METHOD FOR PRODUCING POLYHYDROXYALKANOATE (PHAs) USING HALOBACTERIUM AND HALOBACTERIUM
a technology of halobacterium and polyhydroxyalkanoate, which is applied in the direction of microorganisms, bacteria-based processes, biofuels, etc., can solve the problems of inferior performance and once more high price of biodegradable plastics, and achieve the effect of high salt concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0060]The present invention is described in detail below with reference to Examples.
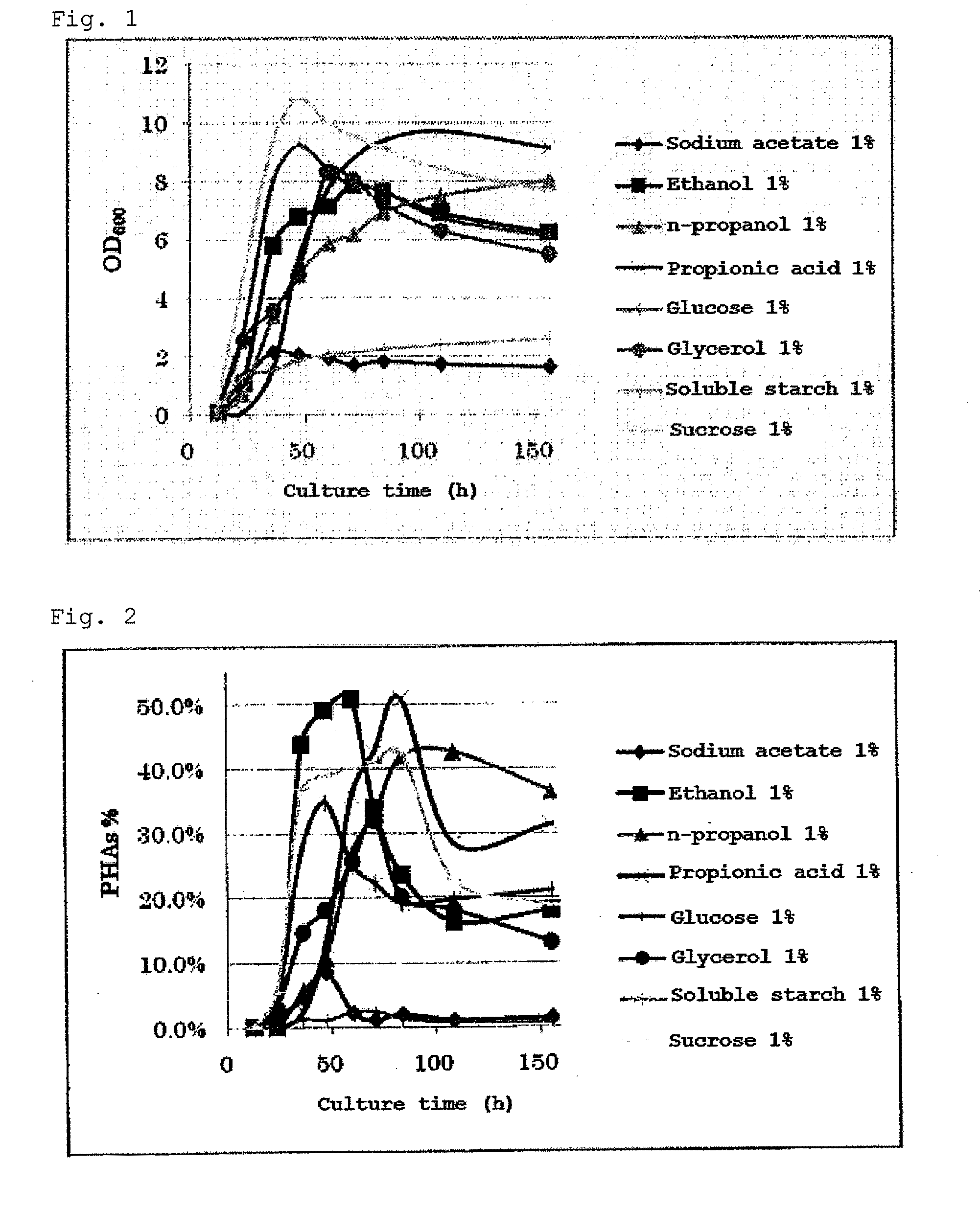
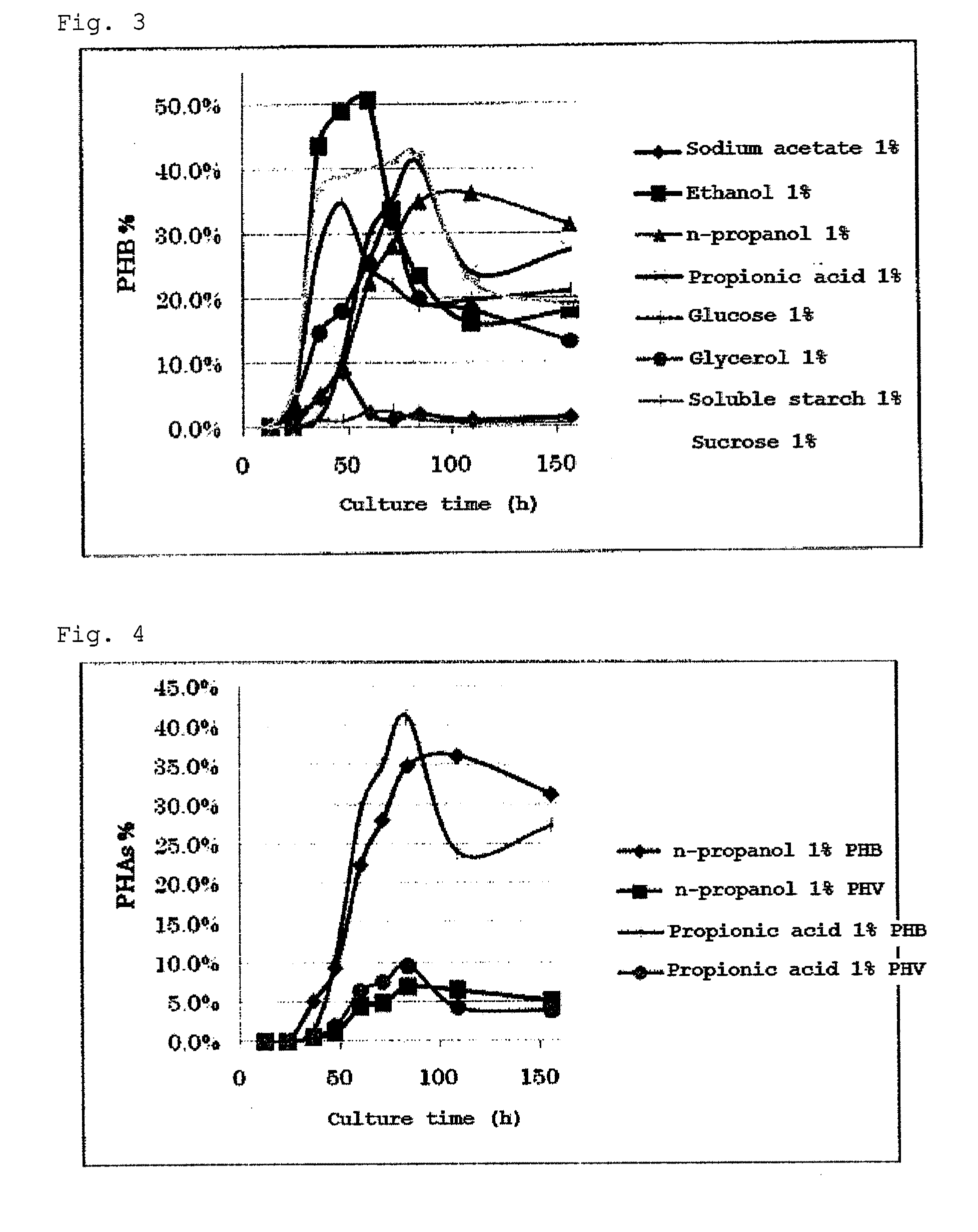
[0061]The Examples illustrate a method of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), which are biodegradable aliphatic-polyester plastics produced by microorganisms.
Medium Composition
[0062]The media used were SOT media (available from the National Institute for Environmental Studies) to which each carbon source had been added.
Medium name: modified SOT (modified Spirulina platensis medium)
Medium constituents:
NaHCO31.68gK2HPO450mgNaNO3250mgK2SO4100mgNaCl100mgMgSO4•7H2O20mgCaCl2•2H2O4mgFeSO4•7H2O1mgNa2 EDTA8mgA5 + Co solution0.1ml
For example, 1.0 g of sodium acetate is used as a carbon source. All of the constituents are dissolved in distilled water, and the total amount is adjusted to 100 ml.
A5 + Co solution (modified)H3BO3286mgMnSO4•7H2O250mgZnSO4•7H2O22.2mgCuSO4•5H2O7.9mgNa2MoO4•2H2O2.1mgCo(NO3)6H2O4.398mgDistilled water100ml
In sterilization, the above medium constituents are divided into two groups:
SOT...
example 2
Culture of Halomonas sp. KM-1 Strain in Different pH Environments
