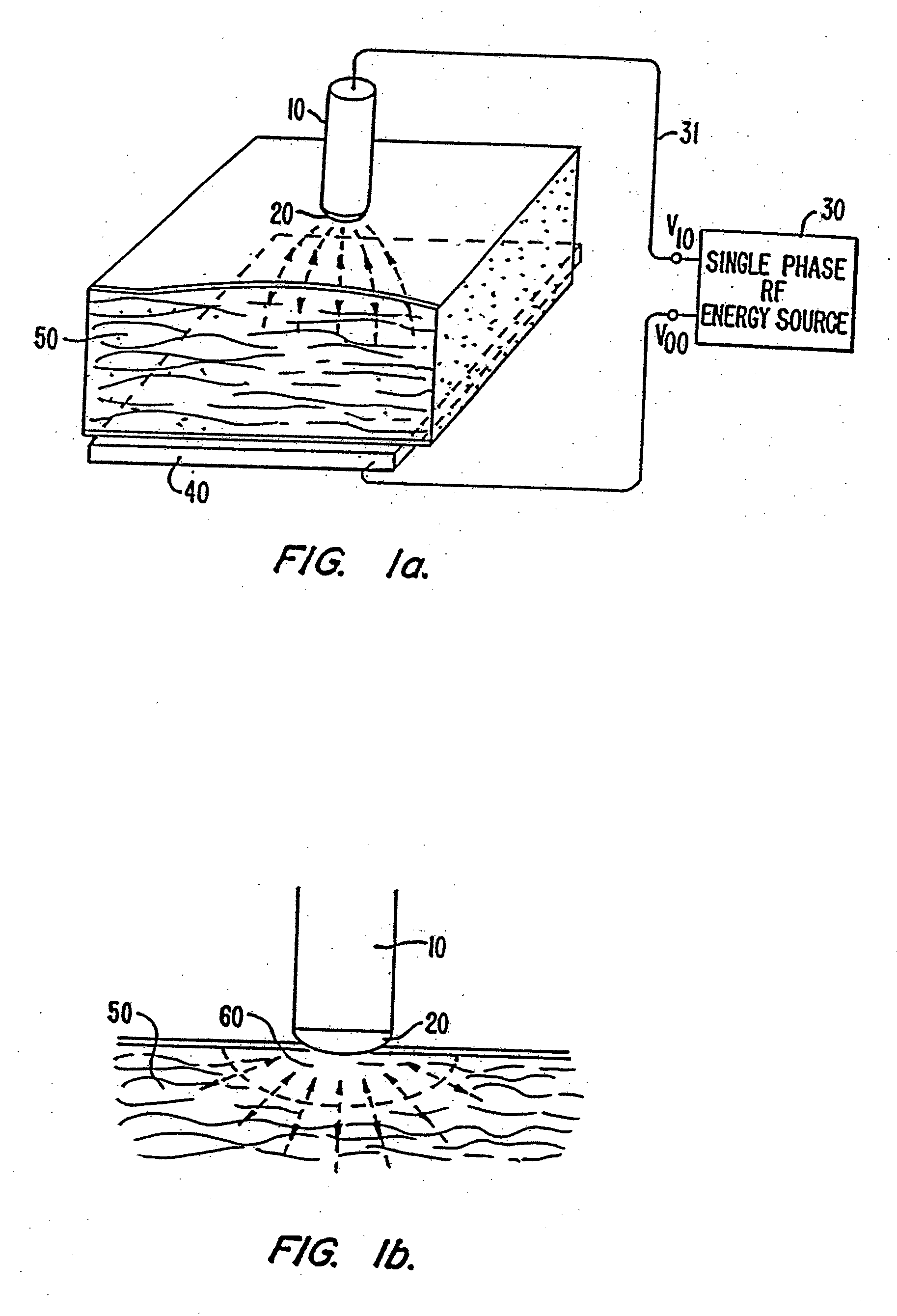
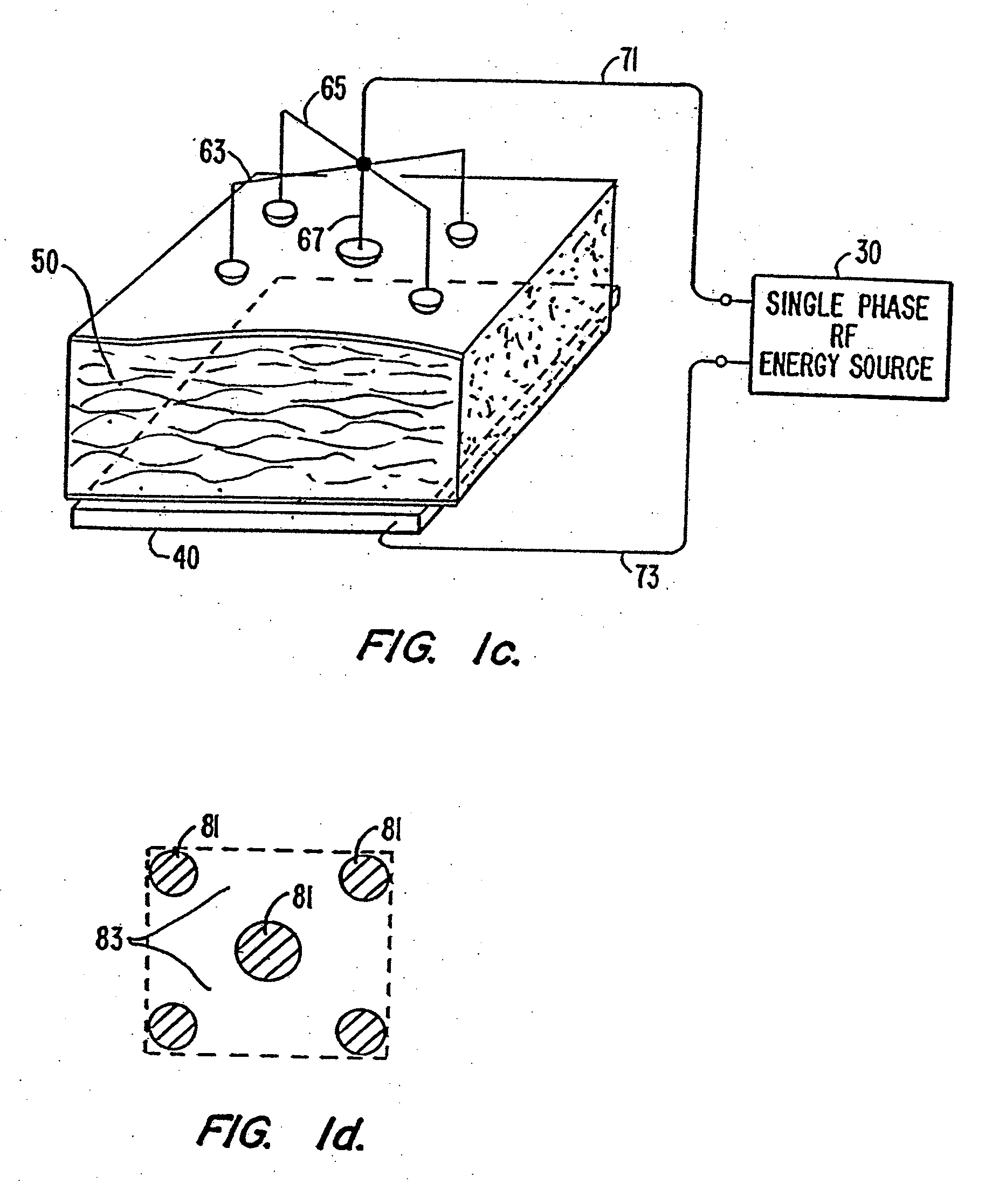
Device and Method for Multi-Phase Radio-Frequency Ablation
InactiveUS20070093806A1Simple power connectionFully filledElectrotherapyControlling energy of instrumentRf ablationAuxiliary electrode
Multi-phase RF ablation employing a two-dimensional or three-dimensional electrode array produces a multitude of currents paths on the surface of the ablation zone. This results in a uniform lesion with a size defined by the span of the electrode array. An orthogonal electrode catheter array suitable for cardiac ablation is used in conjunction with a two-phase RF power source to produce uniform square-shaped lesions of size 1.2 cm2. Lesions of larger size are created by successive adjacent placement of the square-shaped lesions. A temperature sensor at the electrode tip allows monitoring of ablation temperature and regulation of thereof to minimize the electrode tips from being fouled by coagulum. In another embodiment, an external auxiliary electrode is used in combination with the catheter electrodes. This also produces lesions of greater depth. In yet another embodiment, ablation is performed with a sequence of elementary electrode-electrical configurations.
