Coated woodworking tool
a woodworking tool and coating technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, superimposed coating process, flat surface machines, etc., can solve the problems of gumming of the blades, comb cracking, cutting edge chipping, etc., and achieve the effect of long service life of the coated tool
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
exemplary embodiment 1
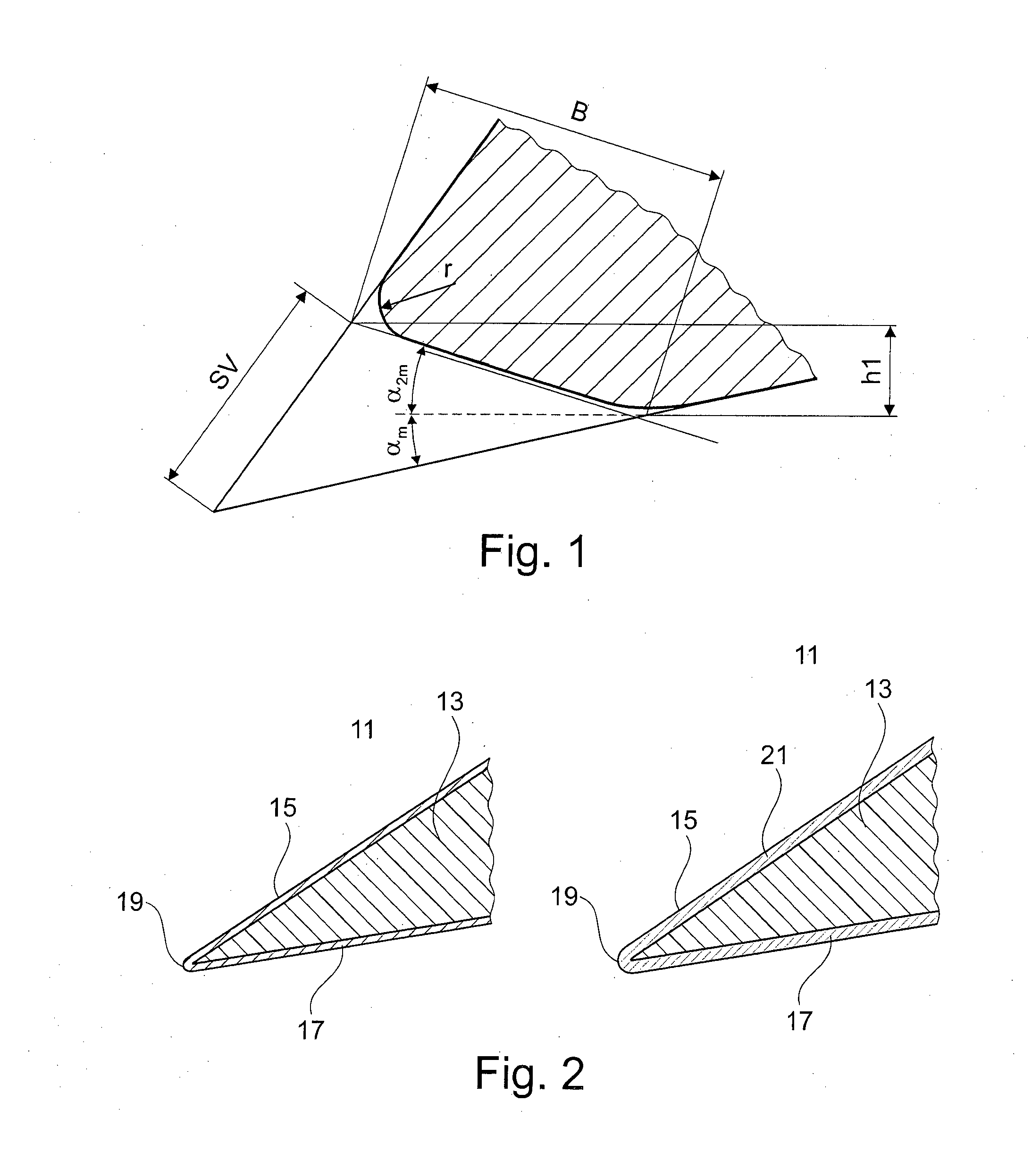
[0049]A woodworking tool A having a defined edge radius is coated by means of a generally known PVD arc method in a coating system as per EP 1 524 329 A1 or WO 0250865 with a base layer containing chromium, for example, CrN. The thickness of the CrN layer is between approx. 1 and 3 micrometres.
