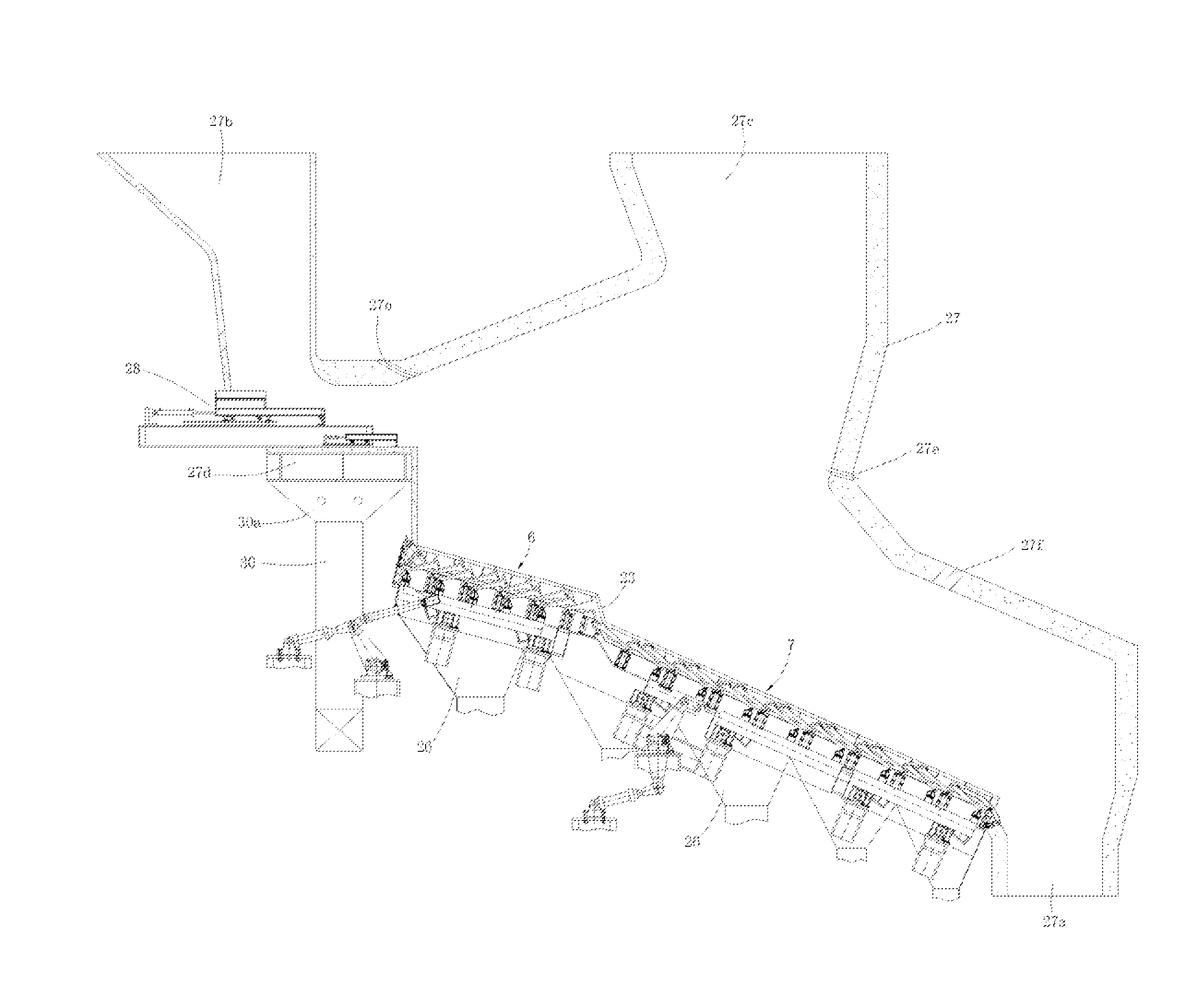
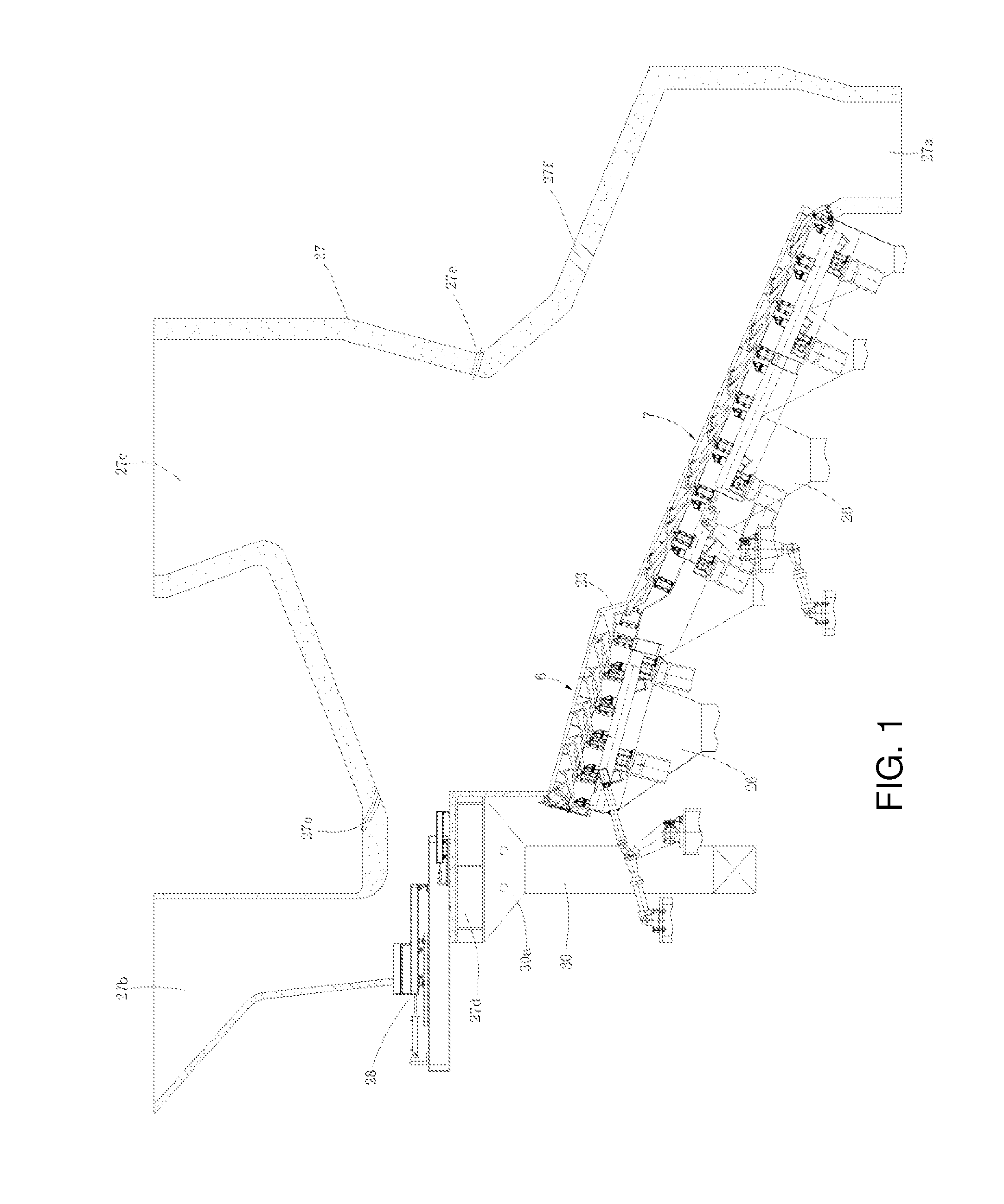
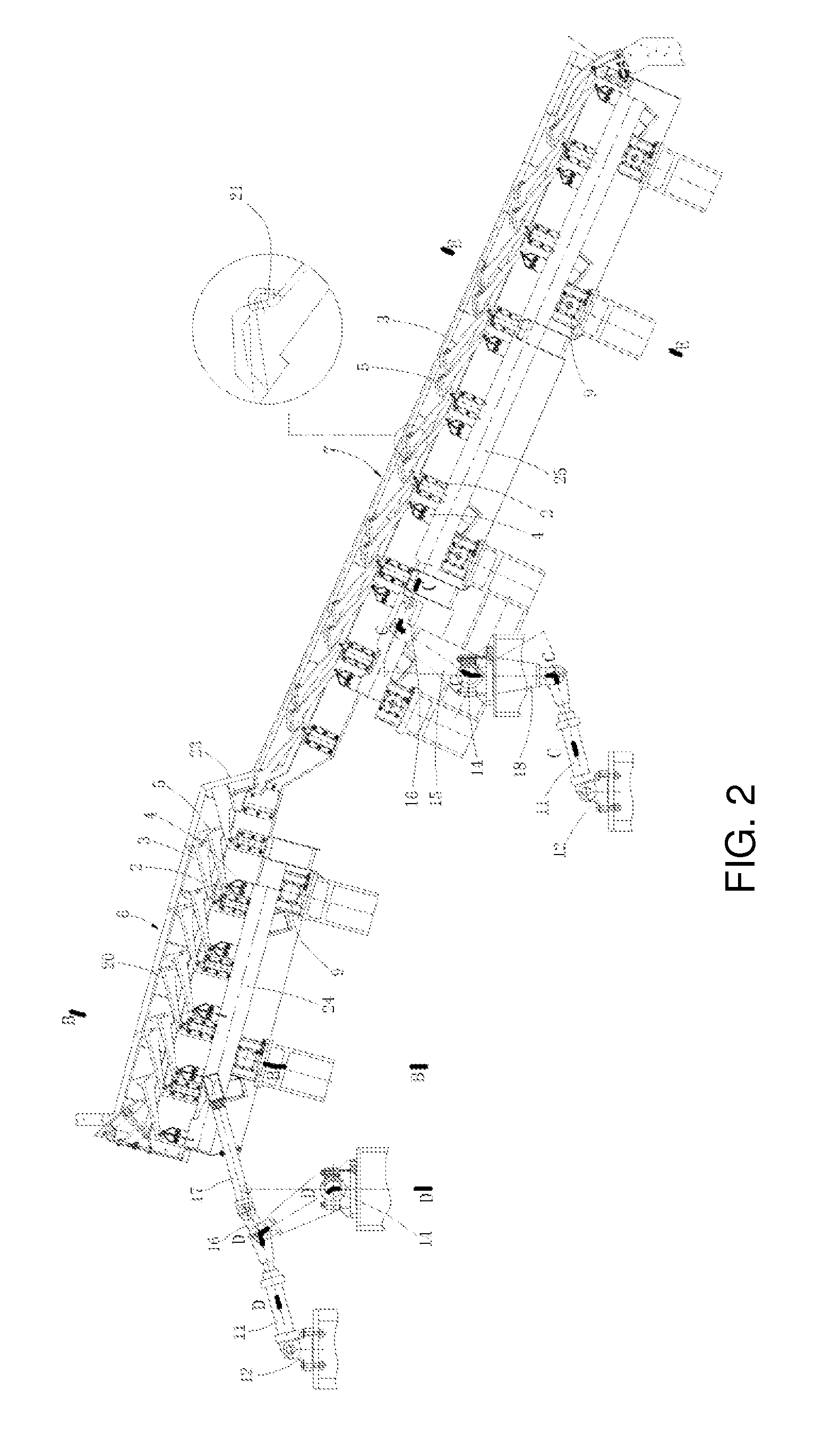
Second, in the
drying stage, the bottom layer waste may stick to the surfaces of the grates locally and thereby block primary air holes on the grates and affect air supplying, in particular on
dryness, and prolong
drying time,
delay ignition to
combustion of the waste, increase the
residence time of the waste inside the incinerator in the whole process, which will directly affect the incineration process inside the incinerator.
The existing problems of this type of incinerator are listed as follows: first, in order to ensure the
residence time of the waste inside the incinerator, the areas of the grates are signed to be larger or the strokes of the grates are designed to be longer, thereby the height or length of the incinerator are increased and the cost is increased.
Second, the grates and the
waste material layers move in the same direction, when the
waste material layers are higher, the relative
height difference between adjacent grates is lower or the relative
stroke is shorter, the moving waste is almost presented in a state of relatively stationary, thereby a poor effect on agitation and mixture is obtained, and the waste is not fully dried and can not be fully combusted resulting in inefficient combustion and low combustion efficiency, which is difficult to meet the requirement of clinker ignition loss.
Third, meanwhile, prior to be evaporated, the
leachate in the waste
layers is pushed to flow forward by the grates, thereby the
drying time of the waste is increased, all the
leachate, which is not gathered in time, is evaporated to be changed into vapor inside the incinerator, which increases the
water content in the
smoke, thereby affects the incineration process.
The waste is delayed of igniting to combustion, thereby the
residence time of the waste inside the incinerator in the whole process is increased and it greatly affects the incineration process.
Fifth, the grates stop during a part of time in the periodically
control mode, if the time is too long, then the grates are likely to be burned out at the lower position of the material layer, whereas the upper position of the material layer is not fully dried and difficult to be completely incinerated, if the time is too short, then it cannot ensure the
residence time inside the incinerator, which will result in low combustion efficiency, in both cases, it is difficult to meet the requirement of clinker ignition loss.
