Process to prepare normal paraffins
a paraffin and normal technology, applied in the field of normal paraffin preparation, can solve the problem of high relative cost of such a vacuum distillation, and achieve the effect of less energy and cost-effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
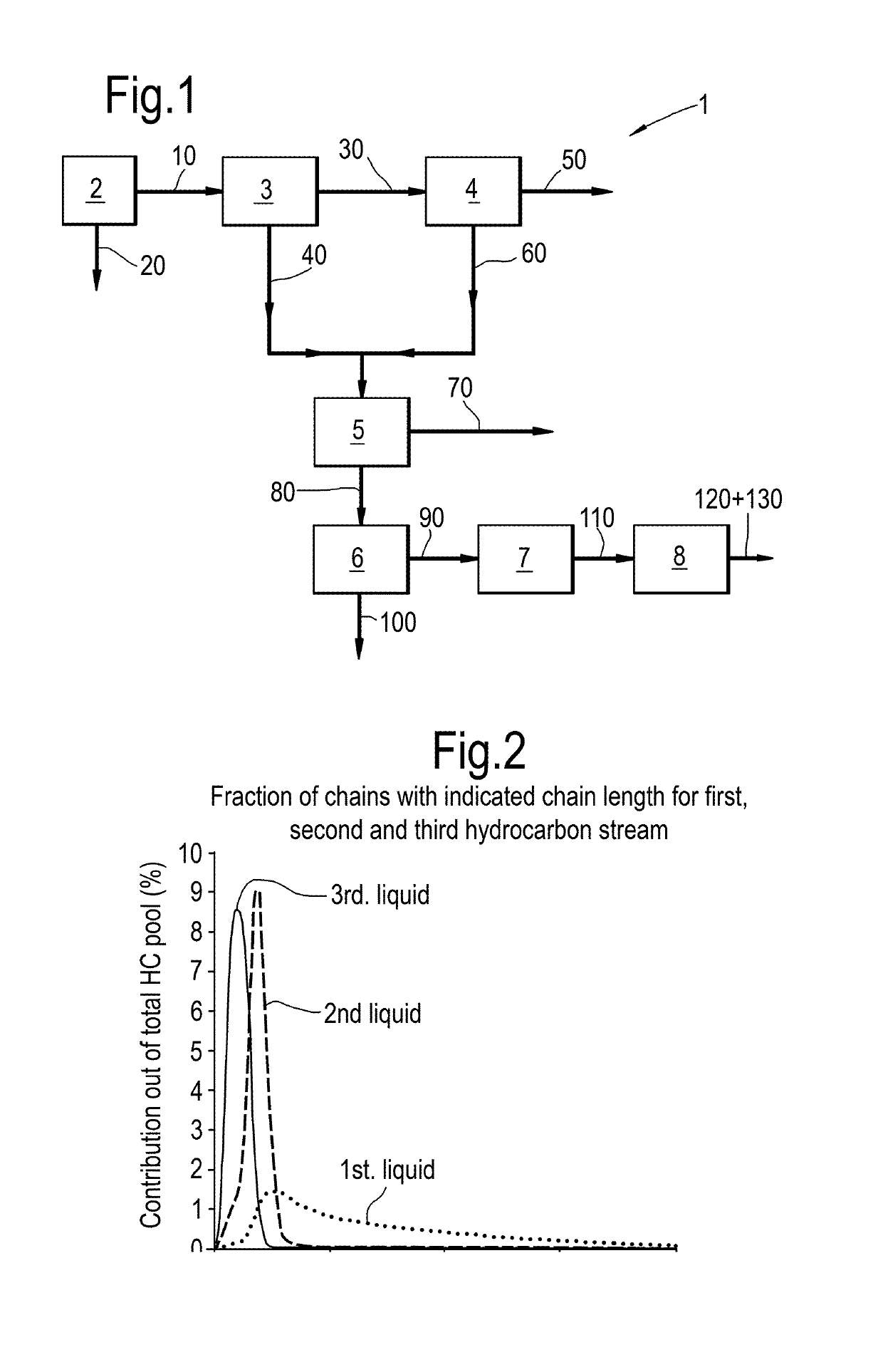
[0054]Product Distribution of the First, Second and Third Liquid Hydrocarbon Streams
[0055]In Table 1 the flows of molecules with indicated chain length in three liquid hydrocarbon streams is given, with full distribution of the streams depicted in FIG. 2. The first liquid stream is obtained at a pressure of 55 bar and a temperature of 215° C., the second liquid stream at a pressure of 55 bar and a temperature of 159° and the third liquid stream at a pressure of 53 bar and a temperature of 15° C. It can be seen that the majority of the normal paraffins is present in the combined stream of 2nd and 3rd liquid.
[0056]The respective starting and end point of the carbon distributions (defined as the chain length equivalent to at least 0.5 wt % of the total amount of hydrocarbon) were 16-88, 5-29 and 3-20 respectively. It can be seen from FIG. 1 that the distributions for the 2nd and 3rd liquid are reasonably sharp, whereas the 1st liquid has significant tailing to higher carbon numbers, wi...
examples 2 to 6
[0057]Process to Prepare Normal Paraffins
[0058]In the comparative examples 2-4 all the liquid hydrocarbon streams are combined and used for the production of normal paraffins. Separation of the normal paraffins from the full product mixture is done using both atmospheric and vacuum distillations at conditions indicated. In example 5 and 6 as per the invention, only the light wax streams, so the 2nd and 3rd liquid hydrocarbon stream were selected. From the results in Table 2 it becomes apparent that in the comparative example atmospheric distillation results in very low recovery of the heavier part of the normal paraffin. For instance the C17 paraffin stream was only 3 tons per day at distillation temperatures of 345 and 370° C. respectively. For these heavier paraffins vacuum distillation is required as can be seen in example 4. Vacuum distillation however requires, which is undesired related to the high cost.
[0059]The cases according to the invention represented by example 5 and 6 ...
example 7
[0061]Process to Prepare C10-13 and C14 to 18 Normal Paraffins
[0062]The recovered paraffins will need further distillation after hydrogenation to meet the product specification of the lighter C10-C13 normal paraffins and C14-C18 normal paraffins final products. The resulting compositions are given in Table 3 and Table 4. It can be seen that the compositions according to the invention are lighter compared to the comparative example.
TABLE 3Composition of LDF for comparative example4 and example 6 as per inventionEx.C9C10C11C12C13C14Mw40.21032.031.925.50.5166.460.21032.231.625.50.5166.3
TABLE 4Composition of HDF for comparative example4 and example 6 as per inventionEx.C13C14C15C16C17C18Mw40.523.824.323.422.65.5220.460.526.725.722.419.35.5218.9
[0063]In Table 5 the normal paraffin final product weight fractions are given. It can be seen that in example 6 according to the invention almost the same amount of LDF is obtained, with a lower amount of HDF. The LDF content out of the NP product...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com