Corrosion reduction system for power generation plants during shutdown
a power generation plant and shutdown technology, applied in the direction of corrosion diminishing boiler components, specific water treatment objectives, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of overheating tube failure, hydrogen damage, and under deposit corrosion attack, so as to reduce or eliminate internal contamination. , the effect of reducing the corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
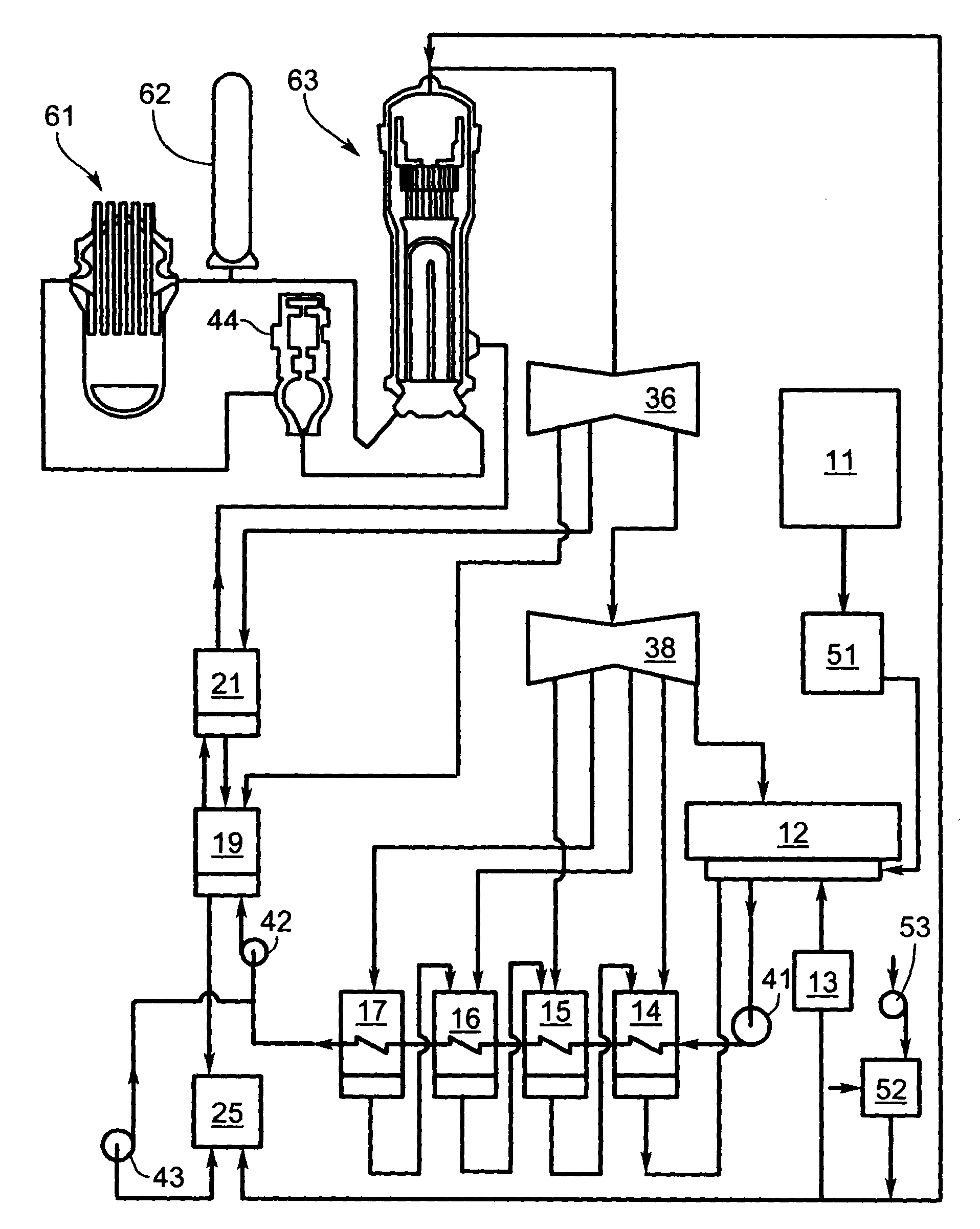
