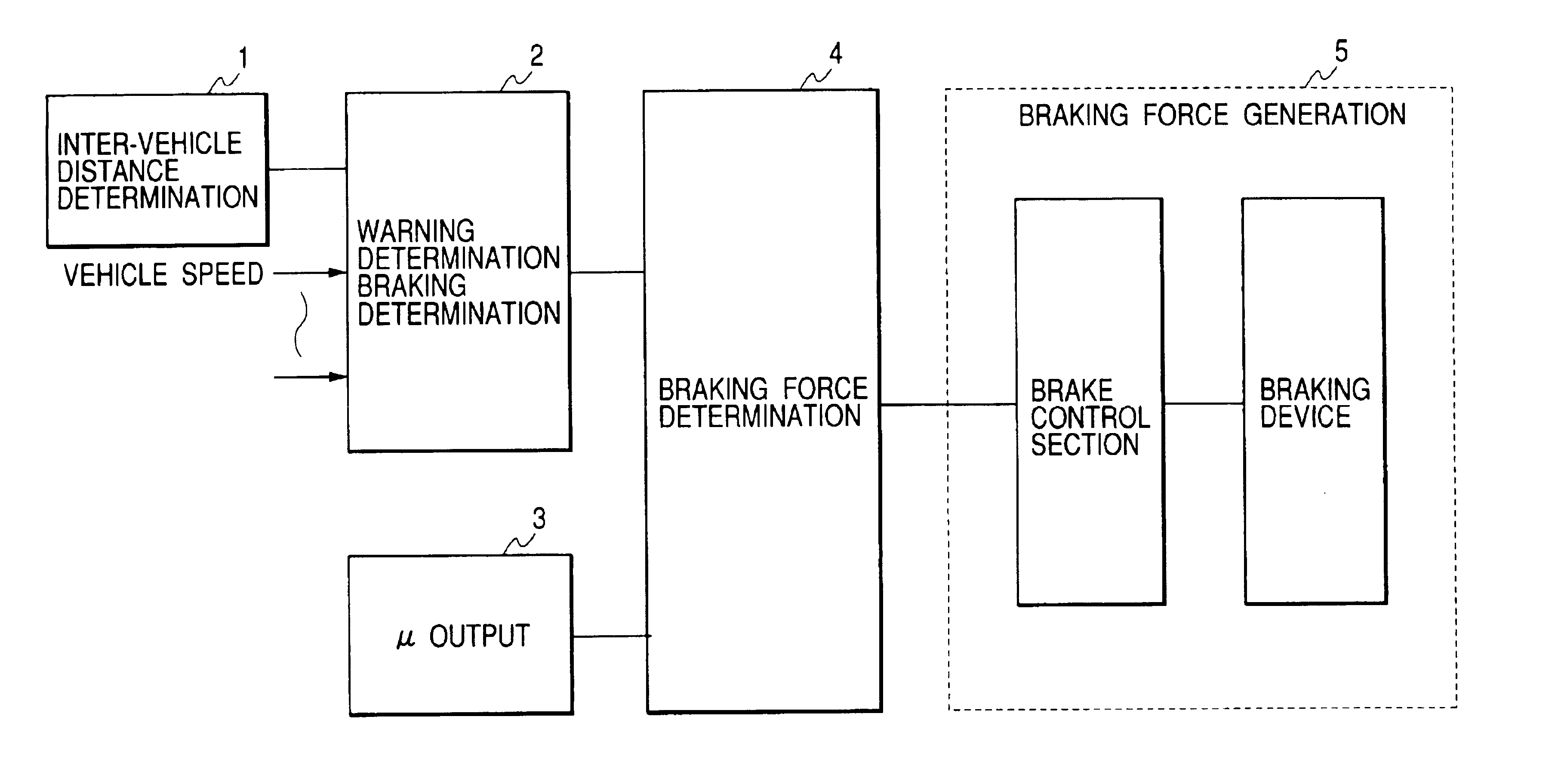
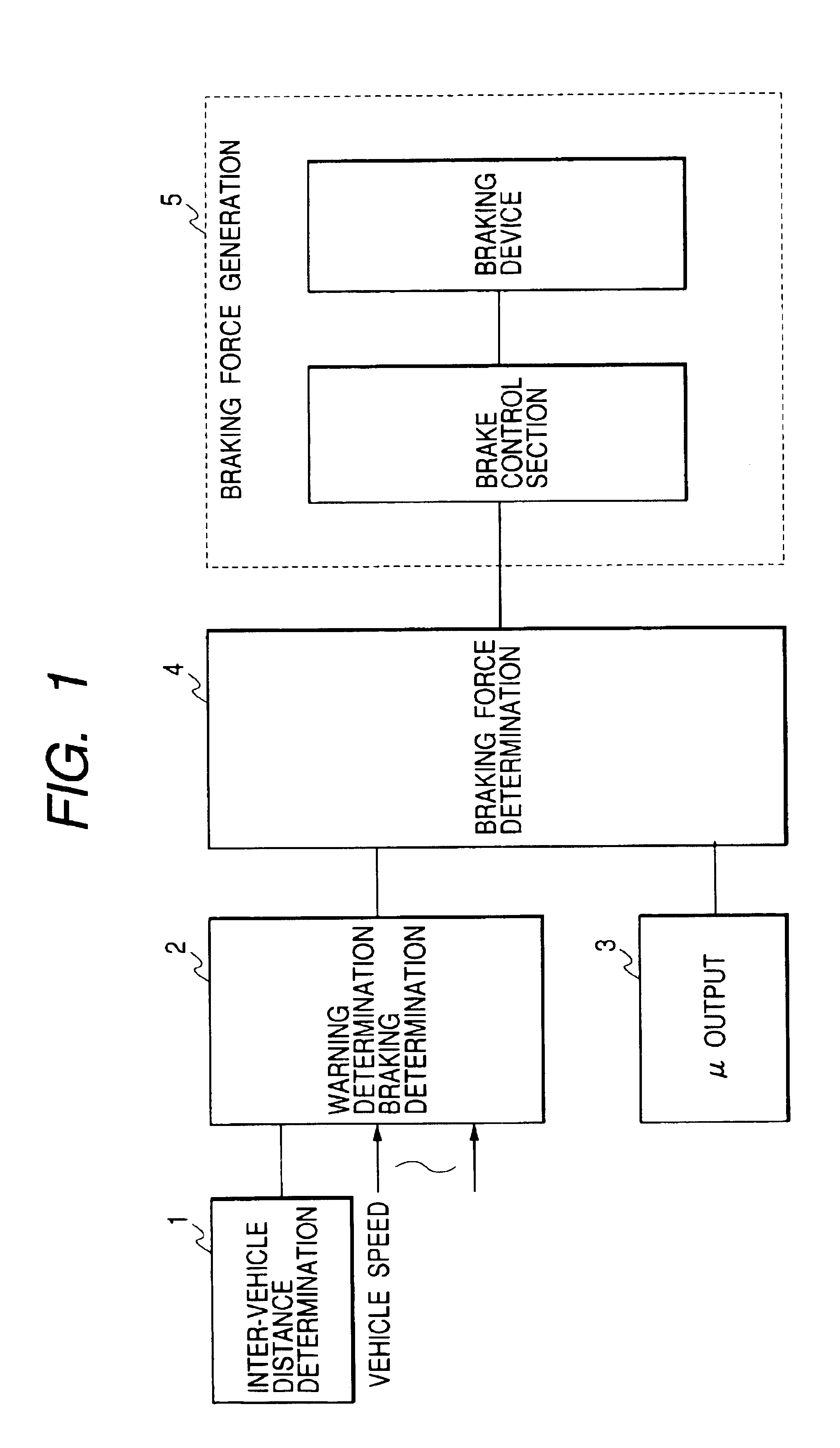
Vehicle brake control apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
modified embodiment 1
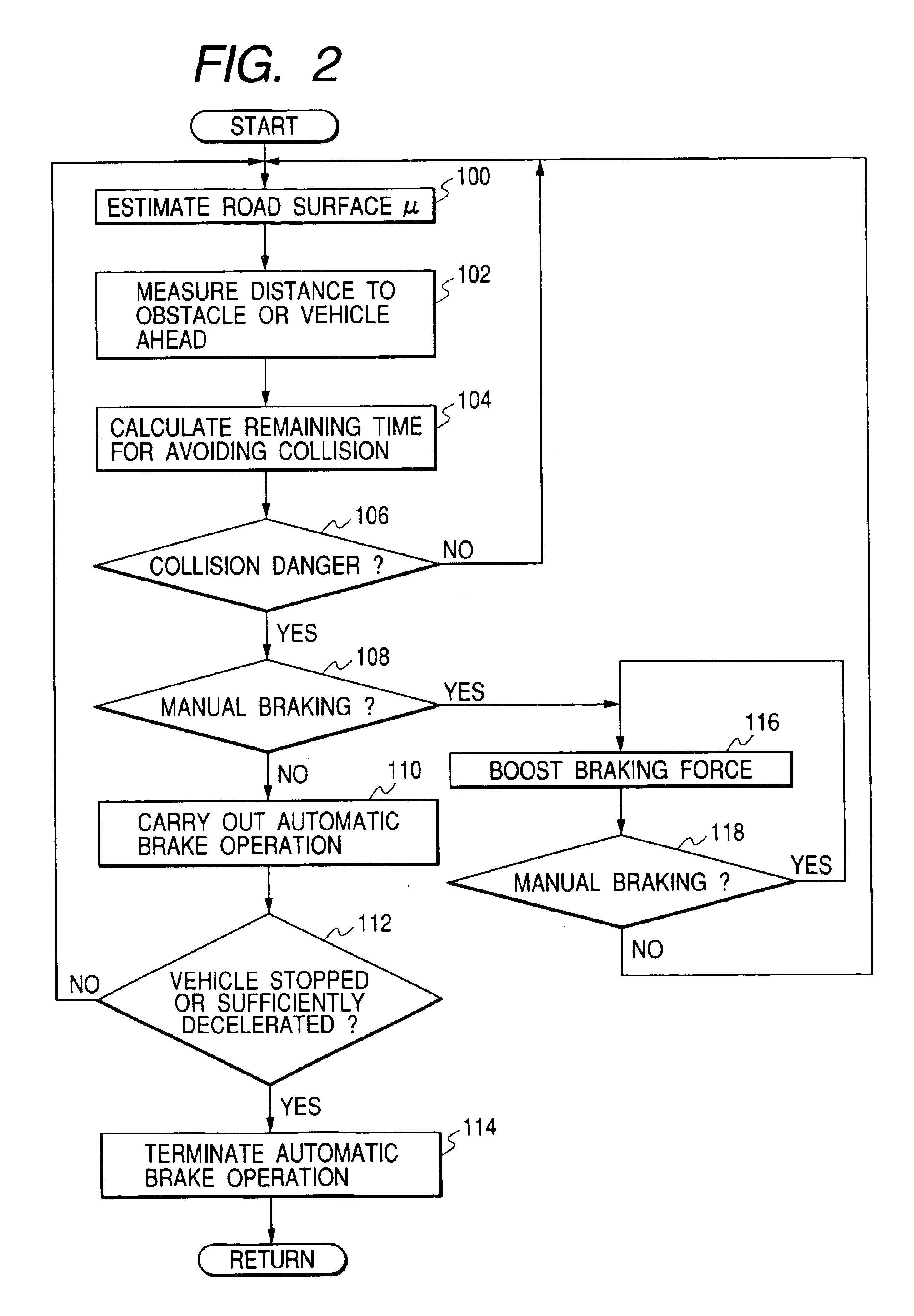
[0056]According to the above-described embodiment, when the manual braking operation is detected in the step S108, the control flow proceeds to the step S116 to increase or boost the target braking force in such a manner that a braking force value corresponding to the present manual braking operation amount is multiplied with a predetermined rate. This multiplying or boosting brake operation is restricted to somewhere in the braking force range being set in the range of the above-described estimated maximum braking force. It is however possible to increase or boost the brake pedal depression amount with a booster in response to detection of the manual braking operation, thereby generating an increased or boosted braking force which is equivalent to predetermined times the braking force to be inherently generated in response to a driver's brake operation amount during the manual braking operation while neglecting the above-described estimated maximum braking force. With this operatio...
