Solar cell and method for manufacturing the same
a solar cell and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of solar cell and manufacturing the same, can solve the problems of increasing the recombination rate at the surface, affecting the conversion efficiency of the final product, and incurred a large amount of fabrication cost, so as to achieve the effect of improving the conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
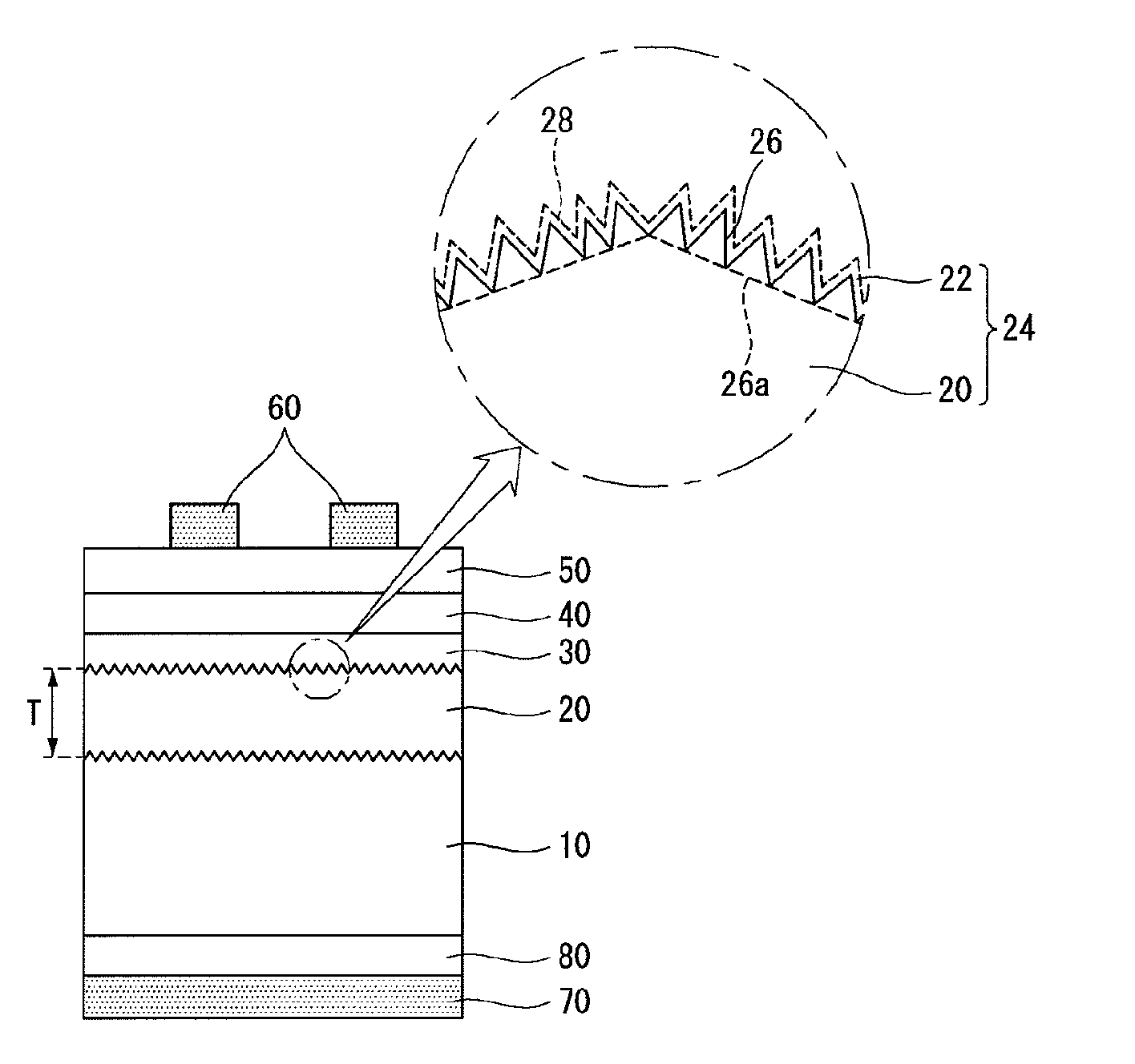
Example embodiments of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as being limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. In the drawings, the shapes and dimensions may be exaggerated for clarity, and the same reference numerals will be used throughout to designate the same or like components.
To clarify multiple layers and regions, the thicknesses of the layers are enlarged in the drawings. When it is said that any part, such as a layer, film, area, or plate, is positioned on another part, it refers to the part being directly on the other part or above the other part with at least one intermediate part. On the other hand, if any part is said to be positioned directly on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com