[0080]The halophilic-bacterium Halomonas sp. KM-1 strain was cultured in different pH environments using glycerol 3 w / v % as a carbon source, and the PHB ratio (PHAs / dry cell) accumulated in the cells was measured. To the SOT-A (NaHCO3: 1.68 g (0.2 M), K2HPO4: 50 mg / 50 ml) double-concentrated aqueous solution, which was a buffer component, a SOT-A′ (Na2CO3: 2.12 g, K2HPO4: 50 mg / 50 ml) double-concentrated aqueous solution was added, and solutions at pH 10 and pH 10.5 were prepared using a pH meter. Each solution was mixed with the same amount of SOT-B double-concentrated solution, and used as a medium. The PHB ratio of each medium was relativized with respect to the culture time, and plotted in FIG. 5.
[0081]The Halomonas sp. KM-1 strain showed a PHA accumulation rate equal to or more than that at pH 8.9 not only under the normal culture conditions (pH 8.9), but also at pHs 10 and 10.5. Further, the possibility of the u...
example 3
[0082]Table 2 shows the typical compositions of waste glycerol formed as a by-product in the production of biodiesel, which has great potential as an organic carbon source.
TABLE 2Analysis results of waste glycerolpHGlycerol (mg / g)K (mg / g)Waste glycerol #110.3035041.8Waste glycerol #210.3840062.1Waste glycerol #310.3535845.9Waste glycerol #410.3735846.0* pH: those measured in samples prepared by dissolving 1 g of waste glycerol in distilled water (total amount: 100 ml) (adapted from Journal of Environmental Conservation Engineering, Vol. 37, No. 5, pp. 48-53)
[0083]In general biodiesel production equipment, KOH having a high solubility in methanol is used as an alkaline catalyst.
[0084]The waste glycerol actually used for culture was a waste glycerol sample that was kindly provided by the Kyoto Municipal Waste Edible Oil Fuel Production Facility on May 1, 2008.
[0085]The pH of this sample was measured in the same manner as described above, and the result was 10.38.
[0086]Then, media comp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com