Lamin A, An Activator of Longevity/Anti-Aging SIRT1 Protein
a technology of longevity and anti-aging sirt1 protein, which is applied in the field of lamin a, an activator of longevity/anti-aging sirt1 protein, can solve the problem of unclear underlying mechanism, and achieve the effects of increasing the activity of deacetylase sirt1, reducing and increasing the binding affinity of lamin a
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
SIRT1 Interacts with Lamin A While Prelamin A or Progerin Jeopardizes the Interaction
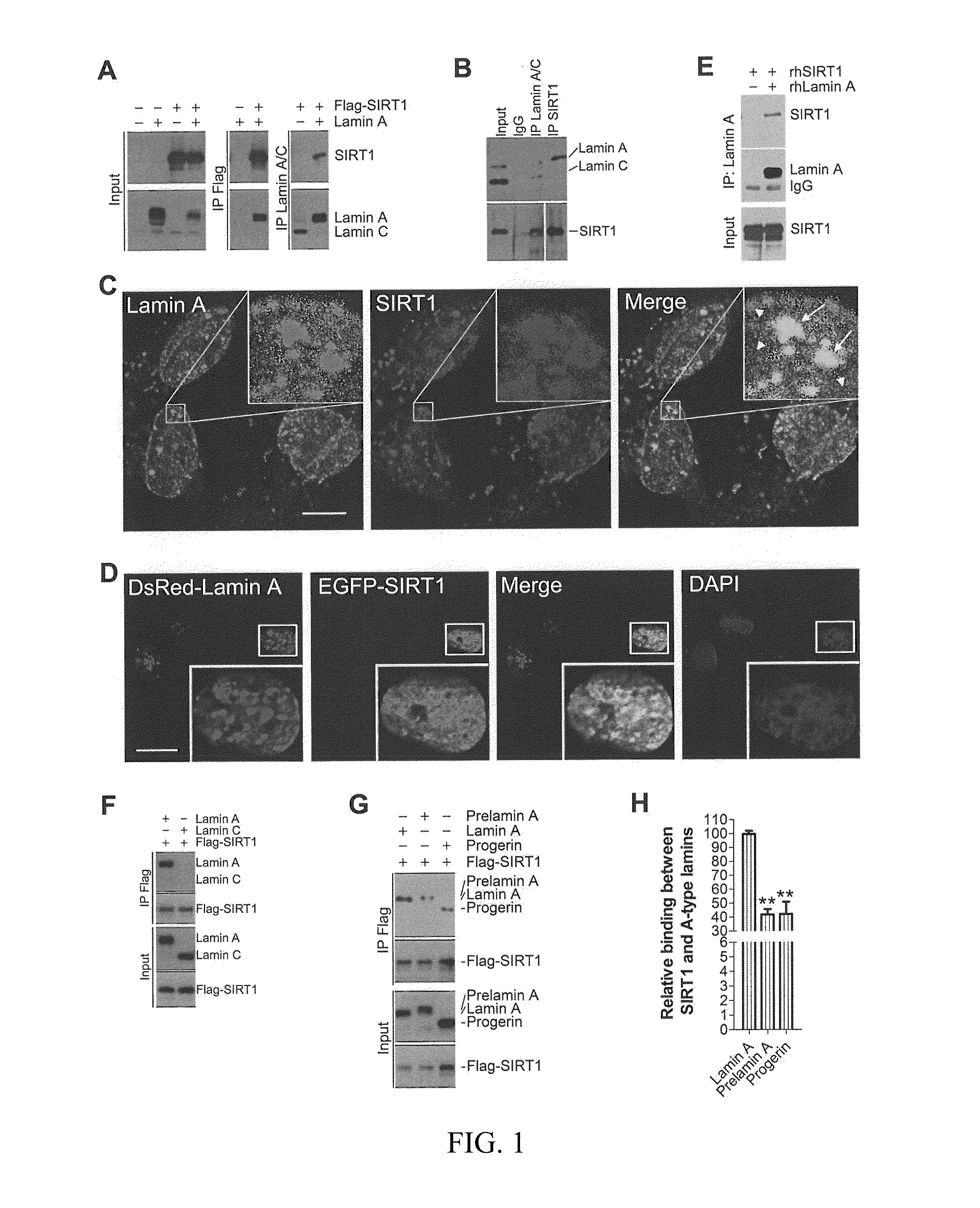
[0116]To determine the potential involvement of SIRT1 in progeria, the potential interaction between lamin A and SIRT1 is examined by co-immunoprecipitation in HEK293 cells expressing ectopic FLAG-tagged SIRT1.
[0117]Lamin A was pulled down in the anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates, while FLAG-SIRT1 was detected in the anti-lamin A / C immunoprecipitates (FIG. 1A). The interaction between endogenous SIRT1 and lamin A / C was confirmed in HEK293 cells, bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs), and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), where anti-SIRT1 immunoprecipitates pulled down lamin A and vice versa (FIGS. 1B, 6A, 6B).