modified embodiment 2
[0057]According to the above-described embodiment, the target braking force during the automatic brake operation is restricted to a value approximately equal to or less than a half of the generable estimated maximum braking force. The brake control technique of this invention can be used for generating a braking force as a warning given to the driver when it is judged that the possibility of collision danger is high. The braking operation for warning, i.e., the warning brake operation, is carried out periodically predetermined times.
[0058]Hereinafter, an explanation is given based on the flowchart shown in FIG. 2. According to this modified embodiment, the braking force for warning (i.e., the warning braking force) is generated at the step S110. The warning braking force is set to a value in a range corresponding to 5% to 60% of the estimated maximum braking force determined based on an estimated road surface friction coefficient μ. The warning brake operation is carried out periodi...
modified embodiment 3
[0060]In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the braking force is for example increased to a maximum value within the range of the estimated maximum braking force, when a driver applies none of manual braking, manual steering, and manual accelerating operations within a predetermined time after the automatic brake operation or the warning brake operation is started.
[0061]This processing will be explained hereinafter with reference to a flowchart shown in FIG. 6.
[0062]When it is judged that no manual operation (i.e., no manual braking, no manual steering, and no manual accelerating operations) is performed (i.e., NO in step S108 in FIG. 2), the control flow proceeds to step S200. In the step S200, it is checked as to whether a predetermined time has elapsed or not after the automatic brake operation of step S110 is started. When the predetermined time has not elapsed yet after the automatic brake operation is started (i.e., NO in step S200), the control flow skips the fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com