Method of improving ischemic muscle function by administering placental growth factor
a technology of placental growth factor and ischemic muscle, which is applied in the field of prevention and treatment of stroke and ischemic diseases, can solve the problems of reducing the function of ischemic muscle, and reducing the risk of stroke, so as to improve the function of ischemic tissue, improve the function of ischemic muscle, and increase the expression of veg
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Protection Against Cerebral Ischemic Infarct Expansion by Chronic Administration of PlGF
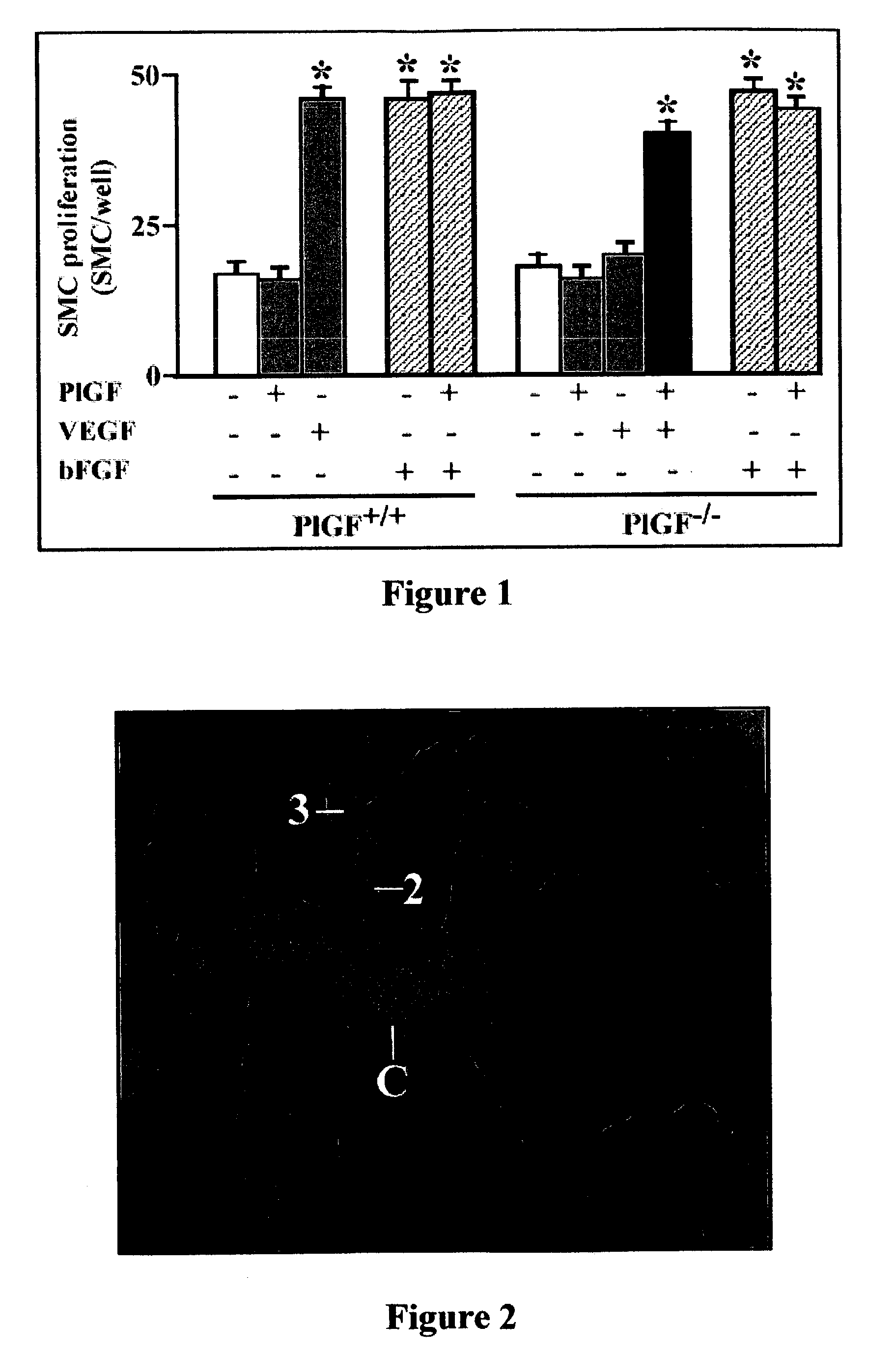
[0085]Infarcted mice were treated with saline (for control), PlGF (715 ng / day) or VEGF days (425 ng / day) or a combination of both. The data of these experiments, presented in Table 1 below, are the mean+-standard error of mean (SEM) values of the infarct size expressed in mmand used as a means for measuring cerebral infarction, including the number of observations between brackets and wherein an asterisk means p=0.001 vs. control. The significance of differences was determined by unpaired t-test. Intracerebral bleeding was not observed in any of the mice. These data indicate that PlGF is as effective as PlGF in suppressing infarct expansion of the penumbra. These data also indicate that there is a synergistic effect of VEGF and PlGF in suppressing infarct expansion of the penumbra
[0086]
TABLE 1Treatment groupInfarct sizeControl 12 ± 1.7 (7)PIGF8.0 ± 2.9 (4)VEGF7.6 ± 2.5 (3)PIGF + VEGF4.6 ± 1.3 (8)...