Owner:MORVIL TECH LLC
Electrical neuromodulation stimulation system and method for treating urinary incontinence
InactiveUS20150328454A1Enhance patient resultImprove therapeutic efficacyExternal electrodesDigestive electrodesElectricityProtection mechanism
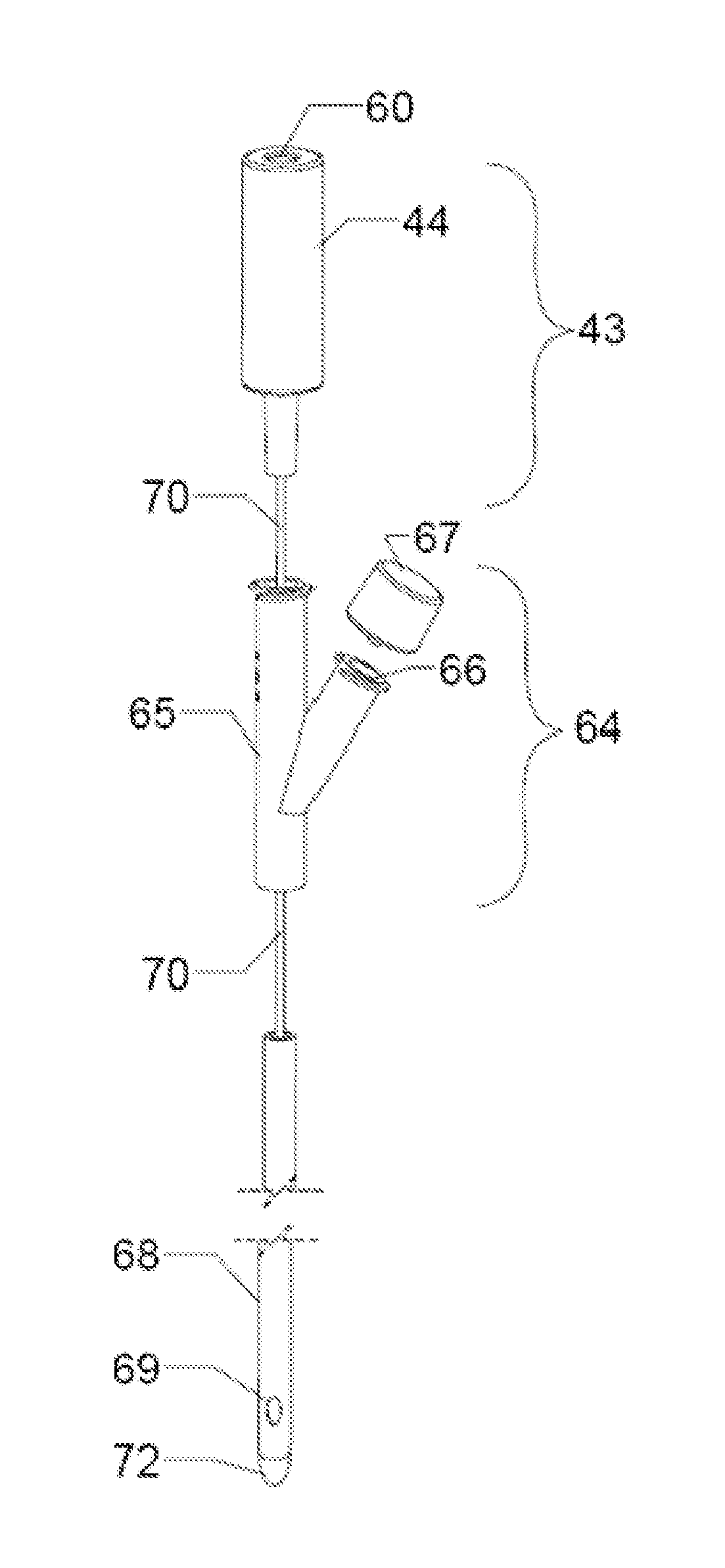
A system and method are provided for using neuromodulation techniques and intravesical electrical stimulation to treat Urinary Incontinence and related bladder-system conditions. The system uses an electrical stimulation module, stimulation electrodes and catheters, and / or a measurement and feedback system to determine an electrical stimulation therapy program as a function of a pre-programmed library and, optionally, measured and patient-provided response data. IVES and other electrical stimulation signals are generated and conveyed to the patient via catheter electrodes placed in and around the bladder system and related nerves, nodes and motor control points. The system employs a variety of safety mechanisms, including safety algorithms, a one-time use catheter connection, and catheter electrical-shock protection mechanisms.
