Cu(i)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloadditions (CUAAC) ligands and methods for carrying out cu(i)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reactions
a technology of azide alkyne and catalyzed azide alkyne, which is applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, separation processes, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the application of nitrogen and oxygen species in living systems, adding another layer of complexity to the application of cuaac in living systems, and strategies cannot meet all the requirements, etc., to achieve high radiochemical purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]It is to be understood that the descriptions of the present disclosure have been simplified to illustrate elements that are relevant for a clear understanding of the present disclosure, while eliminating, for purposes of clarity, other elements that may be well known. Those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that other elements are desirable and / or required in order to implement the present disclosure. However, because such elements are well known in the art, and because they do not facilitate a better understanding of the present disclosure, a discussion of such elements is not provided herein. Additionally, it is to be understood that the present disclosure is not limited to the embodiments described herein, but encompasses any and all embodiments within the scope of the description and the following claims.
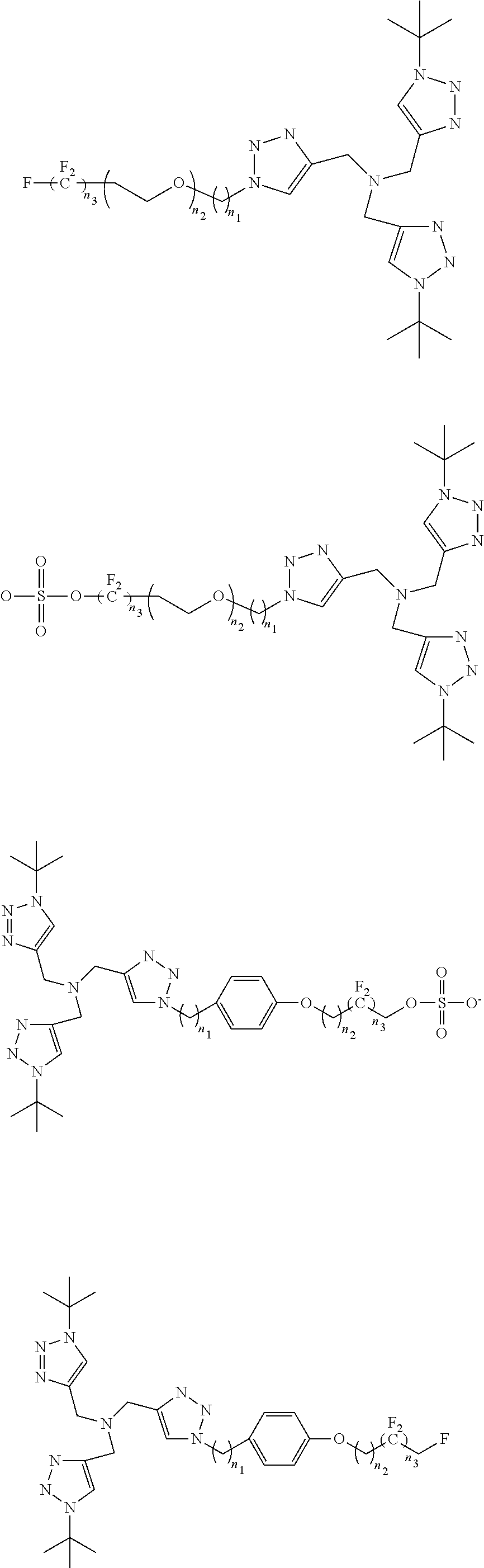
[0030]Cu(I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloadditions (CuAAC) are regarded as an ubiquitous chemical tool with applications in nearly all areas of modern chemistry, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| retention time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com