System and method for diagnosing and controlling incineration facility and solid fuel boiler and managing life cycle of facility through heat exchange and design program and operation mode analysis of operator
a technology of incineration facilities and solid fuel boilers, which is applied in the direction of electric programme control, program control, combustion types, etc., can solve the problems of low energy recovery ratio, lack of accurate operation data analysis, and inefficient facility management, so as to improve waste heat recovery energy, enhance energy power generation efficiency, and maintain efficiently
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
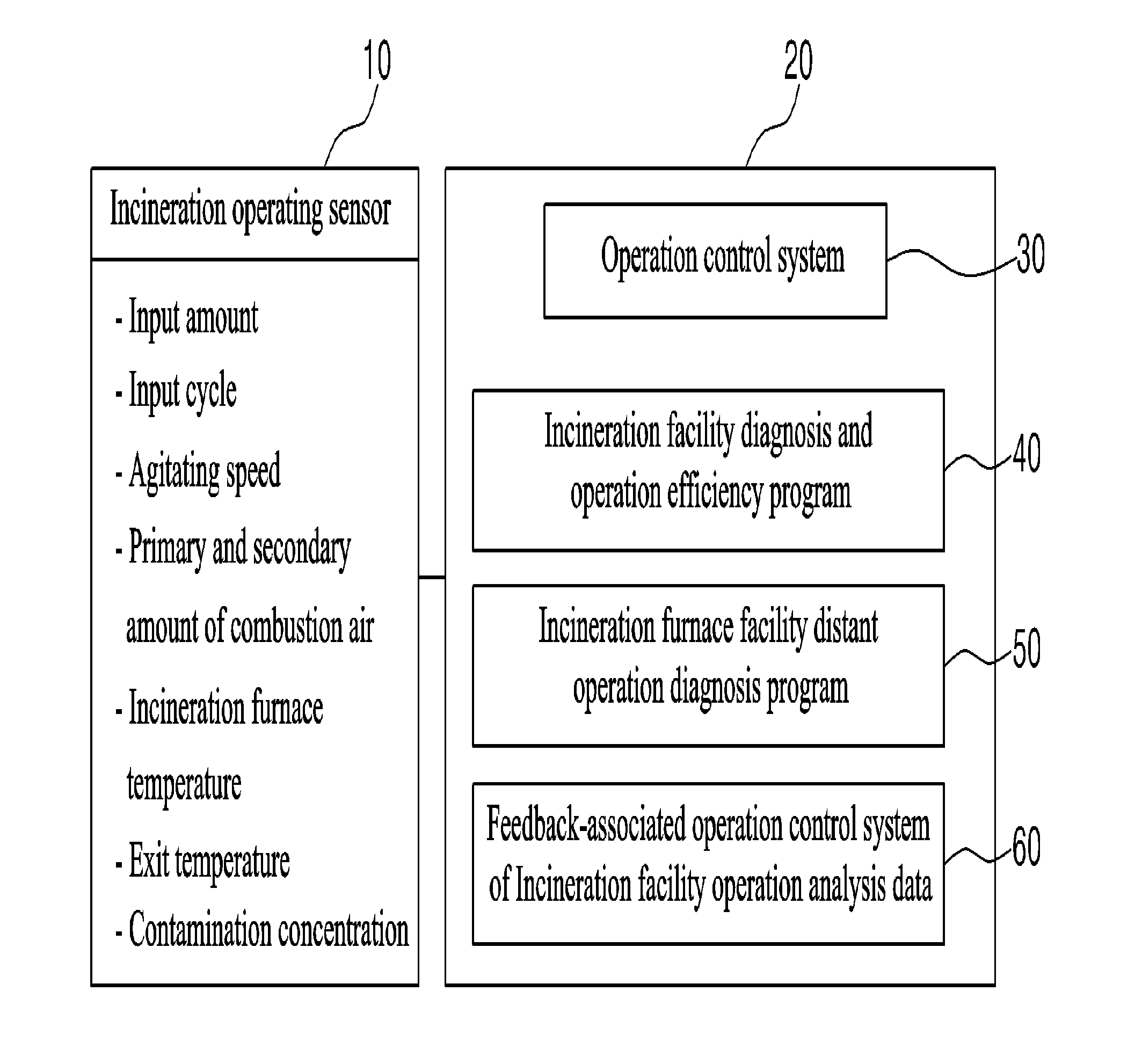
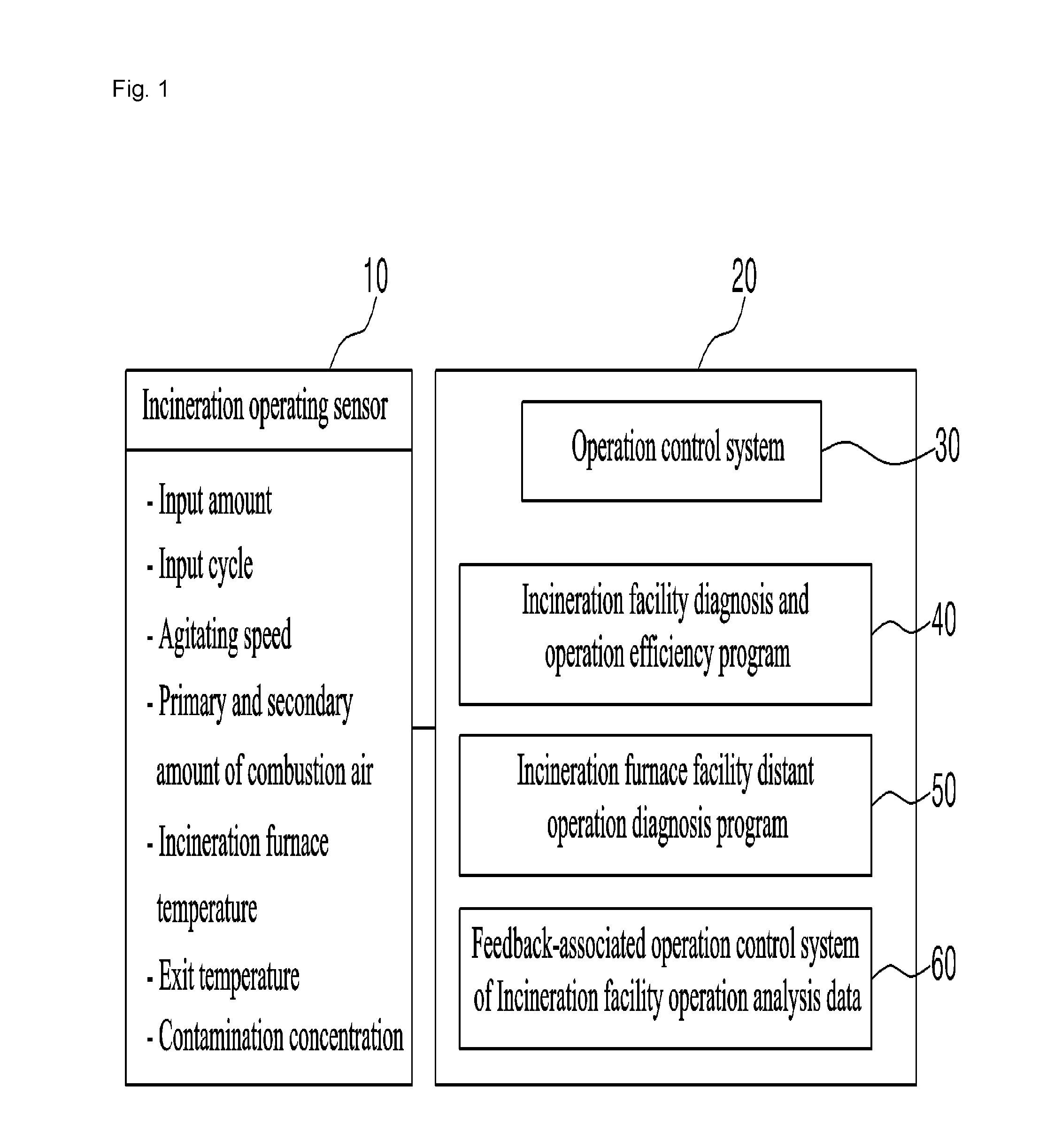
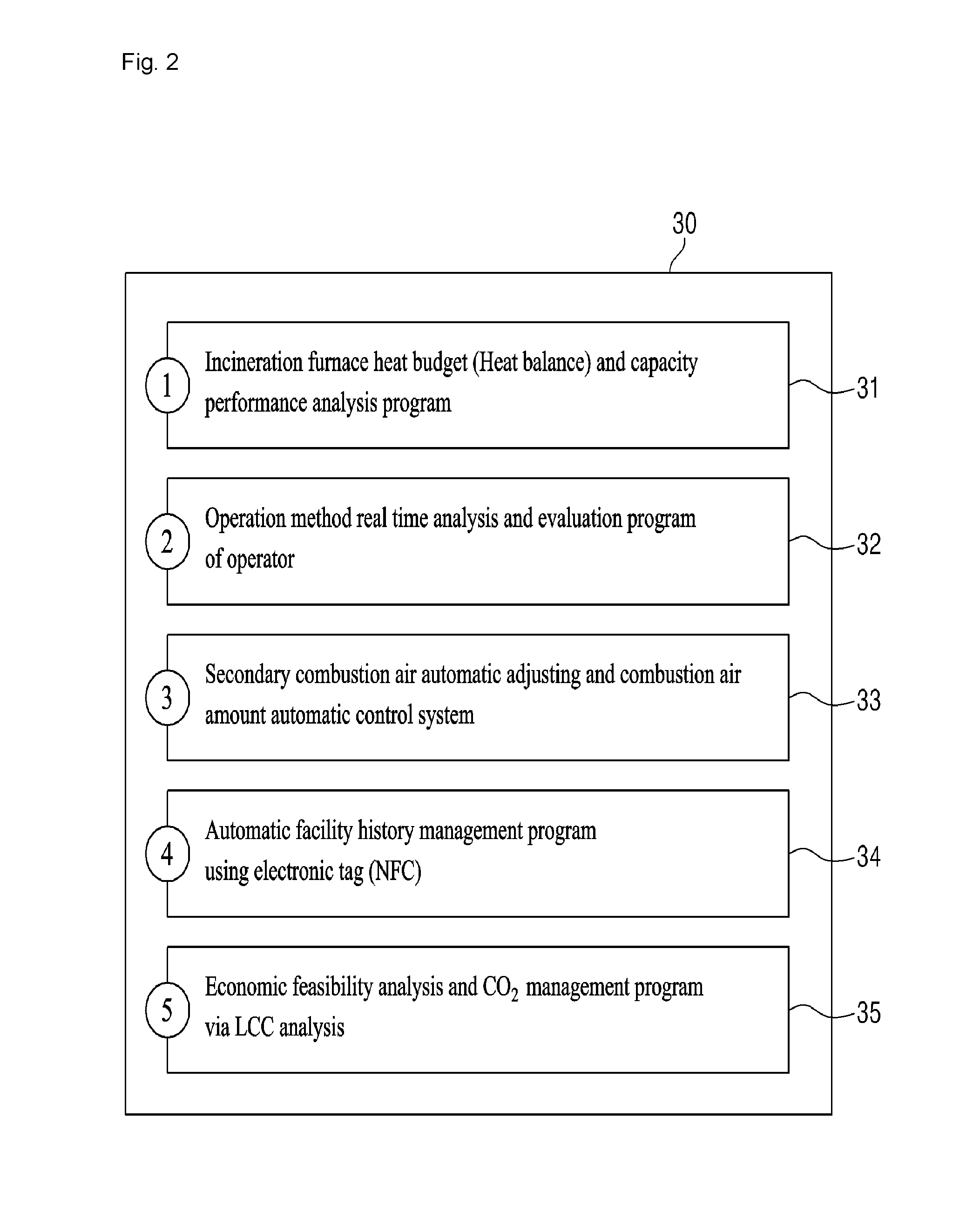
[0053]As illustrated in FIG. 1, the system for diagnosing and controlling an incineration facility and solid fuel boiler and managing the life cycle of a facility through a heat exchange and a design program and an operation mode analysis of an operator according to the present invention may include, but is not limited to, a database (DB) which stores an operation value detected by an operator in an onsite and control room when the incineration facility is in operation and detected by an automatic sensor [hereinafter referred to as “incineration furnace operating sensor (10)] and stored in the MMI (Man Machine Interface), a design value obtained during the initial design of the incineration facility, an measured actual value obtained by the actual operation; and a server 20 which generates a material for the PLM system via a heat balance of an incineration facility based on the data stored in the database and a diagnosis and control via a designing program and an operator's operatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com