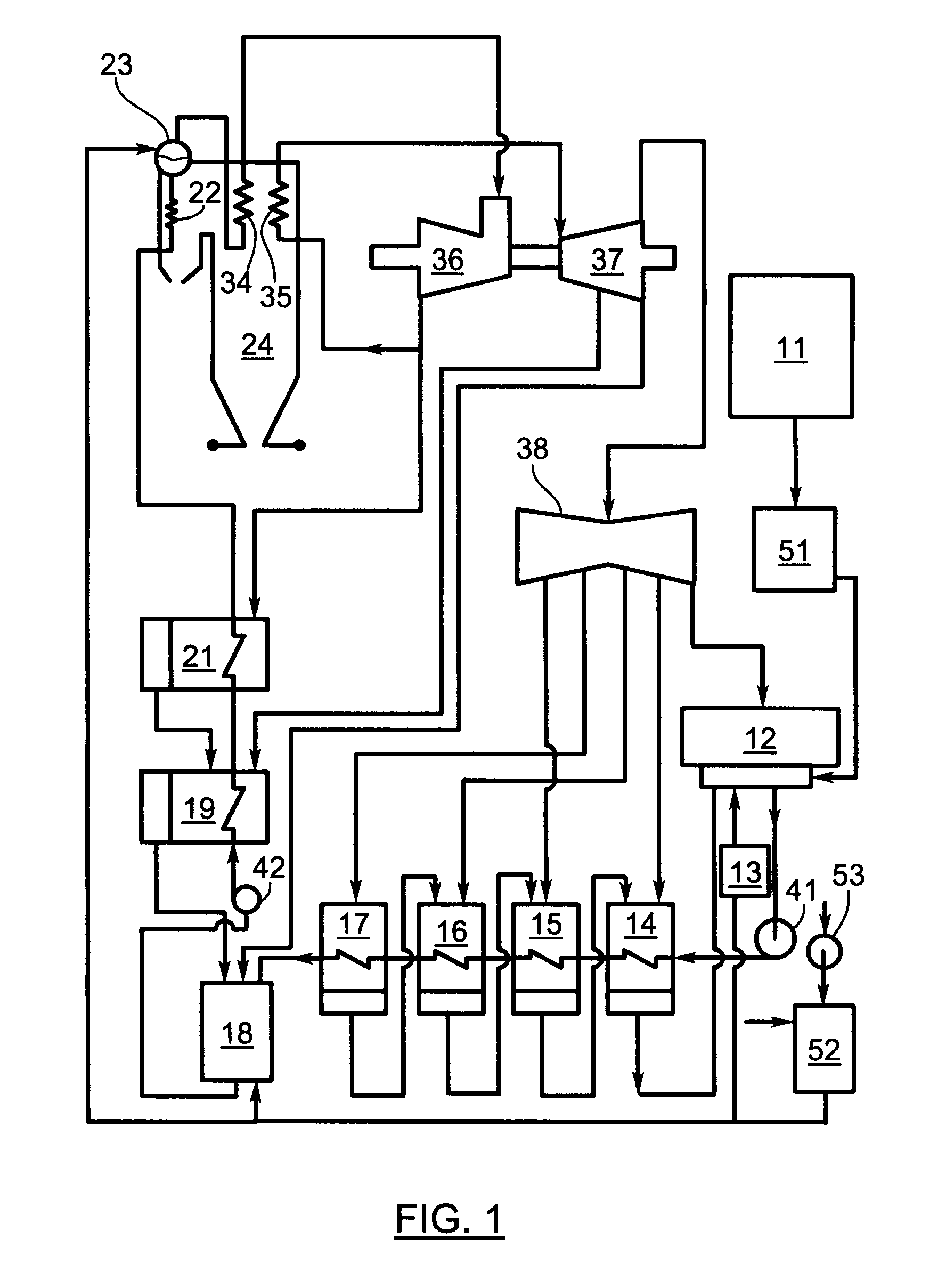
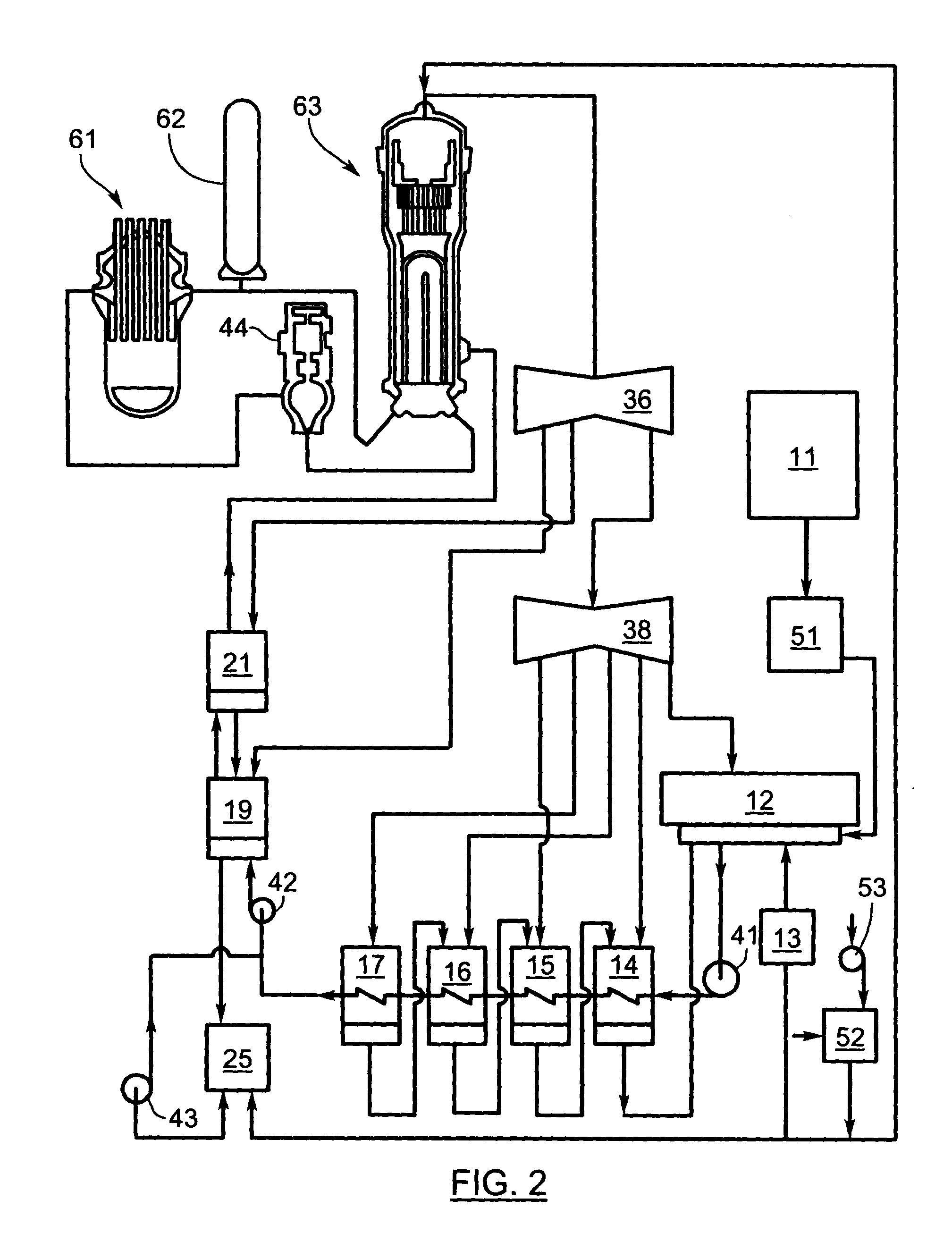
[0024]In order to more clearly understand the present invention part numbers as assigned in the following parts list will be used:
Part NumberDescription11make-up water (condensate) storage12main steam condenser13vacuum breaker14low pressure heater15low pressure heater16low pressure heater17low pressure heater18de-aerating heater19high pressure heater21high pressure heater22economizer23steam drum24boiler25drain tank34superheater35reheater36high pressure turbine37intermediate pressure turbine38low pressure turbine41condensate extraction pump42boiler feed pump43drains pump44pump51water anion polisher52acidic gases filter53air blower61nuclear reactor62pressurizer63steam generator
[0025]The first device (51) is the water anion polisher (WAP), which consists of a tank with anion exchanger designed to remove acidic contaminants from any water flowing into the cycle from a storage tank. It is preferred that the device 51 is installed on the effluent from each water storage tank. As an altern...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com