Coaxial Hollow Cathode Plasma Assisted Directed Vapor Deposition and Related Method Thereof
a hollow cathode and plasma technology, applied in vacuum evaporation coatings, electric discharge tubes, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of poor quality of high-rate growth, low utilization rate of evaporant materials in coatings, and restricted deposition, so as to achieve robust and reliable coaxial plasma capability, increase particle energy, and reduce the effect of carrier gas consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
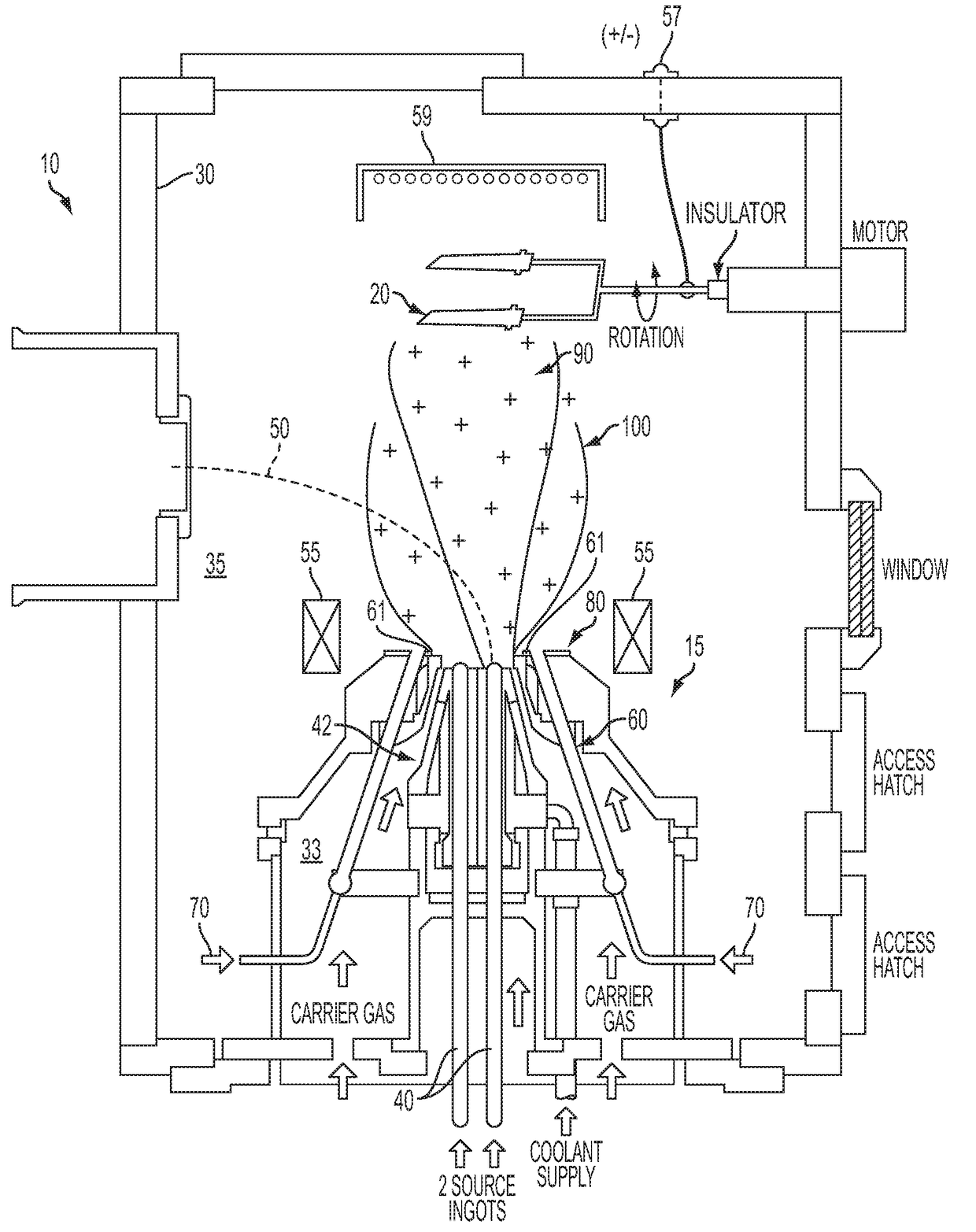
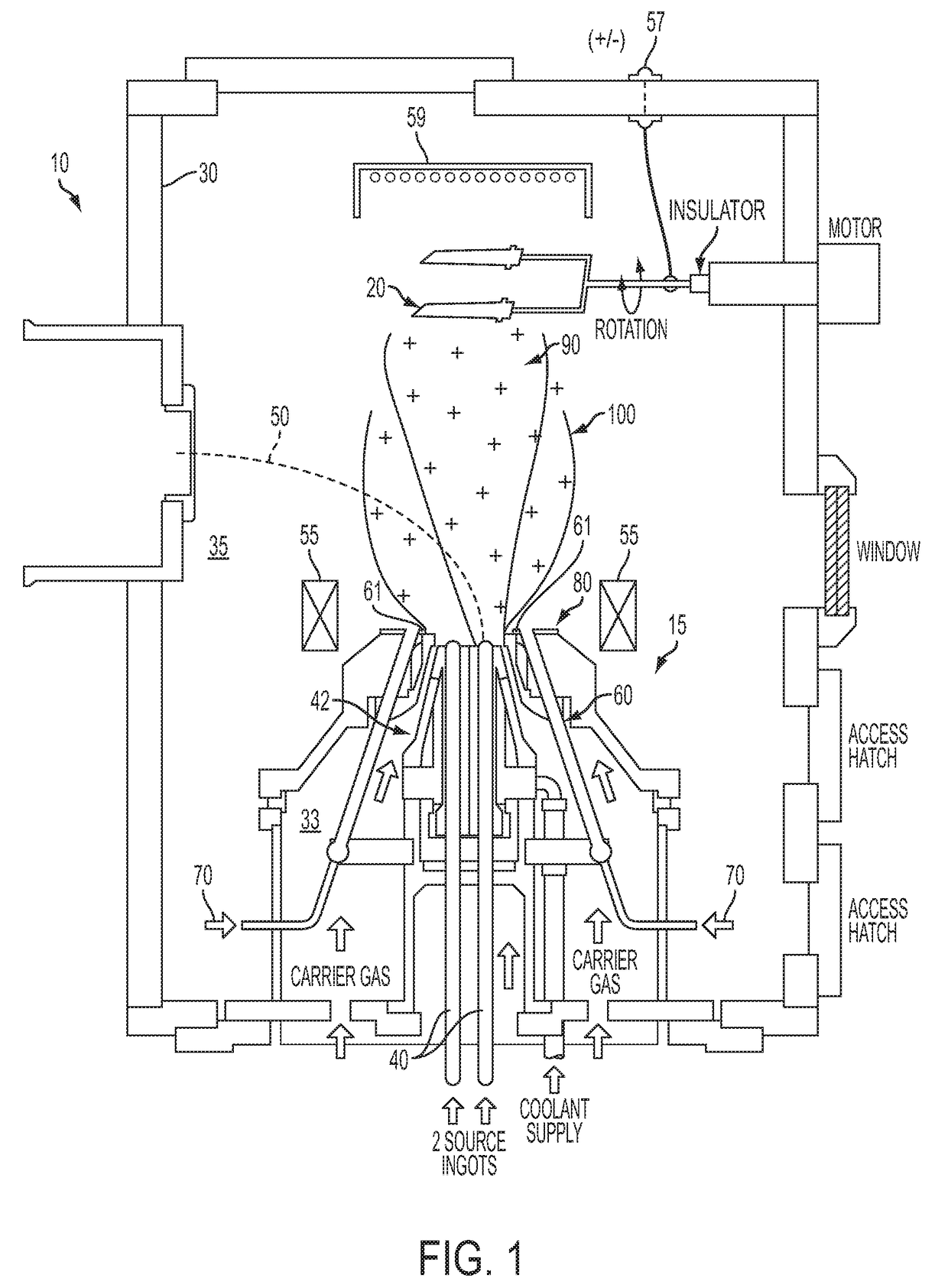