Owner:BIO HEALTH FRONTIERS
Machine learning in determining catheter electrode contact
Cardiac catheterization is carried out by memorizing a designation of a contact state between an electrode of the probe and the heart wall as one of an in-contact state and an out-of-contact state, and making a series of determinations of an impedance phase angle of an electrical current passing through the electrode and another electrode, identifying maximum and minimum phase angles in the series, and defining a binary classifier adaptively as midway between the extremes. A test value is compared to the classifier as adjusted by a hysteresis factor, and a change in the contact state is reported when the test value exceeds or falls below the adjusted classifier.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
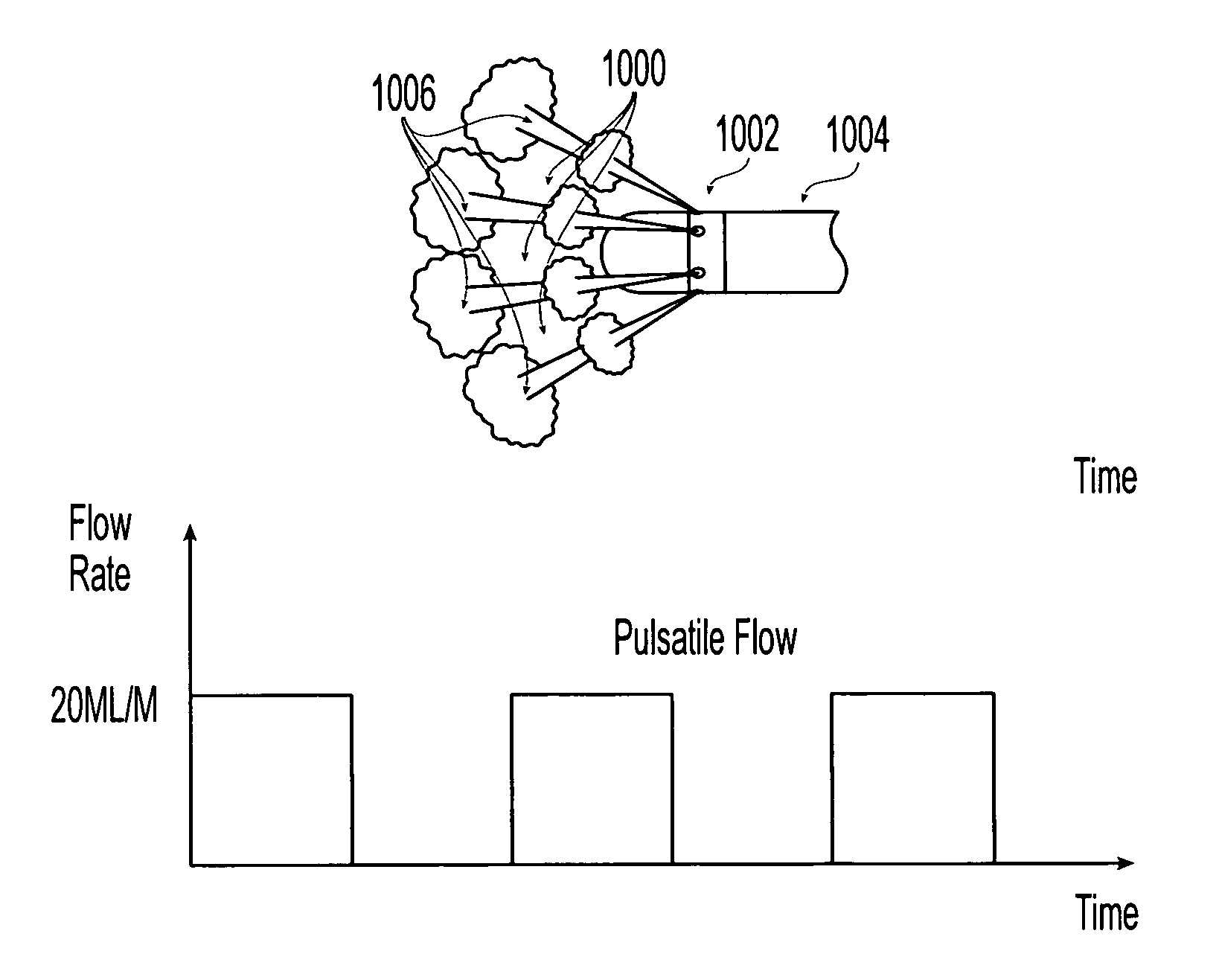
Irrigated ablation catheter system with pulsatile flow to prevent thrombus
ActiveUS8690870B2Prevent thrombusSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesCooling effectThrombus
