Protein sequence of the plant toxin gelonin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Purification and Characterization of Gelonin
Gelonin was isolated from the seeds of the plant Gelonium multiforum essentially according to the procedure as described (Stirpe, et al. (1980) J. Biol. Chem 255 6947-6953). Briefly, gelonin was extracted from the seeds by homogenization in buffered saline solution (pH 7.4). The supernatant was concentrated after dialysis against 5 mM sodium phosphate (pH 6.5) and the gelonin further purified by ion exchange chromatography as described below. The purity of the gelonin toxin was assessed by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and sodium dodecylsulphate-polyacylamide gel electrophoreseis (SDS-Page). Gelonin toxin migrated as a single band with an approximate molecular weight of 29-30,000 daltons.
Gelonin toxin activity was measured as described in Example 2 by protein synthesis inhibition in a cell-free system.
Seeds of Gelonium multiforum were shelled and the nuts ground in a homogenizer with eight volumes of 0.14 M NaCl containing 5 m...
example 2
Assay of Gelonin Activity
The gelonin activity was monitored in a cell-free protein synthesis inhibition assay. The cell-free protein synthesis inhibition assay was performed by sequentially adding to 50 ul rabbit reticulocyte lysate, thawed immediately before use, mixing after each addition, the following components: 0.5 ml of 0.2 M Tris HCl (pH 7.8), 8.9 ml of ethylene glycol, and 0.25 ml of 1 M HCl).
Twenty microliters of a salt-amino acid-energy mixture (SAEM) consisting of: 0.375 M KCl, 10 mM Mg(CH.sub.3 CO.sub.2).sub.2, 15 mM glucose, 0.25-10 mM amino acids (excluding leucine), 5 mM ATP, 1 mM GTP, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), 10 ul Creatinine phosphate-creatinine phosphokinase, 8 ul [.sup.14 C] leucine (Amersham, 348 mCi / mmol), and adding 1.5 ul of solutions containing varying concentrations of the gelonin mixture. The mixture was incubated for 60 minutes at 30.degree. C. .sup.14 C-leucine incorporation was monitored in an aliquot of the mixture by precipitating synthesized protein ...
example 3
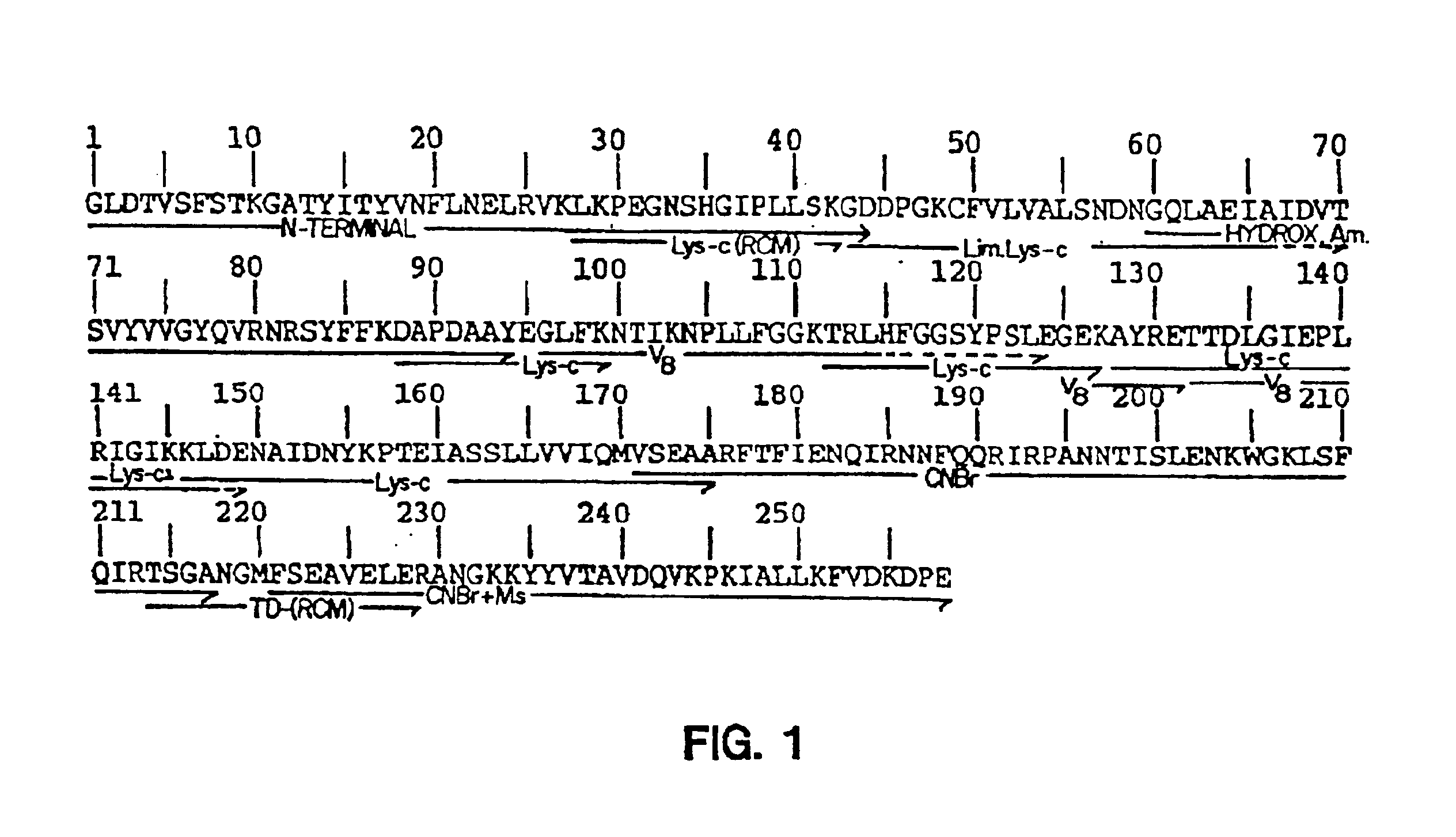
Determination of Gelonin Amino Acid Sequence
The gelonin amino acid sequence was determined by the Edman degradation method using an automated amino acid sequencer as described in European Patent Application No. EP-257735. Large peptides and unfragmented protein were applied to the reverse phase portion of the sequence reaction chamber. Unwanted buffer components were washed off with excess water. The protein or peptide sample was then sequenced by Edman chemistry and the extracted ATZ amino acid derivatives were converted to the PTH form by 25% TFA in H.sub.2 O at 65.degree. C. PTH samples were identified by reverse phase analytical separation on a Np 1090 column.
In order to obtain further amino acid sequence, the protein was digested with various proteolytic and chemical agents and then the peptides were purified by high performances liquid chromatography. Gelonin was found quite resistant to the exposure of trypsin (cleaves after arginine and lysine residues) and acetyl trypsin (c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Chemotherapeutic properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com