[0050]Molybdenum disulphide with a thickness of approx. 1 micrometre is then applied to the tool A in a further coating system by means of a generally known magnetron sputtering method.
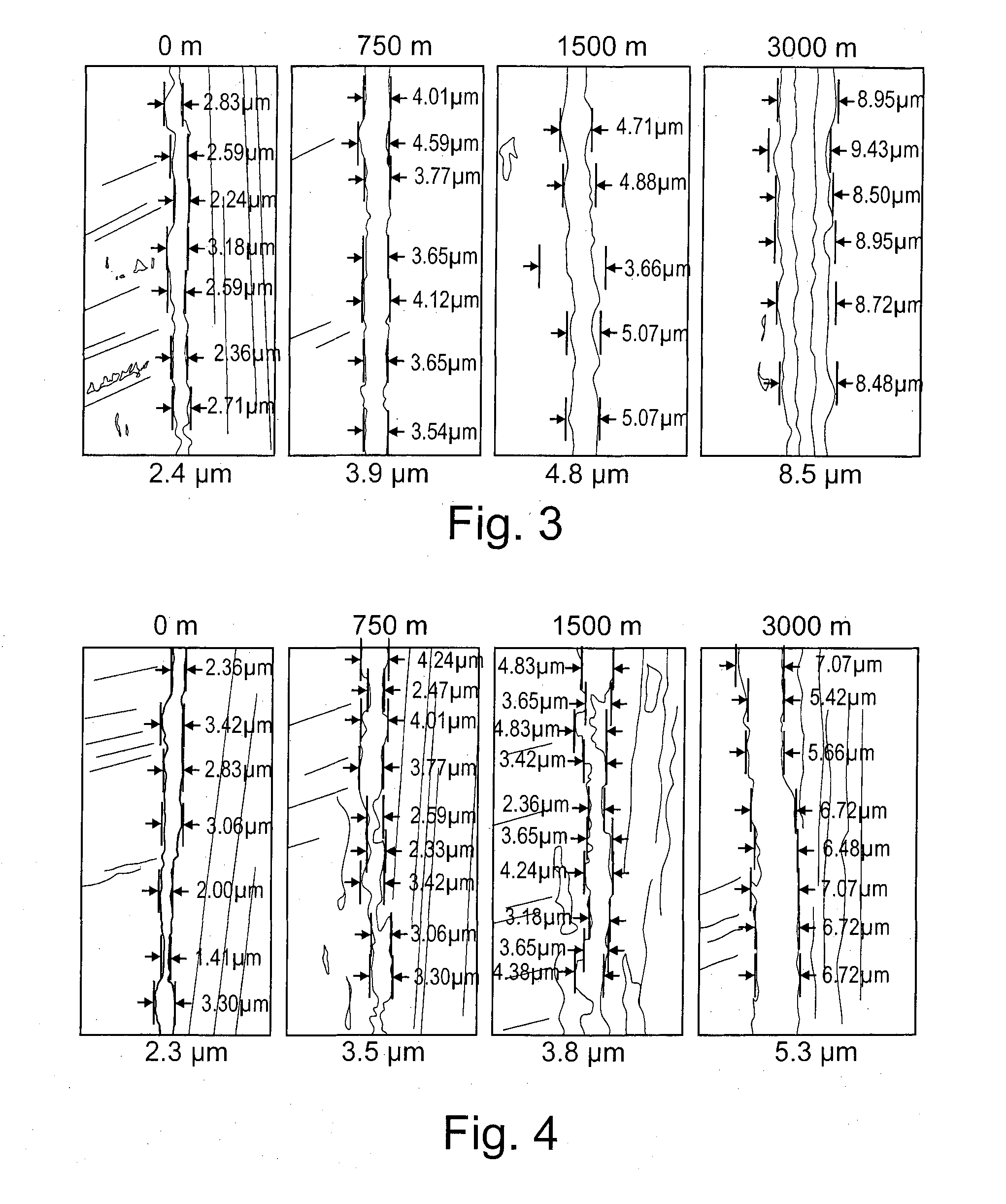
[0051]The measured edge radius was between 2 and 4 micrometres. Resharpening is therefore not necessary.
[0052]The edge radius was checked before and after coating on a scanning electron microscope (FIGS. 3 and 4).
[0053]The tool was then used on a Conturex wood milling machine from Michael Weinig AG. The milling parameters were as follows:
[0054]Speed: 12,000 U / min
[0055]Feed rate: 12,000 mm / min
[0056]The cutting edge radius was measured by means of a scanning electron microscope after 750, 1,500 and 3,000 linear me...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wedge angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com