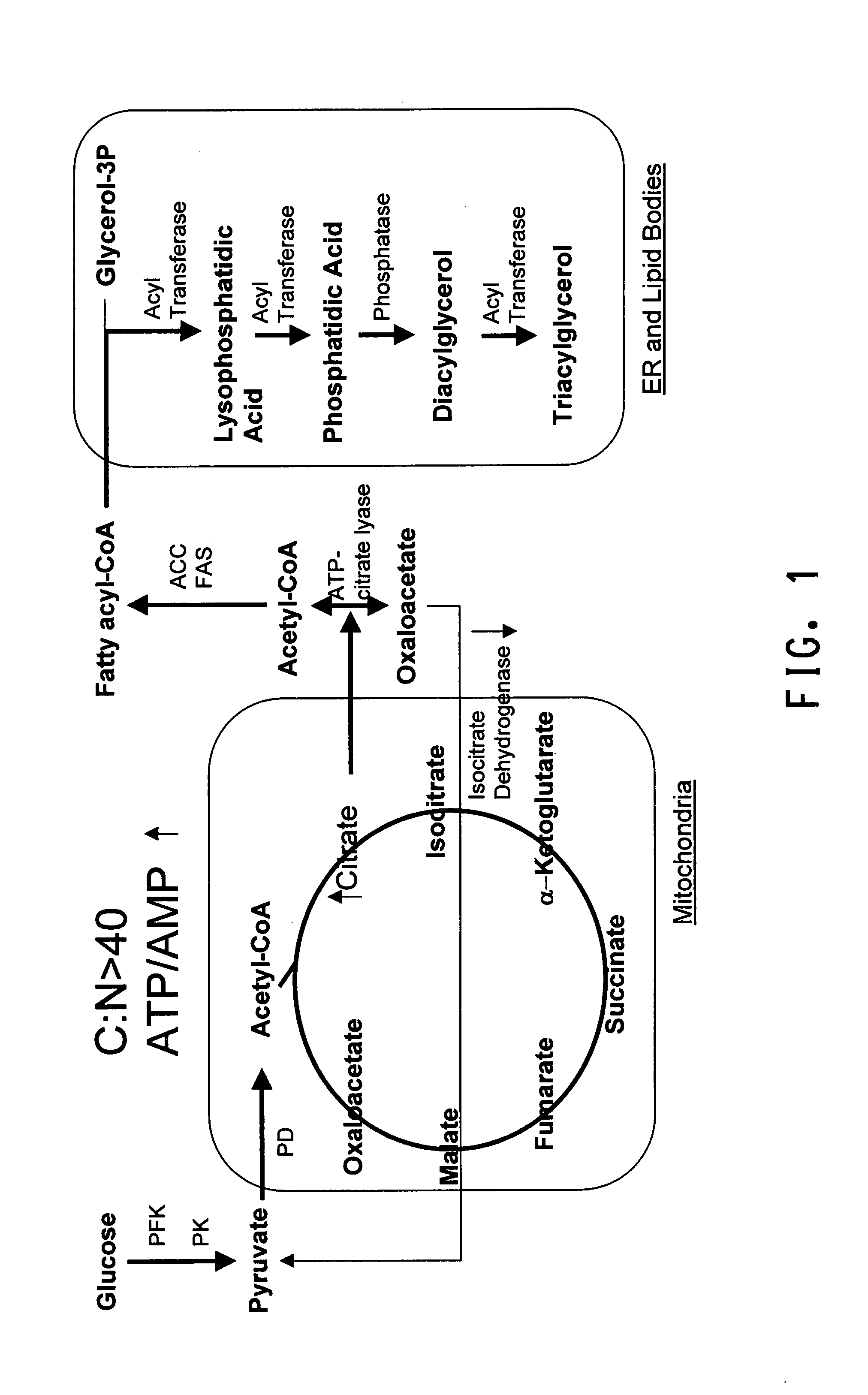
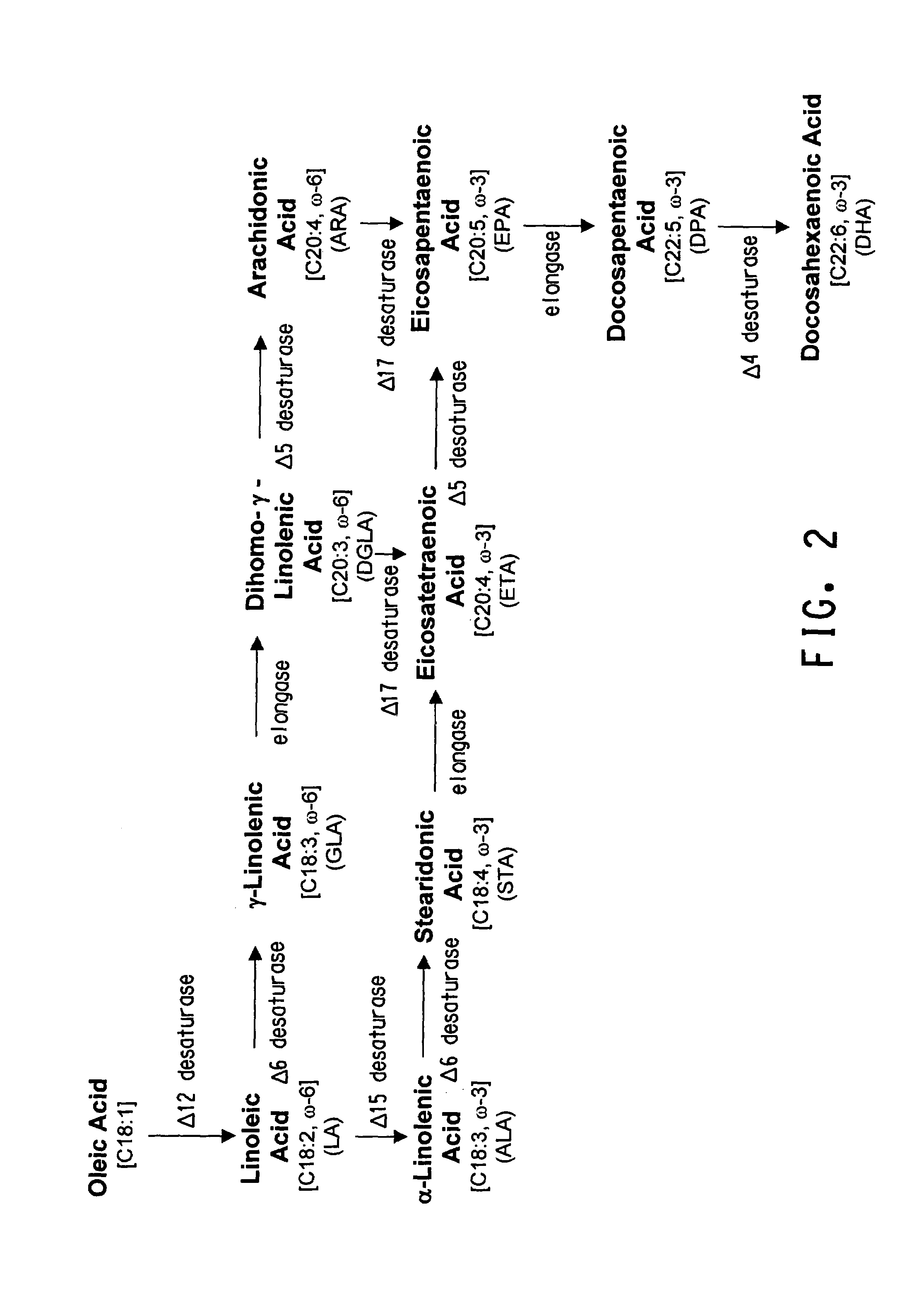
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
a technology of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oleaginous yeast, which is applied in the field of biotechnology, can solve the problems of inacceptable products as food supplements, unpleasant taste and odor, and high heterogeneous oil composition of natural sources such as fish and plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Plasmids Suitable for Heterologous Gene Expression in Yarrowia lipolytica
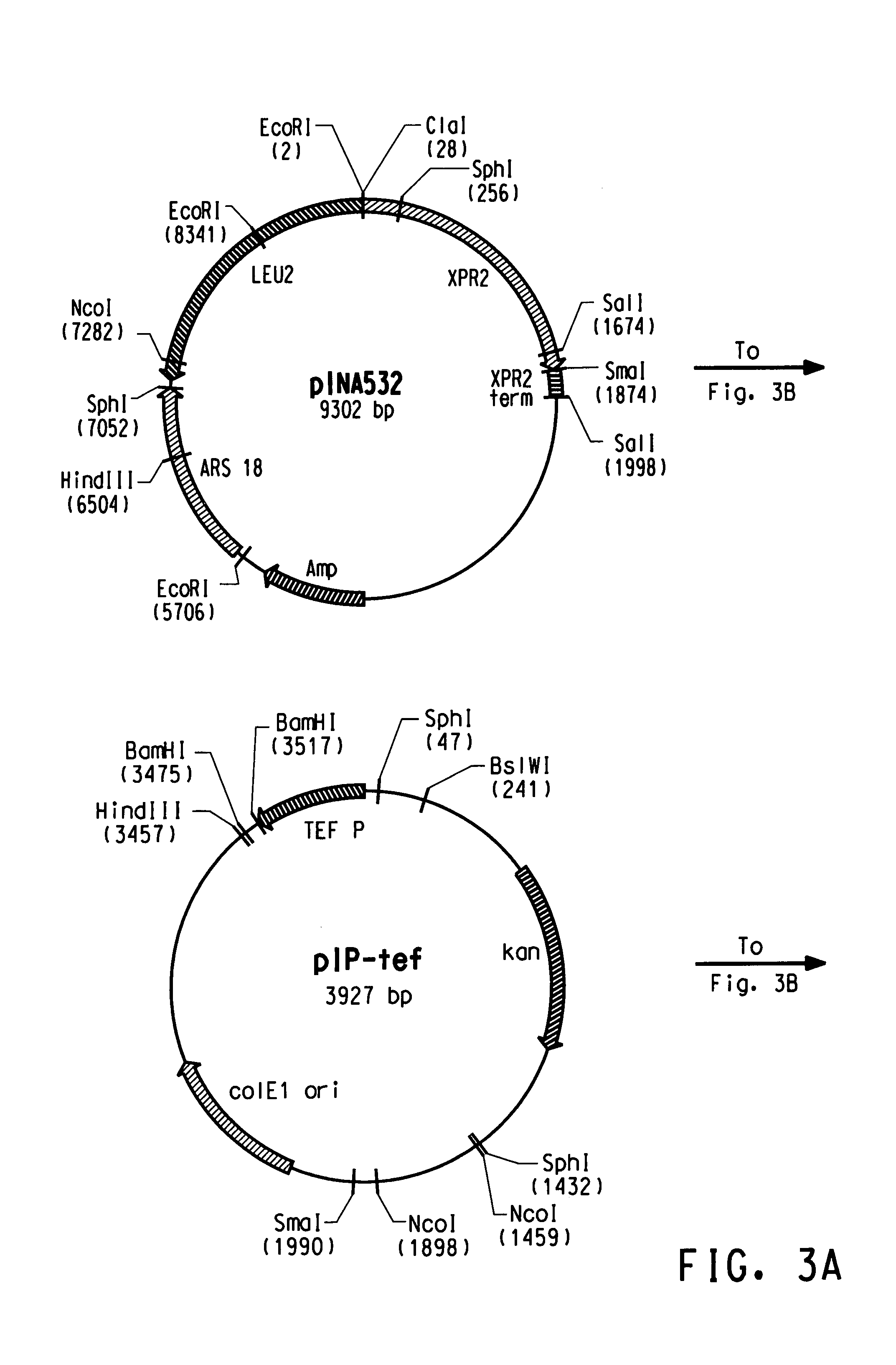
[0239]The plasmid pY5, a derivative of pINA532 (a gift from Dr. Claude Gaillardin, Insitut National Agronomics, Centre de biotechnologie Agro-Industrielle, laboratoire de Genetique Moleculaire et Cellularie INRA-CNRS, F-78850 Thiverval-Grignon, France), was constructed for expression of heterologous genes in Yarrowia lipolytica, as diagrammed in FIG. 3.
[0240]First, the partially-digested 3598 bp EcoRI fragment containing the ARS18 sequence and LEU2 gene of pINA532 was subcloned into the EcoRI site of pBluescript (Strategene, San Diego, Calif.) to generate pY2. The TEF promoter (Muller