Treatment of acute exacerbation of asthma and reduction of likelihood of hospitalization of patients suffering therefrom
a technology for asthma and acute exacerbation, which is applied in the direction of biocide, heterocyclic compound active ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of provoking unwanted cardiovascular side effects, too risky, and not producing significant clinical benefits, so as to reduce the likelihood of hospitalization, improve breathing ability, and reduce the hospitalization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Safety and Efficacy of In Vivo Administration of MN-221
[0082]In preclinical studies, intravenously administered MN-221 (0.04 to 0.4 mg / kg) at the peak of ragweed-induced bronchoconstriction demonstrated a statistically significant, and near maximal reversal of bronchoconstriction in ragweed sensitized dogs between 0.75 and 6.7 min (p<0.001 up to 4.5 min and p<0.01 up to 6.7 min) after dosing.
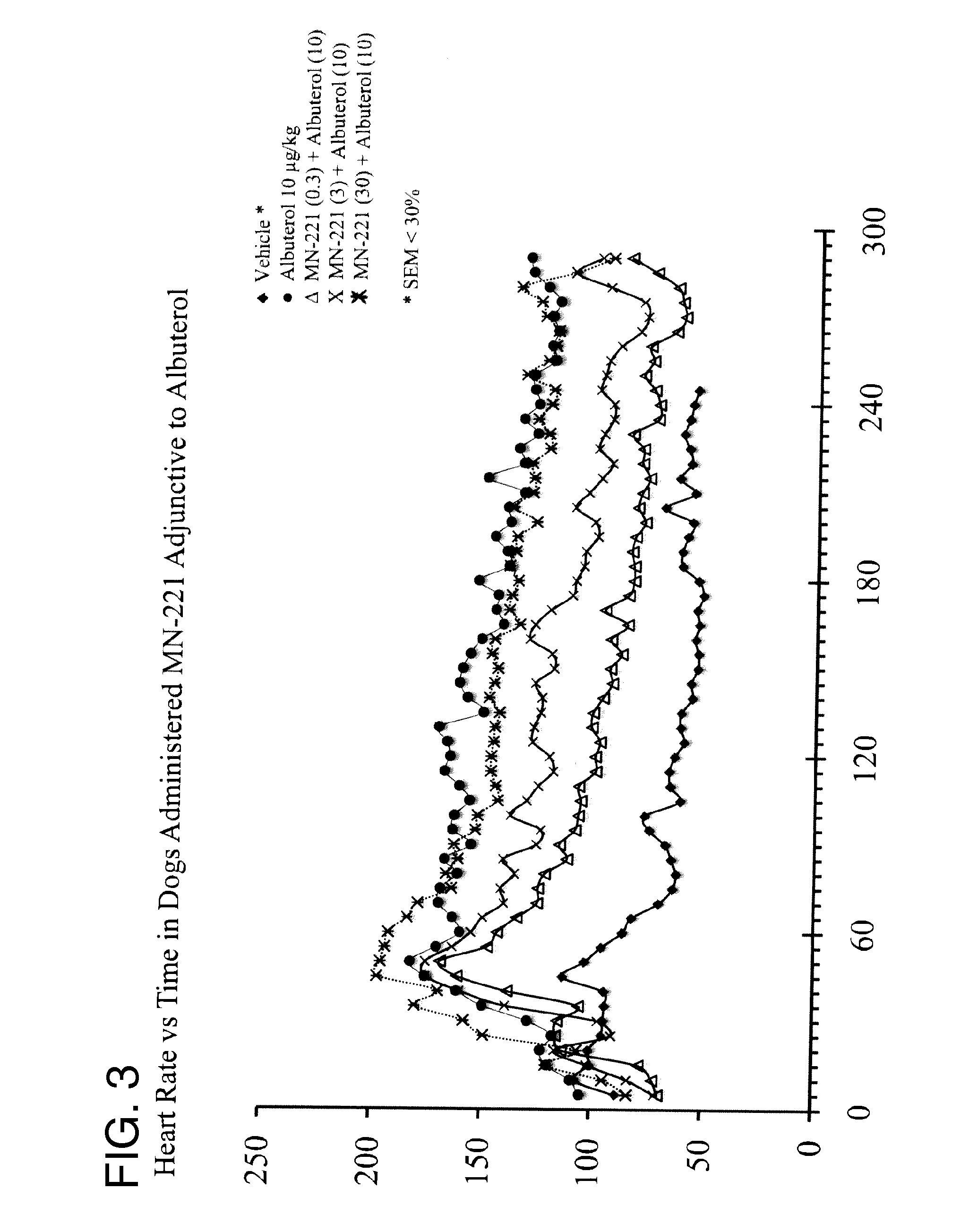
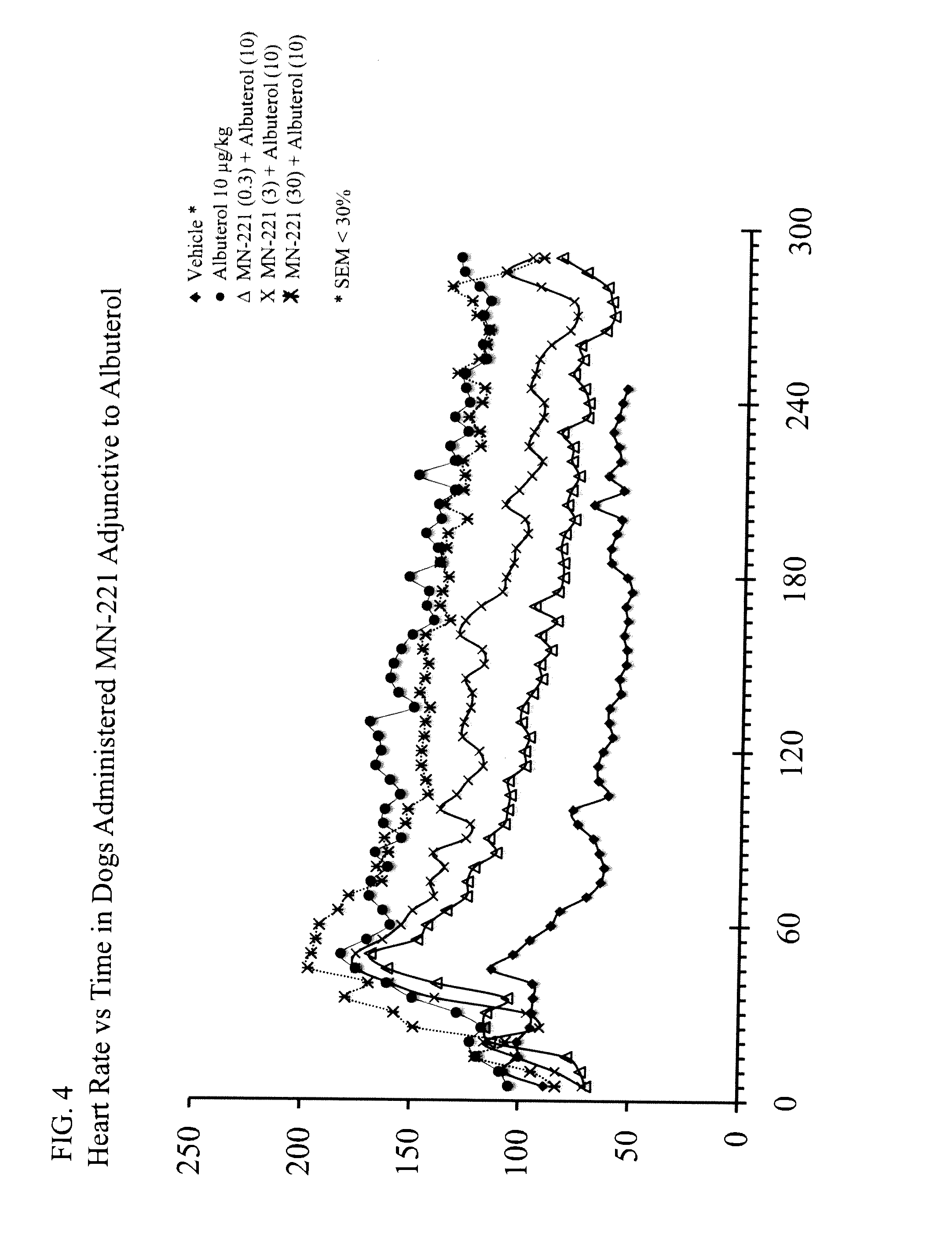
[0083]In a separate study with telemetered dogs at the Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute, the effect of i.v. MN-221 administration in addition to nebulized albuterol was performed to assess cardiovascular changes and safety of the combination therapy. Albuterol was administered by inhalation at 5 or 10 ug / kg and MN-221 was intravenously administered over 15 min at 0.3, 3, or 30 ug / kg. As expected with beta-agonists and as shown in other model systems, both albuterol and MN-221, alone, increased heart rate to a modest level depending on dose. No adverse changes in MAP or QTc were observed w...
