Semiconductor switching device
a switching device and semiconductor technology, applied in electronic switching, waveguide type devices, pulse techniques, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the maximum power allowed to pass through the switching device and insufficient maximum power to transmit signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021]An embodiment of this invention will be described hereinafter with reference to the FIGS. 2–9.
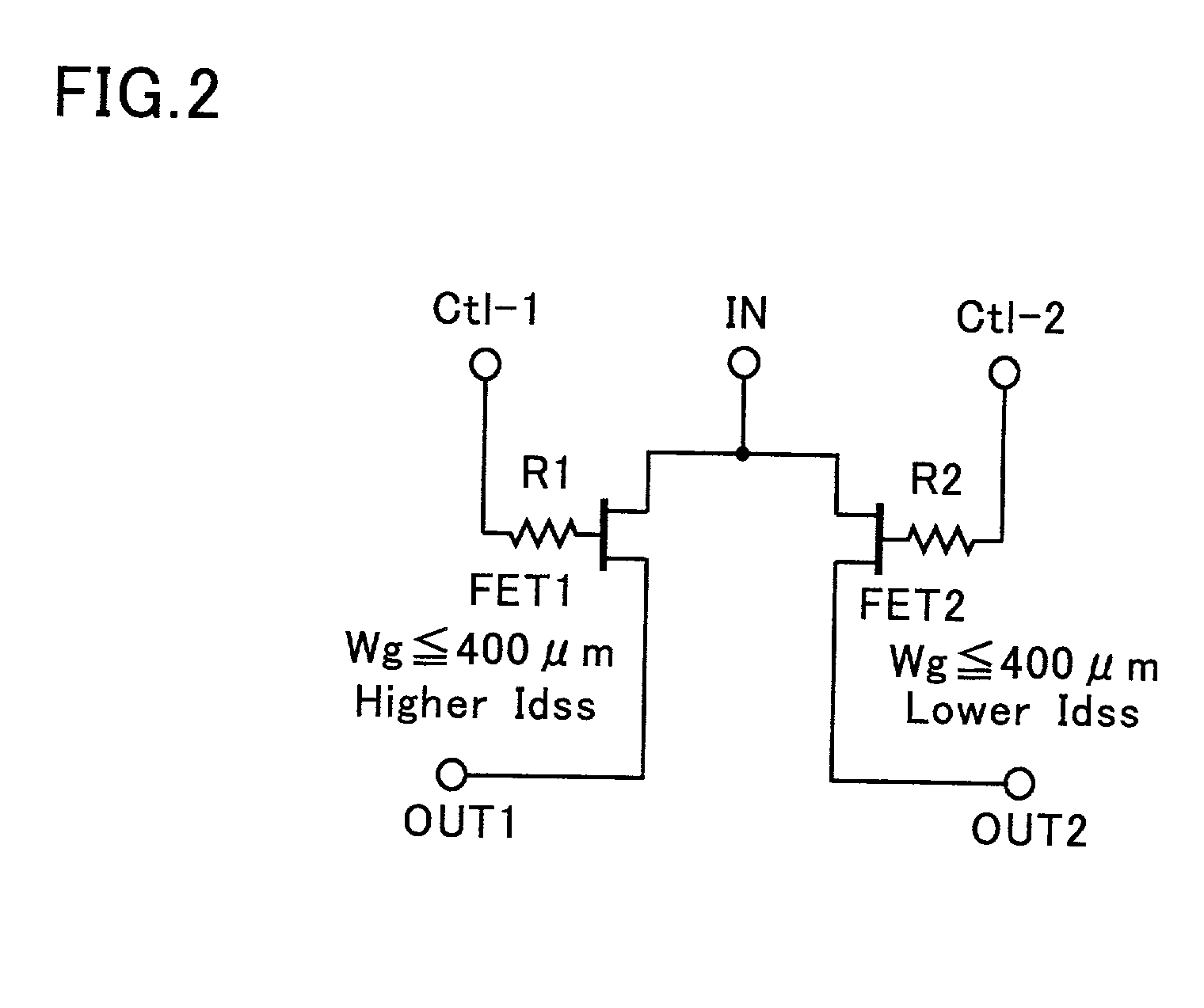
[0022]FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of a semiconductor switching circuit device of an embodiment of this invention, which preferably operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz or higher. The device has first and second FETs (FET1, FET2), each of which has a source electrode, a gate electrode and a drain electrode on its channel layer. The device also has a common input terminal IN connected to the source electrodes (or the drain electrodes) of the FETs (FET1, FET2), a first output terminal connected to the drain electrode (or the source electrode) of the first FET (FET1), and a second output terminal connected to the drain electrode (or the source electrode) of the second FET (FET2). The gate electrode of FET1 is connected to a control terminal Ctl-1 via resistor R1, and the gate electrode of FET2 is connected to a control terminal Ctl-2 via resistor R2. A pair of complementary signals is appli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com