[0118]Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy showed that much of nuclear SIRT1 co-localized with nucleoplasmic lamin A / C in the nuclear interior in human fibroblasts (FIG. 1C). Consistently, ectopic EGFP-SIRT1 and DsRed-lamin A co-existed in the nuclear interior (FIG. 1D). This interaction seems spec...
example 2
SIRT1 is Mislocalized in Progeria Cells
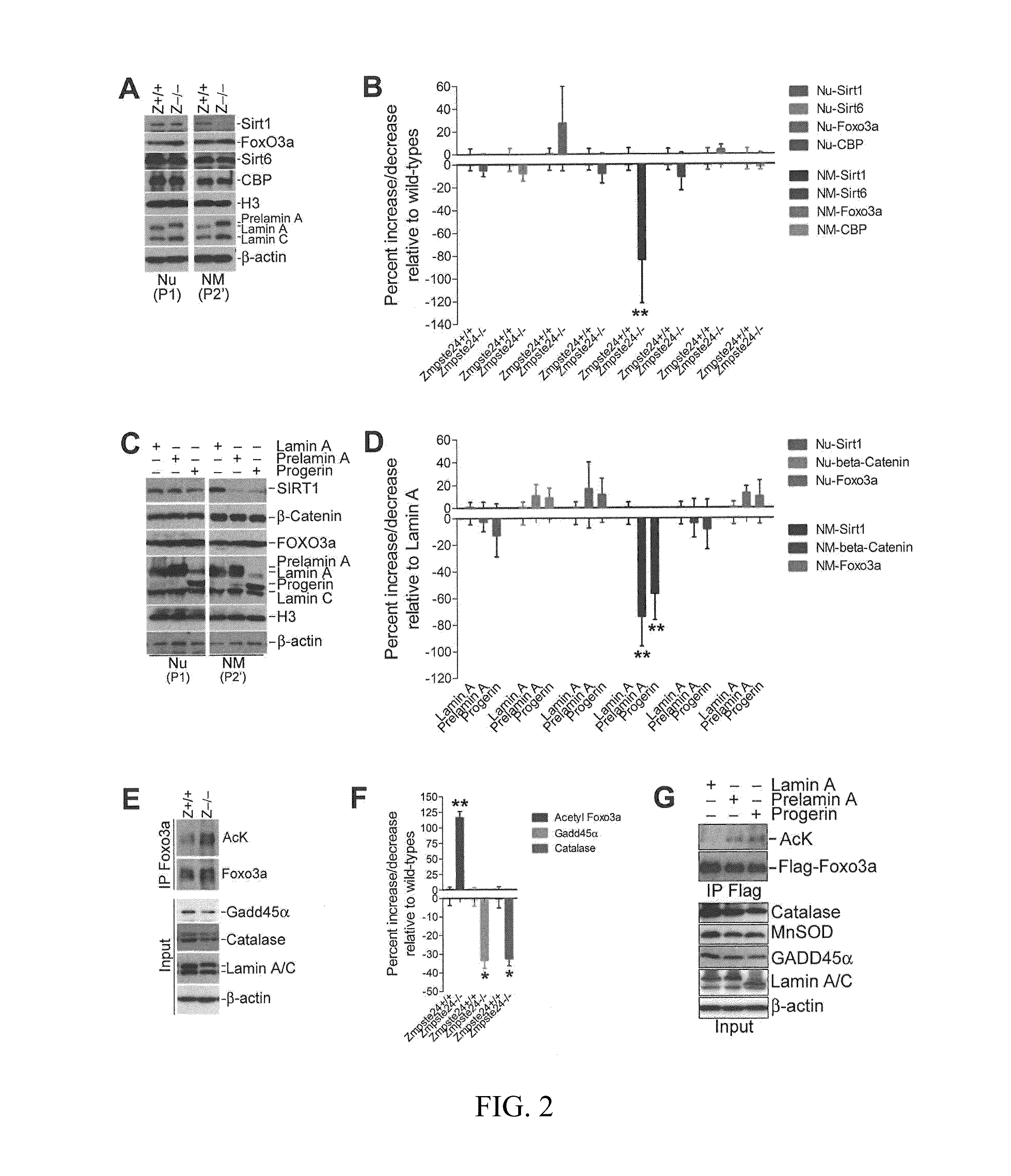
[0123]Lamin A is one of the major components of NM. This Example investigates the association of SIRT1 with the NM by subcellular fractionation. SIRT1− / − cells were utilized as a negative control for the specific staining of SIRT1 protein. KAP-1 (KRAB-associated protein 1, also known as Trim28 or Tif1β) and MCM3 proteins served as positive controls for the purity of the subcellular fractionation.
[0124]KAP-1 is a heterochromatin factor and was reported to be associated with the majority of the micrococcal nuclease-resistant fraction in the nucleus (Goodarzi et al., 2008; Ryan et al., 1999). MCM3 protein is important in preventing excessive DNA replication during S phase and is predominantly associated with chromatin (Mendez and Stillman, 2000).
