Peptoid affinity ligands
a technology of affinity ligands and protein ligands, which is applied in the field of affinity ligands of proteins, can solve the problems of low chemical and biochemical stability, high cost of antibody isolation and purification, and high cost of protein ligands, and achieves high affinity and selectivity for antibodies, wide chemical diversity, and high target specificity and affinity. the effect of high affinity and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Solid-Phase Synthesis of a Tetramer Peptoid Ligand and Use of the Resulting Affinity Adsorbent for the Purification of Human Polyclonal or Monoclonal Antibodies
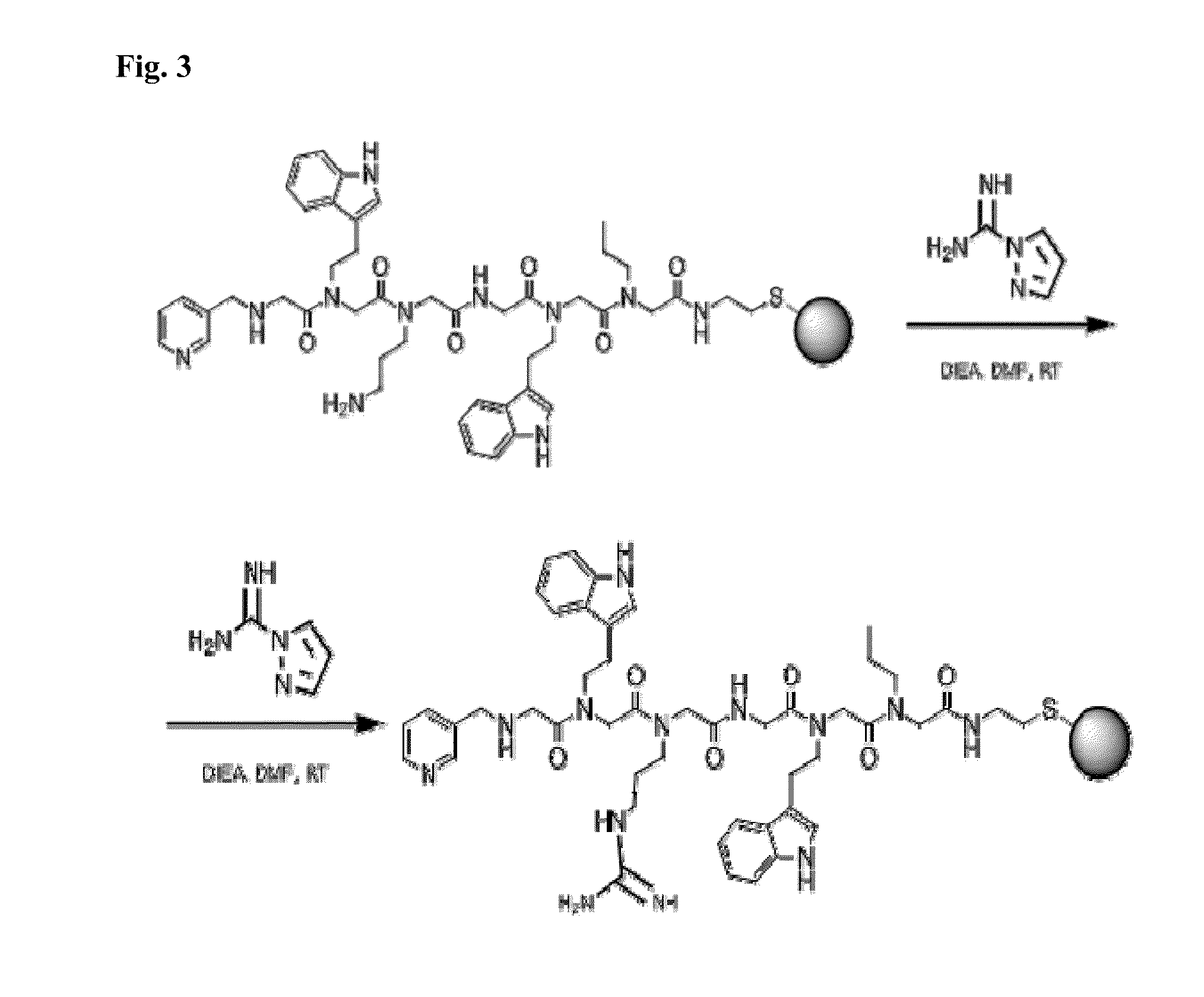
[0076]The selected groups, as numbered from the N- to the C- terminus, are: imidazoyl, indolyl-, guanidyl-, and methyl-. Correspondingly, the amines employed for the peptoid synthesis are respectively histamine, tryptamine, agmatine, and methylamine. Presented in Scheme 1, as follows:
The chromatographic resin Toyopearl AF-Amino-650M is chosen as solid support for synthesis. The synthesis comprises the following steps:[0077]1. Coupling of bromoacetic acid in N,N′-dimethylformamide (DMF) via diisopropylcarbodiimide activation (hereafter referred to as DIC). Wash the resin with DMF and equilibrate with NMP.[0078]2. Coupling of methylamine in N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP). Wash the resin with NMP and equilibrate with DMF.[0079]3. Coupling of bromoacetic acid by DIC. Wash the resin with DMF and equilibrate with NMP.[0080]4. Coupling o...