example 2
Enhanced Revascularization of Acute Myocardial Infarcts by Chronic Administration of PlGF
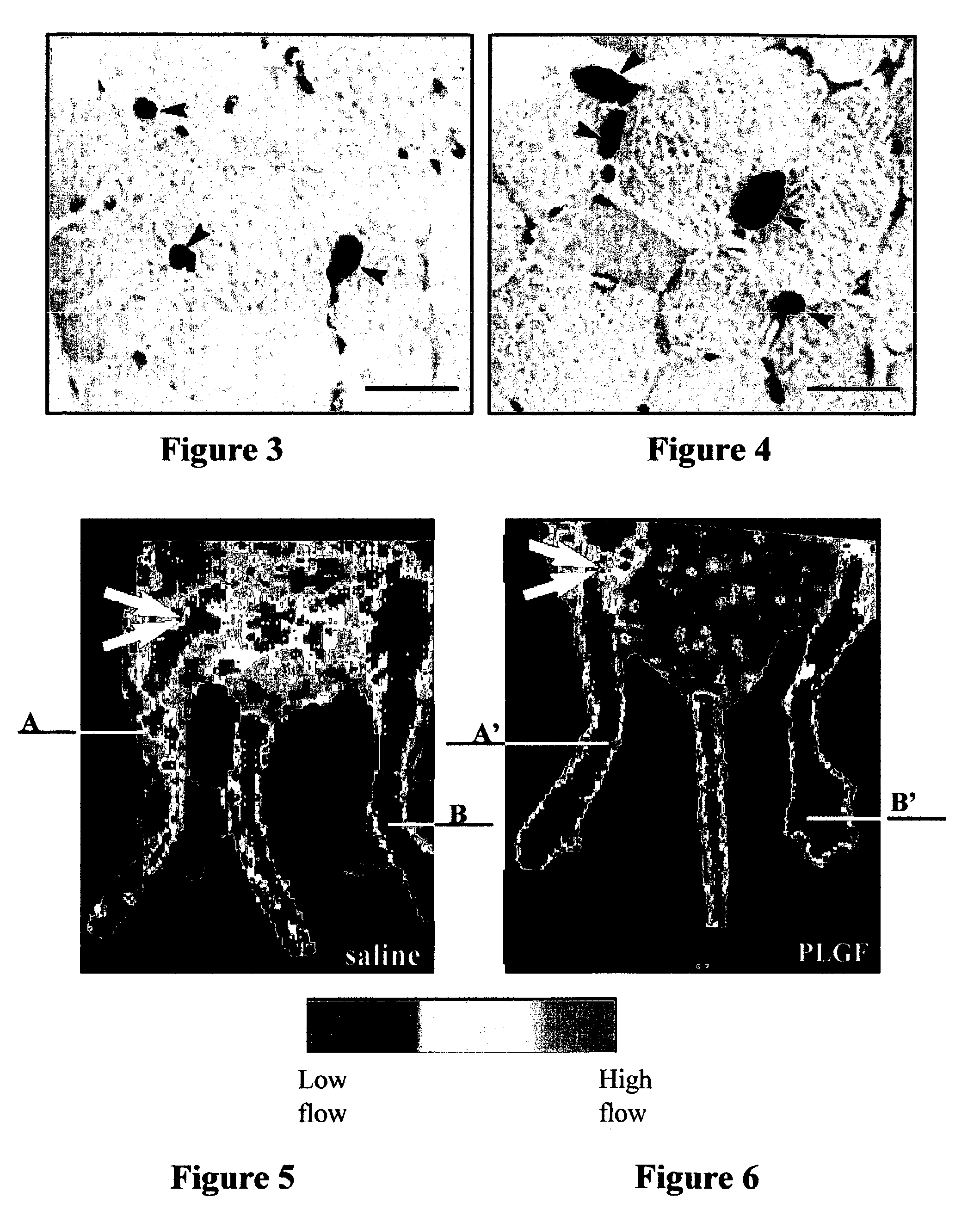
[0087]The therapeutic effect of PlGF and VEGF was compared in a murine model for acute myocardial infarction by delivering the growth factors continuously over 7 days. Treatment of infarcted mice with PlGF (715 ng / day or 3.5 μg / day) was more effective than VEGF (450 ng / day) in improving myocardial angiogenesis and arteriogenesis, as shown in Tables 2 and 3 Moreover, a synergistic effect of PlGF and VEGF can be observed, especially in the formation of medium and large vessels. Table 2 provides the number of vessels (mean±SEM values), identified by thrombomodulin staining of endothelial cells as a measure of angiogenesis, throughout the infarct in groups of 8 to 10 mice each. An asterisk means p<0.05 vs. control. Table 3 provides the number of vessels (mean±SEM values), identified by smooth muscle alpha-actin staining of endothelial cells as a measure of arteriogenesis, throughout the infarct in g...
example 3
PlGF Delivery Did Not Cause Side Effects
[0095]At the dose of 1.5 μg, administered daily for 7 days PlGF did not cause oedema or ectopic angiogenesis in the mouse model for acute myocardial infarction, while local signs of oedema were clearly present around the mini-pumps delivering VEGF. PlGF plasma levels up to about 50 ng / ml (achieved by the delivery of 7 μg hPlGF-2 per day for 7 days) were well tolerated without any sign of distress, while VEGF plasma levels above 10 ng / ml caused severe life threatening signs of oedema and circulatory shock. On the other hand, unlike VEGF, PlGF only minimally affected the blood pressure. Mean arterial blood pressure (measured using high fidelity pressure micromanometers, Miller Instruments, Houston, Tex.) was 93±5 mm Hg under baseline conditions (control mice). Intravenous bolus injection of 3 μg VEGF caused significant hypotension (68±3 mm Hg; p<0.05), while 5 to 10 μg hPlGF-2 did not significantly reduce arterial blood pressure (91±11 mm Hg). T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com