The invention relates to an ablation catheter which controls the temperature and reduces the coagulation of biological fluids on an electrode of a catheter, prevents the impedance rise of tissue in contact with the electrode, and maximizes the potential energy transfer to the tissue, thereby allowing an increase in the lesion size produced by the ablation. The electrode includes passages positioned to allow saline flow out of an inner cavity of the electrode. This fluid flow is pulsatile to increase turbulence, reducing areas of stagnant flow, and produces a desired cooling effect.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for measuring force and torque applied to a catheter electrode tip
InactiveUS20150073245A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInternal electrodesCapacitanceEngineering
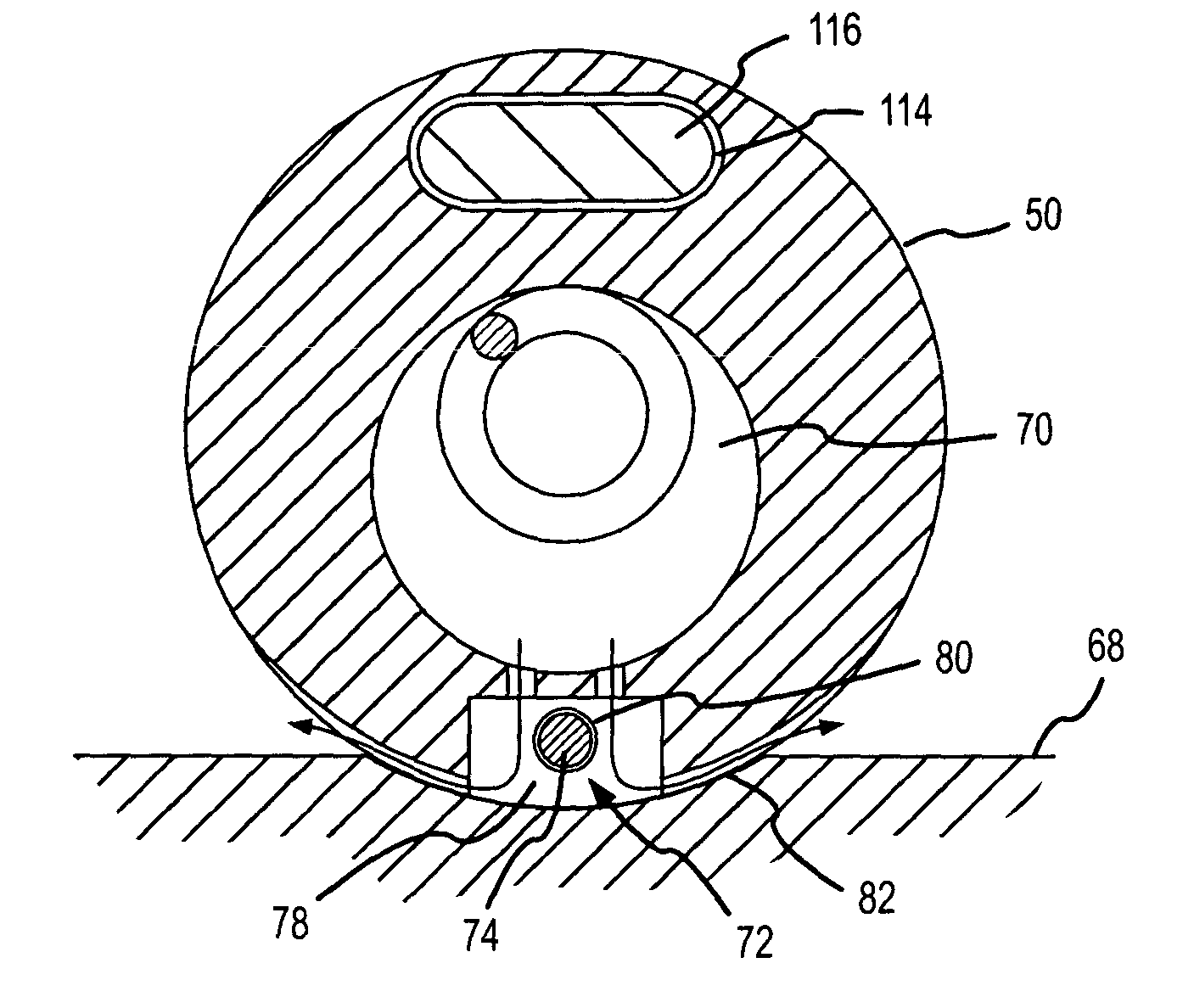
A contact sensing assembly including a catheter including an electrode having a base portion mounted adjacent a head portion of the catheter body. A sensor is disposed adjacent the base portion for measuring compression or tensile forces applied to an electrode tip portion, and includes a predetermined sensitivity. The base and head portions include predetermined rigidity