Strains and methods for improving ruminant health and/or performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Acidosis Model Experimental Design:
[0052]Ten crossbred steers were blocked by weight and assigned to two pens. The daily feed ration for all treatment groups prior to challenge consisted of 45% roughage and 55% concentrate on a dry matter basis. Cattle were fed 15 lbs / head / day of the ration once in the morning and had remaining feed pushed closer to the feeding stanchion late in the afternoon. Both pens were fasted for 24 hours before challenge with the concentrate diet treatments. Concentrate diet treatments consisted of highly fermentable carbohydrate sources of steam flaked corn on a 90% as fed basis. After fasting for 24 hours, the concentrate diet was fed ad libitum at 100 lbs / pen to all pens (0 h). Challenge diet consumption was visually monitored and additional feed added on an as needed basis.
[0053]Rumen fluid samples were obtained from individual animals via oral intubation using a collection tube attached to a vacuum flask. Different flasks and collection tubes were used f...
example 2
In Vitro Strain Testing:
[0067]Rumen fluid was collected for in vitro trials from two yearling Hereford heifers. Heifers were identified by identification tags and were referred to as 101 and 133. Heifers were fed 6 lbs / head / day of dried distillers grain (DDGS) and had access to free choice haylage.
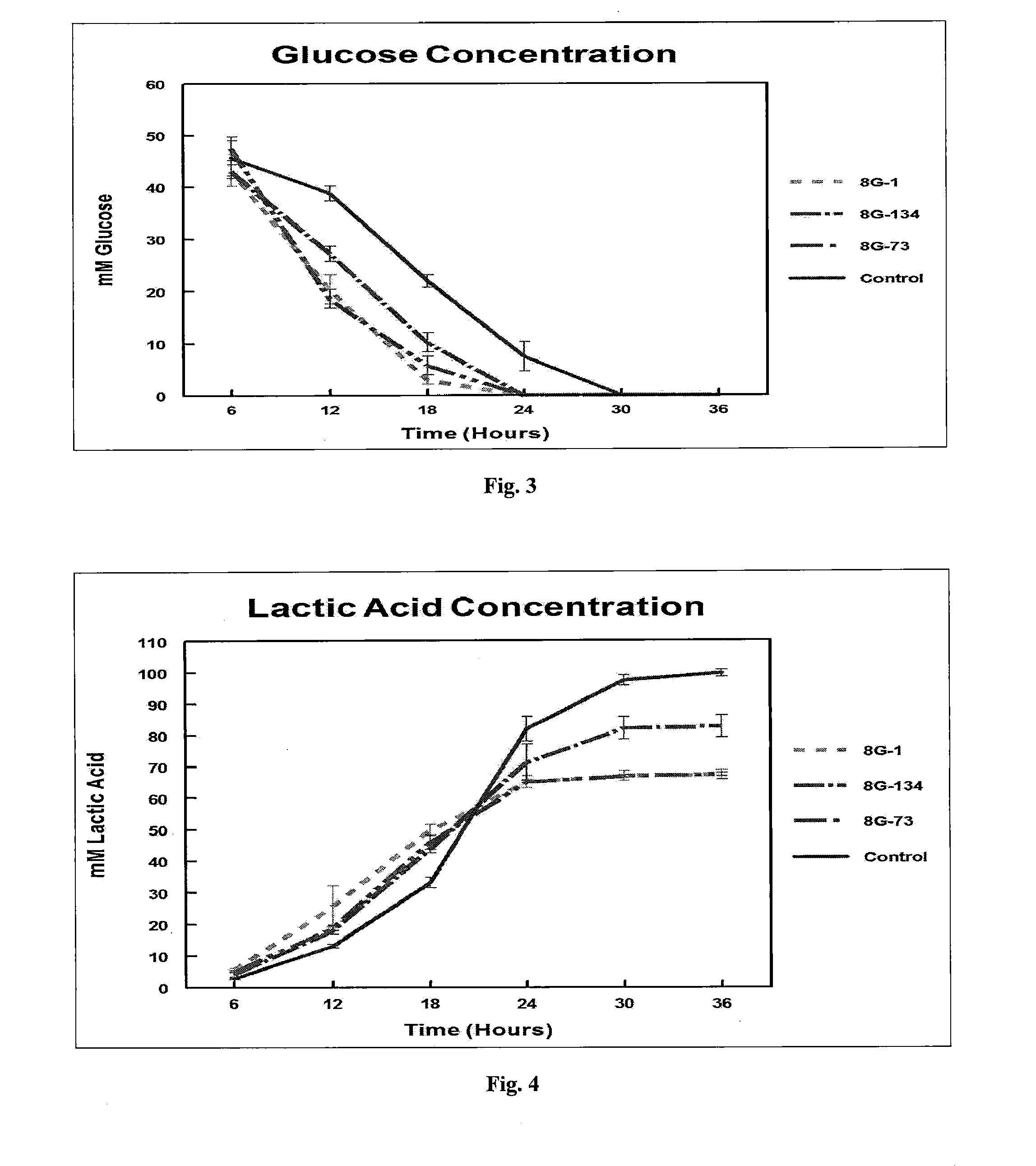
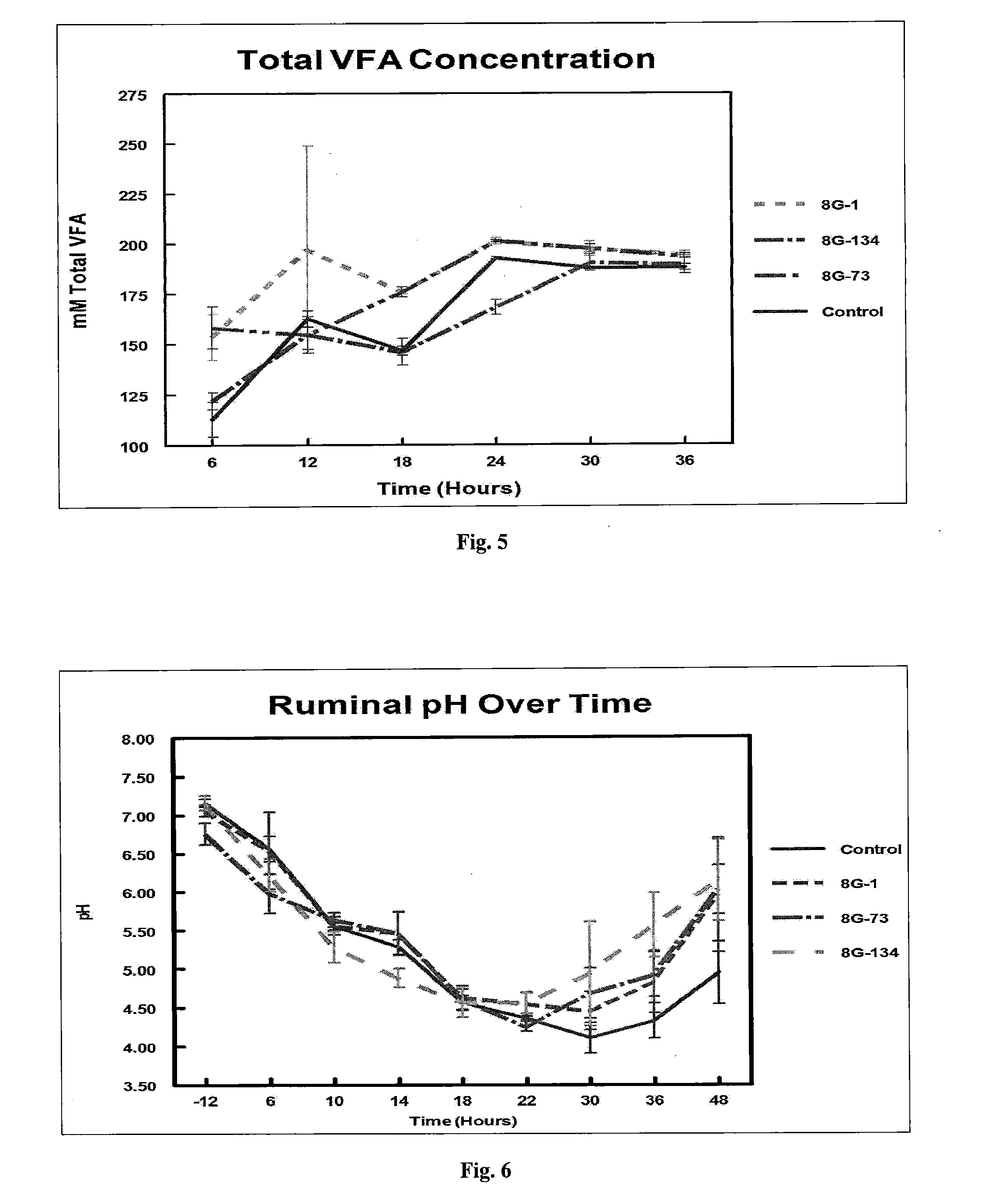