example 2
Preparation of Peptoids Directly to Amine-Containing Resin
[0087]Preparation Procedures: Peptoids were synthesized directly onto Toyopearl AF-amino 650M resin (Tosoh Biosciences) at a 0.1 mmol / mL loading with a Biotage Alstra automated peptide synthesizer under microwave assistance using methods described previously (Fara et al. Tet. Lett. 2006 47, 1011-1014; Olivos et al. Org. Lett. 2002, 4(23), 4057-4059). The Fmoc-protected monomers for glycine, N-(-3-guanidinpropyl)glycine, N-(isobutyl)glycine, N-(3-(Boc-amino)-propyl)glycine and N-(benzyl)glycine were coupled to the peptoid using N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl—O-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)uronium hexafluorophosphate (HBTU) with diisopropylethyl amine as the coupling agent in dimethyl formamide for 30 minutes at 50 C (Huang et al. PNAS 2012, 109(49), 19922-19927.). After coupling, the secondary amine was deprotected using 20% piperidine in DMF. The remaining residues were coupled to the peptoid sequence using a submonomer approach. Chloroaceti...
example 3
Binding of Human Immunoglobulin from PBS in Absence of Other Proteins
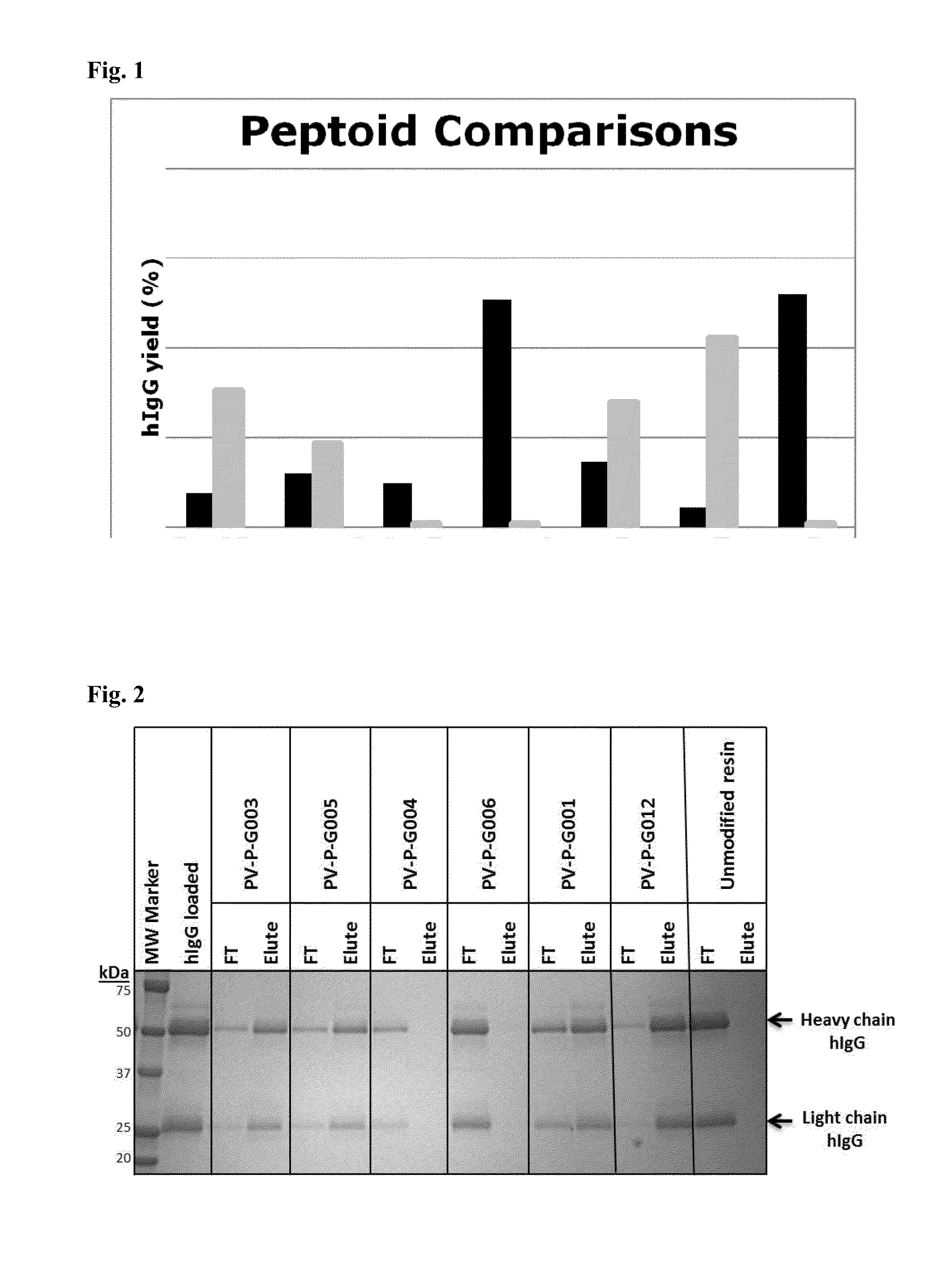
[0094]The ability of the peptoid affinity ligands to bind human IgG molecules was tested in batch mode. A 50% slurry of the resin was prepared, of which 100 μl (˜50 mg resin) was transferred into a spin column. The resin was washed with 2×200 μL of 0.1 M glycine buffer (pH 2.5), and rinsed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), pH 7.4 prior to chromatography. Human polyclonal immunoglobulin G (hIgG) was diluted to 0.5 mg / mL with PBS. After draining the resin, the hIgG solution was added to the resin to obtain a ratio of 2 mg hIgG per mL of resin, and mixed vigorously for 5 minutes at room temperature. After incubation, the resin was centrifuged at 500×g for 2 min and the filtrate was collected and labeled as “flow-through” fraction. The resin was washed with 2×200 μL of PBS. Elution buffer (0.1M glycine, pH 2.5, 200 μL) was added to the resin and mixed vigorously for 5 minutes at room temperature. After centrifugation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| linear velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com