[0125]As expected, Kap-1 was resistant to MNase digestion and remained in the NM fraction (P2′) whereas the majority of Mcm3 was released into the nucleoplasmic and chromatic fraction (S2′) after MNase tre...
example 3
Resveratrol Enhances the Binding of SIRT1 to Lamin A and Stimulates its Deacetylase Activity in a Lamin A-Dependent Manner
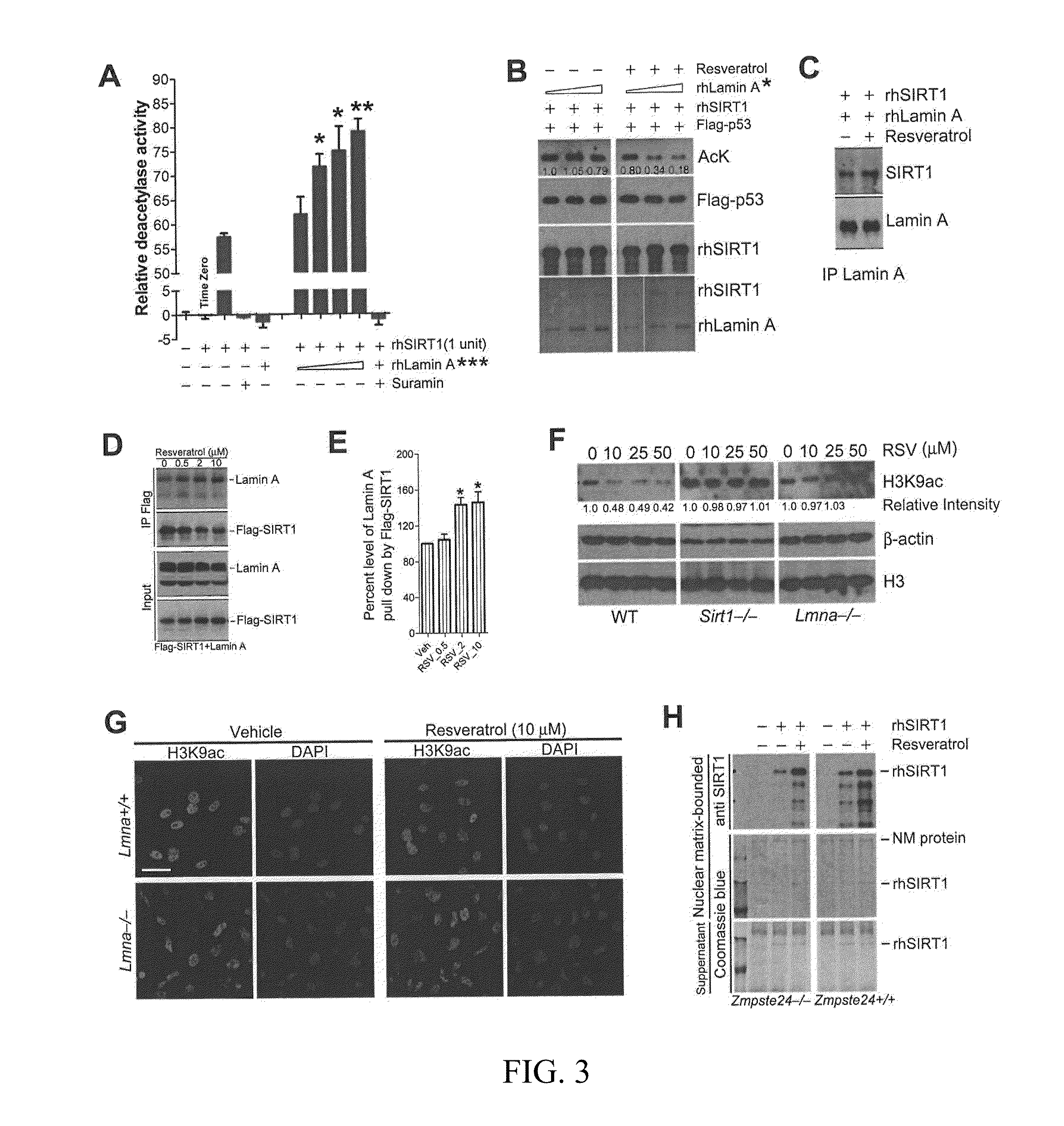
[0132]The NM-localization of SIRT1 and the association of NM with HDAC deacetylase activity (Fey et al., 1991) suggest that NM might contain potential SIRT1 activators. To test this hypothesis, in vitro deacetylase activity of rhSIRT1 by a BioMol® SIRT1 Fluorimetric Drug Discovery Kit (BSDK) was quantified in the presence or absence of NM derived from wild-type or Zmpste24− / − BMSCs.
[0133]Surprisingly, the deacetylase activity of rhSIRT1 was enhanced approximately 3-fold in the presence of NM from wild-type BMSCs compared with the control without NM or with cytoplasmic fraction (FIG. 7E), suggesting the existence of potential SIRT1 activator(s) on the NM. In contrast, the NM from the Zmpste24− / − BMSCs showed a significantly reduced stimulatory effect on rhSIRT1 deacetylase activity.
[0134]This Example further investigates whether lamin A acts as an activator of SI...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com