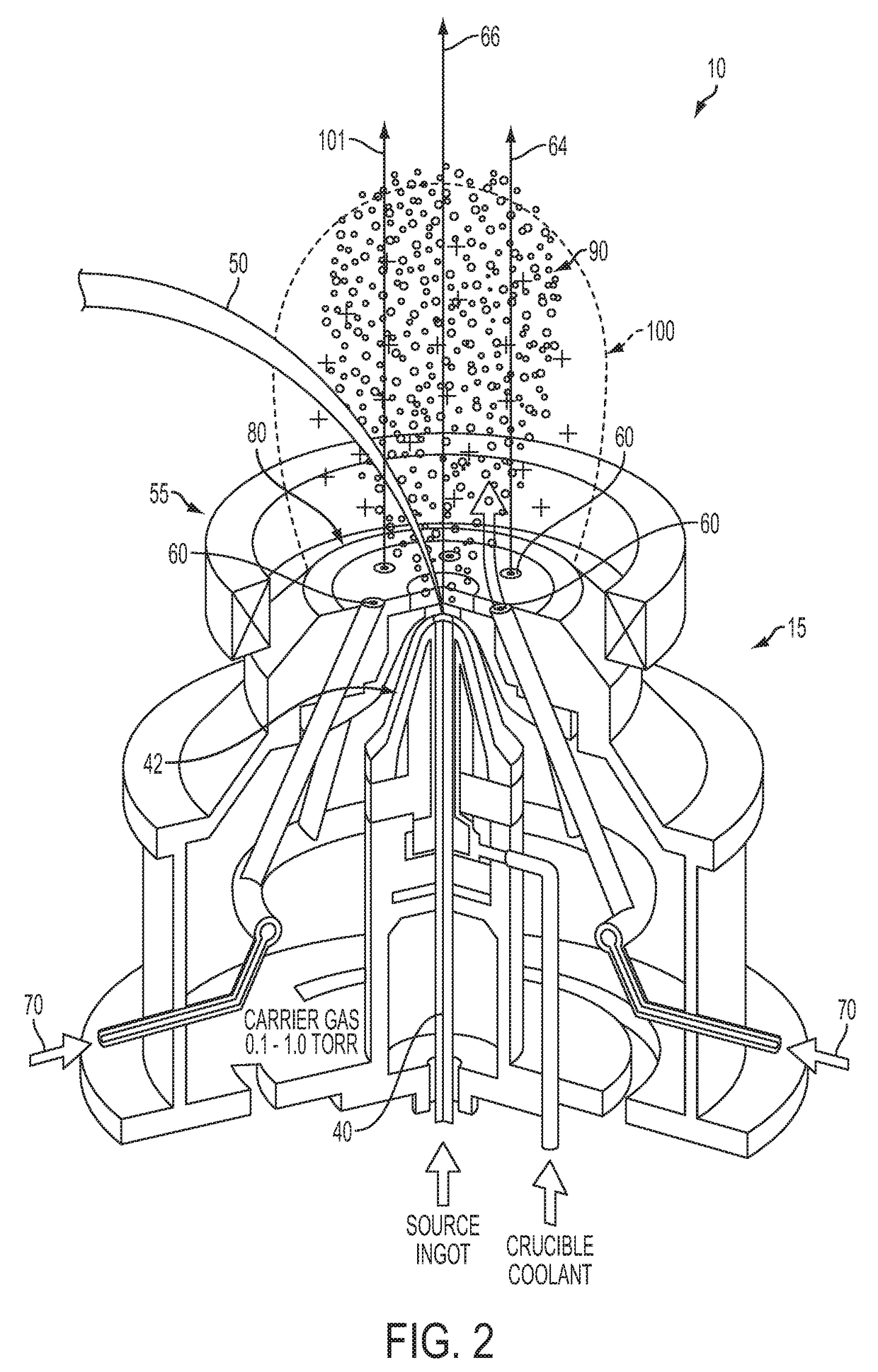
[0028]Turning now to the drawings, an aspect of an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIGS. 1-2, is a method and apparatus 10 for applying at least one coating onto at least one substrate 20 (e.g., sample), utilizing a plasma assisted directed vapor deposition process. The apparatus 10 may include a deposition chamber 30, having an upstream area 33, and downstream area 35, at least one evaporant source 40, at least one energetic beam 50 for impinging the evaporant source 40, at least one hollow cathode 60 aligned at least substantially coaxially with the evaporant source 40 for delivering a discharge current (not shown), at least one plasma-forming gas 70 (e.g., working gas) emitted from the hollow cathode 60, and at least one anode 80 for electrostatically attracting the discharge current from the hollow cathode 60. At least some of the elements included in the apparatus 10 may comprise a “nozzle”15, which may participate in applying at least one coating to at least o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bias voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bias voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bias voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com