so that forces applied to the electrode tip portion are determinable as a function of the sensitivity and a sensor output. A contact sensing assembly also includes an electrode pipe operatively connected to the catheter body for movement and bending with the catheter body, and an electrode wire disposed in the electrode pipe and including isolation. A change in capacitance resulting from movement of the electrode wire toward the electrode pipe or contact of the electrode wire with the electrode pipe during bending of the catheter correlates to a force applied to the catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
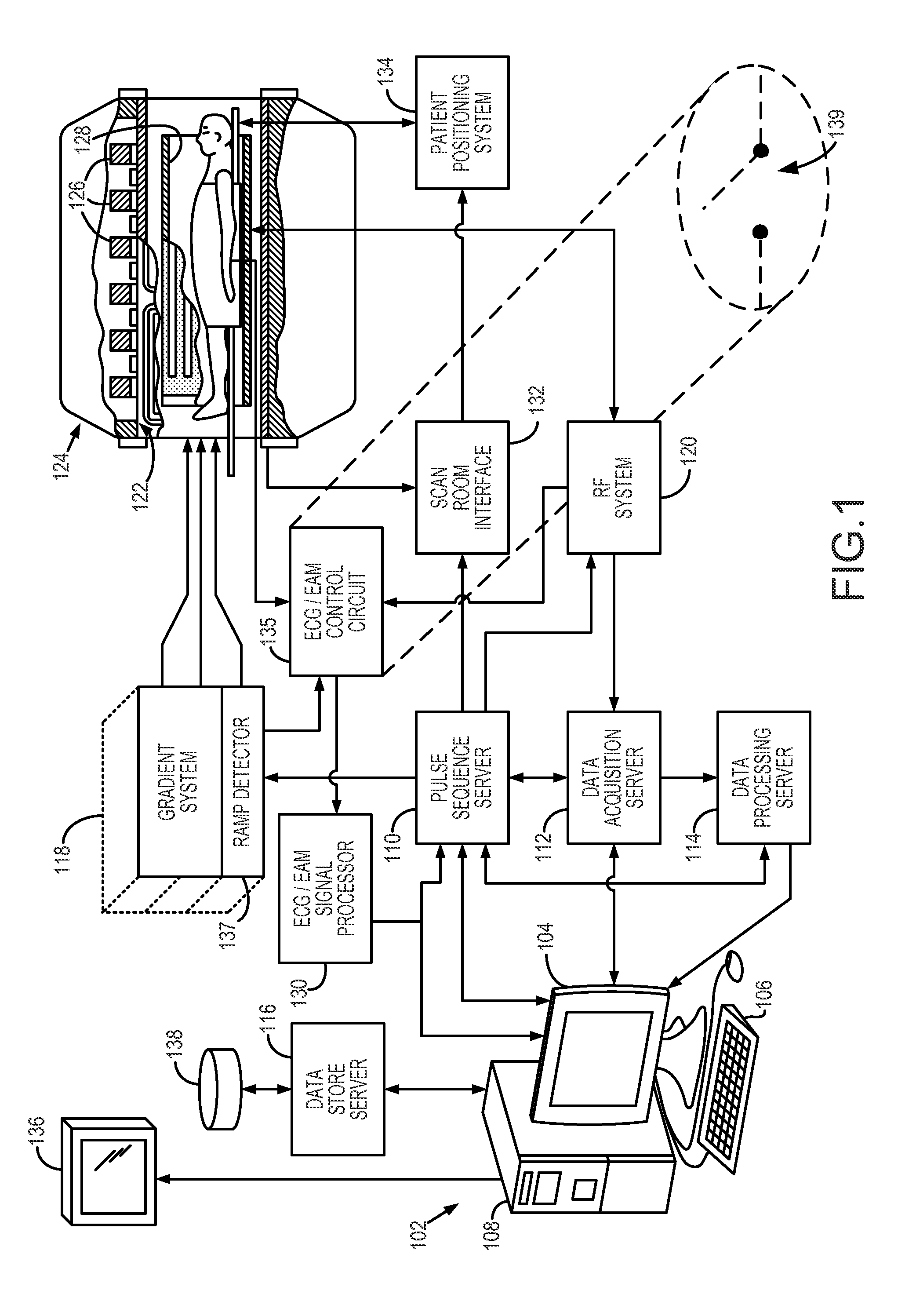
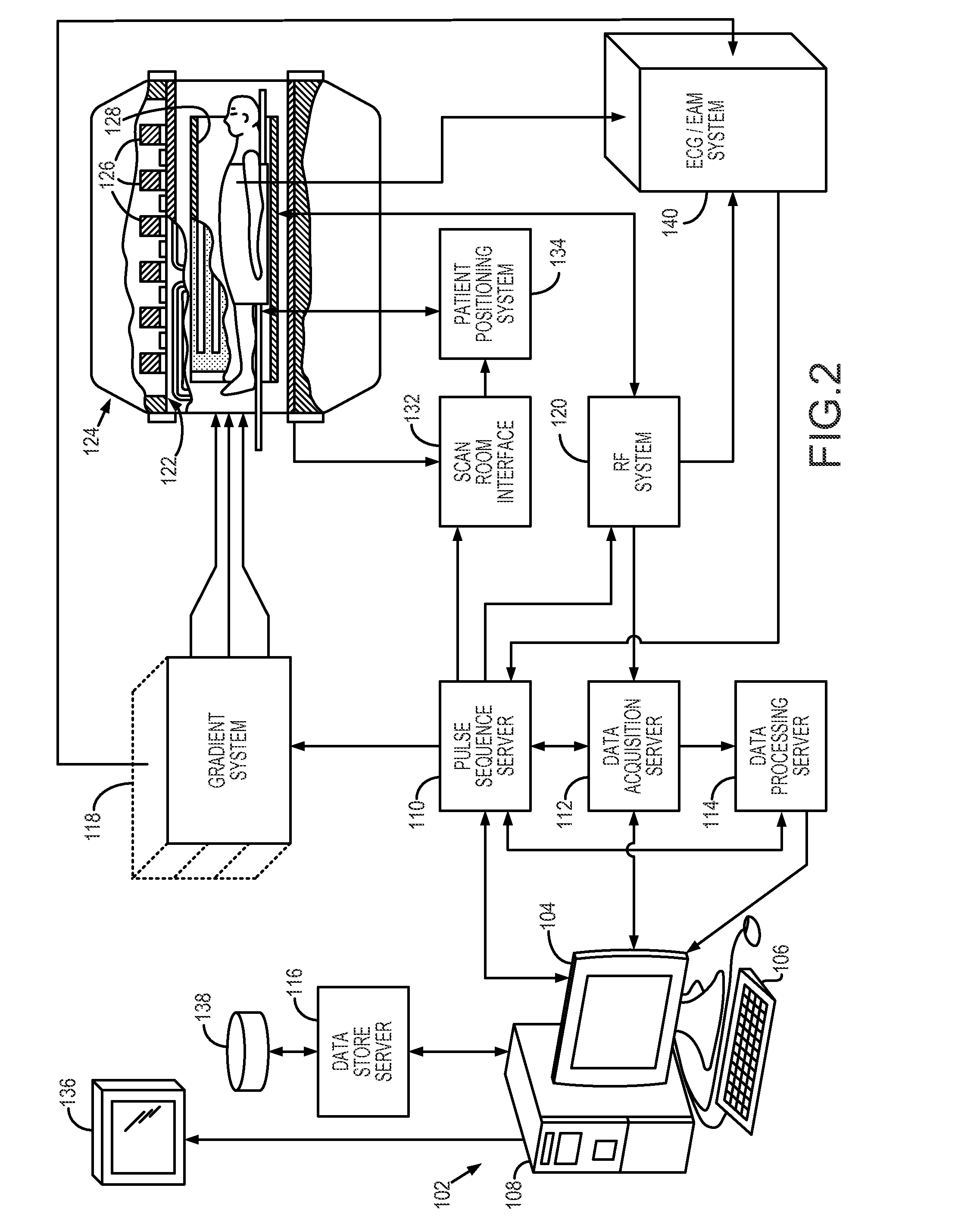
Noise tolerant localization systems and methods
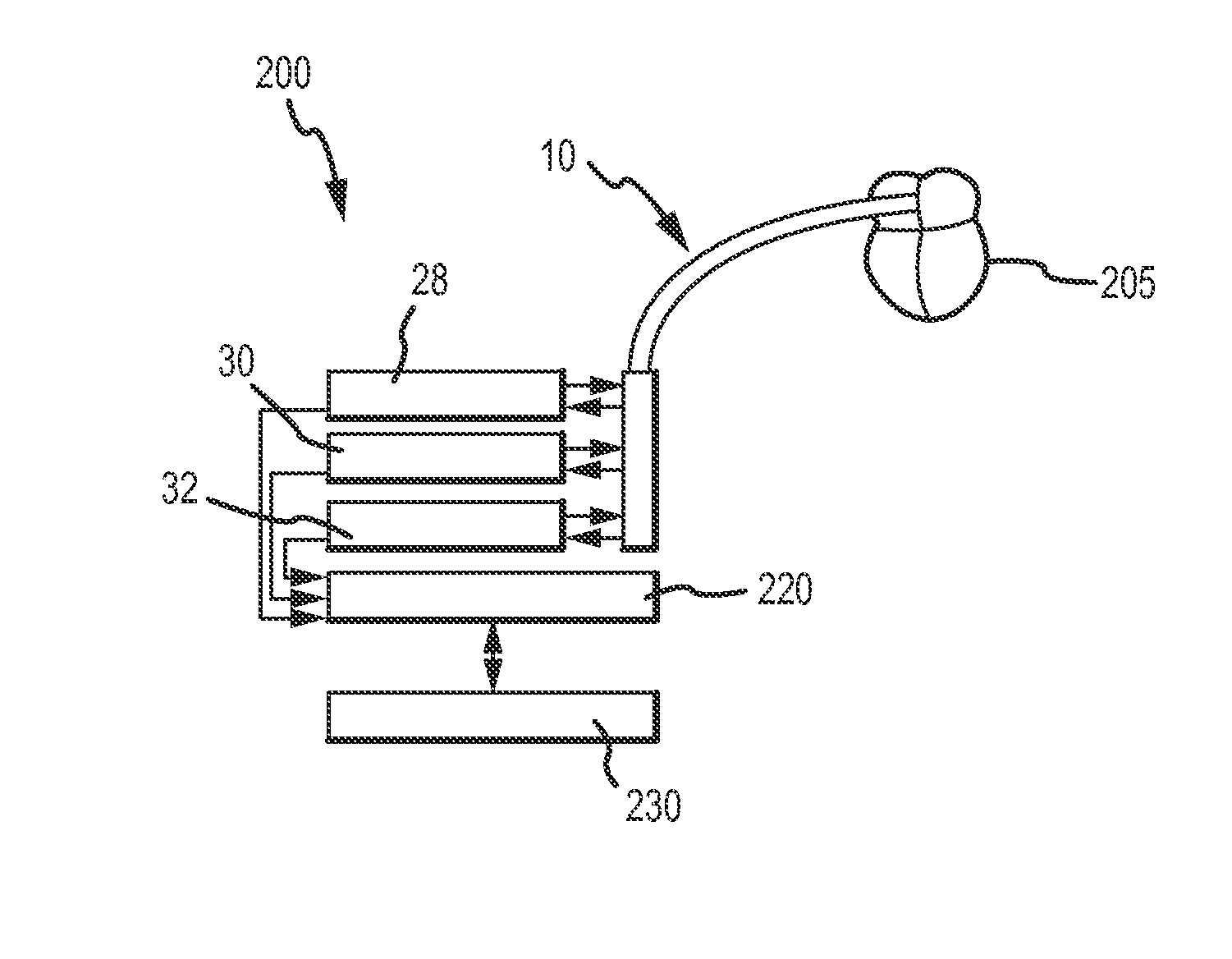
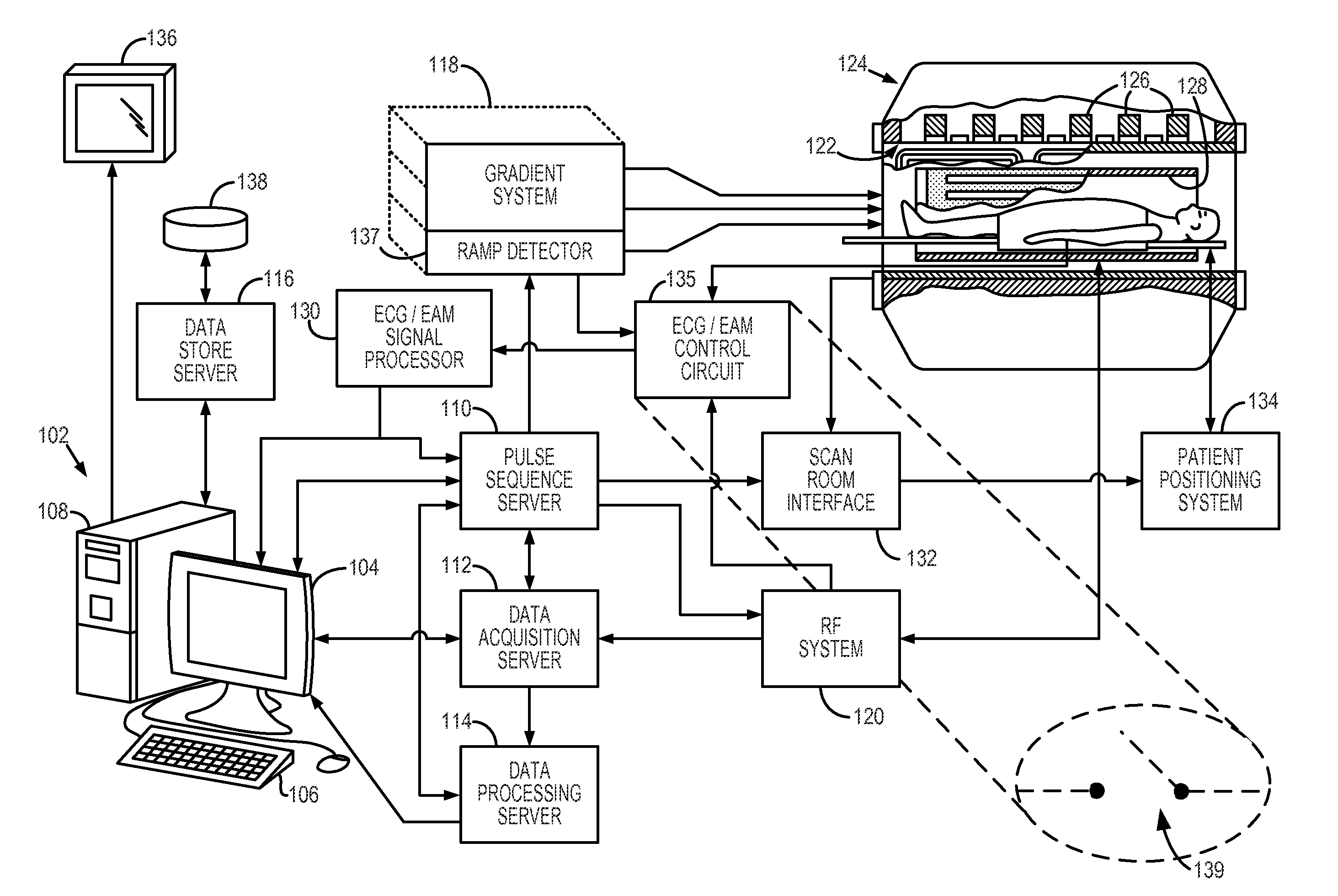
A system and method for tracking catheter electrode locations with the body of a patient during an MRI scan sequence includes mitigation logic configured to identify one or more impedance measurements that were taken during potentially noise-inducing conditions (i.e., magnet gradients, RF