S., et al. Yeast, 14: 1267-1283 (1998)) was amplified from Yarrowia lipolytica genomic DNA by PCR using TEF5′ (SEQ ID NO:38) and TEF3′ (SEQ ID NO:39) as primers. PCR amplification was carried out in a 50 μl total volume containing: 100 ng Yarrowia genomic DNA, PCR buffer containing 10 mM KCl, 10 mM (NH4)2SO4, 20 m...
example 2
Selection of Δ6 Desaturase, Δ5 Desaturase. Δ17 Desaturase and High Affinity PUFA Elongase Genes for Expression in Yarrowia lipolytica
[0250]Prior to the introduction of specific genes encoding an ω-3 and / or ω-6 biosynthetic pathway into oleaginous yeast, it was necessary to confirm the functionality of heterologous Δ6 desaturase, elongase, Δ5 desaturase and Δ17 desaturase genes expressed in Yarrowia. This was accomplished by measuring the conversion efficiency encoded by each wildtype gene in the alternate host. Specifically, four Δ5 desaturases, a Mortierella alpina Δ6 desaturase, a Saprolegnia diclina Δ17 desaturase and a M. alpina high affinity PUFA elongase were separately expressed and screened for activity in substrate-feeding trials. Based on these results, a M. alpina Δ5 desaturase gene was selected for use in conjunction with the Δ6 and Δ17 desaturase and high affinity PUFA elongase genes.
Construction of Expression Plasmids
[0251]In general, wildtype desaturase or elongase g...
example 3
Synthesis and Expression of a Codon-Optimized Δ17 Desaturase Gene in Yarrowia lipolytica
[0282]Based on the results of Example 2, genes encoding Δ6 desaturase, elongase and Δ5 desaturase activies were available that each enabled ˜30% substrate conversion in Yarrowia lipolytica. The Δ17 desaturase from S. diclina, however, had a maximum percent substrate conversion of only 23%. Thus, a codon-optimized Δ17 desaturase gene was designed, based on the Saprolegnia diclina DNA sequence (SEQ ID NO:5), according to the Yarrowia codon usage pattern, the consensus sequence around the ATG translation initiation codon and the general rules of RNA stability (Guhaniyogi, G. and J. Brewer, Gene 265(1-2):11-23 (2001)).
[0283]In addition to modification to the translation initiation site, 127 bp of the 1077 bp coding region (comprising 117 codons) were codon-optimized. A comparison between this codon-optimized DNA sequence (SEQ ID NO:9) and the S. diclina Δ17 desaturase gene DNA sequence (SEQ ID NO:5)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com