Nonwoven fabric and method for producing the same
a nonwoven fabric and nonwoven technology, applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, melt spinning methods, monocomponent polycarbonate artificial filaments, etc., can solve the problems of weak strength, poor handling, and prone to fluff, and achieve the effect of sufficient strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
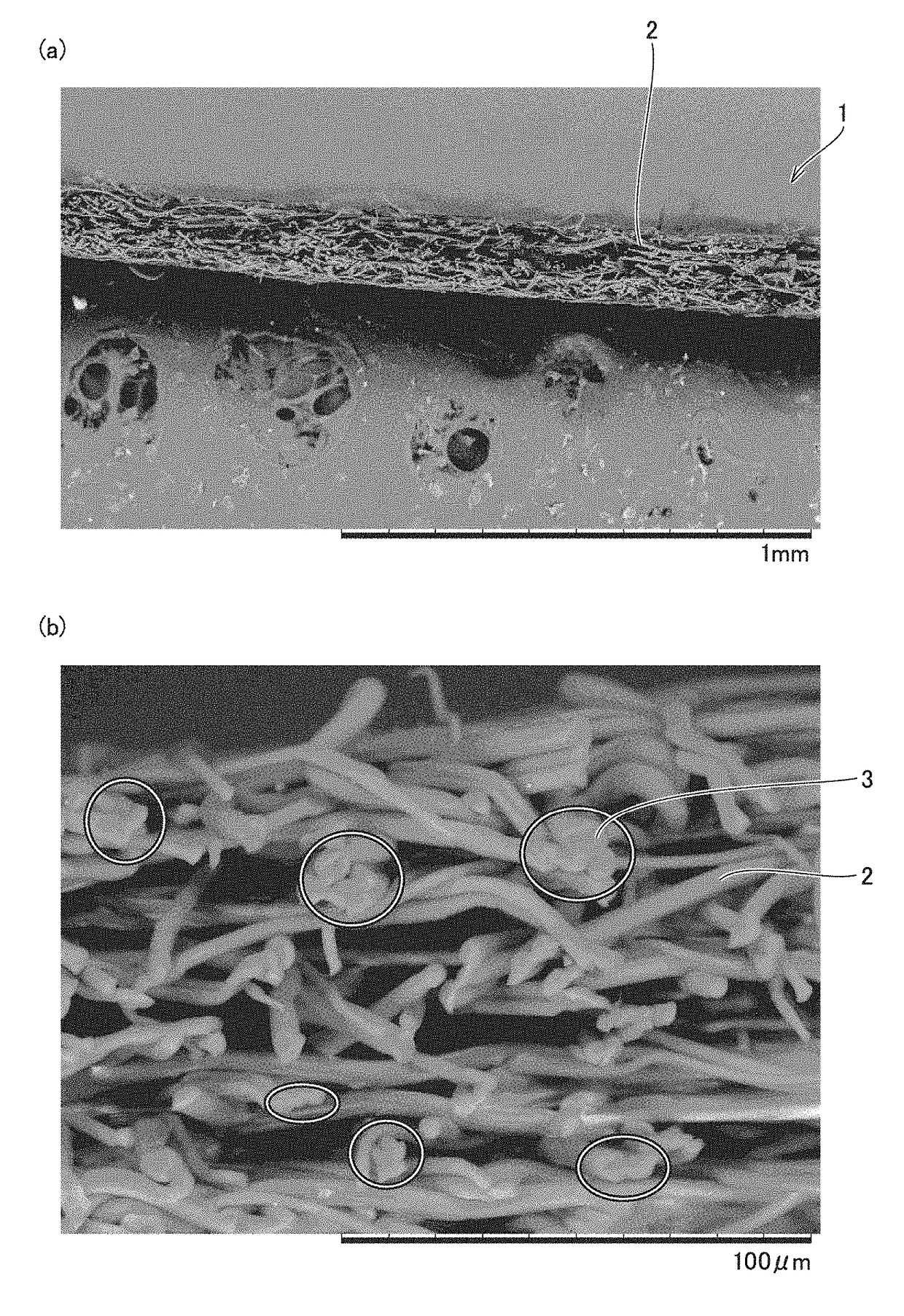
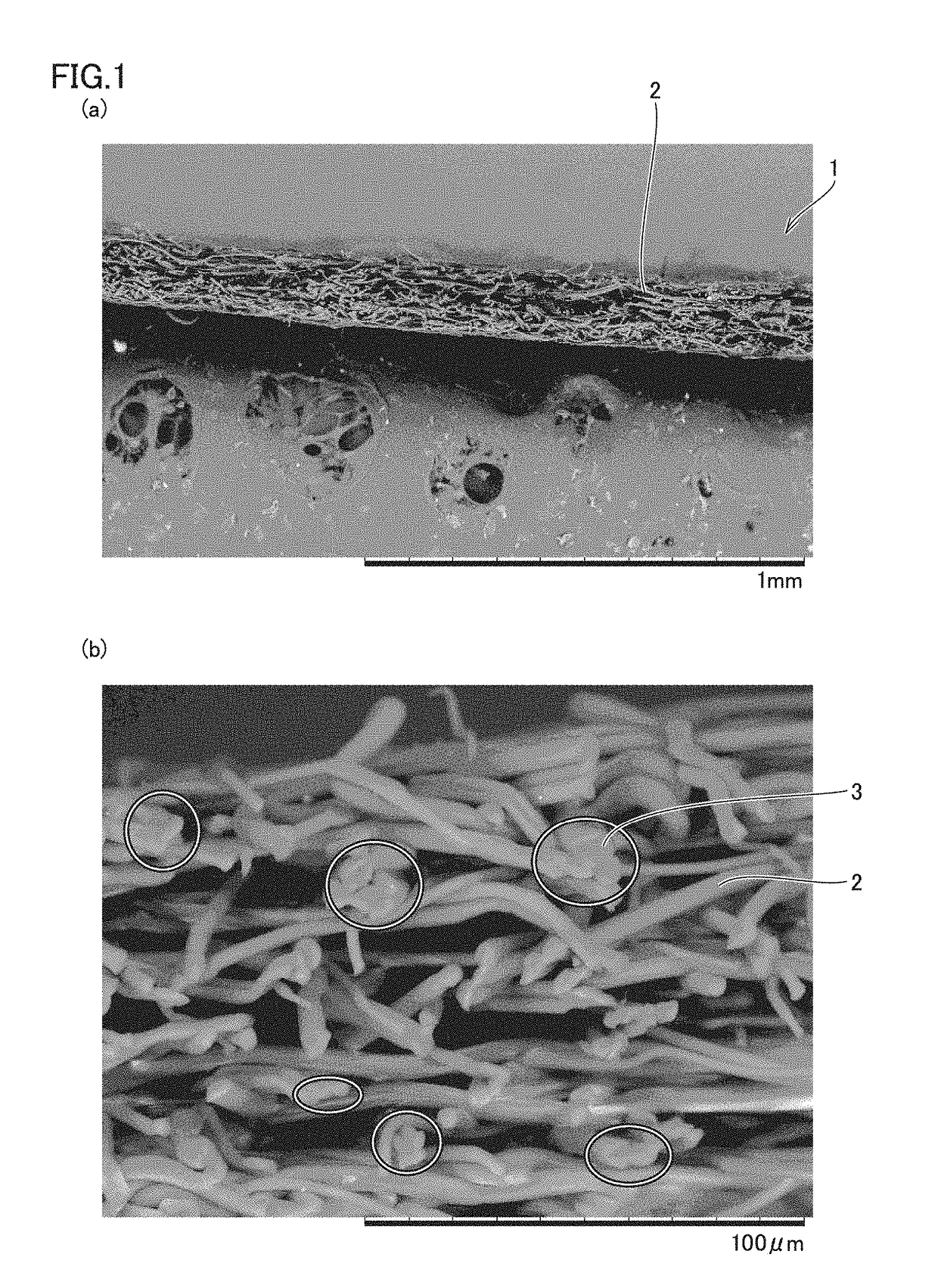
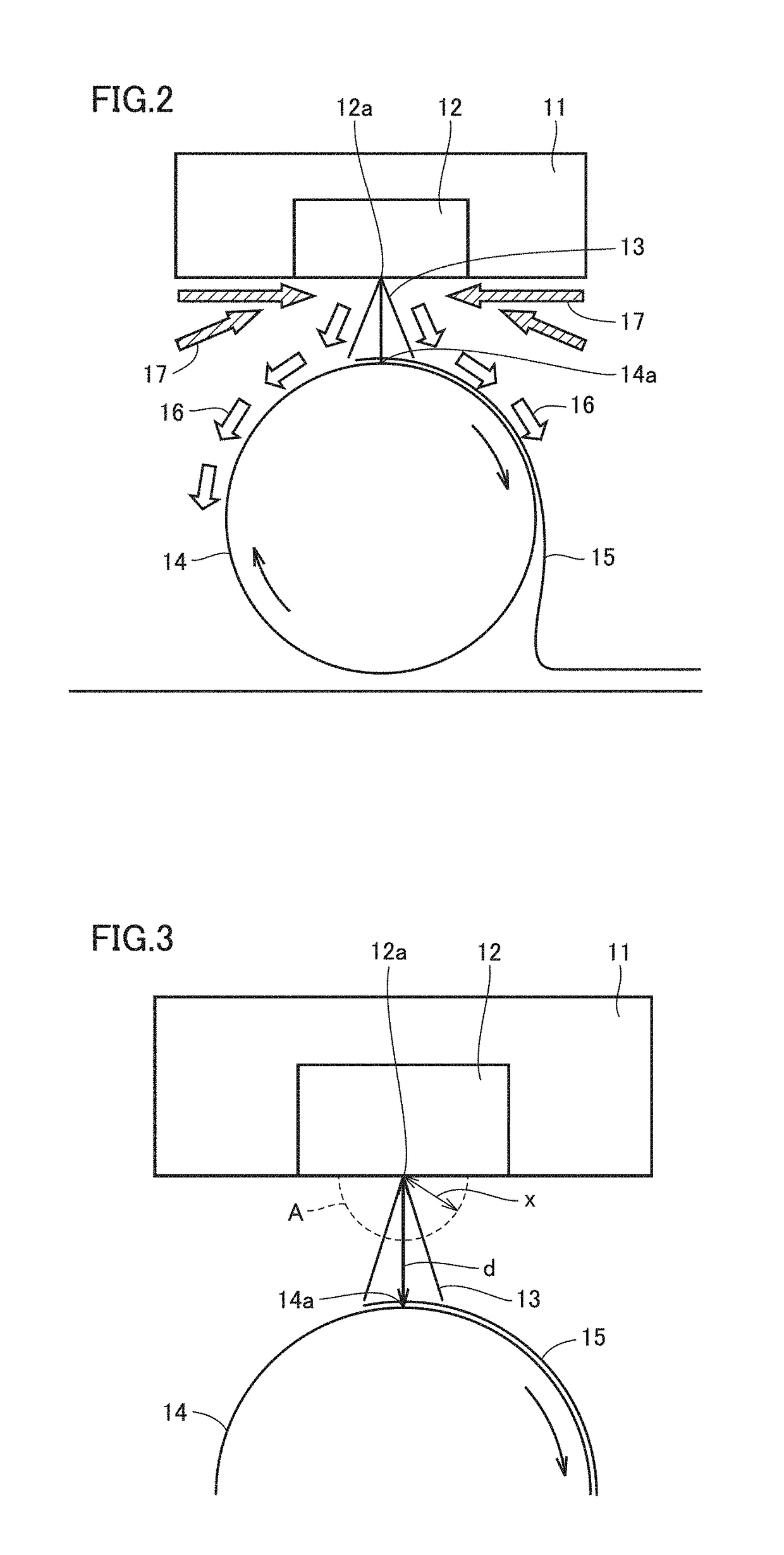
[0087]Amorphous polyetherimide having a melt viscosity at 330° C. of 500 Pa·s was used, and extruded with an extruder to be supplied to a melt blown device having a nozzle with a nozzle hole diameter D (diameter) of 0.3 mm, L (nozzle length) / D=10, and a nozzle hole pitch of 0.75 mm. By blowing hot air to the amorphous polyetherimide at a single hole discharge rate of 