pulses), and were thus subject to corruption by noise. The mitigation logic is configured to replace the potentially corrupt impedance measurements with previously-obtained impedance measurements taken from an immediately preceding acquisition cycle (e.g., from a previous time-slice).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
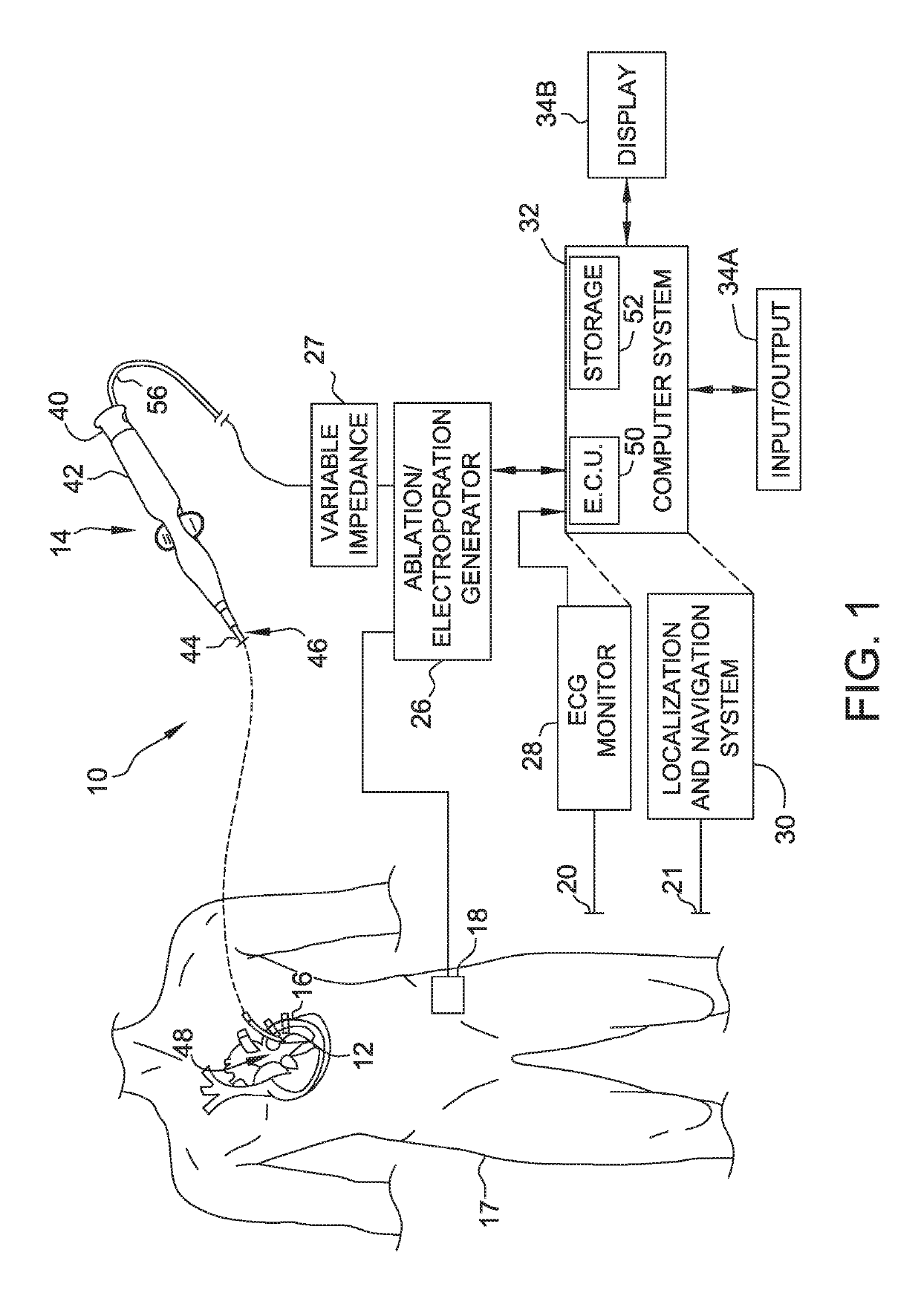
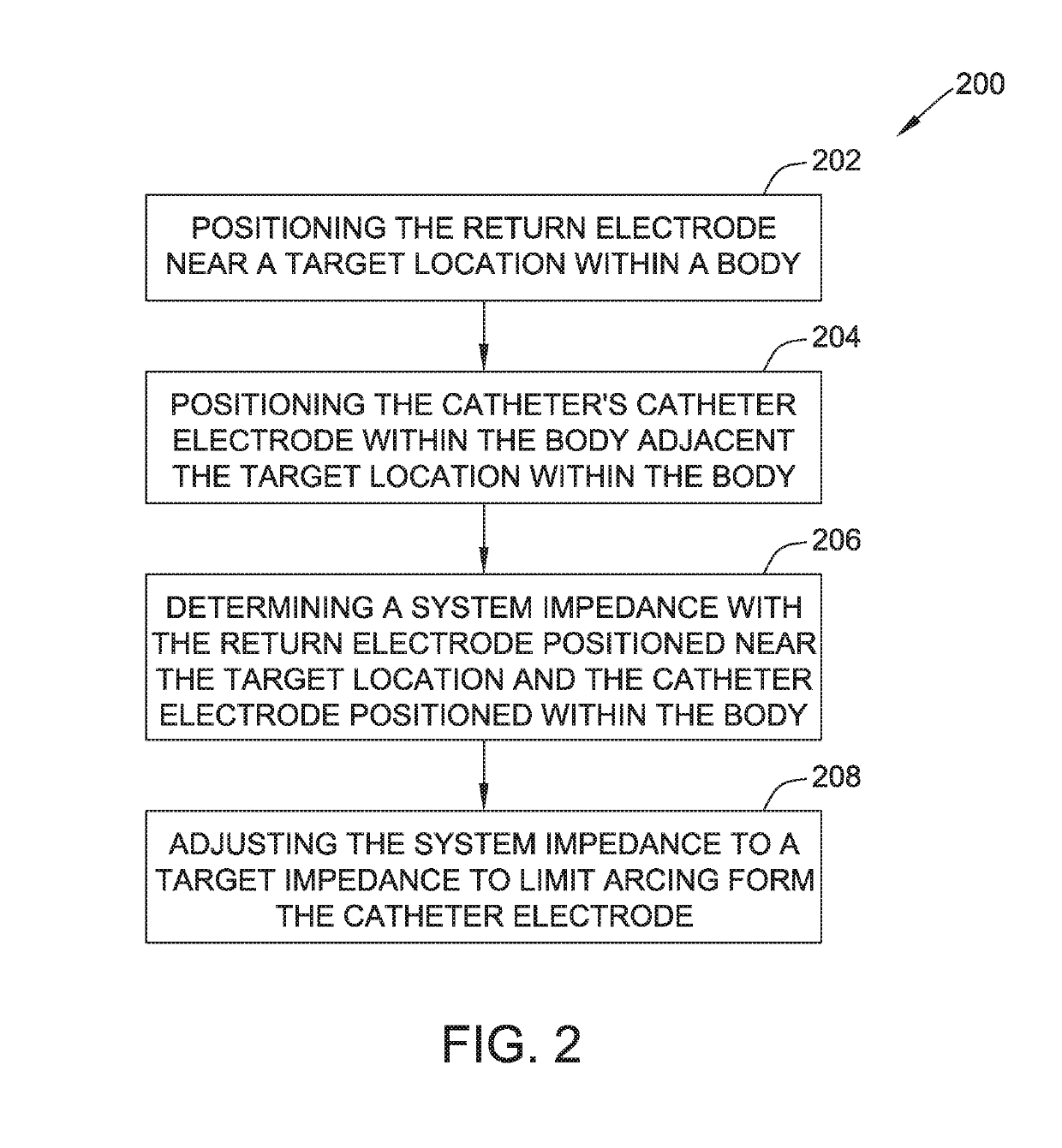
Electroporation systems and catheters for electroporation systems
The present disclosure provides electroporation systems, methods of controlling electroporation systems to limit electroporation arcs through intracardiac catheters, and catheters for electroporation systems. One method of controlling an electroporation system including a direct current (DC) energy source, a return electrode connected to the DC energy source, and a catheter connected to the DC energy source is disclosed. The catheter has a at least one catheter electrode. The method includes positioning the return electrode near a target location within a body and positioning the catheter electrode adjacent the target location within the body. A system