[0068]The in vitro protocol was followed as closely as possible to decrease experimental error between each trial. Briefly, rumen fluid was collected from each heifer and placed into marked, pre-warmed thermoses. Thermoses were transported to Agtech Products, Inc. for processing. Rumen fluid was added in duplicate to bottles containing McDougall's Buffer and 3.0% glucose (final concentration after McDougall's Buffer and rumen fluid have been mixed to a volume of 180 ml), which had been tempered to 39° C. Candidate DFM strains, Enterococcus faecium strain 8G-1, Enterococcus faecium strain 8G-73, and Bacillus pumilus strain 8G-134, were added to designated bottles at 1.0×107 CFU / ml (final co...
example 3
Candidate DFM Testing in Cattle Fed a Readily Fermentable Carbohydrate—an Acute Acidosis Challenge:
[0072]Materials and Methods:
[0073]Cattle and Pens Assignments:
[0074]Twenty cross-bred beef steers were purchased at local sale barns. Cattle were housed at the research facility for a period of two weeks prior to trial initiation for observation of morbidity or mortality. Cattle were randomly blocked across treatment by weight. Five head of cattle were assigned to a pen and pens designated to one of four treatments. Treatments consisted of 3 pens each receiving a different DFM as is detailed below with the fourth pen receiving no DFM (control). Treatment assignments can be seen in Table 2 below.
TABLE 2Treatment assignments by pen.CandidateMinimum DosePen IDDFM (TX)(CFU / Head / Day)16s rRNA Identification1None0None (Control)28G-15 × 1010Enterococcus spp.38G-735 × 1010Enterococcus spp.48G-1345 × 109Bacillus pumilus
The daily feed ration for all treatment groups prior to challenge, consisted ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com