Semiconductor device with chip having low-k-layers
a technology of low-k-layers and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of large deformation, cracks in the brittle low-k-layers of the chip, and stress on the copper/low-k- and ultra-low-k-structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
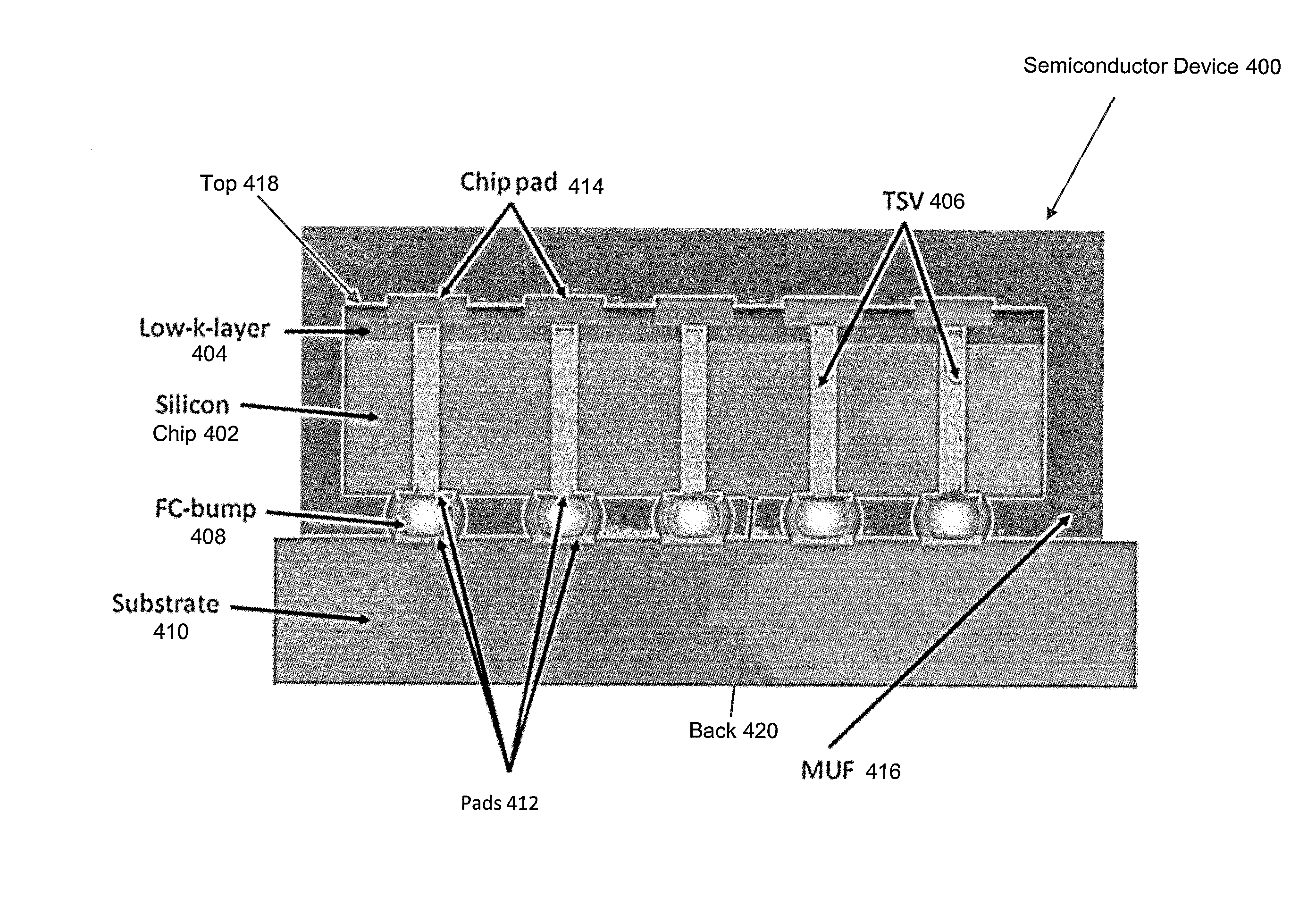
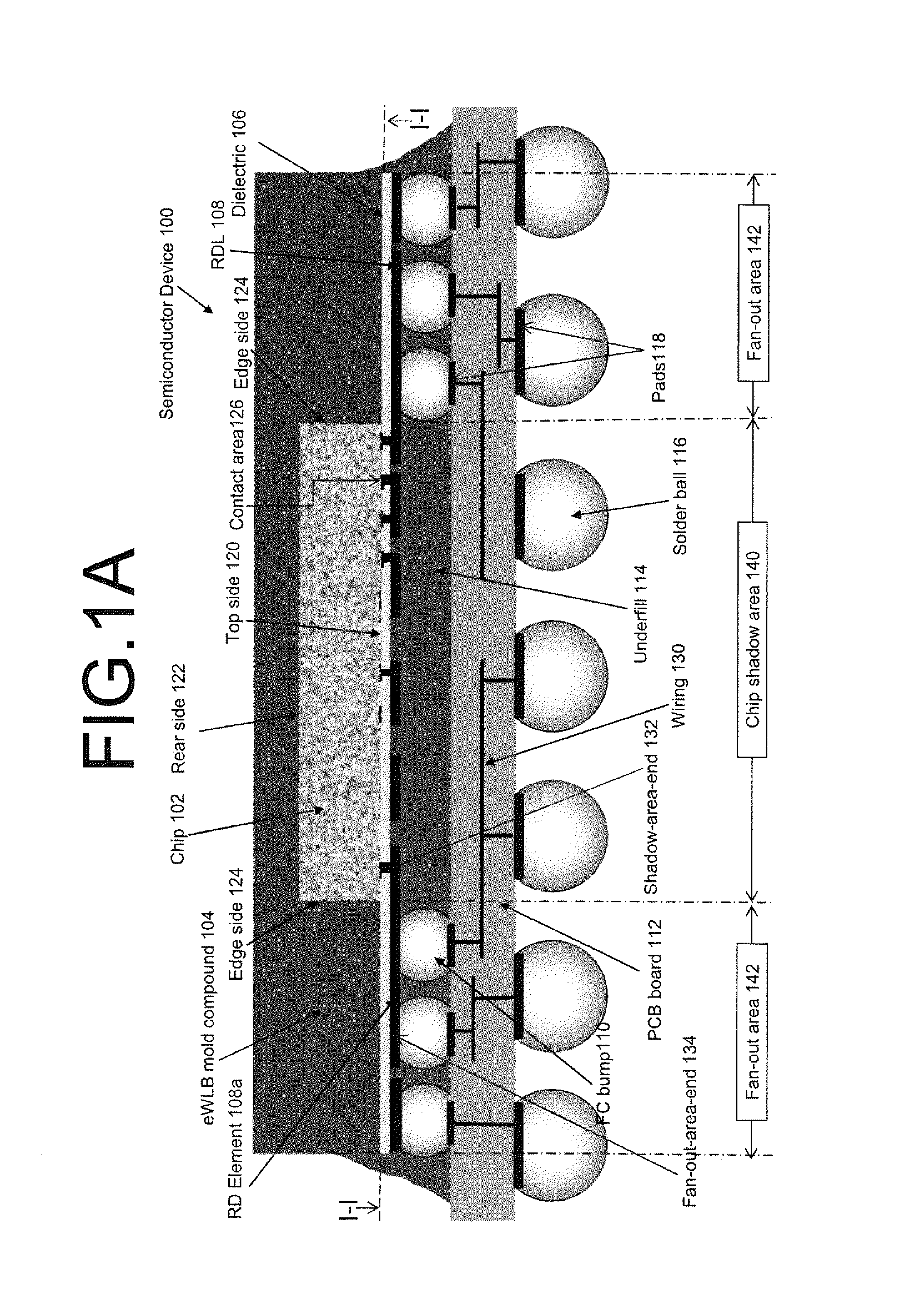
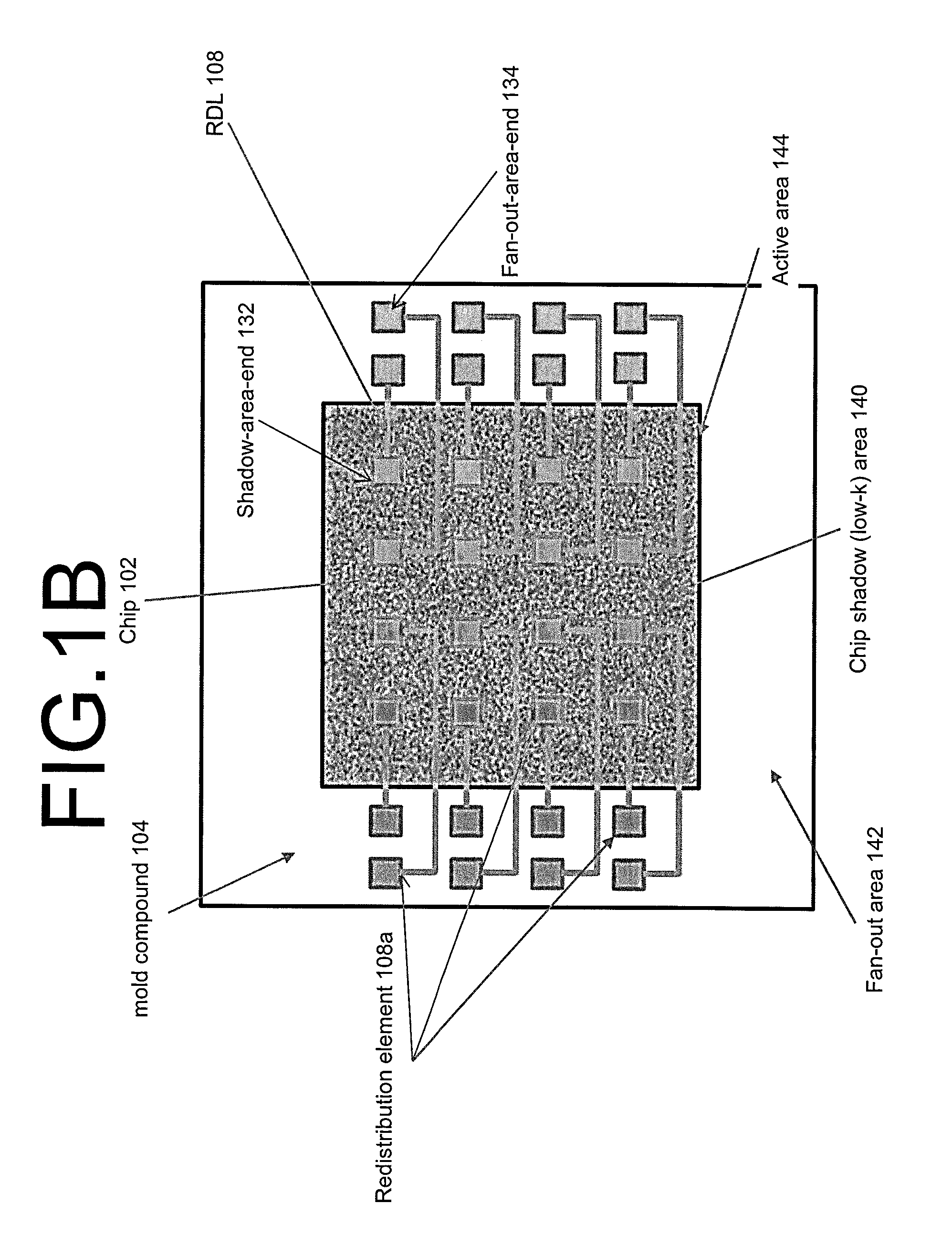
[0031]In the following detailed description, reference is made to the accompanying drawings, which form a part hereof, and in which is shown by way of illustration specific approaches in which the disclosure may be practiced. In this regard, directional terminology, such as “top,”“bottom,” etc., is used with reference to the orientation of the Figure(s) being described. Because components of approaches of the present disclosure can be positioned in a number of different orientations, the directional terminology is used for purposes of illustration and is in no way limiting. It is to be understood that other approach may be utilized and structural or logical changes may be made without departing from the scope of the present disclosure. The following detailed description, therefore, is not to be taken in a limiting sense, and the scope of the present disclosure is defined by the appended claims.
[0032]The present disclosure proposes to decouple the active side of the chip and the inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com