0.09 g / min, a spinning temperature of 390° C., a hot air (primary air) temperature of 420° C., and 10 Nm3 / min per 1 m of nozzle width, a nonwoven fabric having a basis weight of 25 g / m2 was produced. At this time, a hot air injection device as in the example shown in FIG. 4 was arranged so that hot air (secondary air) blows into a tip of the spinning nozzle of the melt blown device, and hot air (secondary air) at a temperature of 260° C. was blown at a flow rate of 2 Nm3 toward the tip of the spinning nozzle. The direct distance d between the tip of the spinning nozzle and a receiving surface of a roller receiving the s...
example 2
[0088]A nonwoven fabric was obtained by using amorphous polyetherimide having a melt viscosity at 330° C. of 900 Pa·s in the similar manner as in Example 1 except that the spinning temperature was 420° C., the average fiber diameter was 3.7 μm, and the temperature measured by a thermometer positioned on a hemispherical outer periphery of a radius x=5 cm around the tip of the spinning nozzle was 253° C. (that is, space A was maintained at a temperature higher than 215° C. that is a glass transition temperature of the amorphous PEI by 38° C.), and the temperature measured by a thermometer arranged so as to be positioned 1 cm from the collection surface on the straight line relative to the direct distance d between the tip of the spinning nozzle and the collection surface of the spun fibers was 261° C. (that is, point B was maintained at a temperature higher than 215° C. that is a glass transition temperature of the amorphous PEI by 46° C.).
example 3
[0089]A nonwoven fabric was obtained in the similar manner as in Example 2 except that the basis weight was changed to 10 g / m2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com