Sixth, if the waste incinerator is divided to too many sections, then the complexity of the mechanism is increased, thereby the
failure rate and the cost are higher, and it brings a higher requirement for the
algorithm of the
control system.
The existing problems of this kind of grate-typed incinerator are listed as follows: first, for the
solid waste in our country having the characteristics of
high water content and complex ingredients, etc., the conveying capacity of the reverse pusher type grates to the waste is weaker, in particular in the process of waste drying, there are the same problems as the whole reverse pusher type grates.
Second, in the
burnout stage with the pusher type grates, the waste is basically incinerated to clinker, most of which is clinker with a very small size, and with the development of the
burnout stage, the clinker content increases until it reaches the requirement of clinker ignition loss, i.e., the movement of the horizontal pusher type grates conveys very small sized clinker, which is very likely to enter into a subjacent primary
air chamber through gaps between the grates or primary air holes, thereby the
air chamber discharges a plenty of clinker, which is unfavorable to the collection and unified treatment of the clinker.
Third, the clinker or ash may enter a movement mechanism part inside the primary air chamber, which will cause severe abrasion wear to kinematic pairs, thereby affect normal operation of the mechanism, and the clinker may gather at a fixed board or a
fixed beam, thereby affect the function of the primary air to pass through the material layers and enter into the incinerator to assist the combustion and burnout of the waste.
1. For the
solid waste in our country having the characteristics of
high water content and complex ingredients, etc., the conveying capacity of the reverse pusher type grates to the waste is relatively weak, in particular in the drying stage, the
waste material layer is very likely to coagulate into masses or cakes and sticks to the surfaces of the grates, thereby affects the drying process and the conveyance of the waste;
2. In the reverse pusher type grates, in the drying stage, the bottom layer waste may stick to the surfaces of the grates locally and thereby block primary air holes on the grates, prolong
drying time, increase the
residence time of the waste inside the incinerator in the whole process, which will directly affect the incineration process inside the incinerator;
3. Because a material pusher continuously feeds material to the incinerator, in the drying stage, the upper layer waste is extruded to be conveyed forward, whereas the bottom layer waste is conveyed relatively slowly, therefore, the moving velocity of the upper layer waste and the bottom layer waste are obviously different;
4. In order to ensure the
residence time of the waste inside the incinerator, the areas of the grates are signed to be larger or the strokes of the grates are designed to be longer, thereby the height or length of the incinerator are increased and the cost is increased;
5. The pusher type grates and the waste material layers move in the same direction, when the waste material layers are higher, the relative
height difference between adjacent grates is lower or the relative
stroke is shorter, the moving waste is almost presented in a state of relatively stationary, thereby a poor effect on agitation and mixture is obtained, the waste is not fully dried and can not be fully combusted resulting in inefficient combustion and low combustion efficiency, which is difficult to meet the requirement of clinker ignition loss;
6. Prior to being evaporated, the
leachate in the waste layers is pushed to flow forward by the pusher type grates, thereby the
drying time of the waste is increased, all the leachate, which is not gathered in time, is evaporated to be changed into vapor inside the incinerator, which increases the
water content in the
smoke, thereby affects the incineration process;
7. For the pusher type grates, the incineration process controls the movement of the grates in a periodically
control mode. For the solid waste in our country having the characteristics of
high water content and complex ingredients etc., the time change on stopping and moving is greater and the process parameters are regulated at relative
high frequency, so the incineration process parameters need to be regulated when the incinerator is used in different regions and the control method also needs to be adjusted correspondingly;
8. The grates stop during a part of time in the periodically
control mode, if the time is too long, then the grates are likely to be burned out at the lower position of the material layer, whereas the upper position of the material layer is not fully dried and difficult to be completely incinerated, if the time is too short, then it can not ensure the residence time inside the incinerator, which will result in low combustion efficiency, in both cases, it is difficult to meet the requirement of clinker ignition loss;
9. If the waste incinerator is divided to too many sections, then the complexity of the mechanism is increased, thereby the
failure rate and the cost are higher, and it brings a higher requirement for the
algorithm of the
control system;
Furthermore, the clinker or ash may enter a movement mechanism part inside the primary air chamber, which will cause severe abrasion wear to kinematic pairs, thereby affect normal operation of the mechanism, and the clinker may gather at a fixed board or a
fixed beam, thereby affect the function of the primary air to pass through the material layers and enter into the incinerator to assist the combustion and burnout of the waste.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More