impedance is determined with the return electrode positioned near the target location and the catheter electrode positioned within the body. The system impedance is adjusted to a target impedance to arcing from the catheter electrode.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Catheter electrode and rail system for cardiac ablation
The instant invention is directed toward an ablation catheter and sheath incorporating wire rail system. The catheter may have a combination of rigid and flexible components to orient an ablation electrode at the distal tip toward the target tissue. The wire rail acts to guide an ablation tip along the tissue to aid in the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions on a trabecular surface, e.g., in the right atrium along the isthmus between the ostium of the inferior vena cava and the tricuspid valve.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
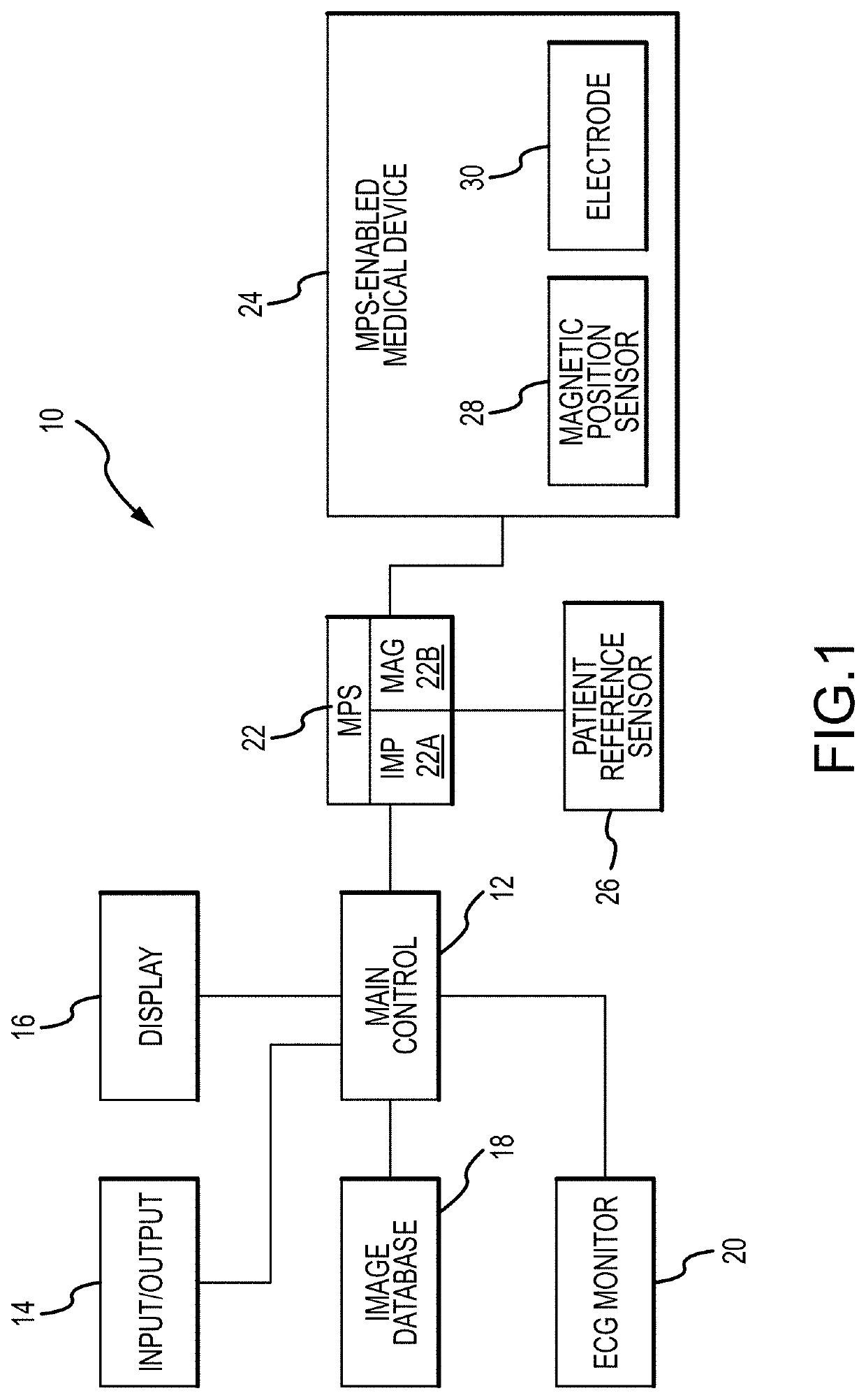
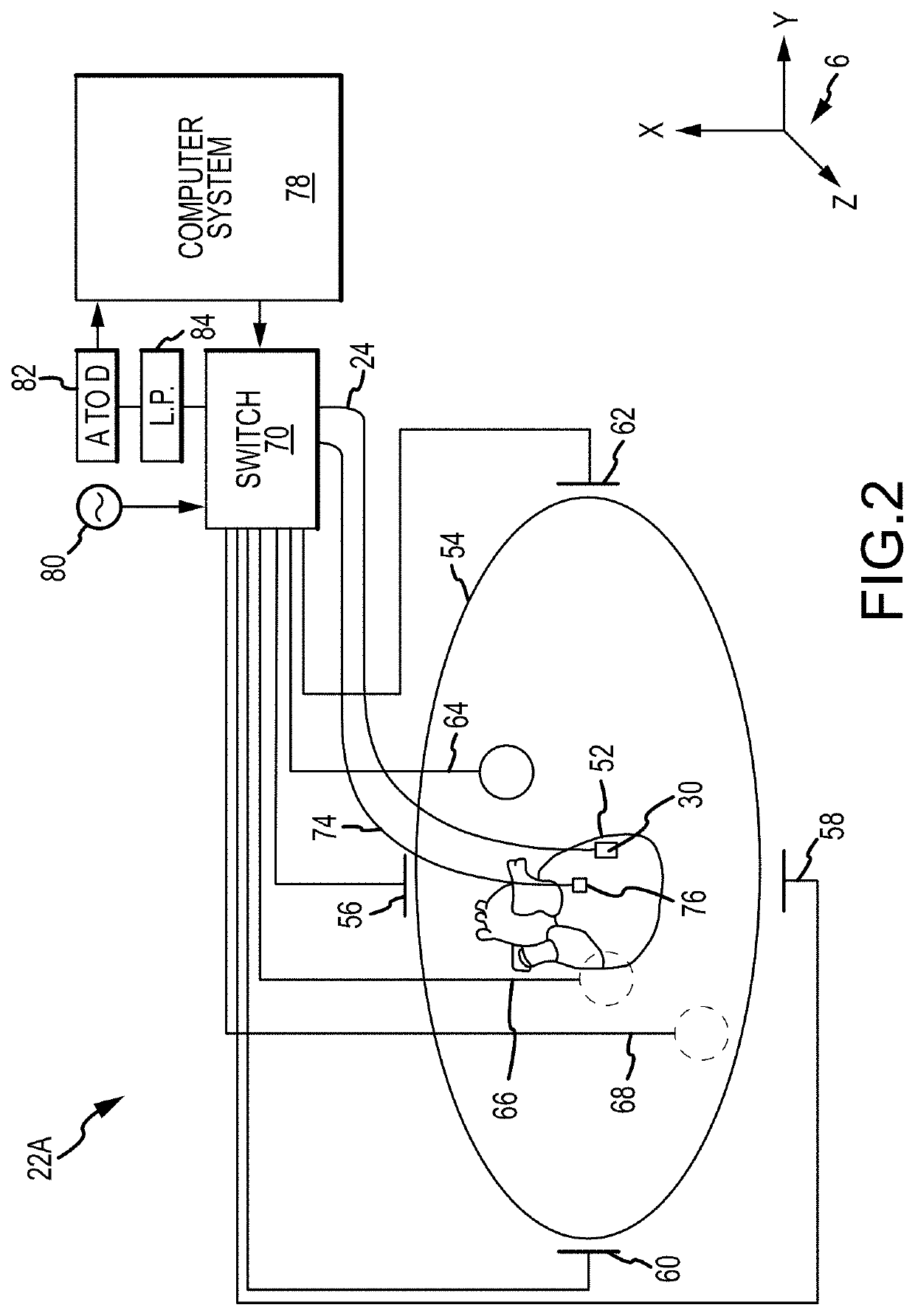
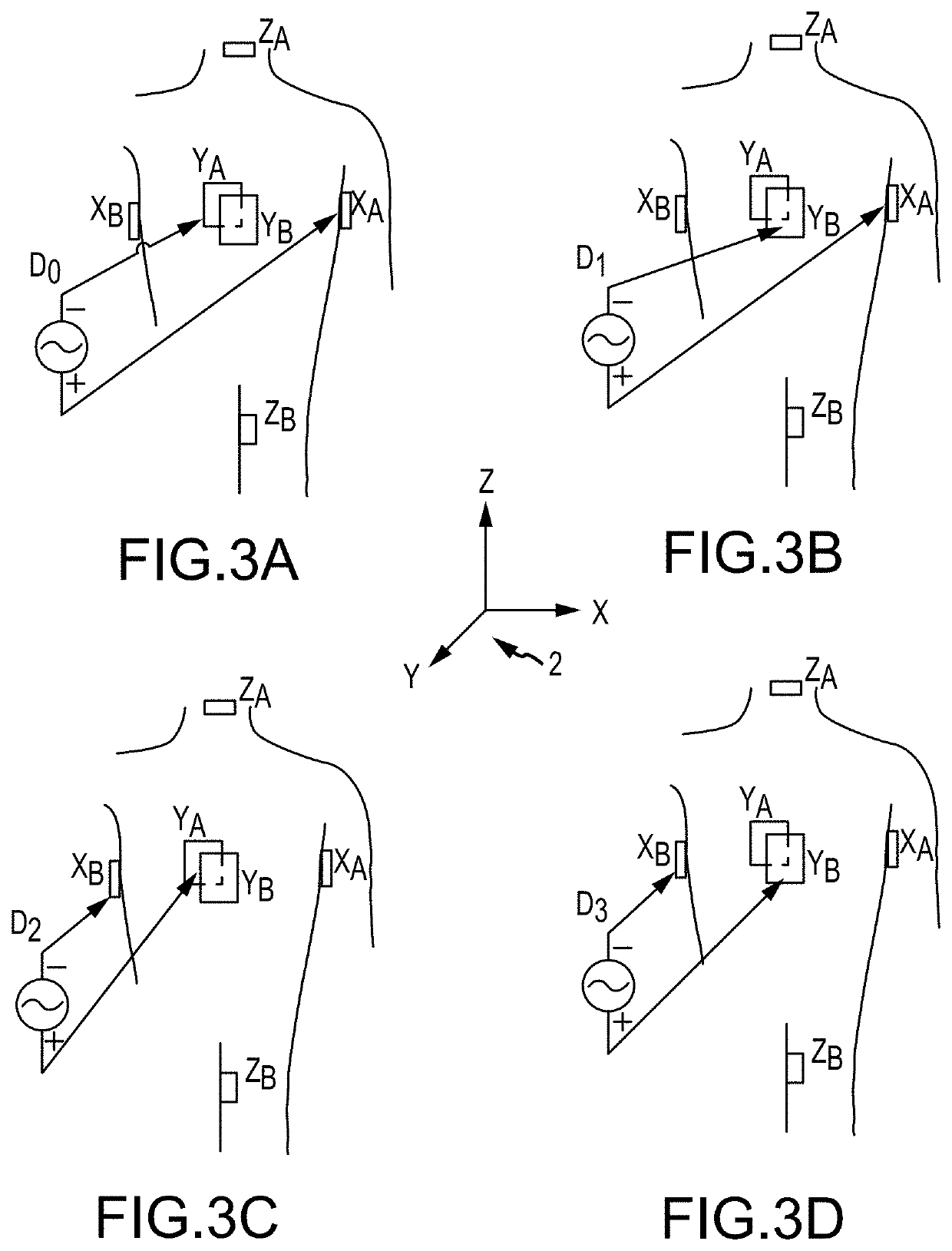
Method for medical device localization based on magnetic and impedance sensors
PendingUS20200138334A1Improve correspondenceAccelerate transformationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineThree-dimensional space
Provided herein are systems and methods for use in identifying location of electrodes of a catheter within a three-dimensional space. The systems and methods initially predict locations of physical electrodes and / or physical magnetic sensors of the catheter in the three-dimensional space. Impedance and / or magnetic responses are predicted for the predicted locations. Actual measurements / responses (e.g., measured responses) are then obtained for the physical electrodes and / or physical sensors. Based on the predicted responses and the measured responses, the systems and methods generate calculated locations of electrodes and / or sensors in the three-dimensional space. The systems and method utilize information from both the predicted responses and the measured responses to produce the calculated locations, which may have an accuracy that is greater than locations produced by either the predicted responses or the measured responses.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com