example 2
Administration of MN-221 for the Treatment of AEA
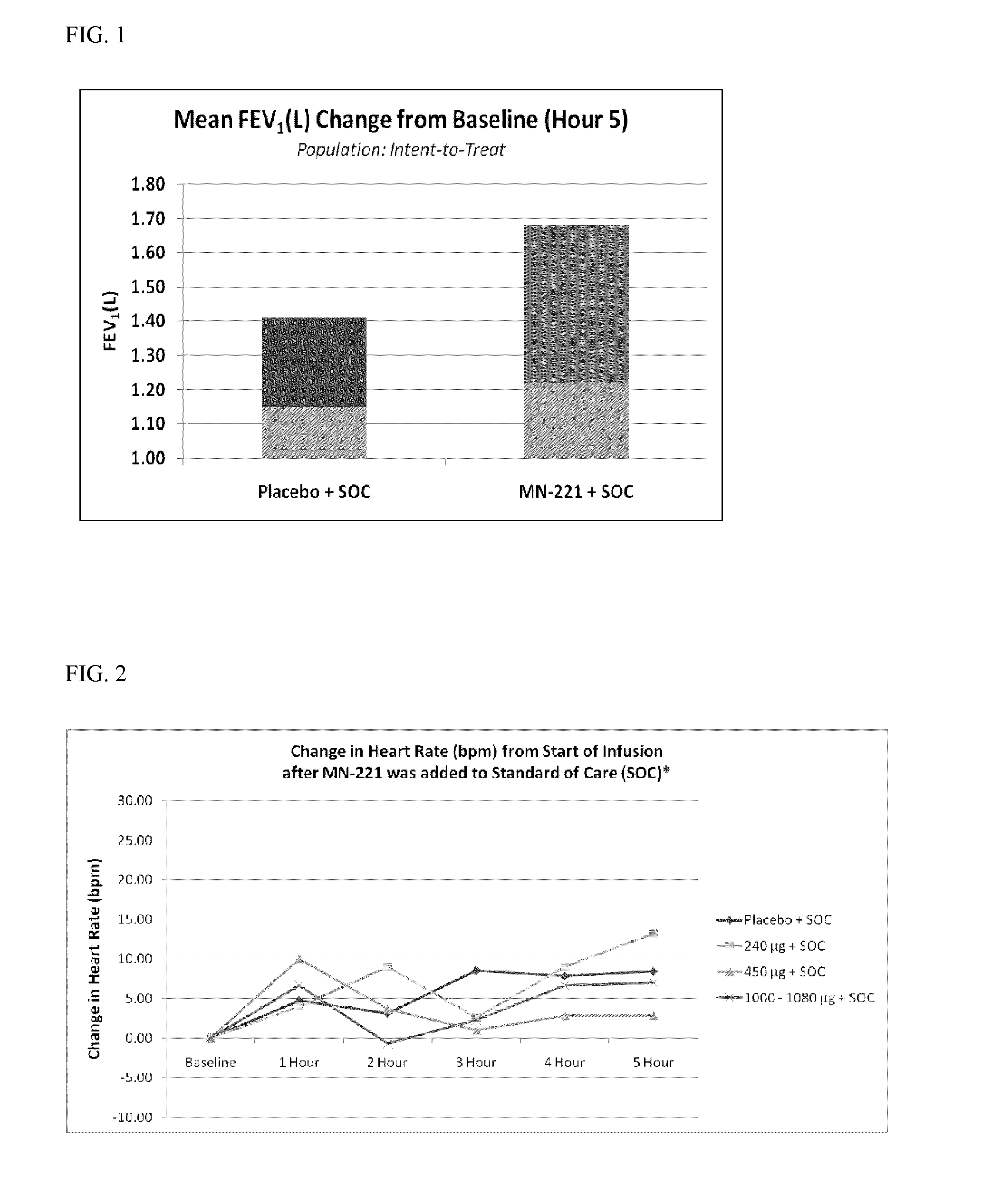
[0084]MN-221 was tested at escalating doses of 240 μg to 1,080 μg in patients with AEA treated in emergency departments (EDs). The study included 29 (13 treated with SOC only and 16 treated with MN-221 in combination with SOC) patients with severe AEA. All patients were administered SOC treatment as follows: supplemental oxygen given to maintain oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry of ≧90%; two doses of inhaled beta2-agonist (in this study, albuterol 5 mg) via nebulizer given approximately every 20 minutes; simultaneously with two doses of an inhaled anti-cholinergic agent (in this study, ipratropium 0.5 mg) via nebulizer given approximately every 20 minutes; one dose of corticosteroid given orally (in this study, prednisone 60 mg) or intravenously (in this study, methylprednisolone 125 mg), and intravenous magnesium sulfate (2 gm, diluted with 50-100 mL normal saline) and given over 10 minutes to patients with an FEV1 ≦25% of...
example 3
Demonstration of Safety and Efficacy of MN-221 Administration to AEA Patients
[0088]A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase II clinical trial is performed for demonstrating the efficacy and safety of administering MN-221 in accordance with the various aspects and embodiments of the methods of the present invention. A patient is administered the following initial SOC treatment regimen (consistent with the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program and the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guidelines). The SOC includes the following: supplemental oxygen given to maintain oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry of ≧90% as needed; albuterol: 10 mg of albuterol via nebulizer prior to the qualifying spirometry evaluation; simultaneously with ipratropium: 1.0 mg of ipratropium via nebulizer prior to the qualifying spirometry evaluation (if a nebulizer is not used, albuterol and ipratropium may be administered using an MDI with spacer as follows; albuterol: 16 pu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com