Thermoformable lap having reinforcement fibres
a technology of reinforcement fibres and laps, which is applied in the direction of layered products, non-woven fabrics, textiles and paper, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of thermoplastic material powder production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
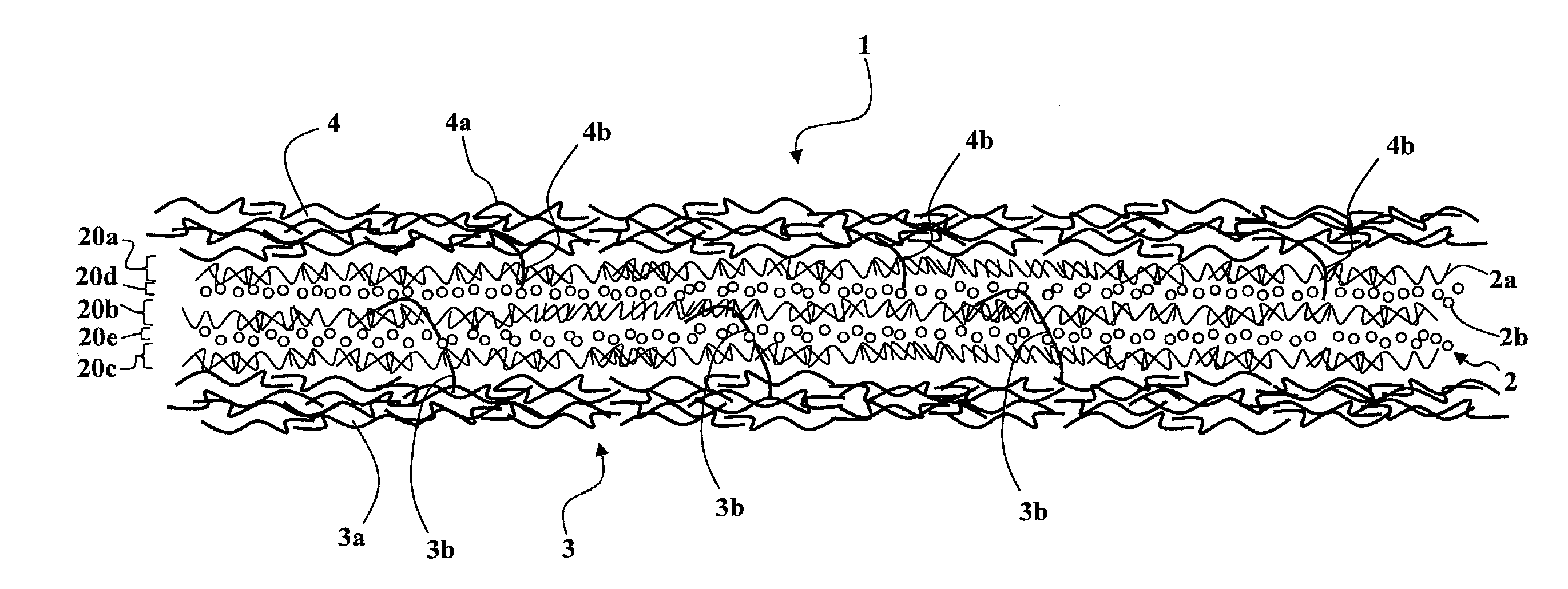
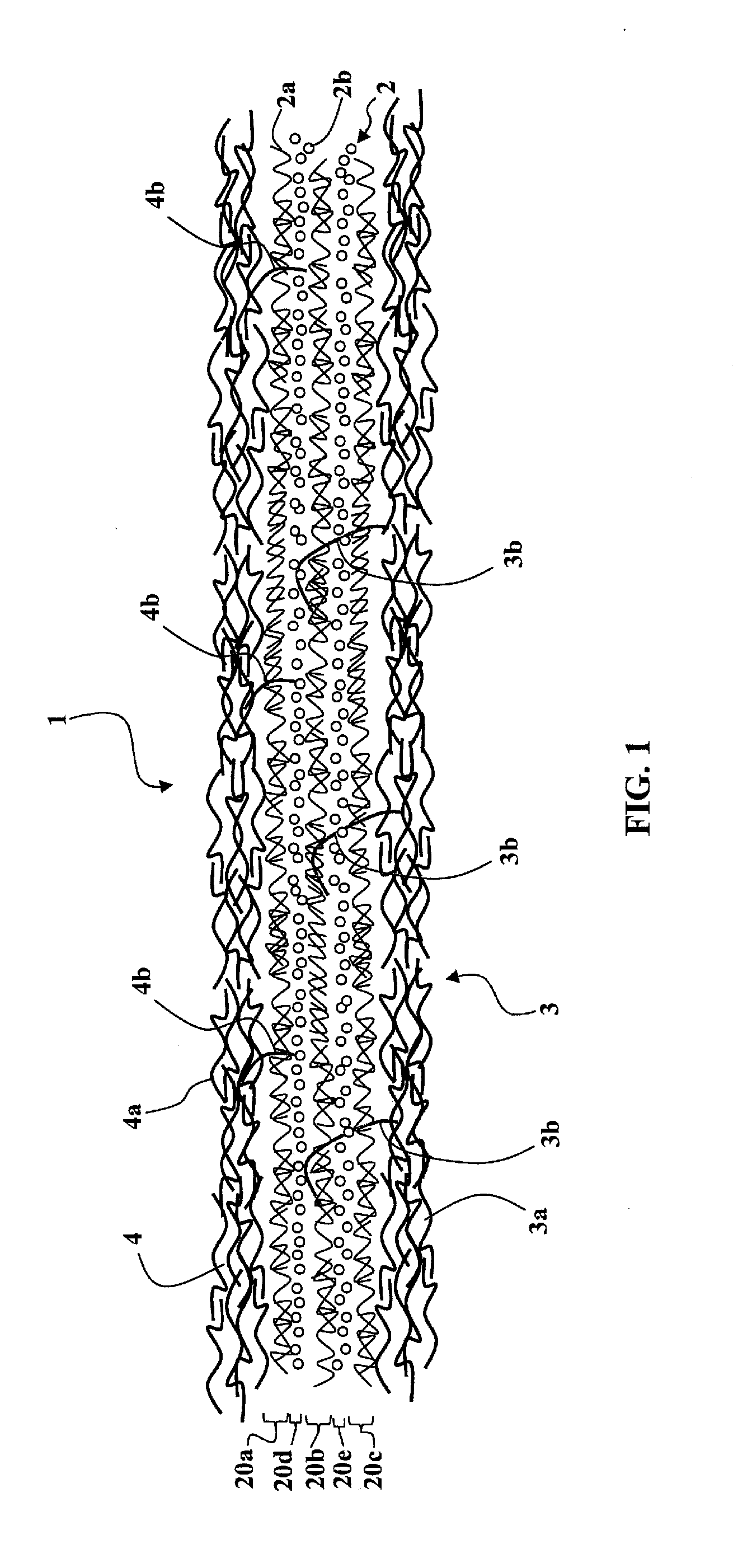
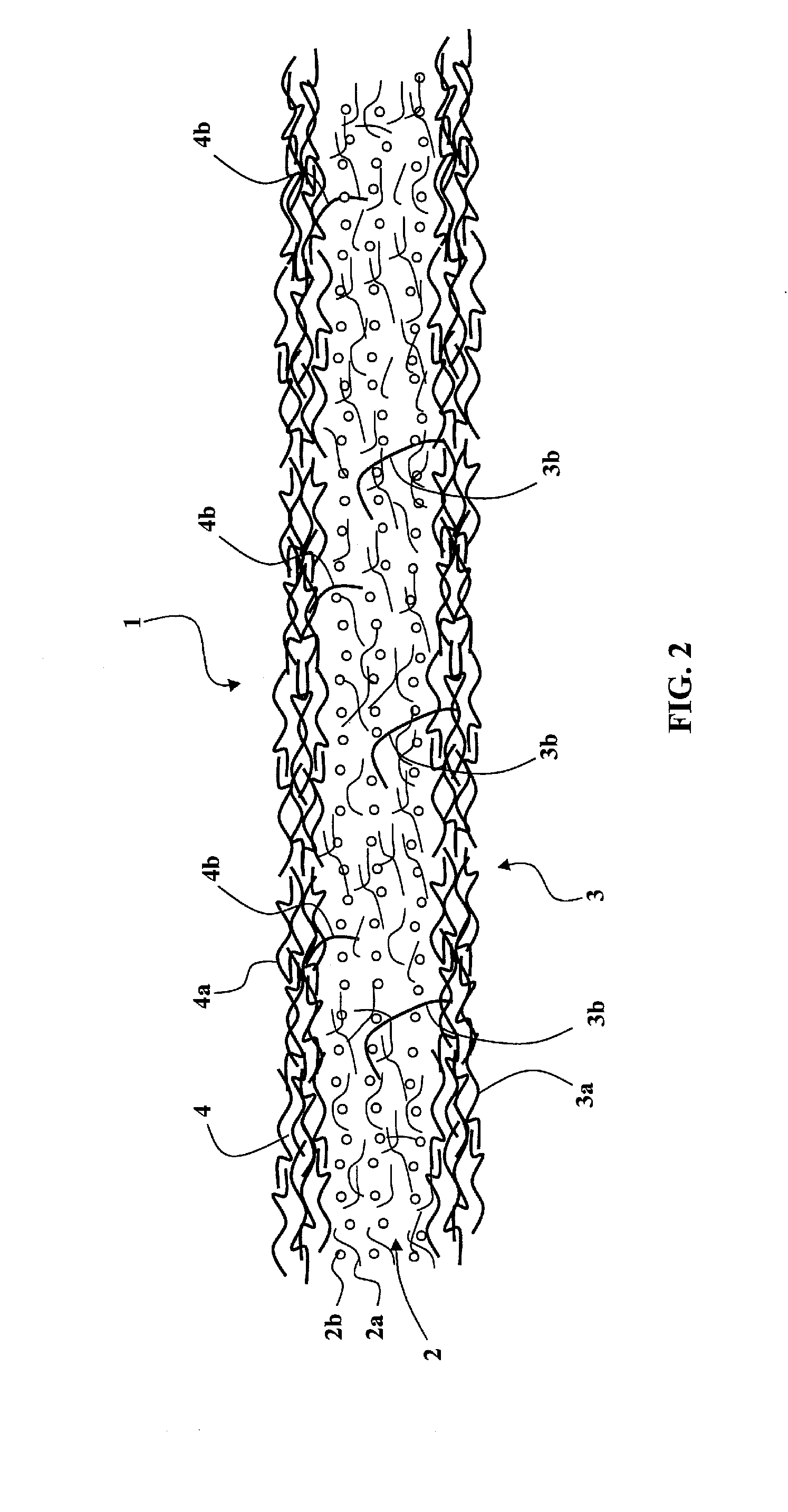
[0067]I) On a planar support in continuous longitudinal displacement, a first web 3 of sections of linking fibers 3a of polyamide having a unitary yarn count of between approximately 2 dernier and approximately 4 dernier is continuously deposited, the web leaving a conventional carding machine.
[0068]II) On the first web 3 in continuous longitudinal displacement, a mixture of reinforcement fibers 2a and of granules 2b is made to fall to constitute an intermediate layer 2; the reinforcement fibers 2a are sections of glass fiber having a unitary yarn count of approximately 30 tex to 100 tex and a length of approximately 50 to 150 millimeters, in all orientations; the granules have a size of approximately 2 millimeters and are of 6×6 type polyamide, having a reactivation temperature of approximately 240° C. to 280° C.
[0069]III) During the continuous longitudinal advance of the assembly formed by the first web 3 and the intermediate layer 2, the second web 4 made of linking fibers 4a is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com